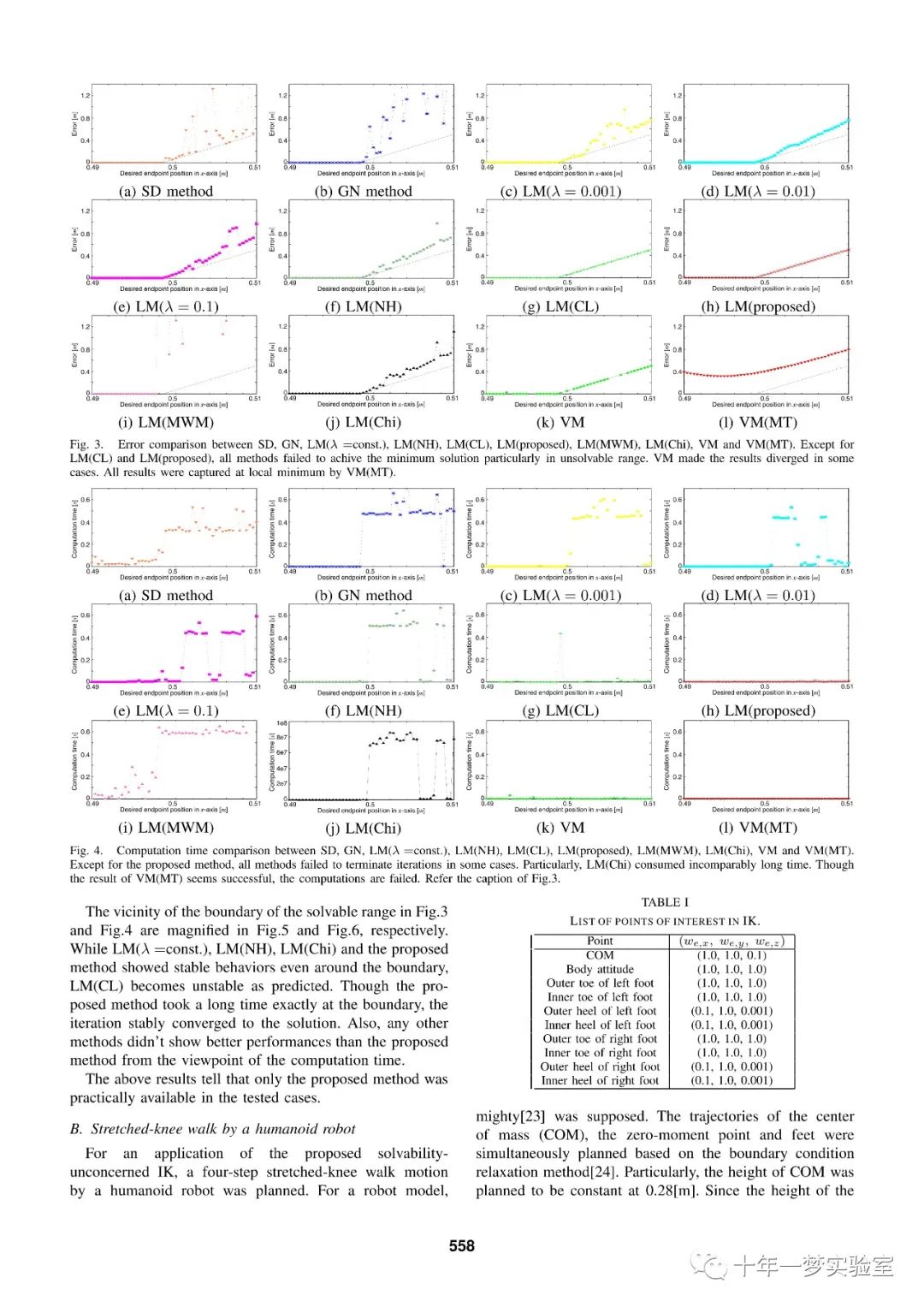
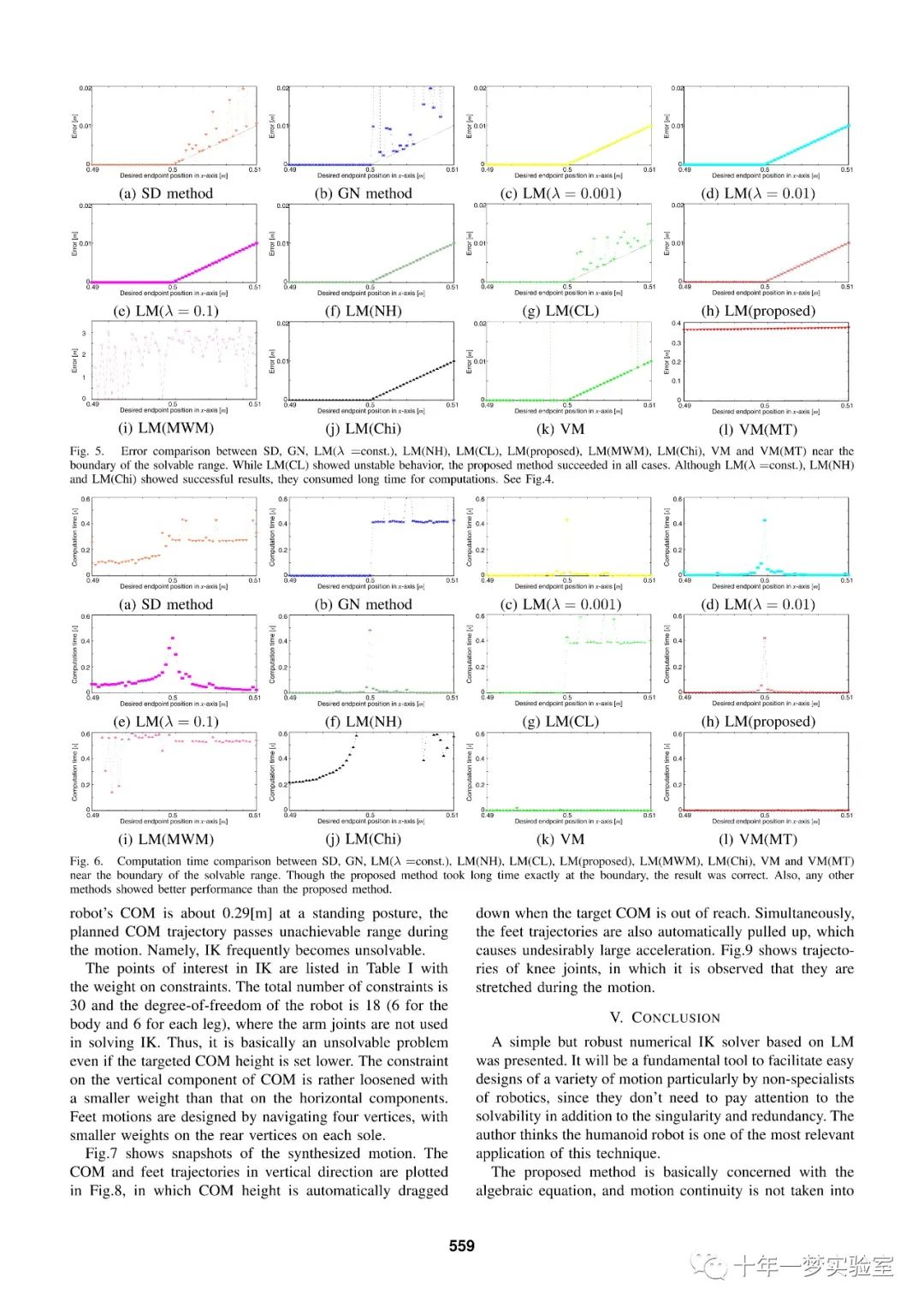
摘要: Python程序实现了基于LM法计算UR3机械臂的位置逆解,并通过插补得到机器人轨迹,发送到Unity客户端,控制机械臂运动。

 Unity场景
Unity场景
操作演示
 代码逻辑
代码逻辑
源代码
一、Unity场景脚本
1.1 客户端Client.cs
// ZeroMQ library for C#
using NetMQ;
using NetMQ.Sockets;
// System libraries
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Default Json library for work with json
using Newtonsoft.Json;
// Unity Engine
using UnityEngine;
// Set up dictonary for receive data
public class Dict
{
[JsonProperty("dtype")]
public string dtype { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("shape")]
public List<int> shape { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("data")]
public List<List<float>> data { get; set; }
}
public class Client : MonoBehaviour
{
// prepare client Thread
private Thread tcpListenerThread;
// get joints root
public Joint m_root;
// bool if is data
private static bool move = false;
// dict class
public static Dict dict;
// check collision bool
public static bool is_collision = false;
// iteration variable
public static int i;
// automatically update and if not collision and data do motion
private void FixedUpdate()
{
if (!is_collision && move)
{
try
{
// from root joint move
Joint current = m_root;
// load data from dict
current.transform.localEulerAngles = new Vector3(0, 0, (-1) * (float)dict.data[i][0]);
current = current.GetChild();
current.transform.localEulerAngles = new Vector3(90, 0, (-1) * (float)dict.data[i][1]);
current = current.GetChild();
current.transform.localEulerAngles = new Vector3(0, 0, (-1) * (float)dict.data[i][2]);
current = current.GetChild();
