from: http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_662234020100pozd.html
MAP(Mean Average Precision)
例如:假设有两个主题,主题1有4个相关网页,主题2有5个相关网页。某系统对于主题1检索出4个相关网页,其rank分别为1, 2, 4,7;对于主题2检索出3个相关网页,其rank分别为1,3,5。对于主题1,平均准确率为(1/1+2/2+3/4+4/7)/4=0.83。对于主题2,平均准确率为(1/1+2/3+3/5+0+0)/3=0.7555。则MAP=(0.83+0.7555)/2=0.79。”
MRR是把标准答案在被评价系统给出结果中的排序取倒数作为它的准确度,再对所有的问题取平均。
Wiki
Precision and recall are single-value metrics based on the wholelist of documents returned by the system. For systems that return aranked sequence of documents, it is desirable to also consider theorder in which the returned documents are presented. Averageprecision emphasizes ranking relevant documents higher. It is theaverage of precisions computed at the point of each of the relevantdocuments in the ranked sequence:
where r is the rank, N the number retrieved,rel() a binary function on the relevance of a given rank,andP(r) precision at a given cut-off rank:
This metric is also sometimes referred to geometrically as thearea under the Precision-Recall curve.
Note that the denominator (number of relevant documents) is thenumber of relevant documents in the entire collection, so that themetric reflects performance over all relevant documents, regardlessof a retrieval cutoff. See:.
^Turpin, Andrew; Scholer, Falk (2006). "User performanceversus precision measures for simple search tasks". Proceedingsof the 29th Annual international ACM SIGIR Conference onResearch and Development in information Retrieval_r(Seattle,Washington, USA, August 06-11, 2006) (New York, NY: ACM):11–18.doi:10.1145/1148170.1148176






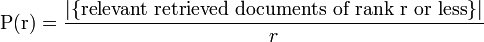
















 3361
3361

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








