文章目录
【全文大纲】 : https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Engineer_LU/article/details/135149485
前言
- 理解一个 实时操作系统(RTOS) 时,阅读其源码无疑是最直接、最深刻的途径。从创建、到启动、到调度、再到通信——我们将不仅仅是在“读代码”,而是在脑海中构建一个动态的、可运行的FreeRTOS世界模型。理解了这些,你不仅能更自信、更高效地使用FreeRTOS,更能将这种对系统资源的精确管理、对并发问题的深刻洞察,应用到任何复杂的嵌入式系统设计之中,看完理解整篇文章,就可以手搓一个RTOS。
- 全文根据核心把各部分关联一起,深入浅出方式开展,细节偏多,力求解析每个细节存在的意义,源码截取核心走向进行描述(不影响每个细节的关联),文中默认核心宏打开的部分,调试/静态相关的宏默认不描述
- 依次从概念,任务创建,任务调度,内存管理,数据结构,任务通信开展,每个流程都是按源码顺序进行
一 : FreeRTOS 概念
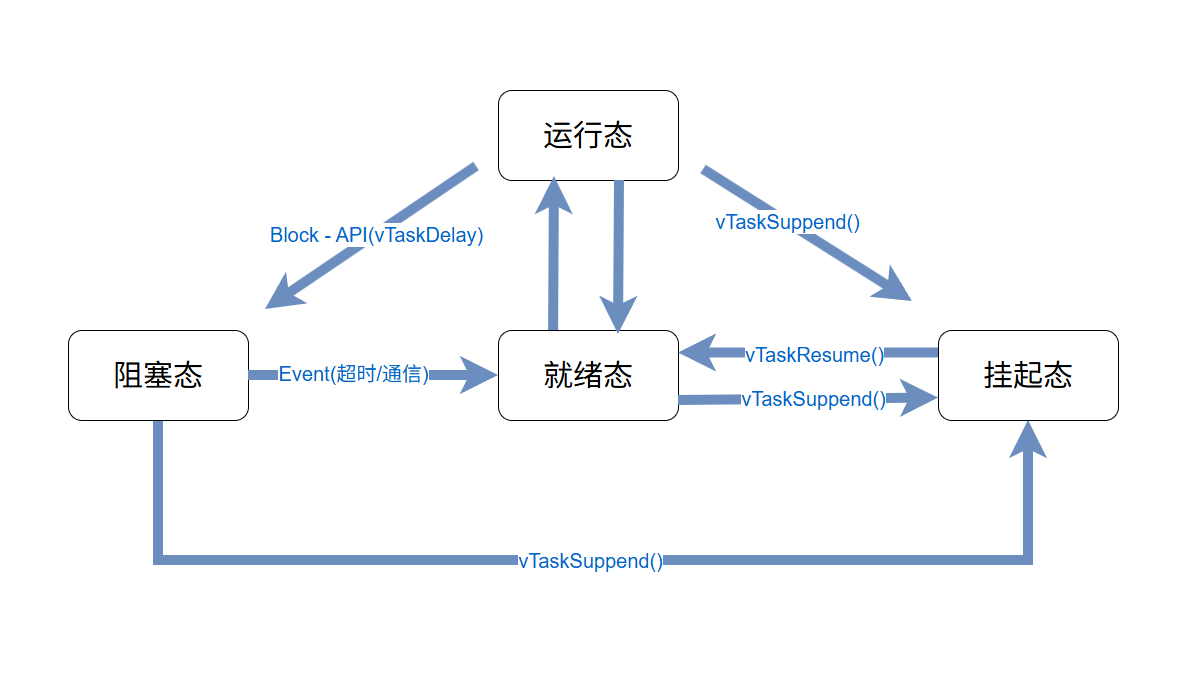
- FreeRTOS有四种状态,分别为运行态,就绪态,阻塞态,挂起态;
- FreeRTOS有五种链表:就绪链表,阻塞链表,挂起链表,缓存链表,回收链表;其中前三个对应状态的运行流程,后两者为缓存操作和删除任务时所用
- FreeRTOS为抢占式实时系统,所以核心调度逻辑高优先级任务优先执行,拥有抢占低优先级任务的权限;因此高优先级任务需要释放掉CPU执行权后,低优先级任务才可以执行,若是优先级相等,则是通过优先级就绪链表中的index遍历执行,就是传统意义上的时间片轮流执行
- FreeRTOS通常通过vTaskDelay,任务通信等主动切换任务,通过Tick中断被动切换任务(阻塞态的任务通过SysTick中断查询来唤醒)
- FreeRTOS的最终任务切换逻辑在PendSV中断里实现
- FreeRTOS写了两套API,分别用于任务与中断,例如队列通信有任务版本,中断版本(不阻塞)
- FreeRTOS的TCB任务控制块主要依靠xState和xEvent链表项放在各链表中进行调度,而链表项中的pvOwner指向当前TCB,pxContainer指向具体的链表,通过这两个在链表中可以关联到每个任务,这样通过管理链表来管理任务调度
- FreeRTOS的链表是双向的,通常End节点为哨兵节点,插入的链表项在End节点之前
- FreeRTOS的内存管理有五种,heap_1~heap_5(详细描述在内存管理章节)
- FreeRTOS的任务通信通常采样队列,事件组,任务通知,流缓冲区,触发通信完成后会顺带触发任务切换,关于队列还有队列集的概念,总而言之是为了让任务间形成独立的空间,通过线程安全的API通信完成多线程逻辑
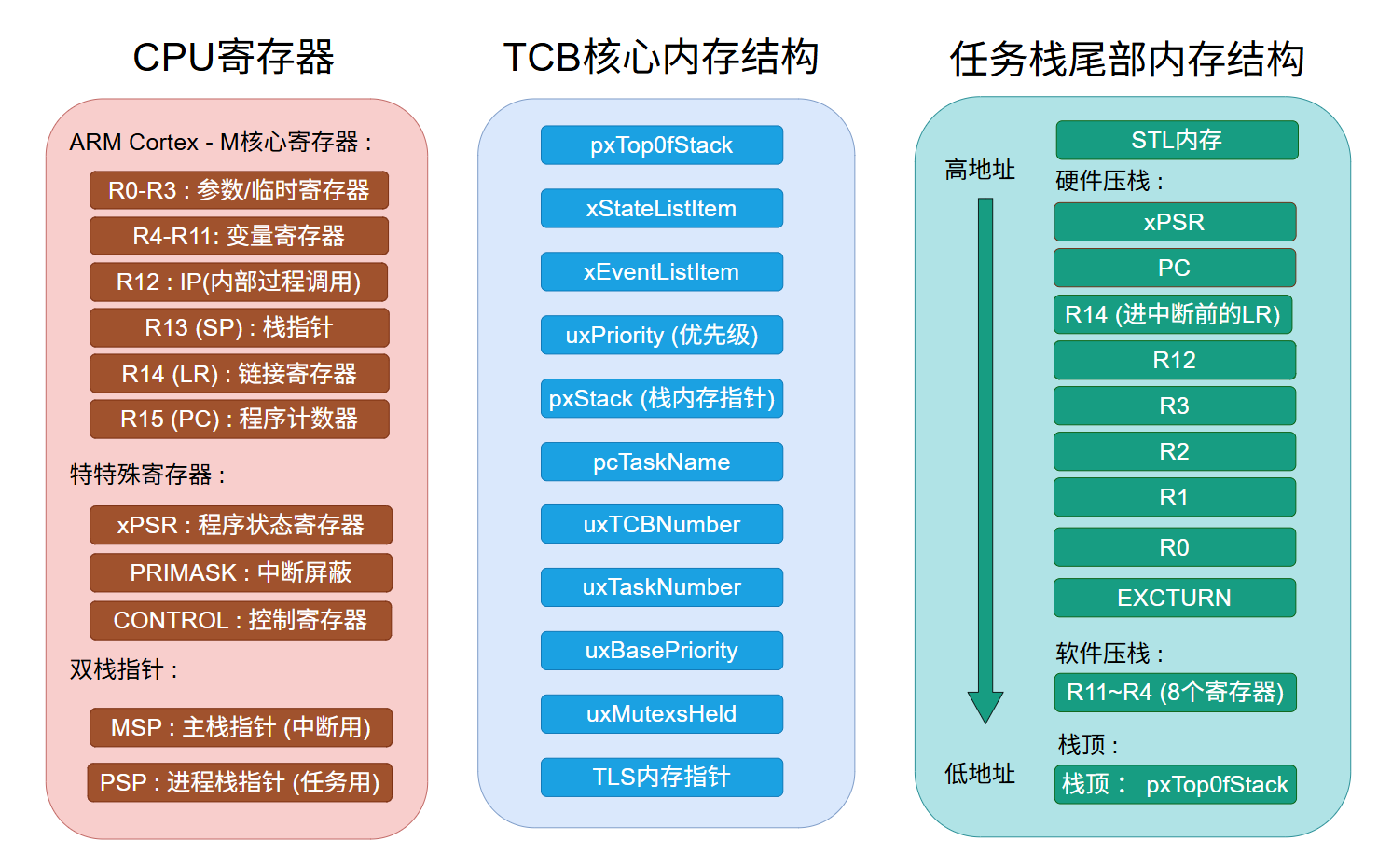
- 内核寄存器与任务栈描述:
TCB任务栈尾部内存结构中,EXCTURN后还有一个保留字(4字节),这个属于ARM M核在MDK编译中的特性,关于核心寄存器中CONTROL(控制寄存器) , PRIMASK(中断屏蔽), BASEPRI (优先级屏蔽寄存器),FAULTMASK 是故障屏蔽寄存器 此处作出描述,
- CONTROL 寄存器是一个32位寄存器,但通常只使用其中4个有效位,其余位为保留位(读取为0,写入无效)。它主要用于配置处理器的特权级别和栈指针选择,是实现FreeRTOS等操作系统任务隔离与模式切换的基础。
- PRIMASK 是 ARM Cortex-M(包括STM32H750)内核中用于快速全局开关中断的优先级屏蔽寄存器。可以把它理解为一个“总中断开关”,但它比“总开关”更精细一些。其核心功能是临时提升处理器执行代码的“优先级”到0级(可编程的最高优先级),以保护极其关键、不允许被任何普通中断打断的代码段。
- BASEPRI 是一个可编程优先级屏蔽寄存器。它比 PRIMASK 更智能,允许你设置一个优先级阈值,只屏蔽那些优先级等于或低于该阈值的中断,而更高优先级的中断仍然可以正常响应。这是实现可嵌套临界区和保证系统实时性的关键。
- FAULTMASK 是故障屏蔽寄存器,它的“屏蔽力度”最强。将它置1后,除了 NMI(不可屏蔽中断),所有其他中断和异常(包括 HardFault)都会被屏蔽。处理器执行权限也会提升到特权级。它主要用于故障处理程序内部,以便在系统严重错误后能安全地执行恢复或关闭操作。
- 内核寄存器常规用法,直接操作要小心:如果因特殊原因需要直接写入(如在某些极端优化的启动代码中),你必须手动屏蔽保留位,并在修改 CONTROL 寄存器后立即添加 DSB 和 ISB 屏障指令。
| CONTROL | 名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| bit0 | nPRIV | 线程模式特权级控制。 0 : 线程模式为特权模式,可以访问所有处理器资源。通常FreeRTOS内核运行于此模式。 1 : 线程模式为用户(非特权)模式,对某些系统寄存器和内存区域的访问受限。FreeRTOS的用户任务可配置为此模式。 |
| bit1 | SPSEL | 栈指针(SP)选择。 0 : 在线程模式下使用主栈指针(MSP)。 1 : 在线程模式下使用进程栈指针(PSP)。这是多任务操作系统的典型配置,每个任务拥有独立的栈空间。 |
| bit2 | FPCA | 浮点上下文激活标志(Cortex-M4/M7特有)。 0 : 当前上下文未使用浮点单元(FPU)。 1 : 当前上下文使用了FPU。在进行任务切换时,系统会根据此位决定是否保存/恢复浮点寄存器以优化性能。 |
| bit3 | SFPA | 安全浮点上下文激活标志(仅支持TrustZone的Cortex-M23/M33/M55等内核)。对于STM32H750(Cortex-M7),此位为保留位,无作用。 |
| [31 : 8] | - | 保留。必须写入0。 |
/* CONTROL寄存器应用 */
// 设置线程模式为特权模式,并使用MSP
__set_CONTROL(0x00);
// 设置线程模式为用户模式,并使用PSP(FreeRTOS任务典型配置)
__set_CONTROL(0x03); // 即 nPRIV=1, SPSEL=1
| PRIMASK | 名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| bit0 | PM | 优先级屏蔽位。 0 : 不屏蔽(默认值),所有中断根据其优先级正常响应。 1 : 屏蔽,除了 NMI(不可屏蔽中断) 和 HardFault 外,屏蔽所有优先级可配置的中断。 |
| [31 : 1] | - | 保留。必须写入0。 |
/* CPRIMASK寄存器 */
// 操作 PRIMASK 寄存器
__disable_irq(); // 等效于 __set_PRIMASK(1);
__enable_irq(); // 等效于 __set_PRIMASK(0);
| BASEPRI | 名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| [7 : 0] | PRI_MASK | 优先级屏蔽字段(在STM32H750等Cortex-M7中通常使用8位中的高4位,即 [7:4])。 0 : 不屏蔽任何中断(与 PRIMASK=0 效果相同,也是默认值)。 非0值 (N) : 屏蔽所有优先级数值大于或等于N的中断。请注意优先级数值的方向:在ARM中,数值越小,优先级越高。因此,BASEPRI=0x10 会屏蔽优先级为 0x10, 0x20, 0x30…(即所有优先级等于或低于 0x10 的)中断,而优先级为 0x0C(更高)的中断仍可通行。 |
| [31 : 8] | - | 保留。必须写入0。 |
/* BASEPRI寄存器应用 */
// FreeRTOS 中常用 configMAX_SYSCALL_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY 来配置 BASEPRI
// 假设 configMAX_SYSCALL_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY 设置为 5 (对应优先级值 0x50)
#define portDISABLE_INTERRUPTS() __set_BASEPRI( ( 5UL << (8 - __NVIC_PRIO_BITS) ) )
#define portENABLE_INTERRUPTS() __set_BASEPRI( 0 )
| FAULTMASK | 名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| bit0 | FM | 故障屏蔽位。 0 : 不屏蔽故障(默认值)。 1 : 屏蔽所有中断和除NMI外的所有异常(包括 HardFault、MemManage 等)。此时处理器运行在“等效于优先级-1”的状态。 |
| [31 : 1] | - | 保留。必须写入0。 |
/* FAULTMASK 寄存器 */
void HardFault_Handler(void) {
__asm volatile (“cpsid f”); // 屏蔽所有,进入最高优先级状态
// 关键操作:将寄存器、栈等信息保存到安全位置
__asm volatile (“cpsie f”); // 恢复,允许其他高优先级故障(如有)被处理
// 可能进入错误处理循环或尝试恢复
while(1);
}
补充描述 :
cpsie i / cpsid i :PRIMASK 开启/关闭中断 除 NMI 和 HardFault 外的所有可屏蔽中断。
cpsie f / cpsid f :FAULTMASK 开启/关闭故障 所有异常(包括大多数Fault)和中断,但 NMI 仍然不可屏蔽。
cpsie i 等价于 __enable_irq()
cpsid i 等价于 __disable_irq()
cpsie f 等价于 __enable_fault_irq()
cpsid f 等价于 __disable_fault_irq()
中断优先级数值 < BASEPRI设定值 中断的实际优先级更高 (允许响应) ,VIP通道,紧急事件,任何情况下都要处理。
中断优先级数值 >= BASEPRI设定值 中断的实际优先级更低(或等于), (被屏蔽) 普通通道,可以被系统临时挂起,以保护关键代码。
假设系统中断优先级使用4位(STM32常见配置),优先级范围是 0(最高)到 15(最低)。
通过 __set_BASEPRI(0x50); 进行设置(0x50是8位表示,其高4位优先级数值为5)。
此时的状态如下:
中断 A,优先级数值为 2 (0x20) → 数值2 < 5 → 更高优先级 → 可以正常运行,不被屏蔽。
中断 B,优先级数值为 5 (0x50) → 数值5 == 5 → 等于阈值 → 被屏蔽,无法响应。
中断 C,优先级数值为 8 (0x80) → 数值8 > 5 → 更低优先级 → 被屏蔽,无法响应。
二 : 源码 : 任务创建
任务创建 API : xTaskCreate(myTask, “myTask”, 512, NULL, 1, &myTaskHandler);
任务创建 Step1 :创建任务成功则添加到就绪列表
任务创建 Step2 :给TCB块以及任务栈申请动态内存
任务创建 Step3 :初始化TCB成员以及栈顶
任务创建 Step4 :创建的任务加入到具体的就绪优先级链表中
跳转置顶
1. 任务创建成功加入就绪链表
-
任务创建Step1 : 创建任务成功则添加到就绪列表,根据下图可以看到创建任务的源码,主要做两件事
1.1 :首先申请 任务控制块(TCB) 内存,申请到的任务栈内存地址传给 pxNewTCB;
1.2 :若成功申请则把当前 pxNewTCB 任务控制块 链表项插入到就绪链表等待调度(任务创建step4分析);BaseType_t xTaskCreate( TaskFunction_t pxTaskCode, const char * const pcName, const configSTACK_DEPTH_TYPE uxStackDepth, void * const pvParameters, UBaseType_t uxPriority, TaskHandle_t * const pxCreatedTask ) { TCB_t * pxNewTCB; BaseType_t xReturn; traceENTER_xTaskCreate( pxTaskCode, pcName, uxStackDepth, pvParameters, uxPriority, pxCreatedTask ); pxNewTCB = prvCreateTask( pxTaskCode, pcName, uxStackDepth, pvParameters, uxPriority, pxCreatedTask ); if( pxNewTCB != NULL ) { #if ( ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) && ( configUSE_CORE_AFFINITY == 1 ) ) { /* Set the task's affinity before scheduling it. */ pxNewTCB->uxCoreAffinityMask = configTASK_DEFAULT_CORE_AFFINITY; } #endif prvAddNewTaskToReadyList( pxNewTCB ); xReturn = pdPASS; } else { xReturn = errCOULD_NOT_ALLOCATE_REQUIRED_MEMORY; } traceRETURN_xTaskCreate( xReturn ); return xReturn; }【A】创建任务的六个参数作用 :
- pxTaskCode // 任务函数指针 - 任务执行体入口;
- pcName // 任务名称字符串 - 用于调试识别;
- uxStackDepth // 栈深度 - 用于任务调度时压栈,任务变量存储,函数调用关联到的核心寄存器压栈;
- pvParameters // 任务参数 - 通过R0传递到任务函数;
- uxPriority // 任务优先级 - 数值赋予越大,任务优先级越高;
- pxCreatedTask // 任务句柄 - 指向TCB的指针;
2. 内存申请
-
任务创建Step2 : 给TCB块以及任务栈申请动态内存,prvCreateTask 函数里主要做三件事。
2.1 :给 TCB 任务控制块申请内存;
2.2 :给任务栈申请内存(TCB的成员指针指向这片内存);
2.3 :调用 prvInitialiseNewTask 初始化任务,步骤往下解析具体如何初始化;
2.1 :给 TCB 任务控制块申请内存;
pxNewTCB = ( TCB_t * ) pvPortMalloc( sizeof( TCB_t ) );
2.2 :给任务栈申请内存(TCB的成员指针指向这片内存);
pxNewTCB->pxStack = ( StackType_t * ) pvPortMallocStack( ( ( ( size_t ) uxStackDepth ) * sizeof( StackType_t ) ) );
2.3 :调用 prvInitialiseNewTask 初始化任务,步骤往下解析具体如何初始化;
prvInitialiseNewTask( pxTaskCode, //任务接口地址 pcName, //任务名称 uxStackDepth, //任务栈深度,以字为单位 pvParameters, //任务参数 uxPriority, //任务优先级 pxCreatedTask,//任务句柄(二级指针) pxNewTCB, //创建任务过程中申请的对象(一级指针)最终赋予TCB指向 NULL //MemoryRegion关于内存分区操作,一般为NULL );
3. 初始化TCB成员以及栈顶
-
任务创建Step3 : 初始化TCB成员以及栈顶,prvInitialiseNewTask 任务解析
3.1 :初始化申请到的任务栈具体数据 tskSTACK_FILL_BYTE 为 0xA5,若是栈溢出,可以检索这些内存来辨识;
3.2 :给pxTopOfStack指向首次栈顶位置,默认按满减递增方式设置栈方向,内存8字节对齐;
3.3 :给TCB控制块设置任务名称;
3.4 :限制优先级,初始化优先级,初始化Base优先级(用于互斥锁优先级反转用);
3.5 :初始化任务xState和xEvent链表项中的pxContainer ,初始的具体行为只是把 pxContainer 指向为 NULL,pxContainer一般指向具体的链表(如就绪链表,阻塞链表等);
3.6 :初始化任务xState和xEvent链表项中的pvOwner指向,pvOwner指向当前创建的任务,所以通过TCB块的pxContainer 和 pvOwner就知道当前任务所属哪个链表,所属哪个任务,另外事件的ItemValue是记录优先级,数越低优先级越高(与任务优先级反过来);
3.7 :初始化一段TLS内存,这段内存在申请的空间的顶部,_tls_size()具体大小根据当前平台申请得出;
3.8 :把核心寄存器进行压栈,具体行为是根据当前栈顶⼿动往下递进依次赋值常量xPSR,PC(应⽤层创建传⼊的任务接⼝地址), LR (⼿动保存为prvTaskExitError函数地址), R12, R3, R2, R1, R0(任务参数指针), EXCTURN,再把栈顶往下8个字( R11 ~ R4) ,总共⼿动设置任务栈寄存器 17 个字,因此任务栈顶在 TLS内存后紧跟着17个字后,任务栈顶指向R4,初始完pxNewTCB后,⽤当初创建任务传⼊的&TCB指针,其实传⼊了个⼆级指针(&指针),那样可以在内部给这个⼆级指针⾥的⼀级指向⼀块区域,这块区域就是任务栈空间,压完寄存器后的地址为栈顶pxTopOfStack
3.1 初始化申请到的任务栈具体数据 tskSTACK_FILL_BYTE 为 0xA5,若是栈溢出,可以检索这些内存来辨识;
( void ) memset ( pxNewTCB->pxStack, ( int ) tskSTACK_FILL_BYTE, //0xA5 ( size_t ) uxStackDepth * sizeof( StackType_t ) );
3.2 :给pxTopOfStack指向首次栈顶位置,默认按满减递增方式设置栈方向,内存8字节对齐;
pxTopOfStack = &( pxNewTCB->pxStack[ uxStackDepth - ( configSTACK_DEPTH_TYPE ) 1 ] ); pxTopOfStack = ( StackType_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE) pxTopOfStack ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) ) #if ( configRECORD_STACK_HIGH_ADDRESS == 1 ) { /* 这里先指向最高位地址,认为是尾部,后面压栈后,形成栈顶与栈尾区别 */ pxNewTCB->pxEndOfStack = pxTopOfStack; } #endif /* configRECORD_STACK_HIGH_ADDRESS */
3.3 :给TCB控制块设置任务名称;
if( pcName != NULL ) { for( x = ( UBaseType_t ) 0; x < ( UBaseType_t ) configMAX_TASK_NAME_LEN; x++ ) { pxNewTCB->pcTaskName[ x ] = pcName[ x ]; /* Don't copy all configMAX_TASK_NAME_LEN if the string is shorter than * configMAX_TASK_NAME_LEN characters just in case the memory after the * string is not accessible (extremely unlikely). */ if( pcName[ x ] == ( char ) 0x00 ) { break; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } /* Ensure the name string is terminated in the case that the string length * was greater or equal to configMAX_TASK_NAME_LEN. */ pxNewTCB->pcTaskName[ configMAX_TASK_NAME_LEN - 1U ] = '\0'; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); }
3.4 :限制优先级,初始化优先级,初始化Base优先级(用于互斥锁优先级反转用);
if( uxPriority >= ( UBaseType_t ) configMAX_PRIORITIES ) { uxPriority = ( UBaseType_t ) configMAX_PRIORITIES - ( UBaseType_t ) 1U; } pxNewTCB->uxPriority = uxPriority; pxNewTCB->uxBasePriority = uxPriority;
3.5 :初始化任务xState和xEvent链表项中的pxContainer ,初始的具体行为只是把 pxContainer 指向为 NULL,pxContainer一般指向具体的链表(如就绪链表,阻塞链表等);
vListInitialiseItem( &( pxNewTCB->xStateListItem ) ); vListInitialiseItem( &( pxNewTCB->xEventListItem ) );
3.6 :初始化任务xState和xEvent链表项中的pvOwner指向,pvOwner指向当前创建的任务,所以通过TCB块的pxContainer 和 pvOwner就知道当前任务所属哪个链表,所属哪个任务,另外事件的ItemValue是记录优先级,数越低优先级越高(与任务优先级反过来);
listSET_LIST_ITEM_OWNER( &( pxNewTCB->xStateListItem ), pxNewTCB ); listSET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxNewTCB->xEventListItem ), ( TickType_t ) configMAX_PRIORITIES - ( TickType_t ) uxPriority ); listSET_LIST_ITEM_OWNER( &( pxNewTCB->xEventListItem ), pxNewTCB );
3.7 :初始化一段TLS内存,这段内存在申请的空间的顶部,_tls_size()具体大小根据当前平台申请得出;
configINIT_TLS_BLOCK( pxNewTCB->xTLSBlock, pxTopOfStack );
3.8 :把核心寄存器进行压栈,具体行为是根据当前栈顶⼿动往下递进依次赋值常量xPSR,PC(应⽤层创建传⼊的任务接⼝地址), LR (⼿动保存为prvTaskExitError函数地址), R12, R3, R2, R1, R0(任务参数指针), EXCTURN,再把栈顶往下8个字( R11 ~ R4) ,总共⼿动设置任务栈寄存器 17 个字,因此任务栈顶在 TLS内存后紧跟着17个字后,任务栈顶指向R4,初始完pxNewTCB后,⽤当初创建任务传⼊的&TCB指针,其实传⼊了个⼆级指针(&指针),那样可以在内部给这个⼆级指针⾥的⼀级指向⼀块区域,这块区域就是任务栈空间,压完寄存器后的地址为栈顶pxTopOfStack
pxNewTCB->pxTopOfStack = pxPortInitialiseStack( pxTopOfStack, pxTaskCode, pvParameters ); StackType_t * pxPortInitialiseStack( StackType_t * pxTopOfStack, TaskFunction_t pxCode, void * pvParameters ) { pxTopOfStack--; *pxTopOfStack = portINITIAL_XPSR; /* xPSR */ pxTopOfStack--; *pxTopOfStack = ( ( StackType_t ) pxCode ) & portSTART_ADDRESS_MASK; /* PC */ pxTopOfStack--; *pxTopOfStack = ( StackType_t ) prvTaskExitError; /* LR */ /* Save code space by skipping register initialisation. */ pxTopOfStack -= 5; /* R12, R3, R2 and R1. */ *pxTopOfStack = ( StackType_t ) pvParameters; /* R0 */ /* A save method is being used that requires each task to maintain its * own exec return value. */ pxTopOfStack--; *pxTopOfStack = portINITIAL_EXC_RETURN; pxTopOfStack -= 8; /* R11, R10, R9, R8, R7, R6, R5 and R4. */ return pxTopOfStack; }
4. 创建的任务加入到对应的就绪优先级链表中
-
任务创建Step4 : 创建的任务加入到具体的就绪优先级链表中,prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxNewTCB );
4.1 :给 TCB 任务控制块申请内存;
4.2 :uxCurrentNumberOfTasks 记录创建的任务数量;
4.3 :确定 pxCurrentTCB的指向,若是首次创建任务则初始化链表(包含就绪链表,两个阻塞链表,缓存链表,待释放链表,挂起链表) ,重初始阻塞链表指针,若是创建任务的优先级高于当前任务优先级,则把创建的任务作为当前任务;
4.4 :uxCurrentNumberOfTasks 和 uxTaskNumber的区别是前者是记录全局任务数量,后者是TCB内部记录当前编号;
4.5 :把任务加入就绪链表,uxTopReadyPriority记录全局任务优先级,创建的任务优先级 ( uxReadyPriorities ) |= ( 1UL << ( uxPriority ) ) ,FreeRTOS从而让最高优先级任务抢占调度
4.6 :由于FreeRTOS是多优先级抢占式,因此就绪链表是数组形式,每个就绪链表对应一个优先级,所以传入对应的优先级链表,把任务 xStateListItem 链表项插入到该优先级链表的当前index链表项之前,由于是双向链表,因此先设置新插入的Next和Previous指向,再通过index索引改变链表对index前一个链表项的指向,重构融于新链表项后的链表,然后记录链表内的链表项数量
4.7 :任务加入到就绪链表后调用 taskYIELD_ANY_CORE_IF_USING_PREEMPTION( pxNewTCB ); 作用是若加入到就绪链表的任务优先级高于当前任务优先级,则⽴刻切换⼀次任务portYIELD_WITHIN_API(),具体切换代码在下方,⾄此创建任务整个流程完成4.1 :给 TCB 任务控制块申请内存;
taskENTER_CRITICAL(); //关闭中断,禁止调度
4.2 :uxCurrentNumberOfTasks 记录创建的任务数量;
uxCurrentNumberOfTasks = ( UBaseType_t ) ( uxCurrentNumberOfTasks + 1U );
4.3 :确定 pxCurrentTCB的指向,若是首次创建任务则初始化链表(包含就绪链表,两个阻塞链表,缓存链表,待释放链表,挂起链表) ,重初始阻塞链表指针,若是创建任务的优先级高于当前任务优先级,则把创建的任务作为当前任务;
if( pxCurrentTCB == NULL ) { /* There are no other tasks, or all the other tasks are in * the suspended state - make this the current task. */ pxCurrentTCB = pxNewTCB; if( uxCurrentNumberOfTasks == ( UBaseType_t ) 1 ) { /* This is the first task to be created so do the preliminary * initialisation required. We will not recover if this call * fails, but we will report the failure. */ prvInitialiseTaskLists(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { /* If the scheduler is not already running, make this task the * current task if it is the highest priority task to be created * so far. */ if( xSchedulerRunning == pdFALSE ) { if( pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority <= pxNewTCB->uxPriority ) { pxCurrentTCB = pxNewTCB; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } }
4.4 :uxCurrentNumberOfTasks 和 uxTaskNumber的区别是前者是记录全局任务数量,后者是TCB内部记录当前编号;
uxTaskNumber++; pxNewTCB->uxTCBNumber = uxTaskNumber;
4.5 :把任务加入就绪链表,uxTopReadyPriority记录全局任务优先级,创建的任务优先级 ( uxReadyPriorities ) |= ( 1UL << ( uxPriority ) ) ,FreeRTOS从而让最高优先级任务抢占调度
prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxNewTCB ); #define prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB ) do { traceMOVED_TASK_TO_READY_STATE( pxTCB ); taskRECORD_READY_PRIORITY( ( pxTCB )->uxPriority ); listINSERT_END( &( pxReadyTasksLists[ ( pxTCB )->uxPriority ] ), &( ( pxTCB )->xStateListItem ) ); tracePOST_MOVED_TASK_TO_READY_STATE( pxTCB ); } while( 0 )) );
4.6 :由于FreeRTOS是多优先级抢占式,因此就绪链表是数组形式,每个就绪链表对应一个优先级,所以传入对应的优先级链表,把任务 xStateListItem 链表项插入到该优先级链表的当前index链表项之前,由于是双向链表,因此先设置新插入的Next和Previous指向,再通过index索引改变链表对index前一个链表项的指向,重构融于新链表项后的链表,然后记录链表内的链表项数量
