1
原始RRT算法运行结果:python,这里以2D_rrt及其衍生相关算法为例(边做边更新)
CV搬运工们,先上github连接:(点个赞呗)(不想要拿github包的后面有现成代码)GitHub - zhm-real/PathPlanning: Common used path planning algorithms with animations.
路径算法的讲解可以看路径规划算法_qq_935160072的博客-优快云博客这篇上放置的B站上up主课程链接
别忘了先阅读README.md,对内容进行简单了解。包含的路径规划算法如下图所示:

那路径规划有什么用呢阿米特的 A* 页面 (stanford.edu)
直接open整个文件包就OK了
在下载文件包后有报错需要修改:
如果发生 from Sampling_based_Planning.rrt_2D import env, plotting, utils
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'Sampling_based_Planning'类似的报错。
from Sampling_based_Planning.rrt_2D import env, plotting, utils将该部分from import 改为
import env
import plotting
import utils如果NO module env,plotting....将对应的代码.py文件该env.py放入rrt.py文件相同的文件夹下即可
该代码是在实现路径规划后再进行绘图显示(需要等待几秒)
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
必须包含3个.py文件 env,plotting,utils分别包含(障碍物,绘图,碰撞检测)
同样我也贴出来:
env.py:
class Env:
def __init__(self):
self.x_range = (0, 50)
self.y_range = (0, 30)
self.obs_boundary = self.obs_boundary()
self.obs_circle = self.obs_circle()
self.obs_rectangle = self.obs_rectangle()
@staticmethod
def obs_boundary():
obs_boundary = [
[0, 0, 1, 30],
[0, 30, 50, 1],
[1, 0, 50, 1],
[50, 1, 1, 30]
]
return obs_boundary
@staticmethod
def obs_rectangle():
obs_rectangle = [
[14, 12, 8, 2],
[18, 22, 8, 3],
[26, 7, 2, 12],
[32, 14, 10, 2]
]
return obs_rectangle
@staticmethod
def obs_circle():
obs_cir = [
[7, 12, 3],
[46, 20, 2],
[15, 5, 2],
[37, 7, 3],
[37, 23, 3],
#[20, 8, 3],
#[31, 20, 3]
]
return obs_cir
plotting:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import os
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) +
"/../../Sampling_based_Planning/")
import env
class Plotting:
def __init__(self, x_start, x_goal):
self.xI, self.xG = x_start, x_goal
self.env = env.Env()
self.obs_bound = self.env.obs_boundary
self.obs_circle = self.env.obs_circle
self.obs_rectangle = self.env.obs_rectangle
def animation(self, nodelist, path, name, animation=False):
self.plot_grid(name)
self.plot_visited(nodelist, animation)
self.plot_path(path)
def animation_connect(self, V1, V2, path, name):
self.plot_grid(name)
self.plot_visited_connect(V1, V2)
self.plot_path(path)
def plot_grid(self, name):
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for (ox, oy, w, h) in self.obs_bound:
ax.add_patch(
patches.Rectangle(
(ox, oy), w, h,
edgecolor='black',
facecolor='black',
fill=True
)
)
for (ox, oy, w, h) in self.obs_rectangle:
ax.add_patch(
patches.Rectangle(
(ox, oy), w, h,
edgecolor='black',
facecolor='gray',
fill=True
)
)
for (ox, oy, r) in self.obs_circle:
ax.add_patch(
patches.Circle(
(ox, oy), r,
edgecolor='black',
facecolor='gray',
fill=True
)
)
plt.plot(self.xI[0], self.xI[1], "bs", linewidth=3)
plt.plot(self.xG[0], self.xG[1], "gs", linewidth=3)
plt.title(name)
plt.axis("equal")
@staticmethod
def plot_visited(nodelist, animation):
if animation:
count = 0
for node in nodelist:
count += 1
if node.parent:
plt.plot([node.parent.x, node.x], [node.parent.y, node.y], "-g")
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event:
[exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
if count % 10 == 0:
plt.pause(0.001)
else:
for node in nodelist:
if node.parent:
plt.plot([node.parent.x, node.x], [node.parent.y, node.y], "-g")
@staticmethod
def plot_visited_connect(V1, V2):
len1, len2 = len(V1), len(V2)
for k in range(max(len1, len2)):
if k < len1:
if V1[k].parent:
plt.plot([V1[k].x, V1[k].parent.x], [V1[k].y, V1[k].parent.y], "-g")
if k < len2:
if V2[k].parent:
plt.plot([V2[k].x, V2[k].parent.x], [V2[k].y, V2[k].parent.y], "-g")
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
if k % 2 == 0:
plt.pause(0.001)
plt.pause(0.01)
@staticmethod
def plot_path(path):
if len(path) != 0:
plt.plot([x[0] for x in path], [x[1] for x in path], '-r', linewidth=2)
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.show()
utils.py:
import math
import numpy as np
import os
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) +
"/../../Sampling_based_Planning/")
import env
class Node:
def __init__(self, n):
self.x = n[0]
self.y = n[1]
self.parent = None
class Utils:
def __init__(self):
self.env = env.Env() #初始化环境信息
self.delta = 0.5
self.obs_circle = self.env.obs_circle
self.obs_rectangle = self.env.obs_rectangle
self.obs_boundary = self.env.obs_boundary
def update_obs(self, obs_cir, obs_bound, obs_rec): #更新环境信息
self.obs_circle = obs_cir
self.obs_boundary = obs_bound
self.obs_rectangle = obs_rec
def get_obs_vertex(self): #获取障碍物点
delta = self.delta
obs_list = [] #障碍物列表
for (ox, oy, w, h) in self.obs_rectangle:
vertex_list = [[ox - delta, oy - delta],
[ox + w + delta, oy - delta],
[ox + w + delta, oy + h + delta],
[ox - delta, oy + h + delta]]
obs_list.append(vertex_list)
return obs_list
def is_intersect_rec(self, start, end, o, d, a, b):
v1 = [o[0] - a[0], o[1] - a[1]] #v1=o和a的xy坐标差
v2 = [b[0] - a[0], b[1] - a[1]] #v2=b和a的xy坐标差
v3 = [-d[1], d[0]]
div = np.dot(v2, v3) #v2, v3点乘
if div == 0: #点乘等于0表示向量垂直
return False
t1 = np.linalg.norm(np.cross(v2, v1)) / div
t2 = np.dot(v1, v3) / div
if t1 >= 0 and 0 <= t2 <= 1:
shot = Node((o[0] + t1 * d[0], o[1] + t1 * d[1]))
dist_obs = self.get_dist(start, shot)
dist_seg = self.get_dist(start, end)
if dist_obs <= dist_seg:
return True
return False
def is_intersect_circle(self, o, d, a, r):
d2 = np.dot(d, d)
delta = self.delta
if d2 == 0:
return False
t = np.dot([a[0] - o[0], a[1] - o[1]], d) / d2
if 0 <= t <= 1:
shot = Node((o[0] + t * d[0], o[1] + t * d[1]))
if self.get_dist(shot, Node(a)) <= r + delta:
return True
return False
def is_collision(self, start, end):
if self.is_inside_obs(start) or self.is_inside_obs(end):
return True
o, d = self.get_ray(start, end) #o, d为起点和终点
obs_vertex = self.get_obs_vertex() #获取更新的障碍物
for (v1, v2, v3, v4) in obs_vertex: #
if self.is_intersect_rec(start, end, o, d, v1, v2):
return True
if self.is_intersect_rec(start, end, o, d, v2, v3):
return True
if self.is_intersect_rec(start, end, o, d, v3, v4):
return True
if self.is_intersect_rec(start, end, o, d, v4, v1):
return True
for (x, y, r) in self.obs_circle:
if self.is_intersect_circle(o, d, [x, y], r):
return True
return False
#通过改变避障方式,增加判断当发生碰撞时改变扩展方向进行障碍物的避绕
def is_inside_obs(self, node): #在障碍物中的数据信息,
delta = self.delta
for (x, y, r) in self.obs_circle: #圆形障碍物
if math.hypot(node.x - x, node.y - y) <= r + delta:
return True
for (x, y, w, h) in self.obs_rectangle: #矩形障碍物
if 0 <= node.x - (x - delta) <= w + 2 * delta \
and 0 <= node.y - (y - delta) <= h + 2 * delta:
return True
for (x, y, w, h) in self.obs_boundary: #边界障碍物
if 0 <= node.x - (x - delta) <= w + 2 * delta \
and 0 <= node.y - (y - delta) <= h + 2 * delta:
return True
return False
@staticmethod
def get_ray(start, end):
orig = [start.x, start.y]
direc = [end.x - start.x, end.y - start.y] #终点-起始点得到生长方向
return orig, direc
@staticmethod
def get_dist(start, end):
return math.hypot(end.x - start.x, end.y - start.y) #两点间的距离
RRT代码介绍连接:(14条消息) RRT算法简介_魂淡1994的博客-优快云博客
仿真结果如下:

具体代码已经贴出:注释自己写的可能有小错误,可以帮忙指出
import os
import sys
import math
import time
import random
import numpy as np
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) +
"/../../Sampling_based_Planning/")
import env #障碍物图
import plotting #画图
import utils
class Node:
def __init__(self, n):
self.x = n[0]
self.y = n[1]
self.parent = None
class Rrt:
def __init__(self, s_start, s_goal, step_len, goal_sample_rate, iter_max):
self.s_start = Node(s_start)
self.s_goal = Node(s_goal)
self.step_len = step_len
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.iter_max = iter_max
self.vertex = [self.s_start]
self.env = env.Env()
self.plotting = plotting.Plotting(s_start, s_goal)
self.utils = utils.Utils()
self.x_range = self.env.x_range
self.y_range = self.env.y_range
self.obs_circle = self.env.obs_circle
self.obs_rectangle = self.env.obs_rectangle
self.obs_boundary = self.env.obs_boundary
self.iterations = 0
def planning(self):
for i in range(self.iter_max):
node_rand = self.generate_random_node(self.goal_sample_rate) #随机生成的节点
node_near = self.nearest_neighbor(self.vertex, node_rand) #最近的节点
node_new = self.new_state(node_near, node_rand) #新节点
"""
######################节点重选择部分
node_vector = np
v_1 = (node_new[0]-node_near[0], node_new[1]-node_near[1])
v_2 = ()
######################节点重选择部分
"""
self.iterations += 1
time.sleep(0.001)
if node_new and not self.utils.is_collision(node_near, node_new):
self.vertex.append(node_new)
dist, _ = self.get_distance_and_angle(node_new, self.s_goal)
if dist <= self.step_len and not self.utils.is_collision(node_new, self.s_goal):
self.new_state(node_new, self.s_goal)
return self.extract_path(node_new)
return None
def generate_random_node(self, goal_sample_rate):
delta = self.utils.delta
if random.randint(0, 100) > goal_sample_rate:
return Node((np.random.uniform(self.x_range[0] + delta, self.x_range[1] - delta),
np.random.uniform(self.y_range[0] + delta, self.y_range[1] - delta)))
return self.s_goal
@staticmethod
def nearest_neighbor(node_list, n):
return node_list[int(np.argmin([math.hypot(nd.x - n.x, nd.y - n.y)
for nd in node_list]))]
def new_state(self, node_start, node_end):
