Lagrange对偶问题
The dual function provides a lower bound on the optimal value for convex optimization problems only.

对偶函数可以为任意优化问题的最优值提供下界。
The dual function of an optimization problem evaluated at some (λ,ν), with λ⪰0, is equal to 42. Enter a number that can represent the optimal value of the original problem.

因为对偶函数为优化问题的最优值提供下界,只有最优值大于等于42即可。
强弱对偶性
Consider a convex optimization problem
that satisfies Slater's constraint qualification.
Which of the following are true?

当原问题是凸问题,且满足Slater约束时,满足强对偶性,所以选项1正确。但是强对偶性成立,并不代表原问题和对有问题可行,选项2,3不正确。
几何解释
If the feasible set of an optimization problem is not convex, then the duality gap is always nonzero.

优化问题的可行集是凸集,大部分情况下对偶间隙是0,即强对偶性成立。但可行集不是凸集时,也可能对偶间隙为0.
优化条件
Consider a convex optimization problem
that satisfies Slater's constraint qualification.
What is the value of if
?

凸优化问题满足Slater约束条件,所以强对偶性成立,所以
所以
而
所以当时,
扰动及灵敏度分析
Consider the convex optimization problem
with variable , where s is some fixed real number. Let
be an optimal dual variable (Lagrange multiplier) associated with the constraint
. Below we consider scenarios in which we change the value of s, and then solve the modified problem. We are interested in the optimal objective value of this modified problem, compared to the original one above.
If is large, then decreasing s
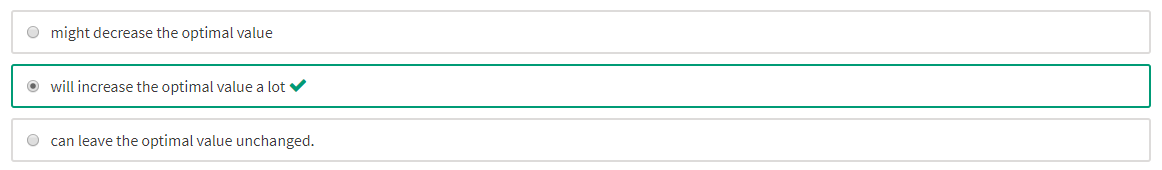
If





 本文探讨了凸优化中的Lagrange对偶问题,强调了对偶函数为原问题提供下界的性质,并讨论了强对偶性和弱对偶性的概念。此外,还通过几何解释和优化条件解释了对偶间隙的含义。文章进一步阐述了扰动分析,举例说明了变量变化如何影响优化问题的最优值。最后,介绍了Lagrangian松弛在布尔线性规划中的应用以及期权价格的界限。
本文探讨了凸优化中的Lagrange对偶问题,强调了对偶函数为原问题提供下界的性质,并讨论了强对偶性和弱对偶性的概念。此外,还通过几何解释和优化条件解释了对偶间隙的含义。文章进一步阐述了扰动分析,举例说明了变量变化如何影响优化问题的最优值。最后,介绍了Lagrangian松弛在布尔线性规划中的应用以及期权价格的界限。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 828
828

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