#define listINSERT_END( pxList, pxNewListItem ) do { ListItem_t * const pxIndex = ( pxList )->pxIndex; ( pxNewListItem )->pxNext = pxIndex; ( pxNewListItem )->pxPrevious = pxIndex->pxPrevious; pxIndex->pxPrevious->pxNext = ( pxNewListItem ); pxIndex->pxPrevious = ( pxNewListItem ); /* Remember which list the item is in. */ ( pxNewListItem )->pxContainer = ( pxList ); ( ( pxList )->uxNumberOfItems ) = ( UBaseType_t ) ( ( ( pxList )->uxNumberOfItems ) + 1U ); } while( 0 )
4.7 :任务加入到就绪链表后调用 taskYIELD_ANY_CORE_IF_USING_PREEMPTION( pxNewTCB ); 作用是若加入到就绪链表的任务优先级高于当前任务优先级,则⽴刻切换⼀次任务portYIELD_WITHIN_API(),具体切换代码在下方,⾄此创建任务整个流程完成
taskYIELD_ANY_CORE_IF_USING_PREEMPTION( pxNewTCB ); #define taskYIELD_ANY_CORE_IF_USING_PREEMPTION( pxTCB ) \ do { \ if( pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority < ( pxTCB )->uxPriority ) \ { \ portYIELD_WITHIN_API(); \ } \ else \ { \ mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); \ } \ } while( 0 ) #define portYIELD_WITHIN_API portYIELD #define portYIELD() \ { \ /* Set a PendSV to request a context switch. */ \ portNVIC_INT_CTRL_REG = portNVIC_PENDSVSET_BIT; \ \ /* Barriers are normally not required but do ensure the code is completely \ * within the specified behaviour for the architecture. */ \ __dsb( portSY_FULL_READ_WRITE ); \ __isb( portSY_FULL_READ_WRITE ); \ }
三 : 源码 : 调度启动与任务切换
任务调度API : vTaskStartScheduler();
任务调度 Step1 :创建空闲任务
任务调度 Step2 :创建定时器任务
任务调度 Step3 :配置调度
任务调度 Step4 :SVC中断 : 任务启动
任务调度 Step5 :PendSV中断 : 任务切换
任务调度 Step6 :SysTick中断 : 系统心跳
任务调度 Step7 :vTaskDelay : 任务阻塞(主动调度)
跳转置顶
1. 创建空闲任务
-
任务调度Step1 : 创建空闲任务
1.1 :空闲任务名默认为"IDLE";
1.2 :函数指针指向静态函数(空闲任务); pxIdleTaskFunction = prvIdleTask;
1.3 :configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE默认为130个字,portPRIVILEGE_BIT默认为0,因此空闲任务优先级最低,xIdleTaskHandles是静态创建的全局TCB指针变量,任务创建执行;xReturn = xTaskCreate( pxIdleTaskFunction, cIdleName, configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE, ( void * ) NULL, portPRIVILEGE_BIT, /* In effect ( tskIDLE_PRIORITY | portPRIVILEGE_BIT ), but tskIDLE_PRIORITY is zero. */ &xIdleTaskHandles[ xCoreID ] );
2. 创建定时器任务
-
任务调度Step2 : 创建定时器任务
2.1 : 进入临界区
2.2 : 初始定时器链表(类似阻塞链表有CurrentTimer和OverflowTimer)
2.3 : 创建队列,定时器任务其实就是专门处理接收定时器命令的队列任务,且带超时阻塞机制实现定时逻辑
2.4 : 队列注册到静态调试队列,方便调试,0x20001000: / TmrQ: 调试阶段,基于调试名显示,方便直观
2.5 : 创建任务,定时器任务名默认“Tmr Svc”;定时器任务栈默认 configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE * 2;定时器任务默认最高 configTIMER_TASK_PRIORITY 宏定义为 configMAX_PRIORITIES - 1
2.1 :进入临界区
taskENTER_CRITICAL();
2.2 :初始定时器链表(类似阻塞链表有CurrentTimer和OverflowTimer)
vListInitialise( &xActiveTimerList1 ); vListInitialise( &xActiveTimerList2 ); pxCurrentTimerList = &xActiveTimerList1; pxOverflowTimerList = &xActiveTimerList2;
2.3 :创建队列,定时器任务其实就是专门处理接收定时器命令的队列任务,且带超时阻塞机制实现定时逻辑
xTimerQueue = xQueueCreate( ( UBaseType_t ) configTIMER_QUEUE_LENGTH, ( UBaseType_t ) sizeof( DaemonTaskMessage_t ) );
2.4 :队列注册到静态调试队列,方便调试,0x20001000: / TmrQ: 调试阶段,基于调试名显示,方便直观
vQueueAddToRegistry( xTimerQueue, "TmrQ" );
2.5 :创建任务,定时器任务名默认“Tmr Svc”;定时器任务栈默认 configMINIMAL_STACK_SIZE * 2;定时器任务默认最高 configTIMER_TASK_PRIORITY 宏定义为 configMAX_PRIORITIES - 1
xReturn = xTaskCreate( prvTimerTask, configTIMER_SERVICE_TASK_NAME, configTIMER_TASK_STACK_DEPTH, NULL, ( ( UBaseType_t ) configTIMER_TASK_PRIORITY ) | portPRIVILEGE_BIT, &xTimerTaskHandle );
3. 配置调度逻辑
-
任务调度Step3 : 配置调度逻辑
3.1 : 关闭中断
3.2 : 初始当前任务TLS段数据(每个线程有自己的TLS数据)
3.3 : 初始调度阻塞的检测限值为最大(Tick查询阻塞态任务时先预检该值),启动调度器标志位,初始xTickCount为0
3.4 : 初始执行逻辑,设PendSV优先级,SysTick优先级,配置SysTick定时频率,复位临界区嵌套计数,使能FPU单元,FPU启用惰性机制,进入启动汇编执行逻辑
3.5 : 加载向量表中的第一个数据赋予MSP实现初始MSP栈顶,control寄存器初始为0(参考寄存器章节描述),cpsie i ; 启用 IRQ 中断(清除 PRIMASK),cpsie f ; 启用 Fault 中断(清除 FAULTMASK),数据与指令同步,svc中断启动, svc x (x : 0~255表示不同服务)
3.1 :关闭中断
portDISABLE_INTERRUPTS();
3.2 :初始当前任务TLS段数据(每个线程有自己的TLS数据)
configSET_TLS_BLOCK( pxCurrentTCB->xTLSBlock );
3.3 :初始调度阻塞的检测限值为最大(Tick查询阻塞态任务时先预检该值),启动调度器标志位,初始xTickCount为0
xNextTaskUnblockTime = portMAX_DELAY; xSchedulerRunning = pdTRUE; xTickCount = ( TickType_t ) configINITIAL_TICK_COUNT;
3.4 :初始执行逻辑,设PendSV优先级,SysTick优先级,配置SysTick定时频率,复位临界区嵌套计数,使能FPU单元,FPU启用惰性机制,进入启动汇编执行逻辑
BaseType_t xPortStartScheduler( void ) { /* Make PendSV and SysTick the lowest priority interrupts. */ portNVIC_SHPR3_REG |= portNVIC_PENDSV_PRI; //设PendSV优先级为最低 portNVIC_SHPR3_REG |= portNVIC_SYSTICK_PRI;//设SysTick优先级为最低 /* Start the timer that generates the tick ISR. Interrupts are disabled * here already. */ vPortSetupTimerInterrupt(); //配置SysTick定时频率,时钟源(主频或主频/8),中断使能,SysTick自身使能 /* Initialise the critical nesting count ready for the first task. */ uxCriticalNesting = 0; //临界区嵌套深度计数,为0说明临界区嵌套调用层数为0没有嵌套 /* Ensure the VFP is enabled - it should be anyway. */ /* 使能处理器的浮点单元(FPU),主要是设置CPACR寄存器。 * 此操作必须在首次使用浮点指令前完成。 */ prvEnableVFP(); /* Lazy save always. */ /* 在FPCCR寄存器中设置ASPEN和LSPEN位,全局启用“惰性堆叠”机制。 * 此配置使得硬件在任务首次使用FPU后,才在上下文切换时自动保存/恢复浮点寄存器, * 从而优化未使用FPU任务的切换开销。此配置是全局性的,作用于所有任务。 */ *( portFPCCR ) |= portASPEN_AND_LSPEN_BITS; /* Start the first task. */ prvStartFirstTask(); //启动第一个任务 /* Should not get here! */ return 0; }
3.5 :加载向量表中的第一个数据赋予MSP实现初始MSP栈顶,control寄存器初始为0(参考寄存器章节描述),cpsie i ; 启用 IRQ 中断(清除 PRIMASK),cpsie f ; 启用 Fault 中断(清除 FAULTMASK),数据与指令同步,svc中断启动, svc x (x : 0~255表示不同服务)
__asm void prvStartFirstTask( void ) { /* *INDENT-OFF* */ PRESERVE8 /* Use the NVIC offset register to locate the stack. */ ldr r0, =0xE000ED08 ldr r0, [ r0 ] ldr r0, [ r0 ] /* Set the msp back to the start of the stack. */ msr msp, r0 /* Clear the bit that indicates the FPU is in use in case the FPU was used * before the scheduler was started - which would otherwise result in the * unnecessary leaving of space in the SVC stack for lazy saving of FPU * registers. */ mov r0, #0 msr control, r0 /* Globally enable interrupts. */ cpsie i cpsie f dsb isb /* Call SVC to start the first task. */ svc 0 nop nop /* *INDENT-ON* */ }
4. SVC中断 : 任务启动
-
任务调度Step4 : SVC中断 : 任务启动
4.1 :获取pxCurrentTCB的栈顶,根据栈顶开始⽤R0来当指针恢复新TCB的R4 ~ R11,R14,msr basepri, r0 恢复中断优先级屏蔽,bx r14触发异常返回序列Handler,Thread,msp,psp,选择Thread,psp模式,当svc中断退出时,触发硬件弹栈,根据psp指针指向任务栈R0处开始弹栈,弹栈完成,此时PC值是新任务控制块保存的PC地址,因此跳转在任务保存的PC值处执⾏
__asm void vPortSVCHandler( void ) { /* *INDENT-OFF* */ PRESERVE8 /* Get the location of the current TCB. */ ldr r3, =pxCurrentTCB ldr r1, [ r3 ] ldr r0, [ r1 ] /* Pop the core registers. */ ldmia r0!, { r4-r11, r14 } msr psp, r0 isb mov r0, #0 msr basepri, r0 bx r14 /* *INDENT-ON* */ }
5. PendSV中断 : 任务切换
-
任务调度Step5 : PendSV中断 : 任务切换
5.1 : 进⼊中断硬件⾃动压栈 : xPSR, PC, LR, R12, R3 ~ R0,EXCTURN,保留字, 此时R14的参数是EXCTURN;R0指向PSP,获取当前 pxCurrentTCB 指向的任务块地址;根据EXCTURN的bit4选择⼿动压栈FPU寄存器,再压R4 ~ R11, R14(因切换任务块所以保存R14 EXCTURN);关⻔中断,调⽤ vTaskSwitchContext 切换任务块;获取新指向的任务控制块栈顶 pxTop0fStack ,⽤R0指向栈顶弹栈 R4~R11, R14,根据R14(EXCTURN) 选择恢复FPU寄存器 s16 ~ s31;PSP指向软件弹栈后的R0,,执⾏bx r14触发异常返回序列;中断退出,此时PSP恰好在栈顶 pxTop0fStack ,在这个新任务控制块的栈顶硬件⾃动弹栈新任务控制块的寄存器
__asm void xPortPendSVHandler( void ) { extern uxCriticalNesting; extern pxCurrentTCB; extern vTaskSwitchContext; /* *INDENT-OFF* */ PRESERVE8 mrs r0, psp isb /* Get the location of the current TCB. */ ldr r3, =pxCurrentTCB ldr r2, [ r3 ] /* Is the task using the FPU context? If so, push high vfp registers. */ tst r14, #0x10 it eq vstmdbeq r0!, {s16-s31} /* Save the core registers. */ stmdb r0!, {r4-r11, r14 } /* Save the new top of stack into the first member of the TCB. */ str r0, [ r2 ] /* 把r0和r3压栈,关闭中断,指令同步后切换TCB块 */ stmdb sp!, { r0, r3 } mov r0, #configMAX_SYSCALL_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY cpsid i msr basepri, r0 dsb isb cpsie i bl vTaskSwitchContext mov r0, #0 msr basepri, r0 ldmia sp!, { r0, r3 } /* 这里r3 是 pxCurrentTCB的地址,[r3]表示解引用二级指针得到当前pxCurrentTCB一级指针指向的地址 */ ldr r1, [ r3 ] /* 解引用pxCurrentTCB,得到第一个成员栈顶,此时r0是栈顶的指向,那么就可以基于栈顶恢复任务状态 */ ldr r0, [ r1 ] /* Pop the core registers. */ ldmia r0!, { r4-r11, r14 } /* Is the task using the FPU context? If so, pop the high vfp registers * too. */ tst r14, #0x10 it eq vldmiaeq r0!, { s16-s31 } msr psp, r0 isb #ifdef WORKAROUND_PMU_CM001 /* XMC4000 specific errata */ #if WORKAROUND_PMU_CM001 == 1 push { r14 } pop { pc } nop #endif #endif bx r14 /* *INDENT-ON* */ }5.2 :vTaskSwitchContext 中核心调用了以下这段代码,基于前导零算法(顺序翻转)获取当前全局最高优先级,基于最高优先级在就绪链表中的pvOwner 索引到TCB任务控制块,至此 pxCurrentTCB 当前全局TCB切换指向为当前优先级就绪链表中的下一个TCB块,完成切换指向,之后PendSV继续执行基于TCB栈顶恢复状态
#define portGET_HIGHEST_PRIORITY( uxTopPriority, uxReadyPriorities ) uxTopPriority = ( 31UL - ( uint32_t ) __clz( ( uxReadyPriorities ) ) ) #define taskSELECT_HIGHEST_PRIORITY_TASK() \ do { \ UBaseType_t uxTopPriority; \ \ /* Find the highest priority list that contains ready tasks. */ \ portGET_HIGHEST_PRIORITY( uxTopPriority, uxTopReadyPriority ); \ configASSERT( listCURRENT_LIST_LENGTH( &( pxReadyTasksLists[ uxTopPriority ] ) ) > 0 ); \ listGET_OWNER_OF_NEXT_ENTRY( pxCurrentTCB, &( pxReadyTasksLists[ uxTopPriority ] ) ); \ } while( 0 ) #define listGET_OWNER_OF_NEXT_ENTRY( pxTCB, pxList ) \ do { \ List_t * const pxConstList = ( pxList ); \ /* Increment the index to the next item and return the item, ensuring */ \ /* we don't return the marker used at the end of the list. */ \ ( pxConstList )->pxIndex = ( pxConstList )->pxIndex->pxNext; \ if( ( void * ) ( pxConstList )->pxIndex == ( void * ) &( ( pxConstList )->xListEnd ) ) \ { \ ( pxConstList )->pxIndex = ( pxConstList )->xListEnd.pxNext; \ } \ ( pxTCB ) = ( pxConstList )->pxIndex->pvOwner; \ } while( 0 )
6 . SysTick中断 : 系统心跳
-
任务调度Step6 : SysTick中断 : 系统心跳
6.1:以下是 FreeRTOS 中作为系统心跳的 SysTick 定时器中断服务程序 xPortSysTickHandler 的核心实现。它在进入时通过 vPortRaiseBASEPRI() 快速提升中断屏蔽级别以保护临界区,然后调用 xTaskIncrementTick() 函数递增系统时钟节拍,并检查是否有延时任务到期或时间片轮转需要触发任务切换;若需要切换,则通过写 portNVIC_INT_CTRL_REG 寄存器设置 PendSV 中断挂起位,将实际耗时的上下文切换工作延迟到低优先级的 PendSV 异常中处理,从而确保 SysTick 中断本身的快速执行与退出;最后通过 vPortClearBASEPRIFromISR() 恢复中断屏蔽状态。此机制是 FreeRTOS 实现基于时间片的任务调度、阻塞超时管理及系统时间基准维护的基础。
void xPortSysTickHandler( void ) { /* The SysTick runs at the lowest interrupt priority, so when this interrupt * executes all interrupts must be unmasked. There is therefore no need to * save and then restore the interrupt mask value as its value is already * known - therefore the slightly faster vPortRaiseBASEPRI() function is used * in place of portSET_INTERRUPT_MASK_FROM_ISR(). */ vPortRaiseBASEPRI(); traceISR_ENTER(); { /* Increment the RTOS tick. */ if( xTaskIncrementTick() != pdFALSE ) { traceISR_EXIT_TO_SCHEDULER(); /* A context switch is required. Context switching is performed in * the PendSV interrupt. Pend the PendSV interrupt. */ portNVIC_INT_CTRL_REG = portNVIC_PENDSVSET_BIT; } else { traceISR_EXIT(); } } vPortClearBASEPRIFromISR(); }6.2 :以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 系统节拍递增与任务调度检查的核心函数 xTaskIncrementTick 的实现,它在调度器未挂起时递增系统节拍计数器 xTickCount,并处理计数器回绕时的延迟列表切换;随后检查该节拍是否已达到或超过下一个任务解除阻塞的时间点 xNextTaskUnblockTime:若是,则遍历延迟任务列表,将所有已到期的任务移出阻塞态并加入就绪列表,同时根据被唤醒任务的优先级与当前任务的优先级比较(在可抢占模式下),或根据就绪列表中同优先级任务的数量(在时间片轮转模式下),来判断是否需要触发一次任务切换;此外,若调度器处于挂起状态,则递增挂起节拍计数。函数最终返回一个布尔值,指示 SysTick 中断服务程序是否需要触发 PendSV 中断以执行实际的任务上下文切换。
BaseType_t xTaskIncrementTick( void ) { TCB_t * pxTCB; TickType_t xItemValue; BaseType_t xSwitchRequired = pdFALSE; #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) BaseType_t xYieldRequiredForCore[ configNUMBER_OF_CORES ] = { pdFALSE }; #endif /* #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) */ traceENTER_xTaskIncrementTick(); /* Called by the portable layer each time a tick interrupt occurs. * Increments the tick then checks to see if the new tick value will cause any * tasks to be unblocked. */ traceTASK_INCREMENT_TICK( xTickCount ); /* Tick increment should occur on every kernel timer event. Core 0 has the * responsibility to increment the tick, or increment the pended ticks if the * scheduler is suspended. If pended ticks is greater than zero, the core that * calls xTaskResumeAll has the responsibility to increment the tick. */ if( uxSchedulerSuspended == ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) { /* Minor optimisation. The tick count cannot change in this * block. */ const TickType_t xConstTickCount = xTickCount + ( TickType_t ) 1; /* Increment the RTOS tick, switching the delayed and overflowed * delayed lists if it wraps to 0. */ xTickCount = xConstTickCount; if( xConstTickCount == ( TickType_t ) 0U ) { taskSWITCH_DELAYED_LISTS(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* See if this tick has made a timeout expire. Tasks are stored in * the queue in the order of their wake time - meaning once one task * has been found whose block time has not expired there is no need to * look any further down the list. */ if( xConstTickCount >= xNextTaskUnblockTime ) { for( ; ; ) { if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( pxDelayedTaskList ) != pdFALSE ) { /* The delayed list is empty. Set xNextTaskUnblockTime * to the maximum possible value so it is extremely * unlikely that the * if( xTickCount >= xNextTaskUnblockTime ) test will pass * next time through. */ xNextTaskUnblockTime = portMAX_DELAY; break; } else { /* The delayed list is not empty, get the value of the * item at the head of the delayed list. This is the time * at which the task at the head of the delayed list must * be removed from the Blocked state. */ /* MISRA Ref 11.5.3 [Void pointer assignment] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-115 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_5_violation] */ pxTCB = listGET_OWNER_OF_HEAD_ENTRY( pxDelayedTaskList ); xItemValue = listGET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ); if( xConstTickCount < xItemValue ) { /* It is not time to unblock this item yet, but the * item value is the time at which the task at the head * of the blocked list must be removed from the Blocked * state - so record the item value in * xNextTaskUnblockTime. */ xNextTaskUnblockTime = xItemValue; break; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* It is time to remove the item from the Blocked state. */ listREMOVE_ITEM( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ); /* Is the task waiting on an event also? If so remove * it from the event list. */ if( listLIST_ITEM_CONTAINER( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ) != NULL ) { listREMOVE_ITEM( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* Place the unblocked task into the appropriate ready * list. */ prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB ); /* A task being unblocked cannot cause an immediate * context switch if preemption is turned off. */ #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) { #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) { /* Preemption is on, but a context switch should * only be performed if the unblocked task's * priority is higher than the currently executing * task. * The case of equal priority tasks sharing * processing time (which happens when both * preemption and time slicing are on) is * handled below.