current.transform.localEulerAngles = new Vector3(0, 0, (-1) * (float)dict.data[i][3]);
current = current.GetChild();
current.transform.localEulerAngles = new Vector3(90, 0, (-1) * (float)dict.data[i][4]);
current = current.GetChild();
current.transform.localEulerAngles = new Vector3(270, 0, (-1) * (float)dict.data[i][5]);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Debug.Log("Exception:" + e);
}
}
}
void Start(){
// Start TcpServer background thread
tcpListenerThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ListenForIncommingRequests));
tcpListenerThread.IsBackground = true;
tcpListenerThread.Start();
Debug.Log("Start Thread");
}
private void ListenForIncommingRequests(){
try
{
using (var client = new RequestSocket())
{
// connect to server
client.Connect("tcp://127.0.0.1:5555");
// send message
client.SendFrame("Start Compute");
// receive dictonary
var msg = client.ReceiveFrameString();
// convert to dict
dict = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Dict>(msg);
// data is in class
move = true;
// iterate throu main and low Thread
for (int k = 0; k < dict.shape[0]; k++)
{
i += 1;
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
move = false;
}
catch (Exception socketException)
{
Debug.Log("SocketException " + socketException);
}
}
// On quit application -> end tasks
void OnApplicationQuit()
{
Thread.Sleep(10);
Debug.Log("End Thread");
// !!!! - Neccesary for quit NetMQ libary -> multiple run issue!
NetMQConfig.Cleanup();
}
}1.2 Joint脚本
using UnityEngine;
public class Joint : MonoBehaviour
{
// set child joint
public Joint m_child;
// check on trigger collision
