目录
6.1 公共类: 图Graph、节点Node、边Edge、子集Subset
书里的目录:
Concept of graphs
Applications
Representation
Adjacency list
Adjacency matrix
Implementation
Node
Edge
Graph
Example-undirected unweighted edges
Example-directed and weighted edges
Traversal 遍历
Depth-first search 深度优先搜索
Breadth-first search 广度优先搜索
Minimum spanning tree 最小生成树
Kruskal's algorithm
Prim's algorithm
Example-telecommunication cable
Coloring
Example-voivodeship map
Sortest path
Example -game map
Summary
6.1 公共类: 图Graph、节点Node、边Edge、子集Subset
/////////////////////// 公用类 ///////////////////////
/* Edge 类 */
namespace Graphs
{
public class Edge<T>
{
public Node<T> From { get; set; }//起点
public Node<T> To { get; set; }//终点
public int Weight { get; set; }//权重
public override string ToString()
{
return $"Edge: {From.Data} -> {To.Data}, weight: {Weight}";
}
}
}
/* Node.cs 节点类*/
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Graphs
{
public class Node<T> //节点
{
public int Index { get; set; } //索引
public T Data { get; set; } //数据
public List<Node<T>> Neighbors { get; set; } = new List<Node<T>>();//邻居
public List<int> Weights { get; set; } = new List<int>();//权重
public override string ToString()
{
return $"Node with index {Index}: {Data}, neighbors: {Neighbors.Count}";
}
}
}
/* Subset.cs 子集 */
namespace Graphs
{
public class Subset<T> //子集
{
public Node<T> Parent { get; set; } //父节点
public int Rank { get; set; } //级别
public override string ToString()
{
return $"Subset with rank {Rank}, parent: {Parent.Data} (index: {Parent.Index})";
}
}
}
/* Graph.cs 图 */
using Priority_Queue;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Graphs
{
public class Graph<T>
{
#region Implementation //图的实现
private bool _isDirected = false;//是否有方向 有向图/无向图
private bool _isWeighted = false;//是否有权重
public List<Node<T>> Nodes { get; set; } = new List<Node<T>>();//节点列表
public Edge<T> this[int from, int to] //获取边
{
get
{
Node<T> nodeFrom = Nodes[from];
Node<T> nodeTo = Nodes[to];
int i = nodeFrom.Neighbors.IndexOf(nodeTo);
if (i >= 0)
{
Edge<T> edge = new Edge<T>()
{
From = nodeFrom,
To = nodeTo,
Weight = i < nodeFrom.Weights.Count ? nodeFrom.Weights[i] : 0
};
return edge;
}
return null;
}
}
//图:构造函数
public Graph(bool isDirected, bool isWeighted)
{
_isDirected = isDirected;
_isWeighted = isWeighted;
}
//添加节点
public Node<T> AddNode(T value)
{
Node<T> node = new Node<T>() { Data = value };
Nodes.Add(node);
UpdateIndices();
return node;
}
//添加边
public void AddEdge(Node<T> from, Node<T> to, int weight = 0)
{
from.Neighbors.Add(to);
if (_isWeighted)
{
from.Weights.Add(weight);
}
if (!_isDirected)
{
to.Neighbors.Add(from);
if (_isWeighted)
{
to.Weights.Add(weight);
}
}
}
//移除节点
public void RemoveNode(Node<T> nodeToRemove)
{
Nodes.Remove(nodeToRemove);
UpdateIndices();
foreach (Node<T> node in Nodes)
{
RemoveEdge(node, nodeToRemove);
}
}
//移除边
public void RemoveEdge(Node<T> from, Node<T> to)
{
int index = from.Neighbors.FindIndex(n => n == to);
if (index >= 0)
{
from.Neighbors.RemoveAt(index);
from.Weights.RemoveAt(index);
}
}
//获取所有边
public List<Edge<T>> GetEdges()
{
List<Edge<T>> edges = new List<Edge<T>>();
foreach (Node<T> from in Nodes)
{
for (int i = 0; i < from.Neighbors.Count; i++)
{
Edge<T> edge = new Edge<T>()
{
From = from,
To = from.Neighbors[i],
Weight = i < from.Weights.Count ? from.Weights[i] : 0
};
edges.Add(edge);