*/ if( pxTCB->uxPriority > pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority ) { xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #else /* #if( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ { prvYieldForTask( pxTCB ); } #endif /* #if( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ } #endif /* #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) */ } } } /* Tasks of equal priority to the currently running task will share * processing time (time slice) if preemption is on, and the application * writer has not explicitly turned time slicing off. */ #if ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configUSE_TIME_SLICING == 1 ) ) { #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) { if( listCURRENT_LIST_LENGTH( &( pxReadyTasksLists[ pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority ] ) ) > 1U ) { xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #else /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ { BaseType_t xCoreID; for( xCoreID = 0; xCoreID < ( ( BaseType_t ) configNUMBER_OF_CORES ); xCoreID++ ) { if( listCURRENT_LIST_LENGTH( &( pxReadyTasksLists[ pxCurrentTCBs[ xCoreID ]->uxPriority ] ) ) > 1U ) { xYieldRequiredForCore[ xCoreID ] = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ } #endif /* #if ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configUSE_TIME_SLICING == 1 ) ) */ #if ( configUSE_TICK_HOOK == 1 ) { /* Guard against the tick hook being called when the pended tick * count is being unwound (when the scheduler is being unlocked). */ if( xPendedTicks == ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { vApplicationTickHook(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* configUSE_TICK_HOOK */ #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) { #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) { /* For single core the core ID is always 0. */ if( xYieldPendings[ 0 ] != pdFALSE ) { xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #else /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ { BaseType_t xCoreID, xCurrentCoreID; xCurrentCoreID = ( BaseType_t ) portGET_CORE_ID(); for( xCoreID = 0; xCoreID < ( BaseType_t ) configNUMBER_OF_CORES; xCoreID++ ) { #if ( configUSE_TASK_PREEMPTION_DISABLE == 1 ) if( pxCurrentTCBs[ xCoreID ]->xPreemptionDisable == pdFALSE ) #endif { if( ( xYieldRequiredForCore[ xCoreID ] != pdFALSE ) || ( xYieldPendings[ xCoreID ] != pdFALSE ) ) { if( xCoreID == xCurrentCoreID ) { xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE; } else { prvYieldCore( xCoreID ); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ } #endif /* #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) */ } else { xPendedTicks += 1U; /* The tick hook gets called at regular intervals, even if the * scheduler is locked. */ #if ( configUSE_TICK_HOOK == 1 ) { vApplicationTickHook(); } #endif } traceRETURN_xTaskIncrementTick( xSwitchRequired ); return xSwitchRequired; }
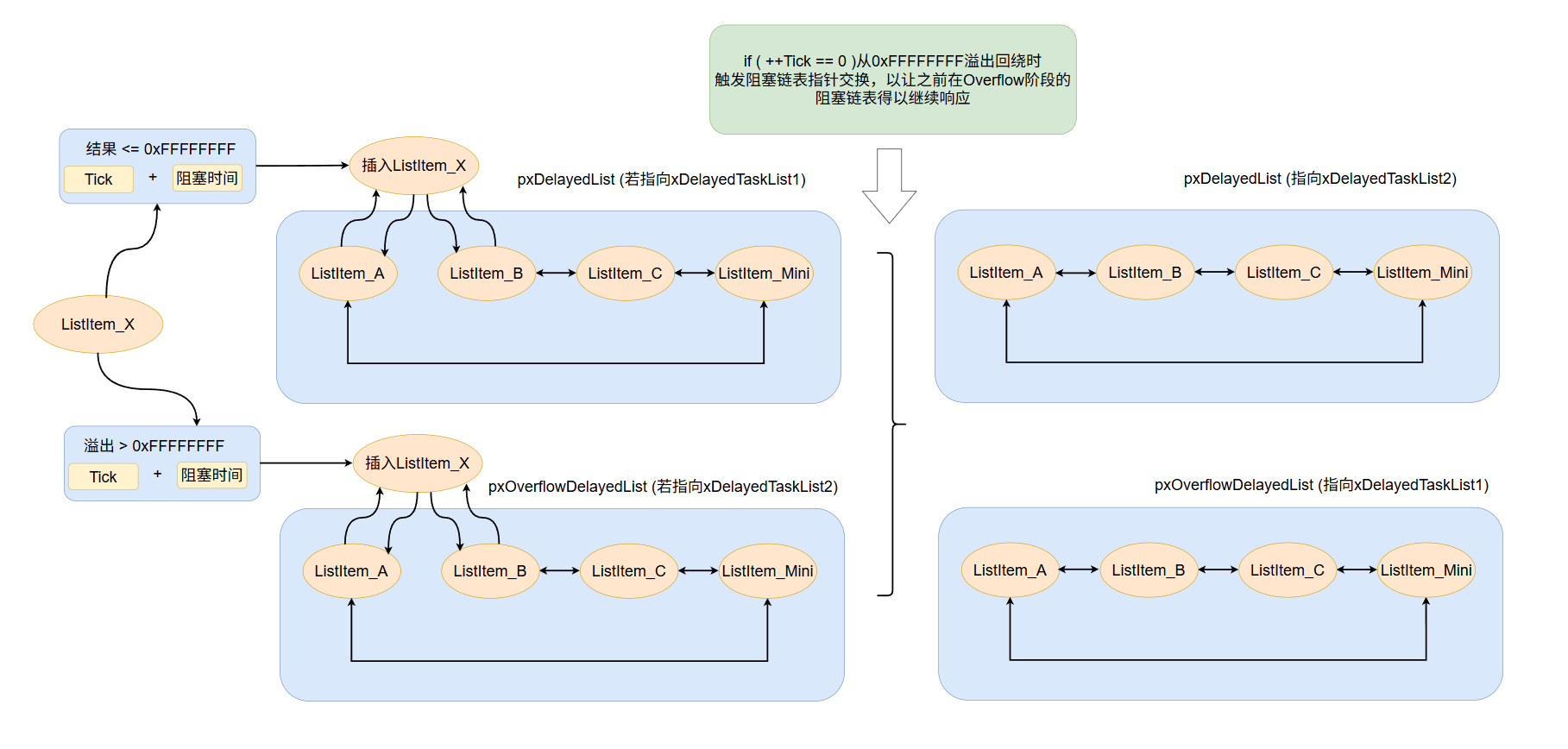
6.3 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中用于处理系统节拍计数器溢出时交换延迟任务列表的宏。当系统节拍计数器xTickCount溢出回绕时,它会交换常规延迟任务列表pxDelayedTaskList和溢出延迟任务列表pxOverflowDelayedTaskList的指针角色,同时递增溢出计数器并重新计算下一个任务唤醒时间。
这个宏与prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList中的溢出处理逻辑相配合:当一个任务的唤醒时间因计算溢出(即xTimeToWake < xConstTickCount)而被放入溢出延迟列表后,当系统节拍计数器实际发生溢出时,通过交换两个列表的指针,原先的"溢出"任务现在实际上已不再溢出,从而能被正常调度唤醒。#define taskSWITCH_DELAYED_LISTS() \ do { \ List_t * pxTemp; \ \ /* The delayed tasks list should be empty when the lists are switched. */ \ configASSERT( ( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( pxDelayedTaskList ) ) ); \ \ pxTemp = pxDelayedTaskList; \ pxDelayedTaskList = pxOverflowDelayedTaskList; \ pxOverflowDelayedTaskList = pxTemp; \ xNumOfOverflows = ( BaseType_t ) ( xNumOfOverflows + 1 ); \ prvResetNextTaskUnblockTime(); \ } while( 0 )
7 . vTaskDelay / xTaskDelayUntil (任务阻塞)
-
任务调度Step7 : vTaskDelay : 任务阻塞(主动调度)
7.1 :以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 中实现任务主动延时功能的核心函数 vTaskDelay 的实现,其主要逻辑是:若传入的延时时间大于零,函数会首先挂起任务调度器,通过调用 prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList 将当前正在执行的任务从就绪列表中移除,并根据延时周期将其置入相应的延迟任务列表,使其进入阻塞态;随后恢复调度器。若延时时间为零,该函数则纯粹作为一个强制任务切换的请求。无论是以上哪种情况,函数最终都会通过检查 xAlreadyYielded 标志或主动调用 taskYIELD_WITHIN_API() 来确保调度器有机会进行一次重新调度,从而使其他就绪的、特别是高优先级的任务得以运行。此机制是任务主动放弃 CPU、实现周期性执行或简单协作调度的基础;
void vTaskDelay( const TickType_t xTicksToDelay ) { BaseType_t xAlreadyYielded = pdFALSE; traceENTER_vTaskDelay( xTicksToDelay ); /* A delay time of zero just forces a reschedule. */ if( xTicksToDelay > ( TickType_t ) 0U ) { vTaskSuspendAll(); { configASSERT( uxSchedulerSuspended == 1U ); traceTASK_DELAY(); /* A task that is removed from the event list while the * scheduler is suspended will not get placed in the ready * list or removed from the blocked list until the scheduler * is resumed. * * This task cannot be in an event list as it is the currently * executing task. */ prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList( xTicksToDelay, pdFALSE ); } xAlreadyYielded = xTaskResumeAll(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* Force a reschedule if xTaskResumeAll has not already done so, we may * have put ourselves to sleep. */ if( xAlreadyYielded == pdFALSE ) { taskYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceRETURN_vTaskDelay(); }7.2 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中将当前任务添加到延迟列表的核心函数,主要功能如下:将当前任务从就绪列表中移除,根据延时时间计算唤醒时间点,然后将其插入到适当的延迟列表中。如果延时时间设置为最大值且允许无限期阻塞,则任务会被挂起;否则,根据唤醒时间是否发生溢出(由于系统节拍计数器回绕),任务会被插入到常规延迟列表或溢出延迟列表中。当任务被添加到常规延迟列表头部时,还会更新下一个任务唤醒时间(xNextTaskUnblockTime)以优化调度效率。
static void prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList( TickType_t xTicksToWait, const BaseType_t xCanBlockIndefinitely ) { TickType_t xTimeToWake; const TickType_t xConstTickCount = xTickCount; List_t * const pxDelayedList = pxDelayedTaskList; List_t * const pxOverflowDelayedList = pxOverflowDelayedTaskList; #if ( INCLUDE_xTaskAbortDelay == 1 ) { /* About to enter a delayed list, so ensure the ucDelayAborted flag is * reset to pdFALSE so it can be detected as having been set to pdTRUE * when the task leaves the Blocked state. */ pxCurrentTCB->ucDelayAborted = ( uint8_t ) pdFALSE; } #endif /* Remove the task from the ready list before adding it to the blocked list * as the same list item is used for both lists. */ if( uxListRemove( &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) ) == ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) { /* The current task must be in a ready list, so there is no need to * check, and the port reset macro can be called directly. */ portRESET_READY_PRIORITY( pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority, uxTopReadyPriority ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } #if ( INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend == 1 ) { if( ( xTicksToWait == portMAX_DELAY ) && ( xCanBlockIndefinitely != pdFALSE ) ) { /* Add the task to the suspended task list instead of a delayed task * list to ensure it is not woken by a timing event. It will block * indefinitely. */ listINSERT_END( &xSuspendedTaskList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) ); } else { /* Calculate the time at which the task should be woken if the event * does not occur. This may overflow but this doesn't matter, the * kernel will manage it correctly. */ xTimeToWake = xConstTickCount + xTicksToWait; /* The list item will be inserted in wake time order. */ listSET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ), xTimeToWake ); if( xTimeToWake < xConstTickCount ) { /* Wake time has overflowed. Place this item in the overflow * list. */ traceMOVED_TASK_TO_OVERFLOW_DELAYED_LIST(); vListInsert( pxOverflowDelayedList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) ); } else { /* The wake time has not overflowed, so the current block list * is used. */ traceMOVED_TASK_TO_DELAYED_LIST(); vListInsert( pxDelayedList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) ); /* If the task entering the blocked state was placed at the * head of the list of blocked tasks then xNextTaskUnblockTime * needs to be updated too. */ if( xTimeToWake < xNextTaskUnblockTime ) { xNextTaskUnblockTime = xTimeToWake; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } } #else /* INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend */ { /* Calculate the time at which the task should be woken if the event * does not occur. This may overflow but this doesn't matter, the kernel * will manage it correctly. */ xTimeToWake = xConstTickCount + xTicksToWait; /* The list item will be inserted in wake time order. */ listSET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ), xTimeToWake ); if( xTimeToWake < xConstTickCount ) { traceMOVED_TASK_TO_OVERFLOW_DELAYED_LIST(); /* Wake time has overflowed. Place this item in the overflow list. */ vListInsert( pxOverflowDelayedList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) ); } else { traceMOVED_TASK_TO_DELAYED_LIST(); /* The wake time has not overflowed, so the current block list is used. */ vListInsert( pxDelayedList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) ); /* If the task entering the blocked state was placed at the head of the * list of blocked tasks then xNextTaskUnblockTime needs to be updated * too. */ if( xTimeToWake < xNextTaskUnblockTime ) { xNextTaskUnblockTime = xTimeToWake; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } /* Avoid compiler warning when INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend is not 1. */ ( void ) xCanBlockIndefinitely; } #endif /* INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend */ }
7.3 :以下这段代码实现了FreeRTOS中精确周期性延迟函数xTaskDelayUntil的核心逻辑:通过挂起调度器确保计算的原子性,它基于任务上次唤醒时间*pxPreviousWakeTime和固定周期xTimeIncrement计算出下一次理论唤醒时间点xTimeToWake,并细致地处理了系统tick计数器可能溢出的情况;然后判断当前时刻是否已超过或到达该唤醒时间——若未到达,则将任务精确阻塞相应时长并加入延迟列表;若已超过(意味着任务因执行过久错过了周期),则立即返回而不阻塞。最后,函数更新唤醒时间为下一次周期的起点,并在必要时强制进行一次任务切换。整个设计旨在为任务提供稳定、可累积误差的固定周期执行能力,总而言之就是若因任务处理时间超出设定的时间,则不延时,立刻返回继续执行任务,否则得到Tick差进行延时,目的是让任务运行时间频率尽量一致,例如10ms执行一次,若有一次任务执行用了8ms,那么xTaskDelayUntil只会再阻塞2ms,若是任务执行用了10ms以上,则不阻塞立刻返回继续执行。
BaseType_t xTaskDelayUntil( TickType_t * const pxPreviousWakeTime, const TickType_t xTimeIncrement ) { TickType_t xTimeToWake; BaseType_t xAlreadyYielded, xShouldDelay = pdFALSE; traceENTER_xTaskDelayUntil( pxPreviousWakeTime, xTimeIncrement ); configASSERT( pxPreviousWakeTime ); configASSERT( ( xTimeIncrement > 0U ) ); vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* Minor optimisation. The tick count cannot change in this * block. */ const TickType_t xConstTickCount = xTickCount; configASSERT( uxSchedulerSuspended == 1U ); /* Generate the tick time at which the task wants to wake. */ xTimeToWake = *pxPreviousWakeTime + xTimeIncrement; if( xConstTickCount < *pxPreviousWakeTime ) { /* The tick count has overflowed since this function was * lasted called. In this case the only time we should ever * actually delay is if the wake time has also overflowed, * and the wake time is greater than the tick time. When this * is the case it is as if neither time had overflowed. */ if( ( xTimeToWake < *pxPreviousWakeTime ) && ( xTimeToWake > xConstTickCount ) ) { xShouldDelay = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { /* The tick time has not overflowed. In this case we will * delay if either the wake time has overflowed, and/or the * tick time is less than the wake time. */ if( ( xTimeToWake < *pxPreviousWakeTime ) || ( xTimeToWake > xConstTickCount ) ) { xShouldDelay = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } /* Update the wake time ready for the next call. */ *pxPreviousWakeTime = xTimeToWake; if( xShouldDelay != pdFALSE ) { traceTASK_DELAY_UNTIL( xTimeToWake ); /* prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList() needs the block time, not * the time to wake, so subtract the current tick count. */ prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList( xTimeToWake - xConstTickCount, pdFALSE ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } xAlreadyYielded = xTaskResumeAll(); /* Force a reschedule if xTaskResumeAll has not already done so, we may * have put ourselves to sleep. */ if( xAlreadyYielded == pdFALSE ) { taskYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceRETURN_xTaskDelayUntil( xShouldDelay ); return xShouldDelay; }
四. 源码 : 内存管理
前言 : 以下五种内存管理方案,笔者在源码中添加了注释,这里前言主要强调两点
- 源码内存管理注重 内存池字节对齐 ,申请的内存起始地址 内存字节对齐;
- 内存池每个空闲块通过头部信息 (头部信息大小为8字节) 管理块,通过链表管理整个内存池
| 内存管理模式 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| heap1 | 只申请内存,不释放内存 |
| heap2 | 申请内存,释放内存,拆分内存 |
| heap3 | 间接调用平台内存申请接口 |
| heap4 | 申请内存,释放内存,拆分内存,合并内存 |
| heap5 | 申请内存,释放内存,拆分内存,合并内存,多段区域内存管理 |
1. heap_1.c 内存管理
内存管理API : pvPortMalloc(); vPortFree();
内存管理heap1 :heap_1.c源码,截全核心代码,每个细节笔者根据自己理解注解
跳转置顶
-
heap_1.c 内存管理
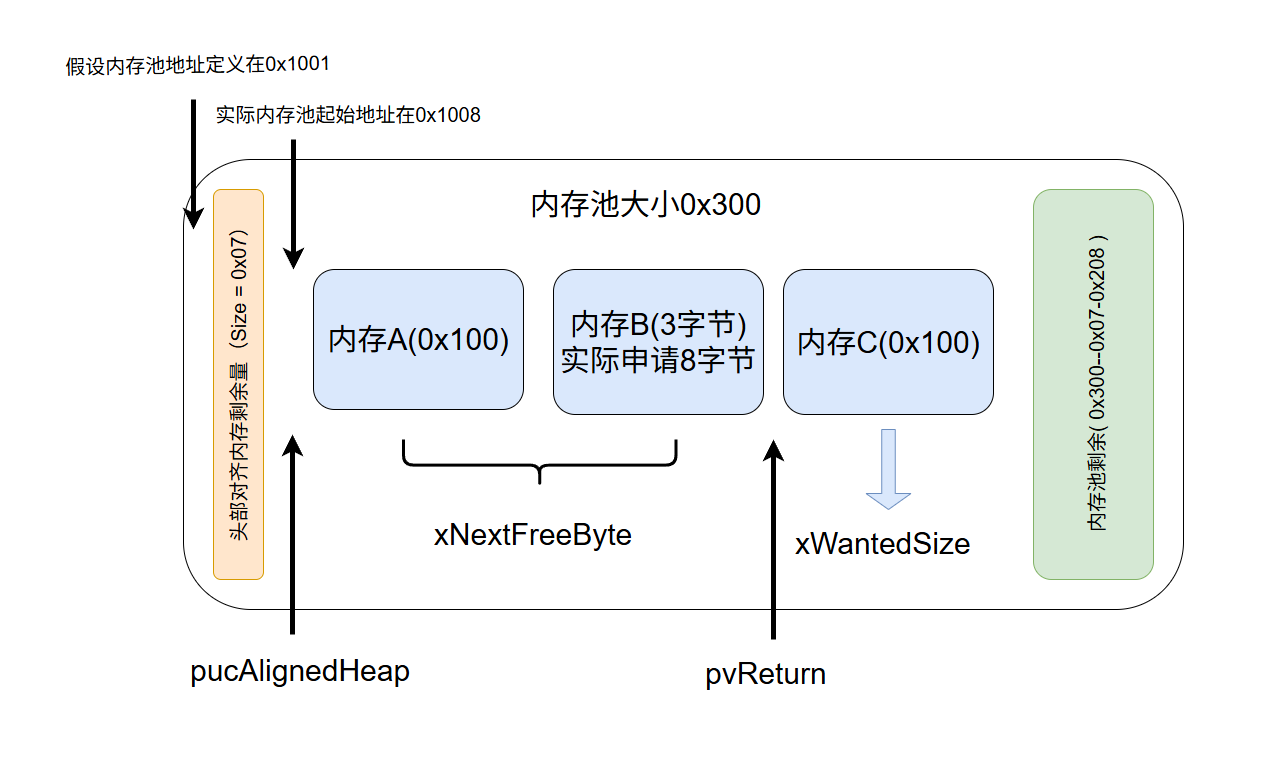
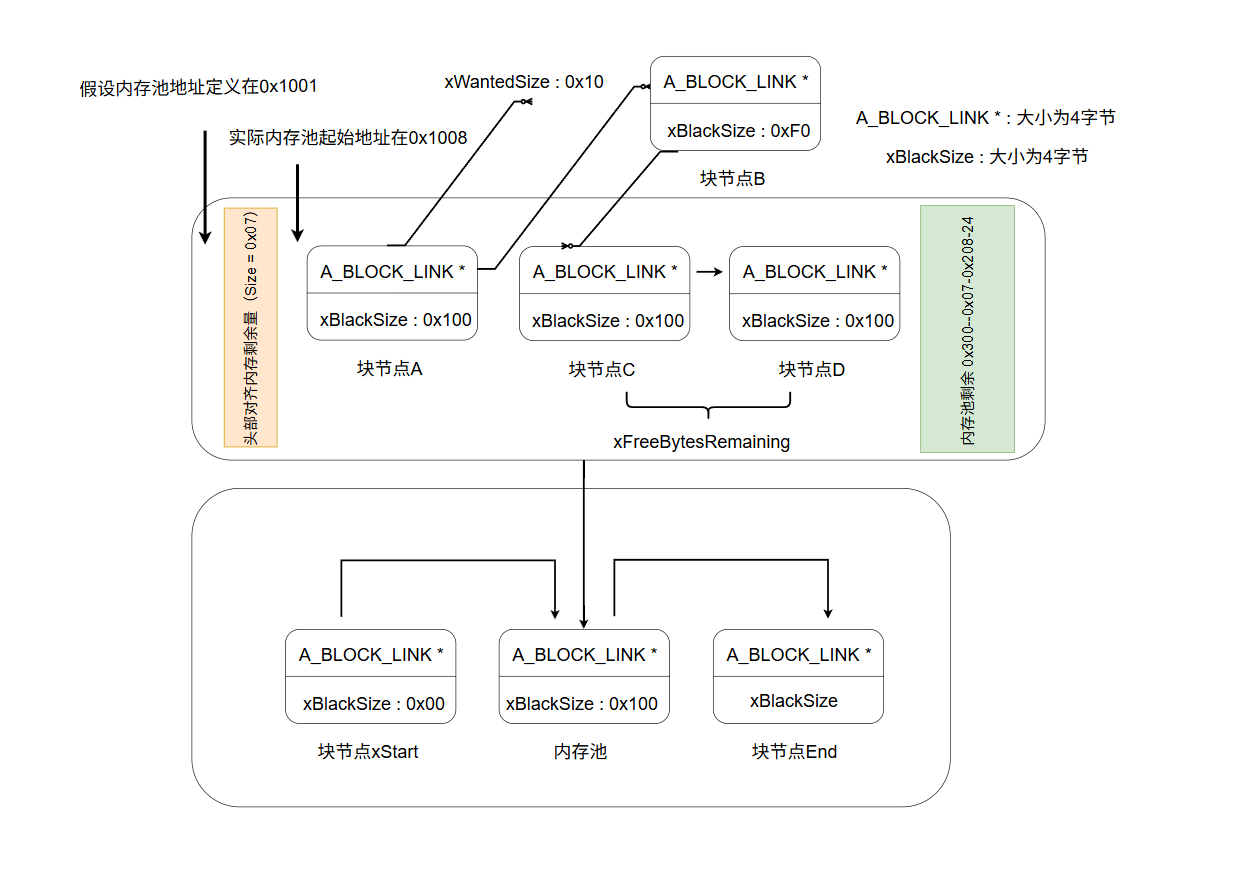
1.1 :heap_1内存管理图解,分开两个对齐,第一个对齐是内存池自身地址对齐,预留八个字节用于向下对齐,例如0x1001,则在0x1001~0x1009之间找到8的倍数对齐,即0x1008,第二个对齐是内存申请的对齐,例如申请3字节,则向上对齐8的倍数,则实际申请内存为8字节
1.2 完整heap_1.c源码解析,这段代码是FreeRTOS中 heap_1内存管理方案的核心实现,它采用一种简单、确定的静态内存分配策略。其核心机制是预先定义一个静态数组ucHeap作为全局内存池,在首次分配时通过地址掩码操作确保返回的起始地址满足字节对齐要求(如8字节)。分配过程通过维护一个全局偏移量xNextFreeByte来顺序分配内存,并在分配时挂起调度器以保证线程安全。该方案的特点是只进行内存分配,不支持释放,所有分配的内存会在应用程序生命周期内一直被占用。它通过xPortGetFreeHeapSize等函数提供剩余内存查询,并通过钩子函数支持分配失败的定制处理,其设计确保了在资源受限的嵌入式环境(尤其是启动阶段)中内存操作的可靠性和可预测性