void OnTriggerEnter(Collider other)
{
Client.is_collision = true;
string objectName = gameObject.name;
Debug.Log("Collision detected: " + objectName);
}
// get chiled joint
public Joint GetChild()
{
return m_child;
}
}二、Python程序
2.1 服务器
import zmq
import time
from IK import IK_LM
def send_array(socket, A):
msg = dict(
dtype = str(A.dtype),
shape = A.shape,
data = A.tolist()
)
socket.send_json(msg)
def start_server():
context = zmq.Context()
socket = context.socket(zmq.REP)
socket.bind("tcp://*:5555")
while True:
print("Server On")
# wait for receive message
msg = socket.recv()
time.sleep(0.5)
if (msg.decode("utf-8") == "Start Compute"):
# compute and send as json dict
a = IK_LM().LM()
send_array(socket, a)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_server()2.2 IK程序
import dill
import numpy as np
from numpy import pi, cos, sin, arctan2
class IK_LM(object):
"""
Accesible methods:
:method 1: LM
:method 2: demo
"""
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""
Load dill file with Jacobian matrix for defined robot.
"""
self.f_new = dill.load(open("Jacobian", "rb"))
# L-M法 计算位置逆解
def LM(self) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Compute IK depands on demo trajectory.
:returns: array of trajectory joints
"""
angles = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
p, r = self.demo(0)
out, angles = self.__compute(angles, p, r) ##初始角度零位,迭代计算p,r位姿的逆解##
for i in range(1,5):
p, r = self.demo(i)
a, angles = self.__compute(angles, p, r)#其他5个路径点逆解##
out = np.r_[out, a] #路径点堆叠
return out
#示例路径点
def demo(self, target: int) -> list:
"""
Defined demo trajectory of robot.