dist, theta = self.get_distance_and_angle(node_start, node_end)
dist = min(self.step_len, dist)
node_new = Node((node_start.x + dist * math.cos(theta),
node_start.y + dist * math.sin(theta)))
node_new.parent = node_start
#a = math.tan(theta) #根据两点计算角度的弧度
#k = -1/a #随机向量垂直的方向
#print(k)
#print(a)
return node_new
def extract_path(self, node_end):
path = [(self.s_goal.x, self.s_goal.y)]
node_now = node_end
while node_now.parent is not None:
node_now = node_now.parent
path.append((node_now.x, node_now.y))
return path
@staticmethod
def get_distance_and_angle(node_start, node_end):
dx = node_end.x - node_start.x
dy = node_end.y - node_start.y
return math.hypot(dx, dy), math.atan2(dy, dx)
def main():
start_time = time.time() # 规划时间
x_start = (2, 2) # Starting node
x_goal = (49, 24) # Goal node
rrt = Rrt(x_start, x_goal, 0.5, 0, 10000) #起点,目标点,步长,随机概率,最大迭代次数
path = rrt.planning()
print((time.time() - start_time))
print(f"迭代次数为: {rrt.iterations}")
#print(f"Path length: {path_length}")
if path:
rrt.plotting.animation(rrt.vertex, path, "RRT", True)
count = 0
for i in path:
count += 1
print("距离长度为:" + str(count) + "mm") #路径有问题
else:
print("No Path Found!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
RRT算法加入目标偏置概率(random()函数,大于设置值取目标点,小于则取随机生成的点)后随机性明显变小(过大过小均不合适),,,修改注释代表的随机概率即可
def main():
start_time = time.time() # 规划时间
x_start = (2, 2) # Starting node
x_goal = (49, 24) # Goal node
rrt = Rrt(x_start, x_goal, 0.5, 0, 10000) #起点,目标点,步长,随机概率,最大迭代次数
path = rrt.planning()
print((time.time() - start_time))
print(f"迭代次数为: {rrt.iterations}")
#print(f"Path length: {path_length}")
if path:
rrt.plotting.animation(rrt.vertex, path, "RRT", True)
count = 0
for i in path:
count += 1
print("距离长度为:" + str(count) + "mm") #路径有问题
else:
print("No Path Found!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()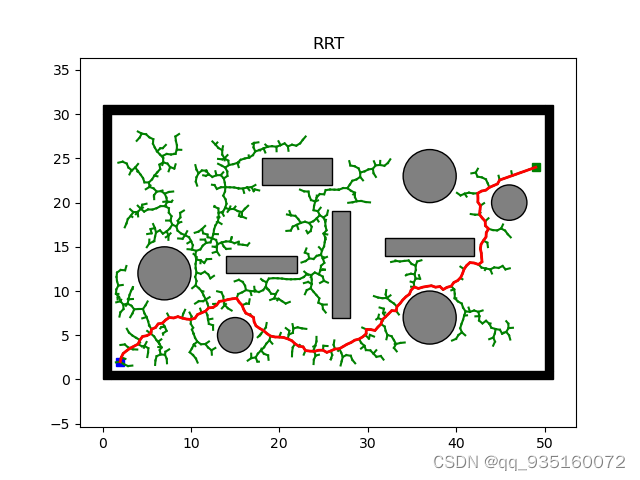
RRT-connect算法采用双向搜索树交替进行搜索(包括目标偏置和贪婪算法)原理介绍链接:(14条消息) RRT-connect算法__yuan_的博客-优快云博客
代码如下(同样贪婪算法部分也标注出来了):
import os
import sys
import math
import copy
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) +
"/../../Sampling_based_Planning/")
import env
import plotting
import utils
class Node: #定义一个节点
def __init__(self, n):
self.x = n[0]
self.y = n[1]
self.parent = None
class RrtConnect:
def __init__(self, s_start, s_goal, step_len, goal_sample_rate, iter_max):
self.s_start = Node(s_start)
self.s_goal = Node(s_goal)
self.step_len = step_len
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.iter_max = iter_max
self.V1 = [self.s_start]
self.V2 = [self.s_goal]
self.env = env.Env()
self.plotting = plotting.Plotting(s_start, s_goal)
self.utils = utils.Utils()
self.x_range = self.env.x_range
self.y_range = self.env.y_range
self.obs_circle = self.env.obs_circle #更新圆形障碍物
self.obs_rectangle = self.env.obs_rectangle #更新矩形障碍物
self.obs_boundary = self.env.obs_boundary #更新地图边界
self.iterations = 0 #初始化迭代次数为0
def planning(self): #定义函数获取路径
for i in range(self.iter_max):
node_rand = self.generate_random_node(self.s_goal, self.goal_sample_rate) #随机点=产生目标点和目标概率