/* 实际可用内存为总内存池减去对齐字节(8) */ #define configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ( configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE - portBYTE_ALIGNMENT ) /* 定义内存池 */ #if ( configAPPLICATION_ALLOCATED_HEAP == 1 ) extern uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; #else static uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; #endif /* configAPPLICATION_ALLOCATED_HEAP */ /* 已申请内存的大小 */ static size_t xNextFreeByte = ( size_t ) 0U; void * pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) { void * pvReturn = NULL; static uint8_t * pucAlignedHeap = NULL; /* 若申请的内存非对齐情况下,叠加对齐剩余量向上对齐,例如申请内存为3字节,而最小对齐字节8字节, 则3+(8-(3&7)) 结果为8,则可以理解为不够8的倍数,则以向上对齐到8的倍数来申请内存 */ #if ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT != 1 ) { if( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) { if( ( xWantedSize + ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) ) > xWantedSize ) { xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ); } else { xWantedSize = 0; } } } #endif /* 实际操作内存池时,挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { if( pucAlignedHeap == NULL ) { /* 这里先指向内存池数组[7]的位置,也就是第八个,通过&上掩码 (~0x00000007) 得到八字节对齐, 例如内存池大小定义为0x1001,0x1001&0xFFF8得到0x1000,所以内存池实际起始地址为向下对齐8字节 */ pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) & ucHeap[ portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ] ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) ); } /* 若是已申请的内存 + 此刻需申请的内存在内存池范围内,且未溢出则认为可向内存池申请 */ if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) < configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ) && ( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) > xNextFreeByte ) ) { /* 返回的内存地址为内存池对齐点 叠加 上一次的内存申请的尾部地址,即是返回新内存申请的头部 */ pvReturn = pucAlignedHeap + xNextFreeByte; /* 内存申请成功,累加申请的内存 */ xNextFreeByte += xWantedSize; } traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); } /* 操作完内存池,恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); #if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) { if( pvReturn == NULL ) { /* 内存申请失败的钩子函数 */ vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); } } #endif return pvReturn; } void vPortFree( void * pv ) { /* heap1只申请内存,不进行释放 */ ( void ) pv; configASSERT( pv == NULL ); } void vPortInitialiseBlocks( void ) { /* 内存积累初始为0 */ xNextFreeByte = ( size_t ) 0; } size_t xPortGetFreeHeapSize( void ) { /* 可用内存减去积累内存得到剩余内存 */ return( configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE - xNextFreeByte ); } void vPortHeapResetState( void ) { /* 内存积累初始为0 */ xNextFreeByte = ( size_t ) 0U; }
2. heap_2.c 内存管理
内存管理API : pvPortMalloc(); vPortFree();
内存管理heap2 :heap_2.c源码,截全核心代码,每个细节笔者根据自己理解注解
跳转置顶
-
heap_2.c 内存管理
2.1 :heap_2内存管理图解,基于heap_1内存管理多了链表管理,拆分功能,释放内存功能
2.2 :完整heap_2.c源码解析,这段代码是 FreeRTOS 中 heap_2 内存管理方案的核心实现,它采用一种基于最佳适配算法的动态内存分配与释放策略。其核心机制是维护一个按块大小排序的单向空闲链表,每个空闲块通过 BlockLink_t 结构体(包含块大小和指向下一空闲块的指针)进行管理。在分配时,算法从链表头部开始遍历,寻找第一个大小足够满足请求的空闲块(最佳适配),如果该块剩余空间足够大,则会进行块拆分,将剩余部分作为新空闲块重新插入链表,并使用最高位标记法将已分配块的块大小字段标记为“已分配”。在释放时,通过指针回退找到内存块的头部信息,清除分配标记后,将整个块作为一个新的空闲块重新按大小顺序插入空闲链表。整个分配和释放过程都在挂起调度器的临界区内进行以确保线程安全,并且通过计算剩余总空闲字节数(xFreeBytesRemaining)来快速评估内存池整体使用情况。该方案支持内存的重复利用,适用于存在动态分配和释放、且分配块大小多变的场景,但其不合并相邻空闲块的设计可能导致内存碎片随时间累积。
/* 释放的内存清零 */ #define configHEAP_CLEAR_MEMORY_ON_FREE 0 /* 实际可用内存为总内存池减去对齐字节(8) */ #define configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ( configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE - portBYTE_ALIGNMENT ) /* 头部预留 8个字节 */ #define heapBITS_PER_BYTE ( ( size_t ) 8 ) /* 常量最大值 */ #define heapSIZE_MAX ( ~( ( size_t ) 0 ) ) /*检查乘法结果溢出*/ #define heapMULTIPLY_WILL_OVERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( ( a ) > 0 ) && ( ( b ) > ( heapSIZE_MAX / ( a ) ) ) ) /* 检查加法结果溢出 */ #define heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( a ) > ( heapSIZE_MAX - ( b ) ) ) /* xBlockSize最高位定义为是否已分配 */ #define heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ( ( ( size_t ) 1 ) << ( ( sizeof( size_t ) * heapBITS_PER_BYTE ) - 1 ) ) /* 判断该块是否未分配标记 */ #define heapBLOCK_SIZE_IS_VALID( xBlockSize ) ( ( ( xBlockSize ) & heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) == 0 ) /* 判断该块是否已分配标记 */ #define heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxBlock ) ( ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) & heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) != 0 ) /* 块分配标记 */ #define heapALLOCATE_BLOCK( pxBlock ) ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) |= heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) /* 块取消分配标记 */ #define heapFREE_BLOCK( pxBlock ) ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) &= ~heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ /* 定义内存池 */ #if ( configAPPLICATION_ALLOCATED_HEAP == 1 ) extern uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; #else PRIVILEGED_DATA static uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; #endif /* 块结构, 头部信息 */ typedef struct A_BLOCK_LINK { struct A_BLOCK_LINK * pxNextFreeBlock; /*<< The next free block in the list. */ size_t xBlockSize; /*<< The size of the free block. */ } BlockLink_t; /* 头部信息大小 */ static const size_t xHeapStructSize = ( ( sizeof( BlockLink_t ) + ( size_t ) ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ) ) & ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ); /* 为了进行拆分,因此需要两倍头部大小进行分配 */ #define heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ( ( size_t ) ( xHeapStructSize * 2 ) ) /* 定义内存池内存起始与内存尾部 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static BlockLink_t xStart, xEnd; /* 内存池剩余空间 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xFreeBytesRemaining = configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE; /* 内存池初始化标志位 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static BaseType_t xHeapHasBeenInitialised = pdFALSE; /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ static void prvHeapInit( void ) PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION; /* 定义个迭代器,从内存起始遍历到可用内存大小满足则新块大小,则插入到此节点 */ #define prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( pxBlockToInsert ) { /* 定义迭代器 */ BlockLink_t * pxIterator; size_t xBlockSize; /* 获取插入块的空间大小 */ xBlockSize = pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize; /* 迭代器的下一个块节点遍历到空闲块空间大于插入块空间的块节点,这样相当于块空间大小排序,从内存维度映射到链表空间维度排序 */ for( pxIterator = &xStart; pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->xBlockSize < xBlockSize; pxIterator = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) \ { /* There is nothing to do here - just iterate to the correct position. */ } /* 插入块的下一个块节点指向刚刚遍历到的块节点的下一个节点 */ pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock; /* 基于块节点将链表索引的下一个节点指向为新块 */ pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlockToInsert; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void * pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) { BlockLink_t * pxBlock; BlockLink_t * pxPreviousBlock; BlockLink_t * pxNewBlockLink; void * pvReturn = NULL; size_t xAdditionalRequiredSize; if( xWantedSize > 0 ) { /* 检测申请内存叠加头部信息是否溢出 */ if( heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( xWantedSize, xHeapStructSize ) == 0 ) { /*申请的内存叠加头部信息大小*/ xWantedSize += xHeapStructSize; /* 这里与heap1一样,内存向上8字节倍数对齐 */ if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0x00 ) { xAdditionalRequiredSize = portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); if( heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( xWantedSize, xAdditionalRequiredSize ) == 0 ) { xWantedSize += xAdditionalRequiredSize; } else { xWantedSize = 0; } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { xWantedSize = 0; } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* 挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { if( xHeapHasBeenInitialised == pdFALSE ) { /* 首次申请内存,则初始化内存池 */ prvHeapInit(); xHeapHasBeenInitialised = pdTRUE; } /* 检查申请的内存块是否已分配 */ if( heapBLOCK_SIZE_IS_VALID( xWantedSize ) != 0 ) { /* 若容量足够,则可继续申请 */ if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize <= xFreeBytesRemaining ) ) { /* 设定块节点指向 */ pxPreviousBlock = &xStart; pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock; /* 从start节点的下一块节点开始遍历链表,寻找空间足够的块,End节点为NULL */ while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != NULL ) ) { pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock; pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; } /* 遍历到尾部节点则认为无空间申请 */ if( pxBlock != &xEnd ) { /* 申请内存的节点指向刚刚遍历到的块节点+头部信息大小后的地址 */ pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + xHeapStructSize ); /* 此时该块当作已分配,因此链表中基于此块索引改变链表链接到下一个节点 */ pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; /* 申请的块空间减去所需若有两倍头部信息以上,则把该块进行拆分 */ if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ) { /* 分出一个新块指向新分配块之后 */ pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize ); /* 设定新块的空间为之前可分配块的剩余空间 */ pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize; /* 申请块的空间大小为分配的空间大小 */ pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize; /* 将新快插入到内存池链表中 */ prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( pxNewBlockLink ) ); } /* 更新内存池剩余空间 */ xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize; heapALLOCATE_BLOCK( pxBlock ); /* 若该块已分配,则该块断开链表联系,下一个块节点设为NULL */ pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; } } } traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); } /* 恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); #if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) { if( pvReturn == NULL ) { vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); } } #endif return pvReturn; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortFree( void * pv ) { uint8_t * puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv; BlockLink_t * pxLink; if( pv != NULL ) { /* 基于待释放空间索引到头部 */ puc -= xHeapStructSize; /* 指向待释放空间的头部 */ pxLink = ( void * ) puc; configASSERT( heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxLink ) != 0 ); configASSERT( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ); /* 若是该块有已分配标记则进如释放流程 */ if( heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxLink ) != 0 ) { /* 分配过的块指向的下一个节点为NULL,符合已分配逻辑,继续进行释放 */ if( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ) { /* 将头部信息的xBlockSize的最高位清除,标记为待分配状态 */ heapFREE_BLOCK( pxLink ); #if ( configHEAP_CLEAR_MEMORY_ON_FREE == 1 ) { /* 将释放块的空间全部初始为0x00 */ ( void ) memset( puc + xHeapStructSize, 0, pxLink->xBlockSize - xHeapStructSize ); } #endif /* 挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* 将释放的块插入回链表中 */ prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) ); /* 更新剩余空间 */ xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize; traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize ); } /* 恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } } } } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ size_t xPortGetFreeHeapSize( void ) { return xFreeBytesRemaining; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortInitialiseBlocks( void ) { /* This just exists to keep the linker quiet. */ } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ /* Calloc申请空间,并数据初始为0x00 */ void * pvPortCalloc( size_t xNum, size_t xSize ) { void * pv = NULL; /* 检查乘法是否溢出 */ if( heapMULTIPLY_WILL_OVERFLOW( xNum, xSize ) == 0 ) { pv = pvPortMalloc( xNum * xSize ); if( pv != NULL ) { ( void ) memset( pv, 0, xNum * xSize ); } } return pv; } static void prvHeapInit( void ) /* PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION */ { /*定义块节点*/ BlockLink_t * pxFirstFreeBlock; uint8_t * pucAlignedHeap; /* 指向内存池(本身索引就是第8个字节的下标),然后向下对齐8字节的地址 */ pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) & ucHeap[ portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ] ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) ); /* 初始内存池start的下一个节点指向内存对齐后的内存池,xStart与End为全局变量节点 */ xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap; /* xStart块节点空间大小为0x00 */ xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0; /* 尾部块节点的初始大小为最大对齐上限大小 */ xEnd.xBlockSize = configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE; /* 尾部块节点不存在下一个节点 */ xEnd.pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; /* 指向内存池对齐地址 */ pxFirstFreeBlock = ( BlockLink_t * ) pucAlignedHeap; /* 基于索引调整大小为最大对齐上限大小,初始后为一整块内存大小 */ pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize = configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE; /* 链接尾部块节点,形成xStart块节点→内存池→End块节点 */ pxFirstFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = &xEnd; }
3. heap_3.c 内存管理
内存管理API : pvPortMalloc(); vPortFree();
内存管理heap3 :heap_3.c源码,截全核心代码,每个细节笔者根据自己理解注解
跳转置顶
-
heap_3.c 内存管理
3.1 :heap_3内存管理图解,间接调用平台的malloc与free接口
3.2 :完整heap_3.c源码解析,这段代码是FreeRTOS中heap_3内存管理方案的核心实现,其本质是对标准C库的malloc()和free()进行了一层轻量级的线程安全封装。该方案自身并不实现独立的内存管理算法,其核心机制是在调用底层malloc/free前后,通过vTaskSuspendAll()和xTaskResumeAll()挂起和恢复任务调度器,以创建一个临时的临界区,从而确保在多任务环境中,对标准库内存管理函数的并发访问是安全的。它完全依赖宿主机操作系统或嵌入式平台C运行库提供的内存管理能力,因此其特性(如碎片处理、分配效率)和行为(如分配失败处理)均由底层库决定。此方案适用于已经具备完整、可靠的标准库内存管理支持的系统(如运行在Linux或Windows上的FreeRTOS移植版本,或某些自带动态内存管理功能的嵌入式平台),使得FreeRTOS能够以最小的开销直接利用系统级的内存资源,但牺牲了在裸机或无库环境下的确定性与可移植性。
void * pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) { void * pvReturn; /* 挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* 调用平台malloc接口 */ pvReturn = malloc( xWantedSize ); traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); } /* 恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); #if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) { if( pvReturn == NULL ) { vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); } } #endif return pvReturn; } void vPortFree( void * pv ) { if( pv != NULL ) { /* 挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* 调用平台free接口 */ free( pv ); traceFREE( pv, 0 ); } /* 恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } } void vPortHeapResetState( void ) { }
4. heap_4.c 内存管理
内存管理API : pvPortMalloc(); vPortFree();
内存管理heap4 :heap_4.c源码,截全核心代码,每个细节笔者根据自己理解注解
跳转置顶
-
heap_4.c 内存管理
4.1 :heap_4内存管理图解,heap_4基于heap_2增加了释放合并功能,其余一致

4.2 :完整heap_4.c源码解析,这段代码是FreeRTOS中 heap_4内存管理方案 的核心实现,它基于heap_2的“最佳适配”算法进行了关键性增强,通过引入 “相邻空闲块合并”机制 来有效缓解和消除内存碎片。其核心工作流程与heap_2相似,同样在挂起调度器的临界区内,维护一个按地址(而非heap_2的大小)排序的单向空闲链表,并使用块头部的最高位标记分配状态。最核心的改进在于释放内存时:当调用 vPortFree 后,prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList 函数不仅将释放的块按地址顺序插回链表,还会立即检查并向前或向后合并物理地址相邻的空闲块,将它们融合为单个更大的空闲块,从而有效减少外部碎片。此外,该方案内置了详细的堆状态统计功能(如历史最小空闲内存、分配/释放次数),并通过可选的 heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER 机制(利用异或操作的“金丝雀值”)来保护链表指针的完整性,防止因内存越界写导致的链表损坏。heap_4因此成为FreeRTOS中最通用、最可靠的内存管理方案,特别适合需要长时间运行、且存在频繁且不可预测的内存分配与释放场景的嵌入式应用。
