目标:学习如何使用系统方法调试与 tf2 相关的问题。
教程级别:中级
时间:10 分钟
目录
背景
调试示例
1 设置和启动示例
2 查找 tf2 请求
3 检查框架
4 检查时间戳
摘要
背景
本教程将引导您完成调试典型 tf2 问题的步骤。它还将使用许多 tf2 调试工具,例如 tf2_echo 、 tf2_monitor 和 view_frames 。本教程假设您已完成学习 tf2 教程。
调试示例
1 设置和启动示例
对于本教程,我们将设置一个有许多问题的演示应用程序。本教程的目标是应用系统的方法来发现和解决这些问题。首先,让我们创建源文件。
转到我们在 tf2 教程https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/Tutorials/Intermediate/Tf2/Tf2-Main.html 中创建的 learning_tf2_cpp 包。在 src 目录中复制源文件 turtle_tf2_listener.cpp 并将其重命名为 turtle_tf2_listener_debug.cpp 。
使用您喜欢的文本编辑器打开文件,并将第 65 行从
std::string toFrameRel = "turtle2";到
std::string toFrameRel = "turtle3";并将第 73-77 行中的 lookupTransform() 调用更改为
try {
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
tf2::TimePointZero);
} catch (const tf2::TransformException & ex) {到
try {
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
this->now());
} catch (const tf2::TransformException & ex) {并保存对文件的更改。为了运行此演示,我们需要在包 learning_tf2_cpp 的 launch 子目录中创建一个启动文件 start_tf2_debug_demo_launch.py :
from launch import LaunchDescription # 从launch模块导入LaunchDescription类
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument # 从launch.actions模块导入DeclareLaunchArgument类
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration # 从launch.substitutions模块导入LaunchConfiguration类
from launch_ros.actions import Node # 从launch_ros.actions模块导入Node类
def generate_launch_description(): # 定义generate_launch_description函数
return LaunchDescription([ # 返回一个LaunchDescription对象
DeclareLaunchArgument( # 声明一个启动参数
'target_frame', default_value='turtle1', # 参数名为'target_frame',默认值为'turtle1'
description='Target frame name.' # 参数描述为'目标坐标系名称'
),
Node( # 定义一个节点
package='turtlesim', # 节点所属包名为'turtlesim'
executable='turtlesim_node', # 可执行文件名为'turtlesim_node'
name='sim', # 节点名称为'sim'
output='screen' # 输出方式为屏幕输出
),
Node( # 定义另一个节点
package='learning_tf2_cpp', # 节点所属包名为'learning_tf2_cpp'
executable='turtle_tf2_broadcaster', # 可执行文件名为'turtle_tf2_broadcaster'
name='broadcaster1', # 节点名称为'broadcaster1'
parameters=[ # 节点参数
{'turtlename': 'turtle1'} # 参数'turtlename'的值为'turtle1'
]
),
Node( # 定义第三个节点
package='learning_tf2_cpp', # 节点所属包名为'learning_tf2_cpp'
executable='turtle_tf2_broadcaster', # 可执行文件名为'turtle_tf2_broadcaster'
name='broadcaster2', # 节点名称为'broadcaster2'
parameters=[ # 节点参数
{'turtlename': 'turtle2'} # 参数'turtlename'的值为'turtle2'
]
),
Node( # 定义第四个节点
package='learning_tf2_cpp', # 节点所属包名为'learning_tf2_cpp'
executable='turtle_tf2_listener_debug', # 可执行文件名为'turtle_tf2_listener_debug'
name='listener_debug', # 节点名称为'listener_debug'
parameters=[ # 节点参数
{'target_frame': LaunchConfiguration('target_frame')} # 参数'target_frame'的值为启动配置中的'target_frame'
]
),
])不要忘记将 turtle_tf2_listener_debug 可执行文件添加到 CMakeLists.txt 并构建包。
add_executable(turtle_tf2_listener_debug src/turtle_tf2_listener_debug.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(
turtle_tf2_listener_debug
geometry_msgs
rclcpp
tf2
tf2_ros
turtlesim
)
install(TARGETS
turtle_tf2_listener_debug
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})现在让我们运行它看看会发生什么:
ros2 launch learning_tf2_cpp start_tf2_debug_demo_launch.py您现在会看到 turtlesim 出现了。同时,如果您在另一个终端窗口中运行 turtle_teleop_key ,您可以使用箭头键来驱动 turtle1 。
ros2 run turtlesim turtle_teleop_key您还会注意到在左下角有第二只乌龟。如果演示正常工作,这只第二只乌龟应该会跟随您可以用箭头键指挥的乌龟。然而,情况并非如此,因为我们必须先解决一些问题。您应该注意到以下消息:
[turtle_tf2_listener_debug-4] [INFO] [1720794987.992667704] [listener_debug]: Could not transform turtle3 to turtle1: "turtle3" passed to lookupTransform argument target_frame does not exist.2 查找 tf2 请求
首先,我们需要找出我们要求 tf2 做什么。因此,我们进入使用 tf2 的代码部分。打开 src/turtle_tf2_listener_debug.cpp 文件,并查看第 65 行:
std::string to_frame_rel = "turtle3";并且第 73-77 行:
try {
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
this->now());
} catch (const tf2::TransformException & ex) {在这里我们实际请求 tf2。三个参数直接告诉我们我们在请求 tf2:在时间 now 从框架 turtle3 转换到框架 turtle1 。
现在,让我们看看为什么这个对 tf2 的请求失败。
3 检查框架
首先,要找出 tf2 是否知道我们在 turtle3 和 turtle1 之间的变换,我们将使用 tf2_echo 工具。
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo turtle3 turtle1输出告诉我们帧 turtle3 不存在:
cxy@ubuntu2404-cxy:~$ ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo turtle3 turtle1
[INFO] [1720795103.137633545] [tf2_echo]: Waiting for transform turtle3 -> turtle1: Invalid frame ID "turtle3" passed to canTransform argument target_frame - frame does not exist那么存在哪些框架呢?如果您想获得此内容的图形表示,请使用 view_frames 工具。
ros2 run tf2_tools view_frames打开生成的 frames.pdf 文件以查看以下输出:
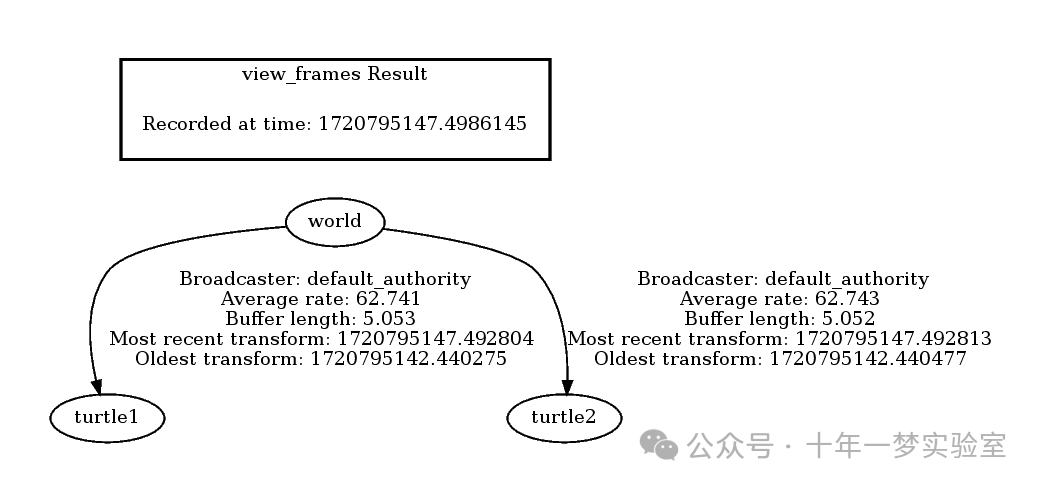
显然问题是我们正在请求来自框架 turtle3 的转换,该框架不存在。要修复此错误,只需将第 65 行中的 turtle3 替换为 turtle2 。
现在停止运行演示,构建它,然后再次运行它:
cxy@ubuntu2404-cxy:~/ros2_ws$ colcon build --packages-select learning_tf2_cpp
Starting >>> learning_tf2_cpp
Finished <<< learning_tf2_cpp [6.68s]
Summary: 1 package finished [6.93s]
cxy@ubuntu2404-cxy:~/ros2_ws$ . install/setup.bash
cxy@ubuntu2404-cxy:~/ros2_ws$ ros2 launch learning_tf2_cpp start_tf2_debug_demo_launch.py[turtle_tf2_listener_debug-4] [INFO] [1720795298.506219442] [listener_debug]: Could not transform turtle2 to turtle1: Lookup would require extrapolation into the future. Requested time 1720795298.505709 but the latest data is at time 1720795298.493177, when looking up transform from frame [turtle1] to frame [turtle2]4 检查时间戳
现在我们解决了框架名称问题,是时候查看时间戳了。记住,我们正在尝试获取 turtle2 和 turtle1 之间在当前时间(即 now )的变换。要获取时间统计信息,请使用相应的框架调用 tf2_monitor 。
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_monitor turtle2 turtle1结果应该看起来像这样:
cxy@ubuntu2404-cxy:~$ ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_monitor turtle2 turtle1
[INFO] [1720795416.402755139] [tf2_monitor_main]: Waiting for transform turtle2 -> turtle1: Invalid frame ID "turtle2" passed to canTransform argument target_frame - frame does not exist
Gathering data on turtle2 -> turtle1 for 10 seconds...
RESULTS: for turtle2 to turtle1
Chain is: turtle1
Net delay avg = 0.00160438: max = 0.0157883
Frames:
Frame: turtle1, published by <no authority available>, Average Delay: 0.000582495, Max Delay: 0.000986814
All Broadcasters:
Node: <no authority available> 125.256 Hz, Average Delay: 0.000661064 Max Delay: 0.00108385
关键部分是从 turtle2 到 turtle1的chain链延迟。输出显示平均延迟约为1.6毫秒。这意味着 tf2 只能在 1.6 毫秒后在乌龟之间进行转换。因此,如果我们要求 tf2 在 1.6毫秒前而不是 now 之间进行转换,tf2 有时会给我们答案。让我们通过将第 73-77 行更改为以下内容来快速测试一下:
try {
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
this->now() - rclcpp::Duration::from_seconds(0.1));
} catch (const tf2::TransformException & ex) {在新代码中,我们要求获取 100 毫秒前乌龟之间的变换。通常使用较长的时间段,以确保变换能够到达。停止演示,构建并运行:
ros2 launch turtle_tf2 start_debug_demo.launch.py
我们最后做的那个修复并不是你真正想要的,只是为了确保那是我们的问题。真正的修复应该是这样的:
try {
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
tf2::TimePointZero);
} catch (const tf2::TransformException & ex) {或者这样:
try {
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
tf2::TimePoint());
} catch (const tf2::TransformException & ex) {您可以在“使用时间”教程中了解更多关于超时的信息,并按如下方式使用它们:
try {
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
this->now(),
rclcpp::Duration::from_seconds(0.05));
} catch (const tf2::TransformException & ex) {摘要
在本教程中,您学习了如何使用系统的方法来调试与 tf2 相关的问题。您还学习了如何使用 tf2 调试工具,例如 tf2_echo 、 tf2_monitor 和 view_frames 来帮助您调试这些 tf2 问题。




















 89
89

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