:param target: switch case inpup
:returns: point, rotation
:raises: case out of range
"""
match target:
case 0:
p1 = [0.0, -0.194, 0.69]
r1 = [-90, 0, -180]
return p1, r1
case 1:
p2 = [-0.21, -0.24, 0.2]
r2 = [-180, 0, -180]
return p2, r2
case 2:
p3 = [-0.21,-0.24, 0.326]
r3 = [-180, 0, -180]
return p3, r3
case 3:
p4 = [-0.21,-0.24, 0.326]
r4 = [-29, 52, -140]
return p4, r4
case 4:
p4 = [-0.21,-0.413, 0.326]
r4 = [-29, 52, -140]
return p4, r4
case _:
raise ("No exist target")
## 根据给定关节角度计算雅克比矩阵##
def __J(self, th1, th2, th3, th4, th5, th6) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Computation Jacobian matrix for UR3 by defined angles[rad]
:param th1-th6: joints angle
"""
return self.f_new(th1, th2, th3, th4, th5, th6).astype('float64')
# 位置正解 #
def __FK(self, th: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Computation of Forward Kinematics by classics D-H tables
:param th: joints angle
"""
# D-H parameters of UR3
o = [pi/2, 0, 0, pi/2, -pi/2, 0]
d = [0.1519, 0, 0, 0.11235, 0.08535, 0.0819]
a = [0, -0.24365, -0.21325, 0, 0, 0]
for i in range(6):
A_x = np.array([
[cos(th[i]), -sin(th[i]) * cos(o[i]), sin(th[i]) * sin(o[i]), a[i] * cos(th[i])],
[sin(th[i]), cos(th[i]) * cos(o[i]), -cos(th[i]) * sin(o[i]), a[i] * sin(th[i])],
[0 , sin(o[i]), cos(o[i]), d[i] ],
[0 , 0, 0, 1 ]
])
if i == 0:
A = A_x
else:
A = A @ A_x
return A
#根据tcp位置和欧拉角 计算期望位姿#
def __comp_t_desired(self, target: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Computation target Forward Kinematics D-H table
:param target: translation, rotation of target
:returns: 4x4 d-h table of target
"""
x = target[0]
y = target[1]
z = target[2]
alfa = target[3]
beta = target[4]
gamma = target[5]
R_x = np.array([
[1, 0, 0 ],
[0, cos(alfa), -sin(alfa)],
[0, sin(alfa), cos(alfa)]
])
R_y = np.array([
[cos(beta), 0, sin(beta)],
[0, 1, 0 ],
[-sin(beta), 0, cos(beta)]
])
R_z = np.array([
[cos(gamma), -sin(gamma), 0],
[sin(gamma), cos(gamma), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
R = R_z @ R_y @ R_x
return np.r_[
np.c_[
R, np.array([x,y,z])
], [np.array([0,0,0,1])]
]
#计算当前位姿到期望位姿的轴角距离#
def __Angle_Axis(self, T_desired: np.ndarray, T_current: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Computation angle-axis distance
:param T_desired: d-h table of target
:param T_current: d-h table current state
:returns: 6x1 array translation, rotation
"""
Td = T_desired[:3,3]
Ti = T_current[:3,3]
Rd = T_desired[:3,:3]
Ri = T_current[:3,:3]
R = Rd @ Ri.T
l = np.array([
[R[2,1] - R[1,2]],
[R[0,2] - R[2,0]],
[R[1,0] - R[0,1]]
])
l_length = np.linalg.norm(l)
if(l_length > 0):
a = ((arctan2(l_length, R[0,0] + R[1,1] + R[2,2] - 1 ) ) / l_length) * l
else:
if(R[0,0] + R[1,1] + R[2,2] > 0):
a = np.array([[0,0,0]]).T
else:
a = pi/2 * np.array([[
R[0,0] + 1,
R[1,1] + 1,
R[2,2] + 1
]]).T
return np.r_[np.array([Td-Ti]).T, a] #[dx;dy;dz;da;db;dc]
#LM法计算位置逆解 给定当前关节角度,计算到目标位姿的关节角度序列
def __compute(self, angles: list, target_position: list, target_rotation: list) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Computation of Levenberg-Marquardt method.