}
}
return edges;
}
//更新所有节点索引
private void UpdateIndices()
{
int i = 0;
Nodes.ForEach(n => n.Index = i++);
}
#endregion
#region Minimum Spanning Tree (Kruskal)
// The presented code is based on the implementation shown at:
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-algorithms-set-2-kruskals-minimum-spanning-tree-mst/
public List<Edge<T>> MinimumSpanningTreeKruskal()
{
List<Edge<T>> edges = GetEdges(); //获取图的所有边
edges.Sort((a, b) => a.Weight.CompareTo(b.Weight)); //根据边的权重排序
Queue<Edge<T>> queue = new Queue<Edge<T>>(edges);//排序的队列
Subset<T>[] subsets = new Subset<T>[Nodes.Count];//子集数组
for (int i = 0; i < Nodes.Count; i++)
{
subsets[i] = new Subset<T>() { Parent = Nodes[i] };//每个节点作为父节点一个子集
}
List<Edge<T>> result = new List<Edge<T>>(); //最小生成树的边列表
while (result.Count < Nodes.Count - 1)//没找全边
{
Edge<T> edge = queue.Dequeue();//取出最小边
Node<T> from = GetRoot(subsets, edge.From);//获取边端点所决定子集的父节点
Node<T> to = GetRoot(subsets, edge.To);//获取边端点所决定子集的父节点
if (from != to)//不构成环
{
result.Add(edge);
Union(subsets, from, to);//更新子集的级别,更新集子集的父节点
}
}
return result;
}
//获取node节点所确定子集的当前父节点
private Node<T> GetRoot(Subset<T>[] subsets, Node<T> node)
{
if (subsets[node.Index].Parent != node)
{
subsets[node.Index].Parent = GetRoot(
subsets,
subsets[node.Index].Parent);
}
return subsets[node.Index].Parent;
}
//组合两个子集,更新其中一个子集的父节点为另一个节点和另一个子集的级别
private void Union(Subset<T>[] subsets, Node<T> a, Node<T> b)
{
if (subsets[a.Index].Rank > subsets[b.Index].Rank)
{
subsets[b.Index].Parent = a;
}
else if (subsets[a.Index].Rank < subsets[b.Index].Rank)
{
subsets[a.Index].Parent = b;
}
else
{
subsets[b.Index].Parent = a;
subsets[a.Index].Rank++;
}
}
#endregion
#region Minimum Spanning Tree (Prim)
// The presented code is based on the implementation shown at:
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-algorithms-set-5-prims-minimum-spanning-tree-mst-2/
public List<Edge<T>> MinimumSpanningTreePrim()
{
int[] previous = new int[Nodes.Count]; //父节点数组
previous[0] = -1;//起点的父节点设置为-1
int[] minWeight = new int[Nodes.Count];//最小权重数组
Fill(minWeight, int.MaxValue);
minWeight[0] = 0;//起点的最小权重0
bool[] isInMST = new bool[Nodes.Count]; //是否已在MST(最小生成树)中
Fill(isInMST, false);
for (int i = 0; i < Nodes.Count - 1; i++)
{
int minWeightIndex = GetMinimumWeightIndex(minWeight, isInMST); //找到最小权重节点索引(节点不在MST中)
isInMST[minWeightIndex] = true;//将最小权重节点放入MST
for (int j = 0; j < Nodes.Count; j++)
{ //遍历与最小权重节点相邻的边
Edge<T> edge = this[minWeightIndex, j];
int weight = edge != null ? edge.Weight : -1;
if (!isInMST[j] //不在MST中
&& weight > 0 //边的权重非负
&& weight < minWeight[j]) //边的权重变小
{
previous[j] = minWeightIndex;//更新最小权重边的父节点索引
minWeight[j] = weight;//最小边的权重,索引j
Console.WriteLine(" --> " + edge.ToString());
}
}
}
//准备结果:最小生成树的边列表
List<Edge<T>> result = new List<Edge<T>>();
for (int i = 1; i < Nodes.Count; i++)
{
Edge<T> edge = this[previous[i], i];
result.Add(edge);
}
return result;
}
//获取最小权重索引: 在MST之外的所有节点
private int GetMinimumWeightIndex(int[] weights, bool[] isInMST)
{
int minValue = int.MaxValue;
int minIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Nodes.Count; i++)
{
if (!isInMST[i] && weights[i] < minValue)
{
minValue = weights[i];
minIndex = i;
}
}
return minIndex;
}
#endregion
#region Shortest Path 最短路
public List<Edge<T>> GetShortestPathDijkstra(Node<T> source, Node<T> target)