node_near = self.nearest_neighbor(self.V1, node_rand) #最近的点与随机点的V1距离
node_new = self.new_state(node_near, node_rand) #new_state()函数返回新节点
self.iterations += 1 #迭代次数+1
time.sleep(0.001)
if node_new and not self.utils.is_collision(node_near, node_new): #utils.py文件中进行碰撞检测
self.V1.append(node_new) #无碰撞后将新节点加入(V1)中
node_near_prim = self.nearest_neighbor(self.V2, node_new) #返回最近节点赋值给node_near_prim(根据最近节点获取方向,得到下面的)
node_new_prim = self.new_state(node_near_prim, node_new) #将新生成的节点赋值给node_new_prim
"""
######################贪婪算法部分
if node_new_prim and not self.utils.is_collision(node_new_prim, node_near_prim): #如果新节点也不发生碰撞(新生成的节点,最近的节点)
#self.V2.append(node_new_prim) #将新生成的节点加入V2
#while True: #发生碰撞则进行下列操作
#node_new_prim2 = self.new_state(node_new_prim, node_new) #因为第一棵树碰撞,与第二棵树交换进行
#if node_new_prim2 and not self.utils.is_collision(node_new_prim2, node_new_prim): #如果与第二棵树没发生碰撞(第二棵树的节点,新生成的节点)
#self.V2.append(node_new_prim2) #然后将该节点加入V2中
#node_new_prim = self.change_node(node_new_prim, node_new_prim2) #交换节点后赋值为新节点
#else:
#break
#if self.is_node_same(node_new_prim, node_new):
#break
#######################贪婪算法部分
"""
if self.is_node_same(node_new_prim, node_new): #is_node_same函数判断新节点是不是目标点
return self.extract_path(node_new, node_new_prim) #返回路径
if len(self.V2) < len(self.V1): #对比第一棵树和第二棵树的长度,平衡随机树长度,交换
list_mid = self.V2
self.V2 = self.V1
self.V1 = list_mid
"""判断偶数进行树扩展的交换
if i % 2 == 0:
list_mid = self.V2
self.V2 = self.V1
self.V1 = list_mid
"""
return None
@staticmethod
def change_node(node_new_prim, node_new_prim2): #交换节点
node_new = Node((node_new_prim2.x, node_new_prim2.y)) #将第二课树的节点赋值为新节点
node_new.parent = node_new_prim #将node_new_prim赋值给父节点
return node_new
@staticmethod
def is_node_same(node_new_prim, node_new): #如果新节点是目标点,则返回True
if node_new_prim.x == node_new.x and \
node_new_prim.y == node_new.y:
return True
return False
def generate_random_node(self, sample_goal, goal_sample_rate): #随机生成数大于目标概率则生成随机点,否则去目标点作为随机点
delta = self.utils.delta
if random.randint(0, 100) > goal_sample_rate:
return Node((np.random.uniform(self.x_range[0] + delta, self.x_range[1] - delta),
np.random.uniform(self.y_range[0] + delta, self.y_range[1] - delta)))
return sample_goal
@staticmethod
def nearest_neighbor(node_list, n): #从节点列表中找到最近节点,并返回
return node_list[int(np.argmin([math.hypot(nd.x - n.x, nd.y - n.y) #返回最近的节点
for nd in node_list]))]
def new_state(self, node_start, node_end): #函数获得新节点扩展的位置
dist, theta = self.get_distance_and_angle(node_start, node_end) #获得了距离,角度
dist = min(self.step_len, dist)
node_new = Node((node_start.x + dist * math.cos(theta),
node_start.y + dist * math.sin(theta)))
node_new.parent = node_start #将父节点作为起点
print(theta) #(theta)<0代表向下,>0代表向下
return node_new #返回新节点位置
@staticmethod
def extract_path(node_new, node_new_prim): #获得生成的路径(path1 + path2)
path1 = [(node_new.x, node_new.y)]
node_now = node_new
while node_now.parent is not None:
node_now = node_now.parent
path1.append((node_now.x, node_now.y))
path2 = [(node_new_prim.x, node_new_prim.y)]
