Tips1:
由于SpinalHDL是基于Scala构建的,Scala本身自带类似变量Boolean,故在此要认准SpinalHDL中采用的是Bool而非Boolean:
- Bool(大写的True和False):True表示1,False表示0
- Boolean(小写的true和false):true表示1,false表示0
Tips2:
SpinalHDL在声明时采用“=”,而在改变电路状态时用“:=”
文章目录
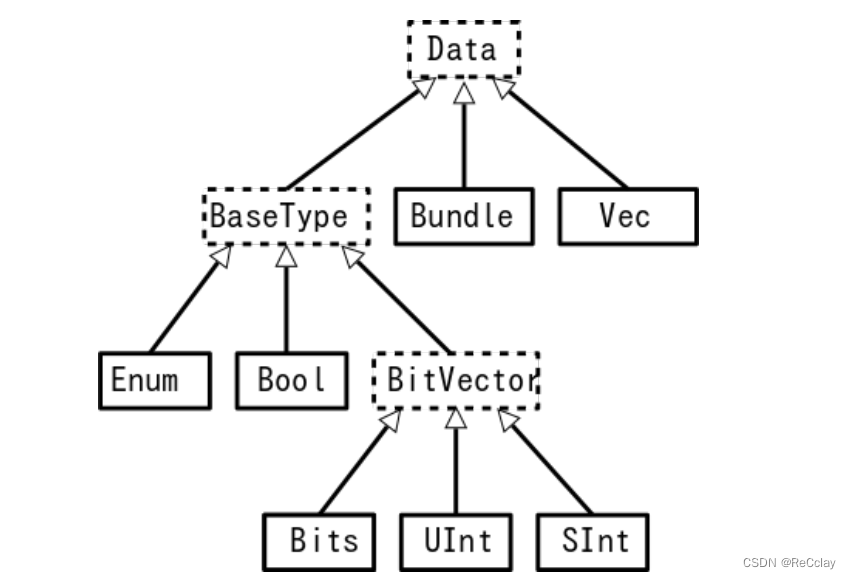
1.1、描述
Bool类型对应于布尔值(True或False)。
1.2、声明
声明布尔值的语法如下:(方括号中的所有内容都是可选项)