{
int[] previous = new int[Nodes.Count];//以最小总成本抵达当前节点的上一节点
Fill(previous, -1);//初始为-1
int[] distances = new int[Nodes.Count]; //访问当前节点的最小距离
Fill(distances, int.MaxValue);//初始为最大
distances[source.Index] = 0; //到起点距离0
SimplePriorityQueue<Node<T>> nodes = new SimplePriorityQueue<Node<T>>(); //优先级队列: 所有节点,优先级为从起点到该节点的最短距离。
for (int i = 0; i < Nodes.Count; i++)
{
nodes.Enqueue(Nodes[i], distances[i]);//按照到节点距离最小优先 添加节点到优先级队列
}
while (nodes.Count != 0)
{
Node<T> node = nodes.Dequeue();//取出访问距离最小的节点
for (int i = 0; i < node.Neighbors.Count; i++) //遍历其邻居节点
{
Node<T> neighbor = node.Neighbors[i]; //邻居节点i
int weight = i < node.Weights.Count ? node.Weights[i] : 0; //邻居节点权重
int weightTotal = distances[node.Index] + weight;//从起点开始到邻居节点的总权重
if (distances[neighbor.Index] > weightTotal) //
{
distances[neighbor.Index] = weightTotal;//更新从起点到邻居的最小总权重
previous[neighbor.Index] = node.Index; //更新访问该邻居节点的上一节点
nodes.UpdatePriority(neighbor, distances[neighbor.Index]);//更新邻居节点在队列的优先级
}
}
}
List<int> indices = new List<int>();
int index = target.Index;//目标点索引
while (index >= 0)
{
indices.Add(index);//依次将上一节点索引添加到indices 数组
index = previous[index];//
}
indices.Reverse();//反转:得到从起点到目标点的节点最短访问顺序
List<Edge<T>> result = new List<Edge<T>>();
for (int i = 0; i < indices.Count - 1; i++)
{
Edge<T> edge = this[indices[i], indices[i + 1]];
result.Add(edge); //从起点到目标点的最短路径 边列表
}
return result;
}
#endregion
#region Coloring 着色
// The presented code is based on the implementation shown at:
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/graph-coloring-set-2-greedy-algorithm/
public int[] Color()
{
int[] colors = new int[Nodes.Count];//初始化节点的颜色索引数组
Fill(colors, -1);//都设置为-1
colors[0] = 0;//首节点 颜色索引0 red
bool[] availability = new bool[Nodes.Count]; //颜色可用性数组,初始化 节点个颜色
for (int i = 1; i < Nodes.Count; i++)
{
Fill(availability, true);//初始化 Nodes.Count个颜色,当前节点都可用
int colorIndex = 0;//颜色索引
foreach (Node<T> neighbor in Nodes[i].Neighbors) //遍历当前节点的邻居
{
colorIndex = colors[neighbor.Index]; //获取邻居颜色索引
if (colorIndex >= 0) //该邻居已着色
{
availability[colorIndex] = false;//设置第 colorIndex 个颜色不可用
}
}
colorIndex = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < availability.Length; j++) //遍历颜色可用性数组
{
if (availability[j]) //第j个颜色 可为当前节点使用
{
colorIndex = j; //获取第j个颜色索引
break;
}
}
colors[i] = colorIndex;//设置当前节点的颜色索引
}
return colors;
}
#endregion
#region Auxiliary 填充数组
private void Fill<Q>(Q[] array, Q value)
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
array[i] = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region Traversal 遍历图
public List<Node<T>> DFS() //深度优先搜索
{
bool[] isExplored = new bool[Nodes.Count]; //存储节点是否已访问的数组
List<Node<T>> result = new List<Node<T>>();
DFS(isExplored, Nodes[0], result);//遍历图:从首节点开始
return result;
}
// node:开始遍历的首节点
private void DFS(bool[] isExplored, Node<T> node, List<Node<T>> result)
{
result.Add(node); //将首节点添加到结果
isExplored[node.Index] = true;//设置首节点已访问
foreach (Node<T> neighbor in node.Neighbors)
{
if (!isExplored[neighbor.Index])
{
DFS(isExplored, neighbor, result);//更新首节点为未访问的邻居节点,递归调用深度优先搜索
}
}
}
public List<Node<T>> BFS()//广度优先搜索
{
return BFS(Nodes[0]);//从首节点开始
}
// The presented code is based on the implementation shown at:
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/breadth-first-traversal-for-a-graph/.