node_now = node_new_prim
while node_now.parent is not None:
node_now = node_now.parent
path2.append((node_now.x, node_now.y))
return list(list(reversed(path1)) + path2)
@staticmethod
def get_distance_and_angle(node_start, node_end): #根据开始的节点和最后的节点获取距离和角度
dx = node_end.x - node_start.x
dy = node_end.y - node_start.y
return math.hypot(dx, dy), math.atan2(dy, dx) #hypot()函数计算两点间的距离
def main():
start_time = time.time() # 规划时间
x_start = (2, 2) # 起始节点
x_goal = (49, 24) # 最终节点
rrt_connect = RrtConnect(x_start, x_goal, 0.5, 0, 5000) #起点,目标点,步长,随机概率,最大迭代次数
path = rrt_connect.planning()
print((time.time() - start_time))
print(f"迭代次数为: {rrt_connect.iterations}")
rrt_connect.plotting.animation_connect(rrt_connect.V1, rrt_connect.V2, path, "RRT_CONNECT")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
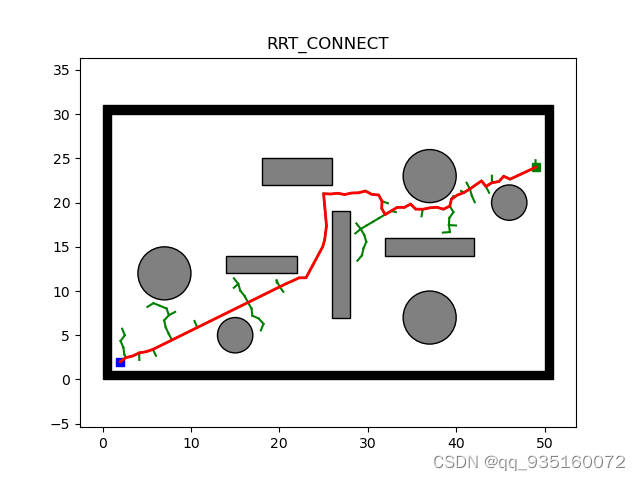
将贪婪算法部分注释掉后的运行结果(为了方便阅读,将全文注释了一遍,但是有些部分目前还没看懂)


RRT*是渐进优化算法(等待时间较长)
代码如下:
"""
RRT_star 2D
@author: huiming zhou
"""
import os
import sys
import math
import time
import numpy as np
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) +
"/../../Sampling_based_Planning/")
import env
import plotting
import utils
import queue
class Node:
def __init__(self, n):
self.x = n[0]
self.y = n[1]
self.parent = None
class RrtStar:
def __init__(self, x_start, x_goal, step_len,
goal_sample_rate, search_radius, iter_max):
self.s_start = Node(x_start)
self.s_goal = Node(x_goal)
self.step_len = step_len
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.search_radius = search_radius
self.iter_max = iter_max
self.vertex = [self.s_start]
self.path = []
self.env = env.Env()
self.plotting = plotting.Plotting(x_start, x_goal)
self.utils = utils.Utils()
self.x_range = self.env.x_range
self.y_range = self.env.y_range
self.obs_circle = self.env.obs_circle
self.obs_rectangle = self.env.obs_rectangle
self.obs_boundary = self.env.obs_boundary
self.iterations = 0
def planning(self):
for k in range(self.iter_max):
node_rand = self.generate_random_node(self.goal_sample_rate)
node_near = self.nearest_neighbor(self.vertex, node_rand)
node_new = self.new_state(node_near, node_rand)
self.iterations += 1
time.sleep(0.001)
if k % 500 == 0:
print(k)
if node_new and not self.utils.is_collision(node_near, node_new):
neighbor_index = self.find_near_neighbor(node_new)
self.vertex.append(node_new)
if neighbor_index:
self.choose_parent(node_new, neighbor_index)
self.rewire(node_new, neighbor_index)
index = self.search_goal_parent()
self.path = self.extract_path(self.vertex[index])
self.plotting.animation(self.vertex, self.path, "rrt*, N = " + str(self.iter_max))
def new_state(self, node_start, node_goal):
dist, theta = self.get_distance_and_angle(node_start, node_goal)
dist = min(self.step_len, dist)
node_new = Node((node_start.x + dist * math.cos(theta),
node_start.y + dist * math.sin(theta)))
node_new.parent = node_start
return node_new
def choose_parent(self, node_new, neighbor_index):
cost = [self.get_new_cost(self.vertex[i], node_new) for i in neighbor_index]