val myBool_1 = Bool() // Create a Bool
myBool_1 := False // := is the assignment operator
val myBool_2 = False // Equivalent to the code above
val myBool_3 = Bool(5 > 12) // Use a Scala Boolean to create a Bool
1.3、运算符
以下运算符可用于布尔类型:
1.3.1、逻辑运算(logic)
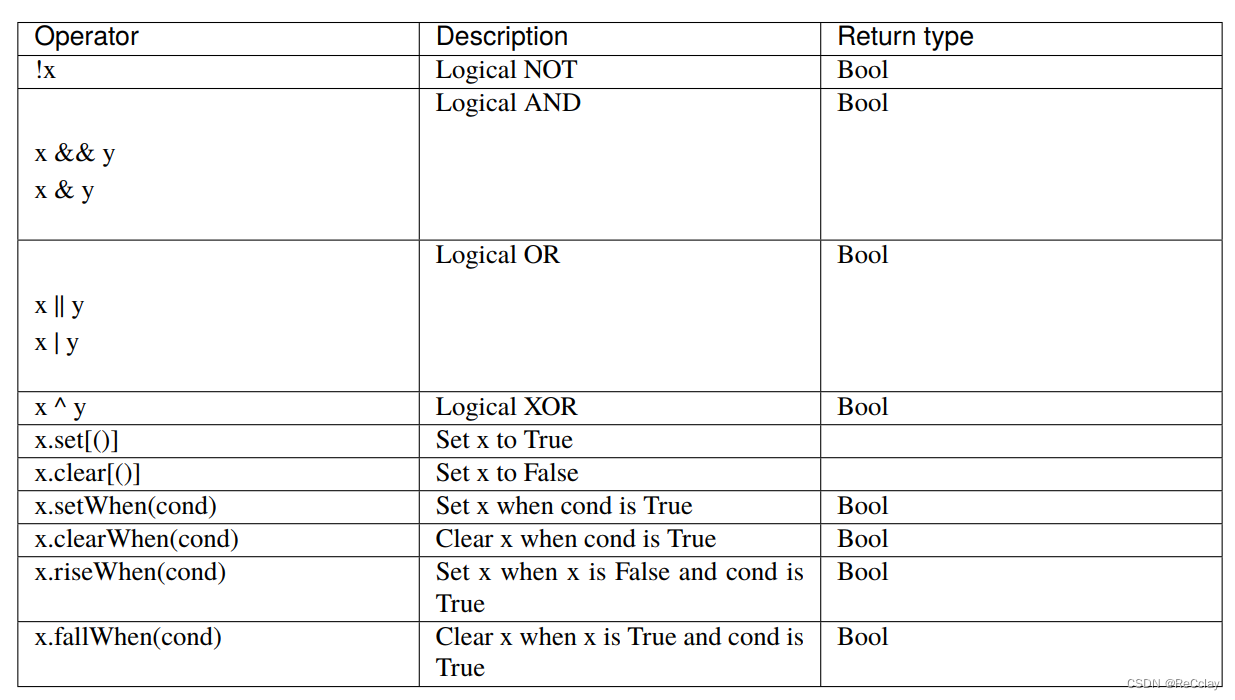
val a, b, c = Bool()
val res = (!a & b) ^ c // ((NOT a) AND b) XOR c
val d = False
when(cond) {
d.set() // equivalent to d := True
}
val e = False
e.setWhen(cond) // equivalent to when(cond) { d := True }
val f = RegInit(False) fallWhen(ack) setWhen(req) //这个理解起来有点难度???
/** equivalent to
* when(f && ack) { f := False }
* when(req) { f := True }
* or
* f := req || (f && !ack)
*/
// mind the order of assignments!
val g = RegInit(False) setWhen(req) fallWhen(ack) //这个理解起来有点难度???
// equivalent to g := ((!g) && req) || (g && !ack)
1.3.2、边沿检测(Edge detection)
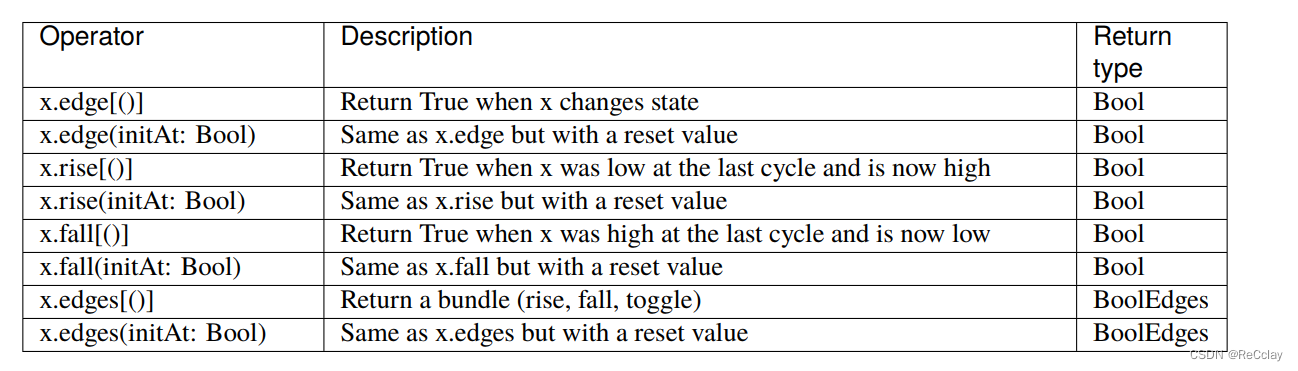
when(myBool_1.rise(False)) { //括号里面表示复位值为低
// do something when a rising edge is detected
}
val edgeBundle = myBool_2.edges(False)
when(edgeBundle.rise) {
// do something when a rising edge is detected
}
when(edgeBundle.fall) {
// do something when a falling edge is detected
}
when(edgeBundle.toggle) {
// do something at each edge
}
1.3.3、比较(Comparison)
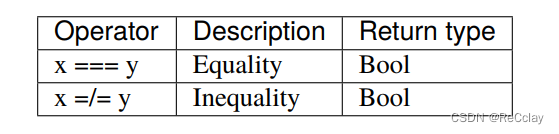
when(myBool) { // Equivalent to when(myBool === True)
// do something when myBool is True
}
when(!myBool) { // Equivalent to when(myBool === False)
// do something when myBool is False
}
1.3.4、类型转换(Type cast)
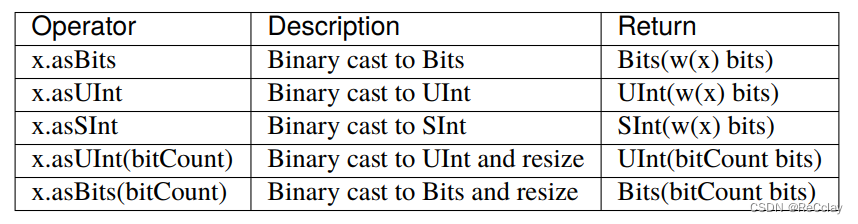
// Add the carry to an SInt value
val carry = Bool()
val res = mySInt + carry.asSInt
1.3.5、杂项(Misc)

就是拼接符,等效Verilog中的
{}
val a, b, c = Bool()
// Concatenation of three Bool into a Bits
val myBits = a ## b ## c
1.3.6、MaskedBoolean
MaskedBoolean 允许使用不确定值。它们通常不单独使用,而是通过MaskedLiteral来使用。
MaskedLiteral值是带有“-”的位向量,表示不关心的值。【下面的M就表示MaskedLiteral】
val myBits = B"1101
val test1 = myBits === M"1-01" // True
val test2 = myBits === M"0---" // False
val test3 = myBits === M"1--1" // True
// first argument: boolean value
// second argument: do we care ?
val masked = new MaskedBoolean(true, false)





 文章详细介绍了SpinalHDL中的Bool类型,包括其与ScalaBoolean的区别、声明方式以及各种运算符的使用,如逻辑运算、边沿检测、比较、类型转换和MaskedBoolean。此外,还展示了如何进行边沿检测和在不同条件下的布尔值操作。
文章详细介绍了SpinalHDL中的Bool类型,包括其与ScalaBoolean的区别、声明方式以及各种运算符的使用,如逻辑运算、边沿检测、比较、类型转换和MaskedBoolean。此外,还展示了如何进行边沿检测和在不同条件下的布尔值操作。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