private List<Node<T>> BFS(Node<T> node)
{
bool[] isExplored = new bool[Nodes.Count]; //节点是否已访问
List<Node<T>> result = new List<Node<T>>();
isExplored[node.Index] = true;//设置首节点已访问
Queue<Node<T>> queue = new Queue<Node<T>>();//存储 要搜索邻居节点的 节点队列
queue.Enqueue(node);//将首节点 天啊及到队列
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
Node<T> next = queue.Dequeue();//取出要搜索邻居的节点
result.Add(next);//添加到结果
foreach (Node<T> neighbor in next.Neighbors)//遍历邻居节点
{
if (!isExplored[neighbor.Index])//未访问的邻居节点
{
isExplored[neighbor.Index] = true;//设置为已访问
queue.Enqueue(neighbor);//将该节点添加到要搜索邻居的节点队列
}
}
}
return result;
}
#endregion
}
}
Graph类示例输出结果:
//////////// 6.1 Graphs 添加 optimizedpriorityqueue PriorityQueue
Minimum Spanning Tree - Kruskal's Algorithm:
Edge: 6 -> 7, weight: 1
Edge: 4 -> 2, weight: 2
Edge: 5 -> 6, weight: 2
Edge: 2 -> 1, weight: 3
Edge: 5 -> 8, weight: 3
Edge: 1 -> 3, weight: 5
Edge: 4 -> 8, weight: 8
Minimum Spanning Tree - Prim's Algorithm:
--> Edge: 1 -> 2, weight: 9
--> Edge: 1 -> 3, weight: 5
--> Edge: 3 -> 4, weight: 12
--> Edge: 4 -> 8, weight: 8
--> Edge: 8 -> 5, weight: 3
--> Edge: 5 -> 6, weight: 2
--> Edge: 5 -> 7, weight: 5
--> Edge: 6 -> 7, weight: 1
Edge: 1 -> 2, weight: 9
Edge: 1 -> 3, weight: 5
Edge: 3 -> 4, weight: 12
Edge: 8 -> 5, weight: 3
Edge: 5 -> 6, weight: 2
Edge: 6 -> 7, weight: 1
Edge: 4 -> 8, weight: 8
Shortest Path - Dijkstra's Algorithm:
Edge: 1 -> 3, weight: 5
Edge: 3 -> 4, weight: 12
Edge: 4 -> 8, weight: 8
Edge: 8 -> 5, weight: 3
Coloring the graph:
Node 1: 0
Node 2: 1
Node 3: 0
Node 4: 0
Node 5: 1
Node 6: 0
Node 7: 0
Node 8: 0
Depth-First Search:
Node with index 0: 1, neighbors: 2
Node with index 1: 2, neighbors: 2
Node with index 3: 4, neighbors: 2
Node with index 7: 8, neighbors: 1
Node with index 4: 5, neighbors: 4
Node with index 5: 6, neighbors: 1
Node with index 6: 7, neighbors: 2
Node with index 2: 3, neighbors: 1
Breath-First Search:
Node with index 0: 1, neighbors: 2
Node with index 1: 2, neighbors: 2
Node with index 2: 3, neighbors: 1
Node with index 3: 4, neighbors: 2
Node with index 7: 8, neighbors: 1
Node with index 4: 5, neighbors: 4
Node with index 5: 6, neighbors: 1
Node with index 6: 7, neighbors: 2/* Graph 类的应用示例*/
/* Graph 类的应用示例*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Graphs
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Undirected and unweighted edges
// Graph<int> graph = new Graph<int>(false, false);
// Node<int> n1 = graph.AddNode(1);
// Node<int> n2 = graph.AddNode(2);
// Node<int> n3 = graph.AddNode(3);
// Node<int> n4 = graph.AddNode(4);
// Node<int> n5 = graph.AddNode(5);
// Node<int> n6 = graph.AddNode(6);
// Node<int> n7 = graph.AddNode(7);
// Node<int> n8 = graph.AddNode(8);
// graph.AddEdge(n1, n2);
// graph.AddEdge(n1, n3);
// graph.AddEdge(n2, n4);
// graph.AddEdge(n3, n4);