:param angles: init angles[°] 初始角度列表
:param target_position: translation of target [x,y,z] [m] 目标位置
:param target_rotation: rotation of target [r,p,y] [°] Euler-angles #目标欧拉角
:returns: X x 6 matrix of path targets #返回路径点对应关节角度列表
"""
angles = np.deg2rad(angles)
target_rotation = np.deg2rad(target_rotation)
target = np.append(target_position, target_rotation)
i = 0
q = np.array([angles])
# init d-h tables
T_desired = self.__comp_t_desired(target) #期望位姿
T_current = self.__FK(q[i,:]) #当前位姿
# error computation
error = np.linalg.norm(T_current - T_desired) #位姿误差范数计算
# do until error will be in specified accuracy #
while error > 0.001:
J_comp = self.__J(q[i,0],q[i,1],q[i,2],q[i,3],q[i,4],q[i,5]) #雅可比矩阵
H_k = J_comp.T @ np.eye(6,6) @ J_comp #运算符@在矩阵运算中的功能是矩阵乘法 近似海森矩阵
g_k = J_comp.T @ np.eye(6,6) @ self.__Angle_Axis(T_desired, T_current) #
if (np.linalg.det(J_comp)!=0):
q = np.r_[q, q[i,:] + (np.linalg.inv(H_k) @ g_k).T] # np.r_是按行增加拼接两个矩阵(效果是每列看上去延长了),就是把两矩阵上下相加,要求列数相等。#
else:
q = np.r_[q, q[i,:] + (np.linalg.pinv(H_k) @ g_k).T] # np.c_是按列增加拼接两个矩阵(效果是每行看上去延长了),就是把两矩阵左右相加,要求行数相等。#
# 计算新的误差
T_current = self.__FK(q[-1,:]) #计算新的位姿
error = np.linalg.norm(T_current - T_desired) #更新误差范数
# 将计算的关节从 360° 限制到 180° -> 防止一些自碰撞
if(np.any(q[-1,:] > pi) or np.any(q[i+1,:] < -pi)): #防止自碰撞
l = np.argwhere(q[-1,:] > pi)
k = np.argwhere(q[-1,:] < -pi)
q[-1,l] = q[i,l] #纠正最后一行对应元素
q[-1,k] = q[i,k]
i += 1 #迭代次数++
"""
! Check Correctness purpose
! Correct by UR - Polyscope
A = self.FK(q[-1,:])
R = A[:3, :3]
beta = arctan2(-R[2,0], np.sqrt(R[0,0]**2 + R[1,0]**2))
alfa = arctan2(R[1,0] / cos(beta), R[0,0] / cos(beta))
gamma = arctan2(R[2,1] / cos(beta), R[2,2] / cos(beta))
rpy = np.rad2deg([gamma, beta, alfa])
xyz = A[:3,3]
# goal = np.rad2deg(q[-1,:])
"""
goal = q[-1,:] #最后一个目标点
# 生成简单路径,包含 100 个样本
nr_pnts = 100 #100个采样点
a = np.zeros((nr_pnts, 6))
#关节 空间插补
for i in range(5): #第6个关节不用管,0
a[:,i] = np.linspace(np.rad2deg(angles[i]), np.rad2deg(goal[i]), nr_pnts)
return a, np.rad2deg(goal)2.3 雅可比计算
import dill
import sympy as sym
import numpy as np
from numpy import pi
from sympy import sin, cos, Matrix, lambdify
# Script generates 6-dof robot Jacobian matrix
# D-H parameters are from Universal Robots UR3 robot
# Script can be easily modifed by add/remove d-h table and
# computation of Forward Kinematics
th1, th2, th3, th4, th5, th6 = sym.symbols('th1, th2, th3, th4, th5, th6')
