一、NLP 文本分类步骤
第一步:准备数据集,X:句子;Y:类别
第二步:分词,并去除停词(中文理由停词,比如而且,逗号之类;英文的话需要做词的时态转换之类)
第三步:word2idx/word2vec;这里word2vec,可以利用语料库,训练一个单词转为向量的model,这个模型你输入单词,会给你一个向量,并且能计算单词的相似度,相当于提前给词语做了归一化;word2idx就直接用词汇表的id作为向量的元素;
第四步:建模训练
二、代码
1、数据准备➕预处理
我们采用,头条新闻数据集作为本次demo的数据集。
https://github.com/aceimnorstuvwxz/toutiao-text-classfication-dataset下载好之后,需要进行预处理,个人习惯转为json字典;并且2/8开分为测试和训练集;
file = open("./toutiao.txt", 'r')
file = file.readlines()
print(file[0],len(file))
print(file[0].split("_!_"))
data = {"train": [],
"test": [],
"class_name":{},
"class_info": {}}
# shuffle data
random.shuffle(file)
max_sentence = 0
for i, line in enumerate(file):
if i < int(0.8 * len(file)):
line = line.split("_!_")
if line[1] not in data["class_name"].keys():
data["class_name"][line[1]] = line[2]
if line[1] not in data["class_info"].keys():
data["class_info"][line[1]] = 1
else:
data["class_info"][line[1]] += 1
data["train"].append({"x": line[3],
"y": line[1]})
max_sentence = len(line[3]) if len(line[3]) > max_sentence else max_sentence
else:
line = line.split("_!_")
if line[1] not in data["class_name"].keys():
data["class_name"][line[1]] = line[2]
if line[1] not in data["class_info"].keys():
data["class_info"][line[1]] = 1
else:
data["class_info"][line[1]] += 1
data["test"].append({"x": line[3],
"y": line[1]})
max_sentence = len(line[3]) if len(line[3]) > max_sentence else max_sentence
data["max_sentence"] = max_sentence
data["num_train"] = len(data["train"])
data["num_test"] = len(data["test"])
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from matplotlib import gridspec
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4.5))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(1, 2, width_ratios=[1, 2.5])
ax1 = plt.subplot(gs[0])
ax2 = plt.subplot(gs[1])
counts = [data["num_train"], data["num_test"]]
colors = ['silver', 'purple']
explode = (0.1, 0) # explode 1st slice
labels = ['train','test']
ax1.pie(counts, explode=explode, labels=labels, colors=colors, autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=True, startangle=140)
counts = []
labels = []
for namecode in data["class_name"].keys():
counts.append(data["class_info"][namecode])
labels.append(data["class_name"][namecode])
print(len(counts),len(labels))
print(counts)
print(labels)
df = pd.DataFrame({"labels": labels,
"counts": counts})
ax2.bar(df["labels"], df["counts"])
ax2.set_title("nums")
ax2.set_ylabel("% nums")
# ax2.set_xticks(rotation=-15)
ax2.set_xticklabels(labels = labels, rotation=-15)
plt.show()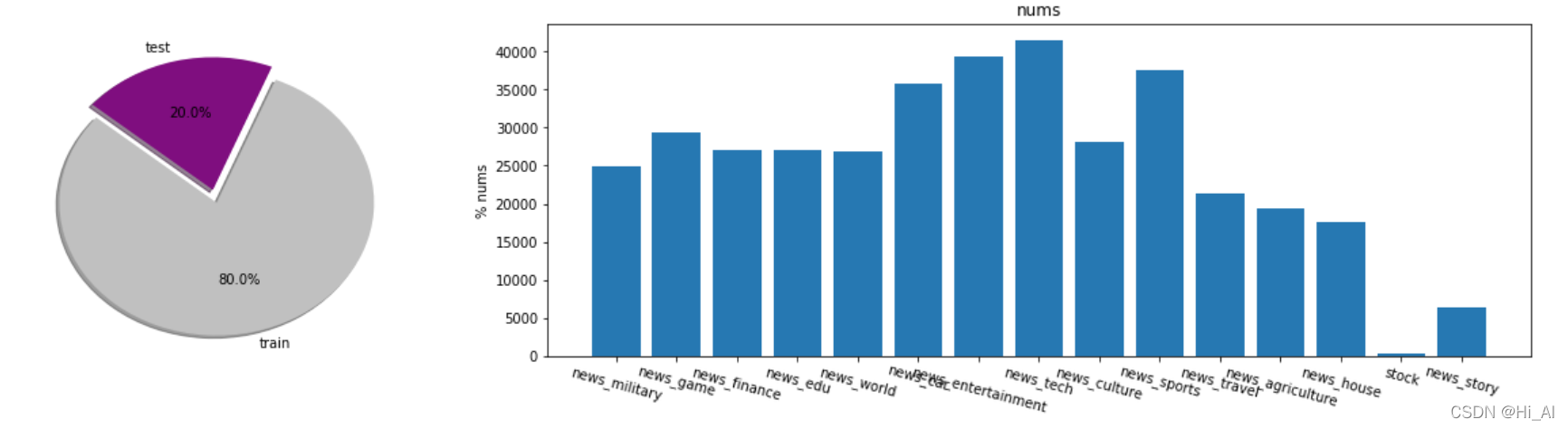
到这里为止,数据分析和预处理就结束了
2、对句子进行分词
stopwords = [i.strip() for i in open('stop_words.txt').readlines()]
def pretty_cut(sentence):
cut_list = jieba.lcut(''.join(re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]', sentence)), cut_all = True)
for i in range(len(cut_list)-1, -1, -1):
if cut_list[i] in stopwords:
del cut_list[i]
return cut_list这里的stop_word.txt 可以在github下载
GitHub - goto456/stopwords: 中文常用停用词表(哈工大停用词表、百度停用词表等)
用“cn_stopwords.txt” 就可以了
效果如下:

3、接下来可以采用多种方式把中文转为向量
方法一:
import logging
import sys
# import gensim.models as word2vec
from gensim.models.word2vec import LineSentence, logger
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
train_data_wv = []
for sentence in data["train"]:
jieba_word = " ".join(pretty_cut(sentence["x"]))
train_data_wv.append(jieba_word)
sentence["x_jieba"] = jieba_word
for sentence in data["test"]:
jieba_word = " ".join(pretty_cut(sentence["x"]))
train_data_wv.append(jieba_word)
sentence["x_jieba"] = jieba_word
train_w2v = Word2Vec(train_data_wv, window=5, min_count=0,vector_size=50, workers=10)
train_w2v.train(train_data_wv, total_examples=len(train_data_wv), epochs=10)方法二:
vocabs = {}
index_word = 1
for se in train_data_wv:
vo = set(se.split(' '))
for word in vo:
if word not in vocabs.keys():
vocabs[word]=index_word
index_word += 1
def get_pretrain_pad_seq(vocab, sentence, maxlen):
transformed_sentence = []
for word in sentence:
tran_word = vocab.get(word, None)
if tran_word:
transformed_sentence.append(tran_word)
else:
transformed_sentence.append(107335)
transformed_sentence += [0 for _ in range(abs(maxlen - len(sentence)))]
return np.array(transformed_sentence)
max_len = 0
for sentence in train_data_wv:
max_len = len(sentence.split(' ')) if len(sentence.split(' ')) > max_len else max_len采用方法二,通常需要词汇量+1,多的那个用来pad,通常是0;
接下来就是把整个数据集进行整理,转化为训练举证
trainX = []
trainY = []
testX = []
testY = []
for sample in data["train"]:
jieba_word = sample["x_jieba"].split(' ')
x = get_pretrain_pad_seq(vocabs, jieba_word, max_len)
trainX.append(x)
trainY.append(int(sample["y"]))
for sample in data["test"]:
jieba_word = sample["x_jieba"].split(' ')
x = get_pretrain_pad_seq(vocabs, jieba_word, max_len)
testX.append(x)
testY.append(int(sample["y"]))
trainX = np.array(trainX)
trainY = np.array(trainY)
testX = np.array(testX)
testY = np.array(testY)
import tensorflow as tf
trainY = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(trainY)
testY = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(testY)
print(trainX.shape, trainY.shape, testX.shape, testY.shape) 4、 建模训练
4、 建模训练
from tensorflow.keras import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, Dense, LSTM
class TextRNN(Model):
def __init__(self,
maxlen,
max_features,
embedding_dims,
class_num=1,
last_activation='sigmoid'):
super(TextRNN, self).__init__()
self.maxlen = maxlen
self.max_features = max_features
self.embedding_dims = embedding_dims
self.class_num = class_num
self.last_activation = last_activation
self.embedding = Embedding(self.max_features, self.embedding_dims, input_length=self.maxlen)
self.rnn = LSTM(128) # LSTM or GRU
self.classifier = Dense(self.class_num, activation=self.last_activation)
def call(self, inputs):
if len(inputs.get_shape()) != 2:
raise ValueError('The rank of inputs of TextRNN must be 2, but now is %d' % len(inputs.get_shape()))
if inputs.get_shape()[1] != self.maxlen:
raise ValueError('The maxlen of inputs of TextRNN must be %d, but now is %d' % (self.maxlen, inputs.get_shape()[1]))
embedding = self.embedding(inputs)
x = self.rnn(embedding)
output = self.classifier(x)
return output上面是模型代码,接下来就是训练代码了:
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import sequence
max_features = 107335 # 单次数+1
maxlen = 80
batch_size = 32
embedding_dims = 32
epochs = 10
print('Build model...') # 15类,但是编码用的百位数
model = TextRNN(max_len, max_features, embedding_dims, class_num=117, last_activation='softmax')
model.compile('adam', 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
print('Train...')
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_accuracy', patience=3, mode='max')
model.fit(trainX, trainY,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=[early_stopping],
validation_data=(testX, testY))
print('Test...')
result = model.predict(testX) 
这里会采用embedding层把每个单词原本index转为词向量:









 该博客介绍了NLP文本分类的步骤,包括数据集准备、预处理、分词、词向量化以及模型训练。使用了头条新闻数据集,通过jieba进行分词并去除停用词,然后利用gensim的Word2Vec进行词向量化。模型选择为TextRNN,使用Keras进行训练,并应用早停策略优化模型。此外,还展示了数据分布的饼图和柱状图。
该博客介绍了NLP文本分类的步骤,包括数据集准备、预处理、分词、词向量化以及模型训练。使用了头条新闻数据集,通过jieba进行分词并去除停用词,然后利用gensim的Word2Vec进行词向量化。模型选择为TextRNN,使用Keras进行训练,并应用早停策略优化模型。此外,还展示了数据分布的饼图和柱状图。
















 6214
6214

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