// graph.AddEdge(n4, n5);
// graph.AddEdge(n4, n8);
// graph.AddEdge(n5, n6);
// graph.AddEdge(n5, n7);
// graph.AddEdge(n5, n8);
// graph.AddEdge(n6, n7);
// graph.AddEdge(n7, n8);
// ---
// Undirected and weighted edges
// Graph<int> graph = new Graph<int>(false, true);
// Node<int> n1 = graph.AddNode(1);
// Node<int> n2 = graph.AddNode(2);
// Node<int> n3 = graph.AddNode(3);
// Node<int> n4 = graph.AddNode(4);
// Node<int> n5 = graph.AddNode(5);
// Node<int> n6 = graph.AddNode(6);
// Node<int> n7 = graph.AddNode(7);
// Node<int> n8 = graph.AddNode(8);
// graph.AddEdge(n1, n2, 3);
// graph.AddEdge(n1, n3, 5);
// graph.AddEdge(n2, n4, 4);
// graph.AddEdge(n3, n4, 12);
// graph.AddEdge(n4, n5, 9);
// graph.AddEdge(n4, n8, 8);
// graph.AddEdge(n5, n6, 4);
// graph.AddEdge(n5, n7, 5);
// graph.AddEdge(n5, n8, 1);
// graph.AddEdge(n6, n7, 6);
// graph.AddEdge(n7, n8, 20);
// graph.AddEdge(n2, n6, 20);
// graph.AddEdge(n2, n5, 20);
// ---
// Directed and weighted edges
Graph<int> graph = new Graph<int>(true, true);
Node<int> n1 = graph.AddNode(1);
Node<int> n2 = graph.AddNode(2);
Node<int> n3 = graph.AddNode(3);
Node<int> n4 = graph.AddNode(4);
Node<int> n5 = graph.AddNode(5);
Node<int> n6 = graph.AddNode(6);
Node<int> n7 = graph.AddNode(7);
Node<int> n8 = graph.AddNode(8);
graph.AddEdge(n1, n2, 9);
graph.AddEdge(n1, n3, 5);
graph.AddEdge(n2, n1, 3);
graph.AddEdge(n2, n4, 18);
graph.AddEdge(n3, n4, 12);
graph.AddEdge(n4, n2, 2);
graph.AddEdge(n4, n8, 8);
graph.AddEdge(n5, n4, 9);
graph.AddEdge(n5, n6, 2);
graph.AddEdge(n5, n7, 5);
graph.AddEdge(n5, n8, 3);
graph.AddEdge(n6, n7, 1);
graph.AddEdge(n7, n5, 4);
graph.AddEdge(n7, n8, 6);
graph.AddEdge(n8, n5, 3);
Console.WriteLine("Minimum Spanning Tree - Kruskal's Algorithm:");
List<Edge<int>> mstKruskal = graph.MinimumSpanningTreeKruskal(); //最小生成树 kruskal算法
mstKruskal.ForEach(e => Console.WriteLine(e));
Console.WriteLine("\nMinimum Spanning Tree - Prim's Algorithm:");
List<Edge<int>> mstPrim = graph.MinimumSpanningTreePrim(); //最小生成树 Prim算法
mstPrim.ForEach(e => Console.WriteLine(e));
Console.WriteLine("\nShortest Path - Dijkstra's Algorithm:");
List<Edge<int>> path = graph.GetShortestPathDijkstra(n1, n5); //最短路 Dijkstra算法
path.ForEach(e => Console.WriteLine(e));
Console.WriteLine("\nColoring the graph:");
int[] colors = graph.Color(); //图着色算法
for (int i = 0; i < colors.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Node {graph.Nodes[i].Data}: {colors[i]}");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nDepth-First Search:");
List<Node<int>> dfsNodes = graph.DFS(); //遍历树: 深度优先算法
dfsNodes.ForEach(n => Console.WriteLine(n));
Console.WriteLine("\nBreath-First Search:");
List<Node<int>> bfsNodes = graph.BFS();//遍历树:广度优先算法
bfsNodes.ForEach(n => Console.WriteLine(n));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}6.2 通讯电缆实例 最小生成树:两种算法