/* 释放的内存清零 */ #define configHEAP_CLEAR_MEMORY_ON_FREE 0 /* 为了进行拆分,因此需要两倍头部大小进行分配 */ #define heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ( ( size_t ) ( xHeapStructSize << 1 ) ) /* 头部预留 8个字节 */ #define heapBITS_PER_BYTE ( ( size_t ) 8 ) /* 常量最大值 */ #define heapSIZE_MAX ( ~( ( size_t ) 0 ) ) /*检查乘法结果溢出*/ #define heapMULTIPLY_WILL_OVERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( ( a ) > 0 ) && ( ( b ) > ( heapSIZE_MAX / ( a ) ) ) ) /* 检查加法结果溢出 */ #define heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( a ) > ( heapSIZE_MAX - ( b ) ) ) /* 获取比较结果 */ #define heapSUBTRACT_WILL_UNDERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( a ) < ( b ) ) /* xBlockSize最高位定义为是否已分配 */ #define heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ( ( ( size_t ) 1 ) << ( ( sizeof( size_t ) * heapBITS_PER_BYTE ) - 1 ) ) /* 判断该块是否未分配标记 */ #define heapBLOCK_SIZE_IS_VALID( xBlockSize ) ( ( ( xBlockSize ) & heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) == 0 ) /* 判断该块是否已分配标记 */ #define heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxBlock ) ( ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) & heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) != 0 ) /* 块分配标记 */ #define heapALLOCATE_BLOCK( pxBlock ) ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) |= heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) /* 块取消分配标记 */ #define heapFREE_BLOCK( pxBlock ) ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) &= ~heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) /* 定义内存池 */ #if ( configAPPLICATION_ALLOCATED_HEAP == 1 ) extern uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; #else PRIVILEGED_DATA static uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; #endif /* 块结构, 头部信息 */ typedef struct A_BLOCK_LINK { struct A_BLOCK_LINK * pxNextFreeBlock; /**< The next free block in the list. */ size_t xBlockSize; /**< The size of the free block. */ } BlockLink_t; /* Canary金丝雀随机值,通过A ^ B = C; A ^ C = B, 对内存池进行溢出攻击保护 */ #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) extern void vApplicationGetRandomHeapCanary( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE * pxHeapCanary ); PRIVILEGED_DATA static portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE xHeapCanary; #define heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ) ( ( BlockLink_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) ( pxBlock ) ) ^ xHeapCanary ) ) #else #define heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ) ( pxBlock ) #endif /* 调试地址 */ #define heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ) \ configASSERT( ( ( uint8_t * ) ( pxBlock ) >= &( ucHeap[ 0 ] ) ) && \ ( ( uint8_t * ) ( pxBlock ) <= &( ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE - 1 ] ) ) ) static void prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( BlockLink_t * pxBlockToInsert ) PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION; static void prvHeapInit( void ) PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION; /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ /* 头部信息大小 */ static const size_t xHeapStructSize = ( sizeof( BlockLink_t ) + ( ( size_t ) ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ) ) ) & ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); /* 定义内存池内存起始与内存尾部,尾部为指针 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static BlockLink_t xStart; PRIVILEGED_DATA static BlockLink_t * pxEnd = NULL; /* 内存池剩余空间大小 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; /* 历史最小空间信息 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; /* 成功分配内存次数 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = ( size_t ) 0U; /* 成功释放内存次数 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = ( size_t ) 0U; /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void * pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) { BlockLink_t * pxBlock; BlockLink_t * pxPreviousBlock; BlockLink_t * pxNewBlockLink; void * pvReturn = NULL; size_t xAdditionalRequiredSize; if( xWantedSize > 0 ) { /* 检测申请内存叠加头部信息是否溢出 */ if( heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( xWantedSize, xHeapStructSize ) == 0 ) { /*申请的内存叠加头部信息大小*/ xWantedSize += xHeapStructSize; /* 这里与heap1一样,内存向上8字节倍数对齐,细节可以回看heap1 */ if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0x00 ) { xAdditionalRequiredSize = portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); if( heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( xWantedSize, xAdditionalRequiredSize ) == 0 ) { xWantedSize += xAdditionalRequiredSize; } else { xWantedSize = 0; } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { xWantedSize = 0; } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* 挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { if( pxEnd == NULL ) { /* pxEnd未指向,则进行内存池初始化 */ prvHeapInit(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* 检查申请的内存块是否已分配 */ if( heapBLOCK_SIZE_IS_VALID( xWantedSize ) != 0 ) { /* 若容量足够,则可继续申请 */ if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize <= xFreeBytesRemaining ) ) { /* 设定块节点指向 */ pxPreviousBlock = &xStart; pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( xStart.pxNextFreeBlock ); heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ); /* 从start节点的下一块节点开始遍历链表,寻找空间足够的块,End节点为NULL */ while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( NULL ) ) ) { pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock; pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ); heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ); } /* 遍历到尾部节点则认为无空间申请 */ if( pxBlock != pxEnd ) { /* 申请内存的节点指向刚刚遍历到的块节点+头部信息大小后的地址 */ pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) ) + xHeapStructSize ); heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pvReturn ); /* 此时该块当作已分配,因此链表中基于此块索引改变链表链接到下一个节点 */ pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; configASSERT( heapSUBTRACT_WILL_UNDERFLOW( pxBlock->xBlockSize, xWantedSize ) == 0 ); /* 申请的块空间减去所需若有两倍头部信息以上,则把该块进行拆分,充足说明至少分配一个头部信息且带8字节块大小剩余空间 */ if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ) { /* 分出一个新块指向新分配块之后 */ pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize ); configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pxNewBlockLink ) & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 ); /* 设定新块的空间为之前可分配块的剩余空间 */ pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize; /* 申请块的空间大小为分配的空间大小 */ pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize; /* 将新快插入到内存池链表中,此处与heap2有区别,heap2会进行一次剩余空间大小排序, 而因为heap4带合并功能,因此不需要剩余空间插入排序 */ pxNewBlockLink->pxNextFreeBlock = pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxNewBlockLink ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* 更新内存池剩余空间 */ xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize; /* 记录内存池剩余空间历史最小值,即使剩余1K,也只是各节点加起来1K,不代表可以分配连续1K内存 */ if( xFreeBytesRemaining < xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining ) { xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xFreeBytesRemaining; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } heapALLOCATE_BLOCK( pxBlock ); /* 若该块已分配,则该块断开链表联系,下一个块节点设为NULL */ pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; /* 记录成功分配次数 */ xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations++; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); } /* 恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); #if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) { if( pvReturn == NULL ) { vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) */ configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pvReturn ) & ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 ); return pvReturn; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortFree( void * pv ) { uint8_t * puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv; BlockLink_t * pxLink; if( pv != NULL ) { /* 基于待释放空间索引到头部 */ puc -= xHeapStructSize; /* 指向待释放空间的头部 */ pxLink = ( void * ) puc; heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxLink ); configASSERT( heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxLink ) != 0 ); configASSERT( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ); /* 若是该块有已分配标记则进如释放流程 */ if( heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxLink ) != 0 ) { /* 分配过的块指向的下一个节点为NULL,符合已分配逻辑,继续进行释放 */ if( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ) { /* 将头部信息的xBlockSize的最高位清除,标记为待分配状态 */ heapFREE_BLOCK( pxLink ); #if ( configHEAP_CLEAR_MEMORY_ON_FREE == 1 ) { if( heapSUBTRACT_WILL_UNDERFLOW( pxLink->xBlockSize, xHeapStructSize ) == 0 ) { /* 将释放块的空间全部初始为0x00 */ ( void ) memset( puc + xHeapStructSize, 0, pxLink->xBlockSize - xHeapStructSize ); } } #endif /* 挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* 更新剩余空间 */ xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize; traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize ); /* 将释放的块插入回链表中,此处接口实现与heap2不同,heap4此处实现带有合并功能 */ prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) ); xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees++; } /* 恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ size_t xPortGetFreeHeapSize( void ) { /* 返回内存池剩余空间 */ return xFreeBytesRemaining; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ size_t xPortGetMinimumEverFreeHeapSize( void ) { /* 返回内存池剩余空间历史最小值 */ return xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortInitialiseBlocks( void ) { } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ /* Calloc申请空间,并数据初始为0x00 */ void * pvPortCalloc( size_t xNum, size_t xSize ) { void * pv = NULL; if( heapMULTIPLY_WILL_OVERFLOW( xNum, xSize ) == 0 ) { pv = pvPortMalloc( xNum * xSize ); if( pv != NULL ) { ( void ) memset( pv, 0, xNum * xSize ); } } return pv; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ static void prvHeapInit( void ) /* PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION */ { /*定义块节点*/ BlockLink_t * pxFirstFreeBlock; portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE uxStartAddress, uxEndAddress; size_t xTotalHeapSize = configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE; /* 指向内存池首地址 */ uxStartAddress = ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) ucHeap; /* 指向内存池(本身索引就是第8个字节的下标),然后向下对齐8字节的地址 */ if( ( uxStartAddress & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 ) { uxStartAddress += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ); uxStartAddress &= ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); xTotalHeapSize -= ( size_t ) ( uxStartAddress - ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) ucHeap ); } #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) { /* 实现一个随机值作为基值设定进行保护 */ vApplicationGetRandomHeapCanary( &( xHeapCanary ) ); } #endif /* 初始内存池start的下一个节点指向内存对齐后的内存池,xStart为全局变量节点 */ xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( void * ) heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( uxStartAddress ); /* xStart块节点空间大小为0x00 */ xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0; /* 尾部块地址初始为起始节点叠加内存池总大小后,从最后往前偏移一个头部信息作为尾部块地址,且进行内存对齐 */ uxEndAddress = uxStartAddress + ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) xTotalHeapSize; uxEndAddress -= ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) xHeapStructSize; uxEndAddress &= ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); /* 尾部块节点指向刚刚计算后的尾部块地址 */ pxEnd = ( BlockLink_t * ) uxEndAddress; /* 尾部块节点空间大小设0x00 */ pxEnd->xBlockSize = 0; /* 尾部块节点不存在下一个节点 */ pxEnd->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( NULL ); /* 指向内存池对齐地址 */ pxFirstFreeBlock = ( BlockLink_t * ) uxStartAddress; /* 基于索引调整大小尾部节点减去起始头部后地址得到总空间,初始后为一整块内存大小 */ pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize = ( size_t ) ( uxEndAddress - ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) pxFirstFreeBlock ); /* 链接尾部块节点,形成xStart块节点→内存池→End块节点 */ pxFirstFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxEnd ); /* 初始历史剩余空间最小值 */ xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize; /* 初始内存池剩余空间 */ xFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ static void prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( BlockLink_t * pxBlockToInsert ) /* PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION */ { /* 定义迭代器 */ BlockLink_t * pxIterator; uint8_t * puc; /* 迭代器的下一个块节点遍历到待分配块节点之前 */ for( pxIterator = &xStart; heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) < pxBlockToInsert; pxIterator = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) ) { } /* 迭代位置不在起始处 */ if( pxIterator != &xStart ) { heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator ); } /* 获取迭代处地址 */ puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator; /* 如果插入节点的前一个节点和插入节点是相邻的,则向前合并成一块连续内存空间的块节点,此情况链表不需要重新改变链接关联指向 */ if( ( puc + pxIterator->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert ) { pxIterator->xBlockSize += pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize; pxBlockToInsert = pxIterator; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* 获取插入块节点地址 */ puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert; /* 如果插入节点的相邻下个节点是待分配的连续内存,则向后合并成一块连续内存空间的块节点,此时需重新改变链表的双向关联指向 */ if( ( puc + pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) ) { /* 向后合并的前提是相邻下一个节点并不是End节点 */ if( heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) != pxEnd ) { /* Form one big block from the two blocks. */ pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize += heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock )->xBlockSize; pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock )->pxNextFreeBlock; } else { /* 否则插入块节点指向End节点 */ pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxEnd ); } } else { /* 插入块节点指向链表中的迭代地址的下一个节点 */ pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock; } /* 非向前合并的情况下,如正常释放,或向后合并需要重新指向链表的关联指向,这里是链表的上一个节点重新指向为新节点 */ if( pxIterator != pxBlockToInsert ) { pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlockToInsert ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortGetHeapStats( HeapStats_t * pxHeapStats ) { BlockLink_t * pxBlock; size_t xBlocks = 0, xMaxSize = 0, xMinSize = portMAX_DELAY; /* 挂起调度器 */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* 获取内存池起始块节点 */ pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( xStart.pxNextFreeBlock ); /* 遍历得到整块内存池节点的最大/最小待分配的空间 */ if( pxBlock != NULL ) { while( pxBlock != pxEnd ) { /* 记录有多少个待分配节点 */ xBlocks++; if( pxBlock->xBlockSize > xMaxSize ) { xMaxSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize; } if( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xMinSize ) { xMinSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize; } pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ); } } } /* 恢复调度器 */ ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); /* 传入索引 */ pxHeapStats->xSizeOfLargestFreeBlockInBytes = xMaxSize; pxHeapStats->xSizeOfSmallestFreeBlockInBytes = xMinSize; pxHeapStats->xNumberOfFreeBlocks = xBlocks; /* 进入临界区 */ taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { /* 内存池剩余空间 */ pxHeapStats->xAvailableHeapSpaceInBytes = xFreeBytesRemaining; /* 成功分配的次数 */ pxHeapStats->xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations; /* 成功释放的次数 */ pxHeapStats->xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees; /* 内存池剩余空间历史最小值 */ pxHeapStats->xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining; } /* 退出临界区 */ taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortHeapResetState( void ) { /* 初始尾部节点 */ pxEnd = NULL; /* 复位记录数据 */ xFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = ( size_t ) 0U; xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = ( size_t ) 0U; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
