Description
Ouroboros is a mythical snake from ancient Egypt. It has its tail in its mouth and continously devours itself.
The Ouroboros numbers are binary numbers of 2^n bits that have the property of “generating” the whole set of numbers from 0 to 2^n - 1. The generation works as follows: given an Ouroboros number, we place its 2^n bits wrapped in a circle. Then, we can take 2^n groups of n bits starting each time with the next bit in the circle. Such circles are called Ouroboros circles for the number n. We will work only with the smallest Ouroboros number for each n.
Example: for n = 2, there are only four Ouroboros numbers. These are 0011;0110;1100; and 1001. In this case, the smallest one is 0011. Here is the Ouroboros circle for 0011:
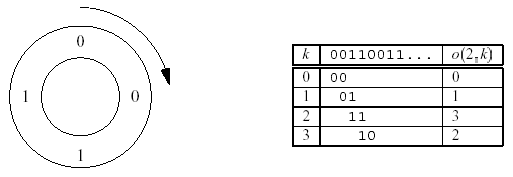
The table describes the function o(n;k) which calculates the k-th number in the Ouroboros circle of the smallest Ouroboros number of size n. This function is what your program should compute.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. For each test case, there will be a line containing two integers n and k (1<=n<=15; 0<=k<2^n). The end of the input file is indicated by a line containing two zeros. Don抰 process that line.
Output
For each test case, output o(n;k) on a line by itself.
Sample Input
2 0
2 1
2 2
2 3
0 0
Sample Output
0
1
3
2
刚开始想如果把每个数看做一个点,把能互相转移的点之间连一条有向边,那么就要求字典序最小的哈密尔顿回路,这是一个NPC,要想办法换成欧拉回路
如果我们把所有的长度为n-1的后缀看做点,能相互转移的后缀之间连边,那么这些边代表的就是所有的数,同时还有新加的数位是0还是1,这样就转化成欧拉回路了
这个图肯定是有解的,为了使字典序最小,肯定从0出发,用Fluery算法求欧拉回路的时候,每次挑字典序小的先走,这样最后的路径reverse一下就是字典序最小的,这个感觉挺对的,大概就是那些0肯定会被放在尽可能后面,reverse完了就到前面了
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <utility>
#include <cctype>
#include <bitset>
#include <sstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define LB long double
#define ull unsigned long long
#define x first
#define y second
#define pb push_back
#define pf push_front
#define mp make_pair
#define Pair pair<int,int>
#define pLL pair<LL,LL>
#define pii pair<double,double>
const int INF=2e9;
const LL LINF=2e16;
const int magic=348;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
const double eps=1e-10;
const double pi=acos(-1);
inline int getint()
{
bool f;char ch;int res;
while (!isdigit(ch=getchar()) && ch!='-') {}
if (ch=='-') f=false,res=0; else f=true,res=ch-'0';
while (isdigit(ch=getchar())) res=res*10+ch-'0';
return f?res:-res;
}
const int MAXN=1e5;
int n,k;
int to[2][MAXN+48];bool used[2][MAXN+48];
int path[MAXN*2+48],tot=0;
inline void dfs(int cur)
{
if (!used[0][cur])
{
used[0][cur]=true;
dfs(to[0][cur]);
path[++tot]=0;
}
if (!used[1][cur])
{
used[1][cur]=true;
dfs(to[1][cur]);
path[++tot]=1;
}
}
int main ()
{
int i,Mask,toMask;
while (scanf("%d%d",&n,&k) && !(!n && !k))
{
for (Mask=0;Mask<=(1<<(n-1))-1;Mask++)
for (i=0;i<=1;i++)
{
toMask=(Mask<<1);toMask|=i;toMask&=((1<<(n-1))-1);
to[i][Mask]=toMask;used[i][Mask]=false;
}
for (i=0;i<=n-2;i++) path[i]=0;tot=n-2;
dfs(0);
reverse(path+n-1,path+tot+1);
memcpy(path+tot+1,path,(tot+1)*sizeof(int));
int ans=0;
for (i=k;i<=k+n-1;i++) ans<<=1,ans|=path[i];
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}























 651
651

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