输出结果:
Minimum Spanning Tree - Kruskal's Algorithm:
Edge: R4 -> R3, weight: 1
Edge: R3 -> R2, weight: 1
Edge: R2 -> R1, weight: 1
Edge: B1 -> B2, weight: 2
Edge: B3 -> B4, weight: 2
Edge: R6 -> R5, weight: 3
Edge: R6 -> B5, weight: 3
Edge: B5 -> B6, weight: 6
Edge: B1 -> B3, weight: 20
Edge: B2 -> R2, weight: 25
Edge: R1 -> R5, weight: 75
Total cost: 139
Minimum Spanning Tree - Prim's Algorithm:
--> Edge: B1 -> B2, weight: 2
--> Edge: B1 -> B3, weight: 20
--> Edge: B1 -> B4, weight: 30
--> Edge: B2 -> B4, weight: 20
--> Edge: B2 -> R2, weight: 25
--> Edge: B3 -> B4, weight: 2
--> Edge: B4 -> R4, weight: 25
--> Edge: R2 -> R1, weight: 1
--> Edge: R2 -> R3, weight: 1
--> Edge: R1 -> R5, weight: 75
--> Edge: R3 -> R4, weight: 1
--> Edge: R3 -> R6, weight: 100
--> Edge: R5 -> R6, weight: 3
--> Edge: R6 -> B5, weight: 3
--> Edge: R6 -> B6, weight: 10
--> Edge: B5 -> B6, weight: 6
Edge: B1 -> B2, weight: 2
Edge: B1 -> B3, weight: 20
Edge: B3 -> B4, weight: 2
Edge: R6 -> B5, weight: 3
Edge: B5 -> B6, weight: 6
Edge: R2 -> R1, weight: 1
Edge: B2 -> R2, weight: 25
Edge: R2 -> R3, weight: 1
Edge: R3 -> R4, weight: 1
Edge: R1 -> R5, weight: 75
Edge: R5 -> R6, weight: 3
Total cost: 139代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace Graphs
{
class Program
{//通讯电缆实例
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Graph<string> graph = new Graph<string>(false, true);
Node<string> nodeB1 = graph.AddNode("B1");
Node<string> nodeB2 = graph.AddNode("B2");
Node<string> nodeB3 = graph.AddNode("B3");
Node<string> nodeB4 = graph.AddNode("B4");
Node<string> nodeB5 = graph.AddNode("B5");
Node<string> nodeB6 = graph.AddNode("B6");
Node<string> nodeR1 = graph.AddNode("R1");
Node<string> nodeR2 = graph.AddNode("R2");
Node<string> nodeR3 = graph.AddNode("R3");
Node<string> nodeR4 = graph.AddNode("R4");
Node<string> nodeR5 = graph.AddNode("R5");
Node<string> nodeR6 = graph.AddNode("R6");
graph.AddEdge(nodeB1, nodeB2, 2);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB1, nodeB3, 20);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB1, nodeB4, 30);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB2, nodeB3, 30);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB2, nodeB4, 20);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB3, nodeB4, 2);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB2, nodeR2, 25);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB4, nodeR4, 25);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR1, nodeR2, 1);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR2, nodeR3, 1);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR3, nodeR4, 1);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR1, nodeR5, 75);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR3, nodeR6, 100);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR5, nodeR6, 3);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR6, nodeB5, 3);