5. heap_5.c 内存管理
内存管理API : pvPortMalloc(); vPortFree();
内存管理heap5 :heap_5.c源码,截全核心代码,每个细节笔者根据自己理解注解
跳转置顶
-
heap_5.c 内存管理
5.1 :heap_5内存管理图解,与heap4内存管理一致,增加多段内存区管理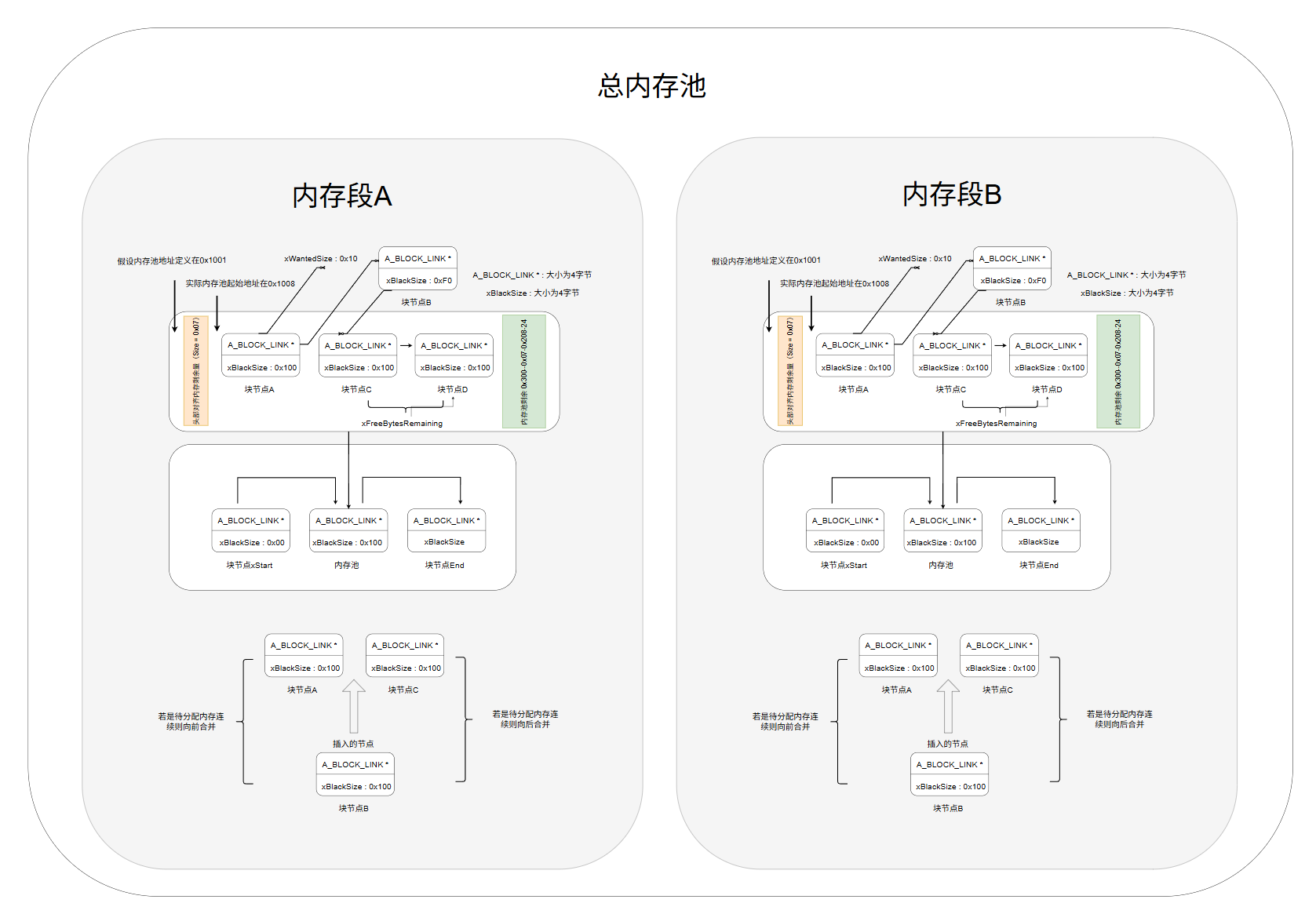
5.2 :完整heap_5.c源码解析,这段代码是FreeRTOS中 heap_5内存管理方案的核心实现,它基于heap_4的“合并式最佳适配”算法进行了关键性扩展,使其能够管理多个物理上非连续的内存区域。其最核心的机制是通过用户提供的 HeapRegion_t 结构体数组,在系统启动时调用 vPortDefineHeapRegions() 函数,将分散的、独立的物理内存块(如片上SRAM、外部SDRAM)初始化并链接成一个逻辑上统一、按地址排序的单向空闲链表。之后,其分配、释放、合并及统计机制与heap_4完全相同,在临界区内执行,并有效合并相邻空闲块以对抗碎片。因此,heap_5是功能最强大的FreeRTOS内存管理器,它既继承了heap_4的抗碎片能力和丰富统计特性,又提供了管理复杂、非连续物理内存布局的灵活性,是使用外部存储器或拥有多块内存的复杂嵌入式系统的理想选择。
/* 定义分区结构体 */ typedef struct HeapRegion { uint8_t *pucStartAddress; << Start address of a block of memory that will be part of the heap. size_t xSizeInBytes; << Size of the block of memory. } HeapRegion_t; /* 定义各分区指向地址,空间大小 */ HeapRegion_t xHeapRegions[] = { { ( uint8_t * ) 0x20000000UL, 0x10000 }, << Defines a block of 0x10000 bytes starting at address 0x80000000 { ( uint8_t * ) 0xC0000000UL, 0xa0000 }, << Defines a block of 0xa0000 bytes starting at address of 0x90000000 { NULL, 0 } << Terminates the array. }; /* 释放的内存清零 */ #define configHEAP_CLEAR_MEMORY_ON_FREE 0 /* 为了进行拆分,因此需要两倍头部大小进行分配 */ #define heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ( ( size_t ) ( xHeapStructSize << 1 ) ) /* 头部预留 8个字节 */ #define heapBITS_PER_BYTE ( ( size_t ) 8 ) /* 常量最大值 */ #define heapSIZE_MAX ( ~( ( size_t ) 0 ) ) /*检查乘法结果溢出*/ #define heapMULTIPLY_WILL_OVERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( ( a ) > 0 ) && ( ( b ) > ( heapSIZE_MAX / ( a ) ) ) ) /* 检查加法结果溢出 */ #define heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( a ) > ( heapSIZE_MAX - ( b ) ) ) /* 获取比较结果 */ #define heapSUBTRACT_WILL_UNDERFLOW( a, b ) ( ( a ) < ( b ) ) /* xBlockSize最高位定义为是否已分配 */ #define heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ( ( ( size_t ) 1 ) << ( ( sizeof( size_t ) * heapBITS_PER_BYTE ) - 1 ) ) /* 判断该块是否未分配标记 */ #define heapBLOCK_SIZE_IS_VALID( xBlockSize ) ( ( ( xBlockSize ) & heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) == 0 ) /* 判断该块是否已分配标记 */ #define heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxBlock ) ( ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) & heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) != 0 ) /* 块分配标记 */ #define heapALLOCATE_BLOCK( pxBlock ) ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) |= heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) /* 块取消分配标记 */ #define heapFREE_BLOCK( pxBlock ) ( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize ) &= ~heapBLOCK_ALLOCATED_BITMASK ) /* Canary金丝雀随机值,通过A ^ B = C; A ^ C = B, 对内存池进行溢出攻击保护 */ #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) #define heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ) ( ( BlockLink_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) ( pxBlock ) ) ^ xHeapCanary ) ) #define heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ) \ configASSERT( ( pucHeapHighAddress != NULL ) && \ ( pucHeapLowAddress != NULL ) && \ ( ( uint8_t * ) ( pxBlock ) >= pucHeapLowAddress ) && \ ( ( uint8_t * ) ( pxBlock ) < pucHeapHighAddress ) ) #else #define heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ) ( pxBlock ) #define heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ) #endif /* 块结构, 头部信息 */ typedef struct A_BLOCK_LINK { struct A_BLOCK_LINK * pxNextFreeBlock; /**< The next free block in the list. */ size_t xBlockSize; /**< The size of the free block. */ } BlockLink_t; /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ static void prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( BlockLink_t * pxBlockToInsert ) PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION; void vPortDefineHeapRegions( const HeapRegion_t * const pxHeapRegions ) PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION; #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) extern void vApplicationGetRandomHeapCanary( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE * pxHeapCanary ); #endif /* configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR */ /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ /* 头部信息大小 */ static const size_t xHeapStructSize = ( sizeof( BlockLink_t ) + ( ( size_t ) ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ) ) ) & ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); /* 定义内存池内存起始与内存尾部,尾部为指针 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static BlockLink_t xStart; PRIVILEGED_DATA static BlockLink_t * pxEnd = NULL; /* 内存池剩余空间大小 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; /* 历史最小空间信息 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; /* 成功分配内存次数 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = ( size_t ) 0U; /* 成功释放内存次数 */ PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = ( size_t ) 0U; #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) PRIVILEGED_DATA static portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE xHeapCanary; PRIVILEGED_DATA static uint8_t * pucHeapHighAddress = NULL; PRIVILEGED_DATA static uint8_t * pucHeapLowAddress = NULL; #endif /* configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR */ /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void * pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) { BlockLink_t * pxBlock; BlockLink_t * pxPreviousBlock; BlockLink_t * pxNewBlockLink; void * pvReturn = NULL; size_t xAdditionalRequiredSize; /* The heap must be initialised before the first call to * pvPortMalloc(). */ configASSERT( pxEnd ); if( xWantedSize > 0 ) { if( heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( xWantedSize, xHeapStructSize ) == 0 ) { xWantedSize += xHeapStructSize; if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0x00 ) { xAdditionalRequiredSize = portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); if( heapADD_WILL_OVERFLOW( xWantedSize, xAdditionalRequiredSize ) == 0 ) { xWantedSize += xAdditionalRequiredSize; } else { xWantedSize = 0; } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { xWantedSize = 0; } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } vTaskSuspendAll(); { if( heapBLOCK_SIZE_IS_VALID( xWantedSize ) != 0 ) { if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize <= xFreeBytesRemaining ) ) { pxPreviousBlock = &xStart; pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( xStart.pxNextFreeBlock ); heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ); while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( NULL ) ) ) { pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock; pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ); heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock ); } if( pxBlock != pxEnd ) { pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) ) + xHeapStructSize ); heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pvReturn ); pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; configASSERT( heapSUBTRACT_WILL_UNDERFLOW( pxBlock->xBlockSize, xWantedSize ) == 0 ); if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ) { pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize ); configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pxNewBlockLink ) & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 ); pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize; pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize; pxNewBlockLink->pxNextFreeBlock = pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxNewBlockLink ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize; if( xFreeBytesRemaining < xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining ) { xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xFreeBytesRemaining; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } heapALLOCATE_BLOCK( pxBlock ); pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations++; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); } ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); #if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) { if( pvReturn == NULL ) { vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) */ configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pvReturn ) & ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 ); return pvReturn; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortFree( void * pv ) { uint8_t * puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv; BlockLink_t * pxLink; if( pv != NULL ) { puc -= xHeapStructSize; pxLink = ( void * ) puc; heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxLink ); configASSERT( heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxLink ) != 0 ); configASSERT( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ); if( heapBLOCK_IS_ALLOCATED( pxLink ) != 0 ) { if( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ) { heapFREE_BLOCK( pxLink ); #if ( configHEAP_CLEAR_MEMORY_ON_FREE == 1 ) { if( heapSUBTRACT_WILL_UNDERFLOW( pxLink->xBlockSize, xHeapStructSize ) == 0 ) { ( void ) memset( puc + xHeapStructSize, 0, pxLink->xBlockSize - xHeapStructSize ); } } #endif vTaskSuspendAll(); { xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize; traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize ); prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) ); xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees++; } ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ size_t xPortGetFreeHeapSize( void ) { return xFreeBytesRemaining; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ size_t xPortGetMinimumEverFreeHeapSize( void ) { return xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void * pvPortCalloc( size_t xNum, size_t xSize ) { void * pv = NULL; if( heapMULTIPLY_WILL_OVERFLOW( xNum, xSize ) == 0 ) { pv = pvPortMalloc( xNum * xSize ); if( pv != NULL ) { ( void ) memset( pv, 0, xNum * xSize ); } } return pv; } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ static void prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( BlockLink_t * pxBlockToInsert ) /* PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION */ { BlockLink_t * pxIterator; uint8_t * puc; for( pxIterator = &xStart; heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) < pxBlockToInsert; pxIterator = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) ) { /* Nothing to do here, just iterate to the right position. */ } if( pxIterator != &xStart ) { heapVALIDATE_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator ); } puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator; if( ( puc + pxIterator->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert ) { pxIterator->xBlockSize += pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize; pxBlockToInsert = pxIterator; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert; if( ( puc + pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) ) { if( heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) != pxEnd ) { /* Form one big block from the two blocks. */ pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize += heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock )->xBlockSize; pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock )->pxNextFreeBlock; } else { pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxEnd ); } } else { pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock; } if( pxIterator != pxBlockToInsert ) { pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlockToInsert ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ /* 与heap4的核心差异点 */ void vPortDefineHeapRegions( const HeapRegion_t * const pxHeapRegions ) /* PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION */ { /* 定义节点指向 */ BlockLink_t * pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion = NULL; BlockLink_t * pxPreviousFreeBlock; portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE xAlignedHeap; size_t xTotalRegionSize, xTotalHeapSize = 0; BaseType_t xDefinedRegions = 0; portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE xAddress; const HeapRegion_t * pxHeapRegion; /* Can only call once! */ configASSERT( pxEnd == NULL ); /* 实现一个随机值作为基值设定进行保护 */ #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) { vApplicationGetRandomHeapCanary( &( xHeapCanary ) ); } #endif /* 指向第一个内存区 */ pxHeapRegion = &( pxHeapRegions[ xDefinedRegions ] ); /* 按定义的内存区遍历到尾部内存区{ NULL, 0 } */ while( pxHeapRegion->xSizeInBytes > 0 ) { /* 获取当前内存区空间大小 */ xTotalRegionSize = pxHeapRegion->xSizeInBytes; /* 获取当前内存区地址 */ xAddress = ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) pxHeapRegion->pucStartAddress; /* 对当前内存区地址内存对齐8字节 */ if( ( xAddress & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 ) { xAddress += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ); xAddress &= ~( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK; /* Adjust the size for the bytes lost to alignment. */ xTotalRegionSize -= ( size_t ) ( xAddress - ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) pxHeapRegion->pucStartAddress ); } /* 得到对齐地址 */ xAlignedHeap = xAddress; /* 若是首个内存段初始,则初始xStart指向该内存段 */ if( xDefinedRegions == 0 ) { xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( BlockLink_t * ) heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( xAlignedHeap ); xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0; } else { /* Should only get here if one region has already been added to the * heap. */ configASSERT( pxEnd != heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( NULL ) ); /* Check blocks are passed in with increasing start addresses. */ configASSERT( ( size_t ) xAddress > ( size_t ) pxEnd ); } /* 记录总内存池中有效内存段对齐的最低地址 */ #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) { if( ( pucHeapLowAddress == NULL ) || ( ( uint8_t * ) xAlignedHeap < pucHeapLowAddress ) ) { pucHeapLowAddress = ( uint8_t * ) xAlignedHeap; } } #endif /* configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR */ /* 先指向尾部节点 */ pxPreviousFreeBlock = pxEnd; /* 复用xAddress得到内存段的尾部地址且进行内存对齐 */ xAddress = xAlignedHeap + ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) xTotalRegionSize; xAddress -= ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) xHeapStructSize; xAddress &= ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); /* 设置内存池尾部节点,若多次遍历,则是多次更新End节点位置 */ pxEnd = ( BlockLink_t * ) xAddress; pxEnd->xBlockSize = 0; pxEnd->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( NULL ); /* 