o1 = pi/2
d1 = 0.1519
a1 = 0
o2 = 0
d2 = 0
a2 = -0.24365
o3 = 0
d3 = 0
a3 = -0.21325
o4 = pi/2
d4 = 0.11235
a4 = 0
o5 = -pi/2
d5 = 0.08535
a5 = 0
o6 = 0
d6 = 0.0819
a6 = 0
A1 = np.array([
[cos(th1), -sin(th1) * cos(o1), sin(th1) * sin(o1), a1 * cos(th1)],
[sin(th1), cos(th1) * cos(o1), -cos(th1) * sin(o1), a1 * sin(th1)],
[0 , sin(o1), cos(o1), d1 ],
[0 , 0, 0, 1 ]
])
A2 = np.array([
[cos(th2), -sin(th2) * cos(o2), sin(th2) * sin(o2), a2 * cos(th2)],
[sin(th2), cos(th2) * cos(o2), -cos(th2) * sin(o2), a2 * sin(th2)],
[0 , sin(o2), cos(o2), d2 ],
[0 , 0, 0, 1 ]
])
A3 = np.array([
[cos(th3), -sin(th3) * cos(o3), sin(th3) * sin(o3), a3 * cos(th3)],
[sin(th3), cos(th3) * cos(o3), -cos(th3) * sin(o3), a3 * sin(th3)],
[0 , sin(o3), cos(o3), d3 ],
[0 , 0, 0, 1 ]
])
A4 = np.array([
[cos(th4), -sin(th4) * cos(o4), sin(th4) * sin(o4), a4 * cos(th4)],
[sin(th4), cos(th4) * cos(o4), -cos(th4) * sin(o4), a4 * sin(th4)],
[0 , sin(o4), cos(o4), d4 ],
[0 , 0, 0, 1 ]
])
A5 = np.array([
[cos(th5), -sin(th5) * cos(o5), sin(th5) * sin(o5), a5 * cos(th5)],
[sin(th5), cos(th5) * cos(o5), -cos(th5) * sin(o5), a5 * sin(th5)],
[0 , sin(o5), cos(o5), d5 ],
[0 , 0, 0, 1 ]
])
A6 = np.array([
[cos(th6), -sin(th6) * cos(o6), sin(th6) * sin(o6), a6 * cos(th6)],
[sin(th6), cos(th6) * cos(o6), -cos(th6) * sin(o6), a6 * sin(th6)],
[0 , sin(o6), cos(o6), d6 ],
[0 , 0, 0, 1 ]
])
T2 = A1 @ A2
T3 = A1 @ A2 @ A3
T4 = A1 @ A2 @ A3 @ A4
T5 = A1 @ A2 @ A3 @ A4 @ A5
T6 = A1 @ A2 @ A3 @ A4 @ A5 @ A6
z0= np.array([0,0,1])
z1 = A1[:3,2]
z2 = T2[:3,2]
z3 = T3[:3,2]
z4 = T4[:3,2]
z5 = T5[:3,2]
p0 = np.array([0,0,0])
p1 = A1[:3,3]
p2 = T2[:3,3]
p3 = T3[:3,3]
p4 = T4[:3,3]
p5 = T5[:3,3]
P = T6[:3,3]
#雅可比矩阵
J = Matrix([
np.append(np.cross(z0, P - p0), z0),
np.append(np.cross(z1, P - p1), z1),
np.append(np.cross(z2, P - p2), z2),
np.append(np.cross(z3, P - p3), z3),
np.append(np.cross(z4, P - p4), z4),
np.append(np.cross(z5, P - p5), z5),
]).T
f = lambdify('th1, th2, th3, th4, th5, th6', J, 'numpy')
dill.settings['recurse'] = True
dill.dump(f, open("testik", "wb"))三、Levenberg-Marquardt 迭代算法文献




The End




 本文介绍了一个基于Python实现的UR3机械臂位置逆解算法,并使用Levenberg-Marquardt方法进行迭代求解。通过Unity客户端接收计算结果并控制机械臂运动,演示了从算法实现到实际应用的全过程。
本文介绍了一个基于Python实现的UR3机械臂位置逆解算法,并使用Levenberg-Marquardt方法进行迭代求解。通过Unity客户端接收计算结果并控制机械臂运动,演示了从算法实现到实际应用的全过程。
















 1277
1277