graph.AddEdge(nodeB5, nodeB6, 6);
graph.AddEdge(nodeR6, nodeB6, 10);
Console.WriteLine("Minimum Spanning Tree - Kruskal's Algorithm:");
List<Edge<string>> mstKruskal = graph.MinimumSpanningTreeKruskal();
mstKruskal.ForEach(e => Console.WriteLine(e));
Console.WriteLine("Total cost: " + mstKruskal.Sum(e => e.Weight));
Console.WriteLine("\nMinimum Spanning Tree - Prim's Algorithm:");
List<Edge<string>> mstPrim = graph.MinimumSpanningTreePrim();
mstPrim.ForEach(e => Console.WriteLine(e));
Console.WriteLine("Total cost: " + mstPrim.Sum(e => e.Weight));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
6.3 VoivodeshipMap 波兰:省级地图着色
PK: 0
LU: 1
PD: 0
WM: 1
MZ: 2
SW: 3
MA: 1
SL: 0
LD: 1
KP: 0
PM: 2
ZP: 0
WP: 3
LB: 1
DS: 0
OP: 2代码:
/* Main 程序 */
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Graphs
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Graph<string> graph = new Graph<string>(false, false);
Node<string> nodePK = graph.AddNode("PK");
Node<string> nodeLU = graph.AddNode("LU");
Node<string> nodePD = graph.AddNode("PD");
Node<string> nodeWM = graph.AddNode("WM");
Node<string> nodeMZ = graph.AddNode("MZ");
Node<string> nodeSW = graph.AddNode("SW");
Node<string> nodeMA = graph.AddNode("MA");
Node<string> nodeSL = graph.AddNode("SL");
Node<string> nodeLD = graph.AddNode("LD");
Node<string> nodeKP = graph.AddNode("KP");
Node<string> nodePM = graph.AddNode("PM");
Node<string> nodeZP = graph.AddNode("ZP");
Node<string> nodeWP = graph.AddNode("WP");
Node<string> nodeLB = graph.AddNode("LB");
Node<string> nodeDS = graph.AddNode("DS");
Node<string> nodeOP = graph.AddNode("OP");
graph.AddEdge(nodePK, nodeLU);
graph.AddEdge(nodePK, nodeSW);
graph.AddEdge(nodePK, nodeMA);
graph.AddEdge(nodeLU, nodeSW);
graph.AddEdge(nodeLU, nodeMZ);
graph.AddEdge(nodeLU, nodePD);
graph.AddEdge(nodePD, nodeMZ);
graph.AddEdge(nodePD, nodeWM);
graph.AddEdge(nodeWM, nodeKP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeWM, nodePM);
graph.AddEdge(nodeWM, nodeMZ);
graph.AddEdge(nodeMZ, nodeKP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeMZ, nodeLD);
graph.AddEdge(nodeMZ, nodeSW);
graph.AddEdge(nodeSW, nodeLD);
graph.AddEdge(nodeSW, nodeSL);
graph.AddEdge(nodeSW, nodeMA);
graph.AddEdge(nodeMA, nodeSL);
graph.AddEdge(nodeSL, nodeOP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeSL, nodeLD);
graph.AddEdge(nodeLD, nodeOP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeLD, nodeWP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeLD, nodeKP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeKP, nodeWP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeKP, nodePM);
graph.AddEdge(nodePM, nodeZP);
graph.AddEdge(nodePM, nodeLB);