利用pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion基于xAlignedHeap索引设置内存段的有效节点空间大小,链接尾部节点 */ pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion = ( BlockLink_t * ) xAlignedHeap; pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->xBlockSize = ( size_t ) ( xAddress - ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion ); pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxEnd ); /* 这里是heap5全文核心,若是首次为NULL,则与heap4一样, 若是多次遍历则把上个内存段区的End地址的下个节点指向下一个内存段的第一个待分配内存段 */ if( pxPreviousFreeBlock != NULL ) { pxPreviousFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion ); } /* 累积总内存段空间大小 */ xTotalHeapSize += pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->xBlockSize; #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) { if( ( pucHeapHighAddress == NULL ) || ( ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion ) + pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->xBlockSize ) > pucHeapHighAddress ) ) { pucHeapHighAddress = ( ( uint8_t * ) pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion ) + pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->xBlockSize; } } #endif /* Move onto the next HeapRegion_t structure. */ /* 遍历下一个内存段 */ xDefinedRegions++; pxHeapRegion = &( pxHeapRegions[ xDefinedRegions ] ); } xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xTotalHeapSize; xFreeBytesRemaining = xTotalHeapSize; /* Check something was actually defined before it is accessed. */ configASSERT( xTotalHeapSize ); } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortGetHeapStats( HeapStats_t * pxHeapStats ) { BlockLink_t * pxBlock; size_t xBlocks = 0, xMaxSize = 0, xMinSize = portMAX_DELAY; /* portMAX_DELAY used as a portable way of getting the maximum value. */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( xStart.pxNextFreeBlock ); if( pxBlock != NULL ) { while( pxBlock != pxEnd ) { xBlocks++; if( pxBlock->xBlockSize > xMaxSize ) { xMaxSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize; } if( pxBlock->xBlockSize != 0 ) { if( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xMinSize ) { xMinSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize; } } pxBlock = heapPROTECT_BLOCK_POINTER( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ); } } } ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); pxHeapStats->xSizeOfLargestFreeBlockInBytes = xMaxSize; pxHeapStats->xSizeOfSmallestFreeBlockInBytes = xMinSize; pxHeapStats->xNumberOfFreeBlocks = xBlocks; taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { pxHeapStats->xAvailableHeapSpaceInBytes = xFreeBytesRemaining; pxHeapStats->xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations; pxHeapStats->xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees; pxHeapStats->xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining; } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/ void vPortHeapResetState( void ) { pxEnd = NULL; xFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = ( size_t ) 0U; xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = ( size_t ) 0U; xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = ( size_t ) 0U; #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) pucHeapHighAddress = NULL; pucHeapLowAddress = NULL; #endif /* #if ( configENABLE_HEAP_PROTECTOR == 1 ) */ } /*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
五. 源码 : 数据结构
1. TCB任务控制块结构
-
TCB任务控制块结构
1.1 :TCB任务控制块重点是 xStateListItem 和 xEventListItem 链表项,FreeRTOS的调度逻辑是依靠就绪链表,阻塞链表,挂起链表等组合形成闭环调度逻辑,每个任务有独立的TCB任务控制块,而每个TCB任务控制块都有唯一的 xState/xEvent 链表项,那么只需要把TCB任务控制块的链表项插入链表中,即可基于链表管理每个任务
1.2 :另外FreeRTOS核心意义是实时,因此TCB中的uxPriority决定着任务在就绪链表中的地位,值越高地位越高,内核调度时抢占优先级越高
1.3 :TCB中的 pxStack 指向创建任务时动态分配申请的空间,每个任务的栈都是独立的,因此留意任务需要的栈大小
1.4 :TCB第一个成员是栈顶,指向的位置是任务栈尾部核心寄存器压栈完的地址(从高到低),基于栈顶可在切换任务时恢复任务状态,也是FreeRTOS调度的核心逻辑typedef struct tskTaskControlBlock /* The old naming convention is used to prevent breaking kernel aware debuggers. */ { volatile StackType_t * pxTopOfStack; /**< Points to the location of the last item placed on the tasks stack. THIS MUST BE THE FIRST MEMBER OF THE TCB STRUCT. */ #if ( portUSING_MPU_WRAPPERS == 1 ) xMPU_SETTINGS xMPUSettings; /**< The MPU settings are defined as part of the port layer. THIS MUST BE THE SECOND MEMBER OF THE TCB STRUCT. */ #endif #if ( configUSE_CORE_AFFINITY == 1 ) && ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) UBaseType_t uxCoreAffinityMask; /**< Used to link the task to certain cores. UBaseType_t must have greater than or equal to the number of bits as configNUMBER_OF_CORES. */ #endif ListItem_t xStateListItem; /**< The list that the state list item of a task is reference from denotes the state of that task (Ready, Blocked, Suspended ). */ ListItem_t xEventListItem; /**< Used to reference a task from an event list. */ UBaseType_t uxPriority; /**< The priority of the task. 0 is the lowest priority. */ StackType_t * pxStack; /**< Points to the start of the stack. */ #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) volatile BaseType_t xTaskRunState; /**< Used to identify the core the task is running on, if the task is running. Otherwise, identifies the task's state - not running or yielding. */ UBaseType_t uxTaskAttributes; /**< Task's attributes - currently used to identify the idle tasks. */ #endif char pcTaskName[ configMAX_TASK_NAME_LEN ]; /**< Descriptive name given to the task when created. Facilitates debugging only. */ #if ( configUSE_TASK_PREEMPTION_DISABLE == 1 ) BaseType_t xPreemptionDisable; /**< Used to prevent the task from being preempted. */ #endif #if ( ( portSTACK_GROWTH > 0 ) || ( configRECORD_STACK_HIGH_ADDRESS == 1 ) ) StackType_t * pxEndOfStack; /**< Points to the highest valid address for the stack. */ #endif #if ( portCRITICAL_NESTING_IN_TCB == 1 ) UBaseType_t uxCriticalNesting; /**< Holds the critical section nesting depth for ports that do not maintain their own count in the port layer. */ #endif #if ( configUSE_TRACE_FACILITY == 1 ) UBaseType_t uxTCBNumber; /**< Stores a number that increments each time a TCB is created. It allows debuggers to determine when a task has been deleted and then recreated. */ UBaseType_t uxTaskNumber; /**< Stores a number specifically for use by third party trace code. */ #endif #if ( configUSE_MUTEXES == 1 ) UBaseType_t uxBasePriority; /**< The priority last assigned to the task - used by the priority inheritance mechanism. */ UBaseType_t uxMutexesHeld; #endif #if ( configUSE_APPLICATION_TASK_TAG == 1 ) TaskHookFunction_t pxTaskTag; #endif #if ( configNUM_THREAD_LOCAL_STORAGE_POINTERS > 0 ) void * pvThreadLocalStoragePointers[ configNUM_THREAD_LOCAL_STORAGE_POINTERS ]; #endif #if ( configGENERATE_RUN_TIME_STATS == 1 ) configRUN_TIME_COUNTER_TYPE ulRunTimeCounter; /**< Stores the amount of time the task has spent in the Running state. */ #endif #if ( configUSE_C_RUNTIME_TLS_SUPPORT == 1 ) configTLS_BLOCK_TYPE xTLSBlock; /**< Memory block used as Thread Local Storage (TLS) Block for the task. */ #endif #if ( configUSE_TASK_NOTIFICATIONS == 1 ) volatile uint32_t ulNotifiedValue[ configTASK_NOTIFICATION_ARRAY_ENTRIES ]; volatile uint8_t ucNotifyState[ configTASK_NOTIFICATION_ARRAY_ENTRIES ]; #endif /* See the comments in FreeRTOS.h with the definition of * tskSTATIC_AND_DYNAMIC_ALLOCATION_POSSIBLE. */ #if ( tskSTATIC_AND_DYNAMIC_ALLOCATION_POSSIBLE != 0 ) uint8_t ucStaticallyAllocated; /**< Set to pdTRUE if the task is a statically allocated to ensure no attempt is made to free the memory. */ #endif #if ( INCLUDE_xTaskAbortDelay == 1 ) uint8_t ucDelayAborted; #endif #if ( configUSE_POSIX_ERRNO == 1 ) int iTaskErrno; #endif } tskTCB;
2 . 链表项数据结构
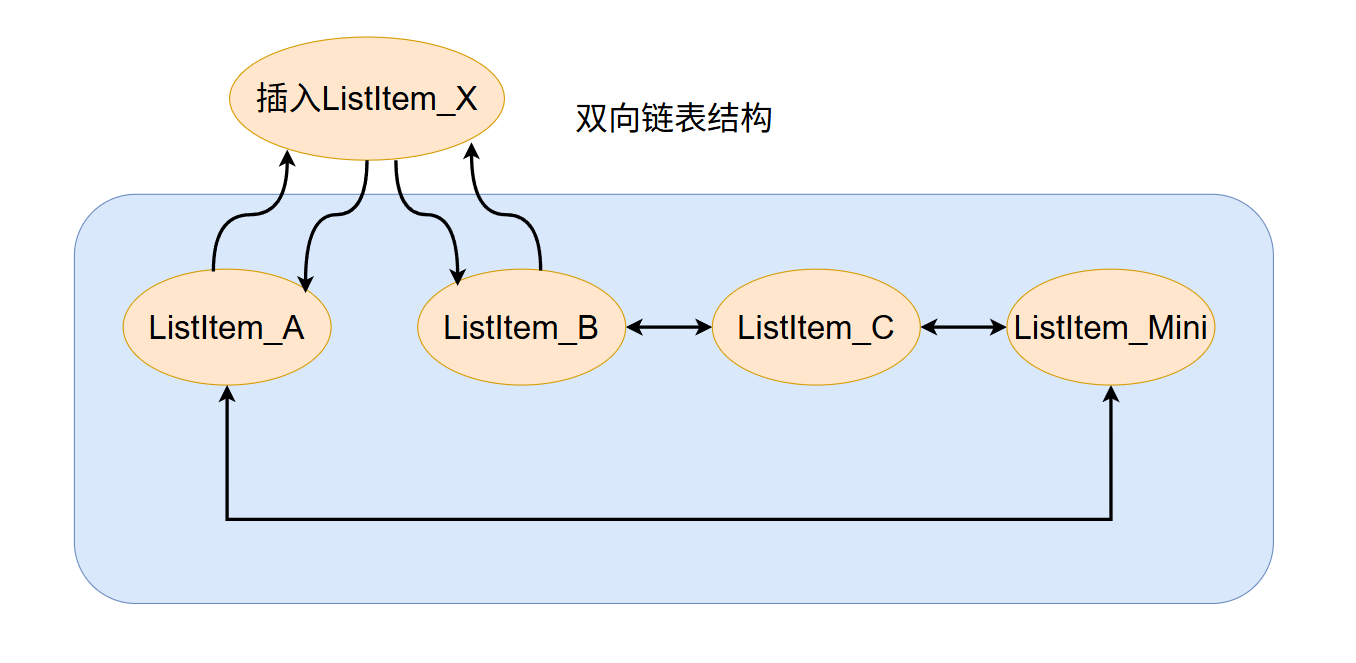
-
链表项数据结构
2.1 :链表项数据结构如下图,FreeRTOS中实现了两种链表项数据结构,常规链表项和MINI链表项,常规链表项是TCB中的xState/xEvent的用法,而MINI链表项用于链表的哨兵节点
2.2 :常规链表项中有魔数(0xA5A5A5A5)添加(宏使能),为安全考虑产生的逻辑,方便调试发现异常
2.3 :xItemValue : 在xState链表项中记录Tick数值,阻塞态时基于此查询唤醒,在xEvent时表示事件优先级(事件值越低,优先级越高,与任务优先级顺序相反,因此源码中常常基于任务优先级数值转下顺序给到xItemValue )
2.4 :pxNext :基于当前链表项在链表中的位置索引下一个链表项节点
2.5 :pxPrevious :基于当前链表项在链表中的位置索引上一个链表项节点
2.6 :pvOwner :链表项中的 pvOwner 指向当前TCB块,因此链表中的任意一个链表项中的 pvOwner 可以索引到TCB任务控制块
2.7 : pxContainer :链表中的 pxContainer 指向某个链表,通过这个指向可以把链表项(任务)指向就绪链表,阻塞链表等
struct xLIST_ITEM { listFIRST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /**< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */ configLIST_VOLATILE TickType_t xItemValue; /**< The value being listed. In most cases this is used to sort the list in ascending order. */ struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxNext; /**< Pointer to the next ListItem_t in the list. */ struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxPrevious; /**< Pointer to the previous ListItem_t in the list. */ void * pvOwner; /**< Pointer to the object (normally a TCB) that contains the list item. There is therefore a two way link between the object containing the list item and the list item itself. */ struct xLIST * configLIST_VOLATILE pxContainer; /**< Pointer to the list in which this list item is placed (if any). */ listSECOND_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /**< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */ }; typedef struct xLIST_ITEM ListItem_t; struct xMINI_LIST_ITEM { listFIRST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /**< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */ configLIST_VOLATILE TickType_t xItemValue; struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxNext; struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxPrevious; }; typedef struct xMINI_LIST_ITEM MiniListItem_t;
3 . 链表数据结构
-
链表数据结构
3.1 :链表数据结构如下图,其中首尾是魔数(0xA5A5A5A5)添加(宏使能),为安全考虑产生的逻辑,方便调试发现异常
3.2 :uxNumberOfItems :记录链表中的链表项数量
3.3 :pxIndex :链表中当前选中的链表项
3.4 :xListEnd :链表哨兵节点,通过哨兵节点的next可以访问回链表头部
typedef struct xLIST { listFIRST_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /**< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */ configLIST_VOLATILE UBaseType_t uxNumberOfItems; ListItem_t * configLIST_VOLATILE pxIndex; /**< Used to walk through the list. Points to the last item returned by a call to listGET_OWNER_OF_NEXT_ENTRY (). */ MiniListItem_t xListEnd; /**< List item that contains the maximum possible item value meaning it is always at the end of the list and is therefore used as a marker. */ listSECOND_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /**< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */ } List_t;
4 . 队列数据结构
-
队列数据结构
4.1 :pcHead指向队列的首地址;
4.2 :pcWriteTo为下一个数据项应该被写入的位置;
4.3 :xQueue 和 xSemaphore共用同一段内存,xQueue 用于队列:管理环形缓冲区的“尾”和“读位置”;xSemaphore用于互斥量:管理“持有者”和“递归计数”
4.4 :xQueue 结构中的 pcTail 是队列存储区的尾后指针。它指向实际为队列分配的内存块的最后一个字节的下一个字节。它作为一个“哨兵”或边界标记,用于判断pcWriteTo和pcReadFrom指针何时需要从物理末尾折返(Wrap)到开头(pcHead),从而实现环形缓冲区;
4.5 :xQueue 结构中的 pcReadFrom 对应下一个出队(读取)位置。指向队列中下一个待读取数据项的起始地址。当任务调用 xQueueReceive 时,即从此处读取数据,读取后该指针会向后移动一个数据项的大小(uxItemSize),并在到达pcTail时折返到pcHead。
4.6 :xSemaphore结构中的xMutexHolder是互斥量持有者。记录当前是哪个任务成功获取(Take)了这个互斥量。这是实现优先级继承协议以防止优先级反转的关键:当高优先级任务因等待此互斥量而阻塞时,内核可以临时提升持有者任务 (xMutexHolder) 的优先级。对于二值信号量和计数信号量,此成员无意义。
4.7 :xSemaphore结构中的uxRecursiveCallCount是递归获取计数。仅用于递归互斥量。记录同一个任务已经成功获取(xSemaphoreTakeRecursive)此递归互斥量但尚未释放(xSemaphoreGiveRecursive)的次数。每次成功获取时计数加1,释放时减1,只有当计数减为0时,互斥量才真正被释放给其他任务。对于普通互斥量或信号量,此值为0。
4.8 : xTasksWaitingToSend 和 xTasksWaitingToReceive 用于记录有哪些任务在队列阻塞态
4.9 :uxMessagesWaiting 记录队列目前有多少个数据项可读
4.10 : uxLength 记录队列总共有多少个数据项
4.11 : uxItemSize 记录队列每个数据项的大小
4.12 : cRxLock 和 cTxLock 是为了在中断操作队列快速退出的机制,回到队列任务后再根据锁深来唤醒记录的任务
4.13 : pxQueueSetContainer 是队列集,把队列集合在一起对于应用层的好处是只需要等待队列集结果,而无需应用层遍历N个队列唤醒任务
typedef struct QueueDefinition /* The old naming convention is used to prevent breaking kernel aware debuggers. */ { int8_t * pcHead; /**< Points to the beginning of the queue storage area. */ int8_t * pcWriteTo; /**< Points to the free next place in the storage area. */ union { QueuePointers_t xQueue; /**< Data required exclusively when this structure is used as a queue. */ SemaphoreData_t xSemaphore; /**< Data required exclusively when this structure is used as a semaphore. */ } u; List_t xTasksWaitingToSend; /**< List of tasks that are blocked waiting to post onto this queue. Stored in priority order. */ List_t xTasksWaitingToReceive; /**< List of tasks that are blocked waiting to read from this queue. Stored in priority order. */ volatile UBaseType_t uxMessagesWaiting; /**< The number of items currently in the queue. */ UBaseType_t uxLength; /**< The length of the queue defined as the number of items it will hold, not the number of bytes. */ UBaseType_t uxItemSize; /**< The size of each items that the queue will hold. */ volatile int8_t cRxLock; /**< Stores the number of items received from the queue (removed from the queue) while the queue was locked. Set to queueUNLOCKED when the queue is not locked. */ volatile int8_t cTxLock; /**< Stores the number of items transmitted to the queue (added to the queue) while the queue was locked. Set to queueUNLOCKED when the queue is not locked. */ #if ( ( configSUPPORT_STATIC_ALLOCATION == 1 ) && ( configSUPPORT_DYNAMIC_ALLOCATION == 1 ) ) uint8_t ucStaticallyAllocated; /**< Set to pdTRUE if the memory used by the queue was statically allocated to ensure no attempt is made to free the memory. */ #endif #if ( configUSE_QUEUE_SETS == 1 ) struct QueueDefinition * pxQueueSetContainer; #endif #if ( configUSE_TRACE_FACILITY == 1 ) UBaseType_t uxQueueNumber; uint8_t ucQueueType; #endif } xQUEUE; /* The old xQUEUE name is maintained above then typedefed to the new Queue_t * name below to enable the use of older kernel aware debuggers. */ typedef xQUEUE Queue_t; typedef struct QueuePointers { int8_t * pcTail; /**< Points to the byte at the end of the queue storage area. Once more byte is allocated than necessary to store the queue items, this is used as a marker. */ int8_t * pcReadFrom; /**< Points to the last place that a queued item was read from when the structure is used as a queue. */ } QueuePointers_t; typedef struct SemaphoreData { TaskHandle_t xMutexHolder; /**< The handle of the task that holds the mutex. */ UBaseType_t uxRecursiveCallCount; /**< Maintains a count of the number of times a recursive mutex has been recursively 'taken' when the structure is used as a mutex. */ } SemaphoreData_t;
六. 源码 : 任务通信
1 . 队列
前言 : 队列数据结构包含常规环形指针操作数据的队列,关联队列发送/队列接收的任务(操作队列唤醒),记录队列可读的数据项,以及总共多少数据项,每个数据项大小等,并且考虑实现中断快速操作队列,减少阻塞,诞生了cTxLock/cRxLock意指中断中操作完队列,回到任务时再决定唤醒在中断记录的多个任务,考虑到一个任务与多个队列通信通信的方便性,诞生了队列集的概念,只要设置了队列关联到队列集,那么关联的任意队列都可以唤醒同一个任务,源码部分围绕创建,任务/中断发送,任务/中断接收开展
队列创建 Step1 :描述队列创建与初始的过程