cost_min_index = neighbor_index[int(np.argmin(cost))]
node_new.parent = self.vertex[cost_min_index]
def rewire(self, node_new, neighbor_index):
for i in neighbor_index:
node_neighbor = self.vertex[i]
if self.cost(node_neighbor) > self.get_new_cost(node_new, node_neighbor):
node_neighbor.parent = node_new
def search_goal_parent(self):
dist_list = [math.hypot(n.x - self.s_goal.x, n.y - self.s_goal.y) for n in self.vertex]
node_index = [i for i in range(len(dist_list)) if dist_list[i] <= self.step_len]
if len(node_index) > 0:
cost_list = [dist_list[i] + self.cost(self.vertex[i]) for i in node_index
if not self.utils.is_collision(self.vertex[i], self.s_goal)]
return node_index[int(np.argmin(cost_list))]
return len(self.vertex) - 1
def get_new_cost(self, node_start, node_end):
dist, _ = self.get_distance_and_angle(node_start, node_end)
return self.cost(node_start) + dist
def generate_random_node(self, goal_sample_rate):
delta = self.utils.delta
if np.random.random() > goal_sample_rate:
return Node((np.random.uniform(self.x_range[0] + delta, self.x_range[1] - delta),
np.random.uniform(self.y_range[0] + delta, self.y_range[1] - delta)))
return self.s_goal
def find_near_neighbor(self, node_new):
n = len(self.vertex) + 1
r = min(self.search_radius * math.sqrt((math.log(n) / n)), self.step_len)
dist_table = [math.hypot(nd.x - node_new.x, nd.y - node_new.y) for nd in self.vertex]
dist_table_index = [ind for ind in range(len(dist_table)) if dist_table[ind] <= r and
not self.utils.is_collision(node_new, self.vertex[ind])]
return dist_table_index
@staticmethod
def nearest_neighbor(node_list, n):
return node_list[int(np.argmin([math.hypot(nd.x - n.x, nd.y - n.y)
for nd in node_list]))]
@staticmethod
def cost(node_p):
node = node_p
cost = 0.0
while node.parent:
cost += math.hypot(node.x - node.parent.x, node.y - node.parent.y)
node = node.parent
return cost
def update_cost(self, parent_node):
OPEN = queue.QueueFIFO()
OPEN.put(parent_node)
while not OPEN.empty():
node = OPEN.get()
if len(node.child) == 0:
continue
for node_c in node.child:
node_c.Cost = self.get_new_cost(node, node_c)
OPEN.put(node_c)
def extract_path(self, node_end):
path = [[self.s_goal.x, self.s_goal.y]]
node = node_end
while node.parent is not None:
path.append([node.x, node.y])
node = node.parent
path.append([node.x, node.y])
return path
@staticmethod
def get_distance_and_angle(node_start, node_end):
dx = node_end.x - node_start.x
dy = node_end.y - node_start.y
return math.hypot(dx, dy), math.atan2(dy, dx)
def main():
start_time = time.time() # 规划时间
x_start = (2, 2) # Starting node
x_goal = (49, 24) # Goal node
rrt_star = RrtStar(x_start, x_goal, 1, 0, 20, 10000)
rrt_star.planning()
print((time.time() - start_time))
print(f"迭代次数为: {rrt_star.iterations}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
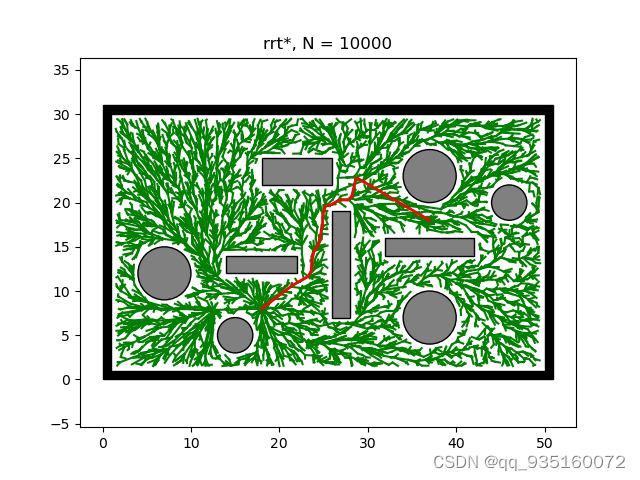
这三种算法的介绍连接如下 :(12条消息) RRT、RRT_Connect、RRT*_-点灯-的博客-优快云博客_rrt-connect























 6095
6095

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