graph.AddEdge(nodePM, nodeWP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeZP, nodeLB);
graph.AddEdge(nodeWP, nodeDS);
graph.AddEdge(nodeWP, nodeOP);
graph.AddEdge(nodeWP, nodeLB);
graph.AddEdge(nodeLB, nodeDS);
graph.AddEdge(nodeDS, nodeOP);
int[] colors = graph.Color();
for (int i = 0; i < colors.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{graph.Nodes[i].Data}: {colors[i]}");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
6.4 GameMap 游戏地图:搜索最短路
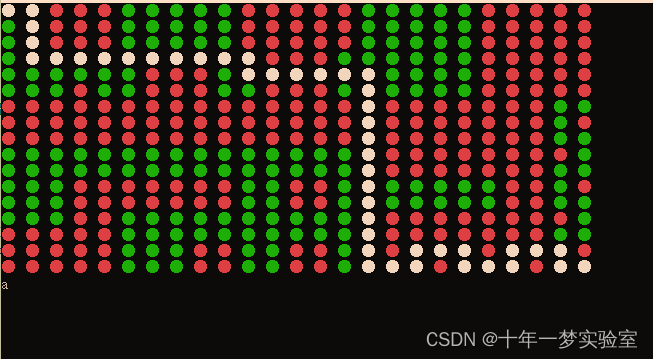
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Graphs
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] lines = new string[]
{
"0011100000111110000011111",
"0011100000111110000011111",
"0011100000111110000011111",
"0000000000011100000011111",
"0000001110000000000011111",
"0001001110011100000011111",
"1111111111111110111111100",
"1111111111111110111111101",
"1111111111111110111111100",
"0000000000000000111111110",
"0000000000000000111111100",
"0001111111001100000001101",
"0001111111001100000001100",
"0001100000000000111111110",
"1111100000000000111111100",
"1111100011001100100010001",
"1111100011001100001000100"
};
bool[][] map = new bool[lines.Length][];
for (int i = 0; i < lines.Length; i++)
{
map[i] = lines[i]
.Select(c => int.Parse(c.ToString()) == 0)
.ToArray(); //基于字符串的地图表示,转换为 布尔 2D 数组。 0位置对应true
}
//根据地图构建 无向图,有权重为1的 水平和垂直边。
Graph<string> graph = new Graph<string>(false, true);//无向图,有权重
for (int i = 0; i < map.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < map[i].Length; j++)
{
if (map[i][j]) // true位置
{
Node<string> from = graph.AddNode($"{i}-{j}");//构建节点 row-column
if (i > 0 && map[i - 1][j])//垂直向上的地图点为true
{ //根据节点数据查找节点
Node<string> to = graph.Nodes.Find(n => n.Data == $"{i - 1}-{j}");//垂直向上的节点
graph.AddEdge(from, to, 1);//添加边: 垂直向上
}
if (j > 0 && map[i][j - 1])
{
Node<string> to = graph.Nodes.Find(n => n.Data == $"{i}-{j - 1}"); //水平向左的节点
graph.AddEdge(from, to, 1);//添加边:水平向左
}
}
}
}
//起点
Node<string> source = graph.Nodes.Find(n => n.Data == "0-0");
Node<string> target = graph.Nodes.Find(n => n.Data == "16-24");//终点
List<Edge<string>> path = graph.GetShortestPathDijkstra(source, target);//最短路搜索
Console.OutputEncoding = Encoding.UTF8;
for (int row = 0; row < map.Length; row++)
{
for (int column = 0; column < map[row].Length; column++)
{
ConsoleColor color = map[row][column] ? ConsoleColor.Green : ConsoleColor.Red;//设置地图点颜色:0-绿色 1-红色
if (path.Any(e => e.From.Data == $"{row}-{column}" || e.To.Data == $"{row}-{column}"))
{
color = ConsoleColor.White;//最短路径的边端点 白色
}
Console.ForegroundColor = color;//地图点:圆圈颜色
Console.Write("\u25cf ");// 圈
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;// 灰色
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}























 57
57

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