队列发送 Step2 :任务/中断操作队列发送的核心实现
队列接收 Step3 :任务/中断操作队列接收的核心实现
跳转置顶
-
队列创建,描述 xQueue = xQueueCreate(10, sizeof(int)); 的内部过程;
1.1 :队列创建的过程;
1.2 :队列初始的过程;
1.1 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS内核中动态创建队列(或信号量/互斥量)的核心函数 xQueueGenericCreate 的实现。其主要逻辑是:首先对传入的队列长度和项大小进行严格的乘法与加法溢出校验,防止分配异常内存;若校验通过,则计算队列存储区所需的总字节数,并调用 pvPortMalloc 一次性分配足以容纳队列控制结构体(Queue_t)和全部存储空间的连续内存块。若内存分配成功,代码通过指针运算跳过结构体部分(因队列内存是队列结构体头部信息+数据项),精确定位到紧随其后的实际数据存储区起始地址,并设置动态创建标志,最后调用 prvInitialiseNewQueue 函数,利用传入的长度、项大小、存储区指针和队列类型,完成该队列对象内部所有成员(如头尾指针、任务等待列表、计数等)的初始化,最终返回创建好的队列句柄。
#define xQueueCreate( uxQueueLength, uxItemSize ) \ xQueueGenericCreate( ( uxQueueLength ), ( uxItemSize ), ( queueQUEUE_TYPE_BASE ) ) QueueHandle_t xQueueGenericCreate( const UBaseType_t uxQueueLength, const UBaseType_t uxItemSize, const uint8_t ucQueueType ) { Queue_t * pxNewQueue = NULL; size_t xQueueSizeInBytes; uint8_t * pucQueueStorage; traceENTER_xQueueGenericCreate( uxQueueLength, uxItemSize, ucQueueType ); if( ( uxQueueLength > ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) && /* 检测乘法溢出 */ ( ( SIZE_MAX / uxQueueLength ) >= uxItemSize ) && /* 检测加法溢出(头部+数据项所需) */ ( ( UBaseType_t ) ( SIZE_MAX - sizeof( Queue_t ) ) >= ( uxQueueLength * uxItemSize ) ) ) { /* 计算总各数据项所需的大小 */ xQueueSizeInBytes = ( size_t ) ( ( size_t ) uxQueueLength * ( size_t ) uxItemSize ); /* 申请内存(头部信息 + 各数据项) */ pxNewQueue = ( Queue_t * ) pvPortMalloc( sizeof( Queue_t ) + xQueueSizeInBytes ); if( pxNewQueue != NULL ) { /* 基于申请的内存头部偏移到有效数据项地址 */ pucQueueStorage = ( uint8_t * ) pxNewQueue; pucQueueStorage += sizeof( Queue_t ); #if ( configSUPPORT_STATIC_ALLOCATION == 1 ) { /* 默认非静态分配 */ pxNewQueue->ucStaticallyAllocated = pdFALSE; } #endif /* configSUPPORT_STATIC_ALLOCATION */ /* 初始队列 */ prvInitialiseNewQueue( uxQueueLength, uxItemSize, pucQueueStorage, ucQueueType, pxNewQueue ); } else { traceQUEUE_CREATE_FAILED( ucQueueType ); mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { configASSERT( pxNewQueue ); mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceRETURN_xQueueGenericCreate( pxNewQueue ); return pxNewQueue; }
1.2 :这段代码是FreeRTOS中初始化一个新创建队列的核心函数 prvInitialiseNewQueue 的实现,它首先根据队列项大小(uxItemSize)判断队列用途:若项大小为0(表示创建的是信号量或互斥量,而非数据队列),则将队列结构体自身的地址赋给 pcHead 指针,作为一个无害且有效的占位符;若项大小不为0(表示创建的是普通数据队列),则将指向独立存储区的指针 pucQueueStorage 赋给 pcHead。接着,函数设置队列的基础属性——长度(uxLength)与项大小(uxItemSize),并调用 xQueueGenericReset 函数完成队列运行状态的初始化(如重置读写指针、清空任务等待列表、将消息计数归零等)。最后,根据系统配置,选择性设置队列类型标识(ucQueueType)和队列集容器指针(pxQueueSetContainer),从而完成整个队列对象的构建,使其进入可操作的就绪状态。
static void prvInitialiseNewQueue( const UBaseType_t uxQueueLength, const UBaseType_t uxItemSize, uint8_t * pucQueueStorage, const uint8_t ucQueueType, Queue_t * pxNewQueue ) { /* Remove compiler warnings about unused parameters should * configUSE_TRACE_FACILITY not be set to 1. */ ( void ) ucQueueType; if( uxItemSize == ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) { /* No RAM was allocated for the queue storage area, but PC head cannot * be set to NULL because NULL is used as a key to say the queue is used as * a mutex. Therefore just set pcHead to point to the queue as a benign * value that is known to be within the memory map. */ pxNewQueue->pcHead = ( int8_t * ) pxNewQueue; } else { /* Set the head to the start of the queue storage area. */ pxNewQueue->pcHead = ( int8_t * ) pucQueueStorage; } /* Initialise the queue members as described where the queue type is * defined. */ pxNewQueue->uxLength = uxQueueLength; pxNewQueue->uxItemSize = uxItemSize; ( void ) xQueueGenericReset( pxNewQueue, pdTRUE ); #if ( configUSE_TRACE_FACILITY == 1 ) { pxNewQueue->ucQueueType = ucQueueType; } #endif /* configUSE_TRACE_FACILITY */ #if ( configUSE_QUEUE_SETS == 1 ) { pxNewQueue->pxQueueSetContainer = NULL; } #endif /* configUSE_QUEUE_SETS */ traceQUEUE_CREATE( pxNewQueue ); }
-
队列发送,描述任务/中断发送队列的内部过程;
2.1 :任务发送队列的核心实现
2.2 :中断发送队列的核心实现2.1 : 以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中实现队列发送(或信号量释放)的通用函数xQueueGenericSend的核心逻辑,它首先在临界区内检查队列状态:若队列未满或处于覆盖发送模式,则调用prvCopyDataToQueue完成数据拷贝,随后检查并唤醒xTasksWaitingToReceive列表中等待数据的最高优先级任务,并在必要时触发任务切换后直接返回成功;若队列已满且指定了非零阻塞时间,则配置超时结构后退出临界区,挂起调度器并锁定队列,随后在循环中检查超时:若未超时且队列仍满,则将当前任务挂入xTasksWaitingToSend列表并解锁队列、恢复调度器以等待空位;若期间队列变为非满,则重新尝试发送流程;若超时发生,则清理队列锁并返回队列满错误;若未指定阻塞时间且队列满,则直接返回队列满错误。整个流程通过精细的状态检查、数据操作、任务列表管理和超时处理,实现了支持阻塞、覆盖及队列集通知的完整队列发送机制。
#define xQueueSend( xQueue, pvItemToQueue, xTicksToWait ) \ xQueueGenericSend( ( xQueue ), ( pvItemToQueue ), ( xTicksToWait ), queueSEND_TO_BACK ) BaseType_t xQueueGenericSend( QueueHandle_t xQueue, const void * const pvItemToQueue, TickType_t xTicksToWait, const BaseType_t xCopyPosition ) { BaseType_t xEntryTimeSet = pdFALSE, xYieldRequired; TimeOut_t xTimeOut; Queue_t * const pxQueue = xQueue; traceENTER_xQueueGenericSend( xQueue, pvItemToQueue, xTicksToWait, xCopyPosition ); configASSERT( pxQueue ); configASSERT( !( ( pvItemToQueue == NULL ) && ( pxQueue->uxItemSize != ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) ) ); configASSERT( !( ( xCopyPosition == queueOVERWRITE ) && ( pxQueue->uxLength != 1 ) ) ); #if ( ( INCLUDE_xTaskGetSchedulerState == 1 ) || ( configUSE_TIMERS == 1 ) ) { configASSERT( !( ( xTaskGetSchedulerState() == taskSCHEDULER_SUSPENDED ) && ( xTicksToWait != 0 ) ) ); } #endif for( ; ; ) { taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { /* Is there room on the queue now? The running task must be the * highest priority task wanting to access the queue. If the head item * in the queue is to be overwritten then it does not matter if the * queue is full. */ if( ( pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting < pxQueue->uxLength ) || ( xCopyPosition == queueOVERWRITE ) ) { traceQUEUE_SEND( pxQueue ); #if ( configUSE_QUEUE_SETS == 1 ) { const UBaseType_t uxPreviousMessagesWaiting = pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting; xYieldRequired = prvCopyDataToQueue( pxQueue, pvItemToQueue, xCopyPosition ); if( pxQueue->pxQueueSetContainer != NULL ) { if( ( xCopyPosition == queueOVERWRITE ) && ( uxPreviousMessagesWaiting != ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) ) { /* Do not notify the queue set as an existing item * was overwritten in the queue so the number of items * in the queue has not changed. */ mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } else if( prvNotifyQueueSetContainer( pxQueue ) != pdFALSE ) { /* The queue is a member of a queue set, and posting * to the queue set caused a higher priority task to * unblock. A context switch is required. */ queueYIELD_IF_USING_PREEMPTION(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { /* If there was a task waiting for data to arrive on the * queue then unblock it now. */ if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) == pdFALSE ) { if( xTaskRemoveFromEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) != pdFALSE ) { /* The unblocked task has a priority higher than * our own so yield immediately. Yes it is ok to * do this from within the critical section - the * kernel takes care of that. */ queueYIELD_IF_USING_PREEMPTION(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else if( xYieldRequired != pdFALSE ) { /* This path is a special case that will only get * executed if the task was holding multiple mutexes * and the mutexes were given back in an order that is * different to that in which they were taken. */ queueYIELD_IF_USING_PREEMPTION(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } #else /* configUSE_QUEUE_SETS */ { xYieldRequired = prvCopyDataToQueue( pxQueue, pvItemToQueue, xCopyPosition ); /* If there was a task waiting for data to arrive on the * queue then unblock it now. */ if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) == pdFALSE ) { if( xTaskRemoveFromEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) != pdFALSE ) { /* The unblocked task has a priority higher than * our own so yield immediately. Yes it is ok to do * this from within the critical section - the kernel * takes care of that. */ queueYIELD_IF_USING_PREEMPTION(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else if( xYieldRequired != pdFALSE ) { /* This path is a special case that will only get * executed if the task was holding multiple mutexes and * the mutexes were given back in an order that is * different to that in which they were taken. */ queueYIELD_IF_USING_PREEMPTION(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* configUSE_QUEUE_SETS */ taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceRETURN_xQueueGenericSend( pdPASS ); return pdPASS; } else { if( xTicksToWait == ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { /* The queue was full and no block time is specified (or * the block time has expired) so leave now. */ taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); /* Return to the original privilege level before exiting * the function. */ traceQUEUE_SEND_FAILED( pxQueue ); traceRETURN_xQueueGenericSend( errQUEUE_FULL ); return errQUEUE_FULL; } else if( xEntryTimeSet == pdFALSE ) { /* The queue was full and a block time was specified so * configure the timeout structure. */ vTaskInternalSetTimeOutState( &xTimeOut ); xEntryTimeSet = pdTRUE; } else { /* Entry time was already set. */ mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); /* Interrupts and other tasks can send to and receive from the queue * now the critical section has been exited. */ vTaskSuspendAll(); prvLockQueue( pxQueue ); /* Update the timeout state to see if it has expired yet. */ if( xTaskCheckForTimeOut( &xTimeOut, &xTicksToWait ) == pdFALSE ) { if( prvIsQueueFull( pxQueue ) != pdFALSE ) { traceBLOCKING_ON_QUEUE_SEND( pxQueue ); vTaskPlaceOnEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToSend ), xTicksToWait ); /* Unlocking the queue means queue events can effect the * event list. It is possible that interrupts occurring now * remove this task from the event list again - but as the * scheduler is suspended the task will go onto the pending * ready list instead of the actual ready list. */ prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); /* Resuming the scheduler will move tasks from the pending * ready list into the ready list - so it is feasible that this * task is already in the ready list before it yields - in which * case the yield will not cause a context switch unless there * is also a higher priority task in the pending ready list. */ if( xTaskResumeAll() == pdFALSE ) { taskYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } } else { /* Try again. */ prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } } else { /* The timeout has expired. */ prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); traceQUEUE_SEND_FAILED( pxQueue ); traceRETURN_xQueueGenericSend( errQUEUE_FULL ); return errQUEUE_FULL; } } }
2.2 :这段代码是FreeRTOS中断服务程序(ISR)中向队列发送数据的核心函数 xQueueGenericSendFromISR 的实现,它在通过中断优先级验证后,使用 taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR 进入中断临界区以保护共享数据,然后检查队列是否非满或为覆盖模式:若条件满足,则调用 prvCopyDataToQueue 执行数据拷贝,并根据队列的发送锁状态(cTxLock)决定后续操作——若队列未锁定,则直接检查并唤醒 xTasksWaitingToReceive 列表中等待数据的最高优先级任务,并通过 pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken 参数输出是否需要上下文切换的标志;若队列已锁定,则递增发送锁计数以延迟唤醒操作;最后退出临界区并返回成功;若队列已满且非覆盖模式,则直接返回队列满错误。整个流程确保了在中断上下文中的快速、非阻塞且线程安全的队列操作,并正确处理了任务唤醒与潜在上下文切换的协调。
BaseType_t xQueueGenericSendFromISR( QueueHandle_t xQueue, const void * const pvItemToQueue, BaseType_t * const pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken, const BaseType_t xCopyPosition ) { BaseType_t xReturn; UBaseType_t uxSavedInterruptStatus; Queue_t * const pxQueue = xQueue; traceENTER_xQueueGenericSendFromISR( xQueue, pvItemToQueue, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken, xCopyPosition ); configASSERT( pxQueue ); configASSERT( !( ( pvItemToQueue == NULL ) && ( pxQueue->uxItemSize != ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) ) ); configASSERT( !( ( xCopyPosition == queueOVERWRITE ) && ( pxQueue->uxLength != 1 ) ) ); portASSERT_IF_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY_INVALID(); uxSavedInterruptStatus = ( UBaseType_t ) taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR(); { if( ( pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting < pxQueue->uxLength ) || ( xCopyPosition == queueOVERWRITE ) ) { const int8_t cTxLock = pxQueue->cTxLock; const UBaseType_t uxPreviousMessagesWaiting = pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting; traceQUEUE_SEND_FROM_ISR( pxQueue ); ( void ) prvCopyDataToQueue( pxQueue, pvItemToQueue, xCopyPosition ); if( cTxLock == queueUNLOCKED ) { #if ( configUSE_QUEUE_SETS == 1 ) { if( pxQueue->pxQueueSetContainer != NULL ) { if( ( xCopyPosition == queueOVERWRITE ) && ( uxPreviousMessagesWaiting != ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) ) { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } else if( prvNotifyQueueSetContainer( pxQueue ) != pdFALSE ) { if( pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken != NULL ) { *pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) == pdFALSE ) { if( xTaskRemoveFromEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) != pdFALSE ) { /* The task waiting has a higher priority so * record that a context switch is required. */ if( pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken != NULL ) { *pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } #else /* configUSE_QUEUE_SETS */ { if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) == pdFALSE ) { if( xTaskRemoveFromEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ) ) != pdFALSE ) { /* The task waiting has a higher priority so record that a * context switch is required. */ if( pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken != NULL ) { *pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* Not used in this path. */ ( void ) uxPreviousMessagesWaiting; } #endif /* configUSE_QUEUE_SETS */ } else { /* Increment the lock count so the task that unlocks the queue * knows that data was posted while it was locked. */ prvIncrementQueueTxLock( pxQueue, cTxLock ); } xReturn = pdPASS; } else { traceQUEUE_SEND_FROM_ISR_FAILED( pxQueue ); xReturn = errQUEUE_FULL; } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR( uxSavedInterruptStatus ); traceRETURN_xQueueGenericSendFromISR( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
-
队列接收,描述任务/中断接收队列的内部过程;
3.1 :任务接收队列的核心实现
3.2 :中断接收队列的核心实现
3.1 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中实现从队列接收数据的核心函数 xQueueReceive 的实现,它首先在临界区内检查队列当前数据计数:若有数据,则调用 prvCopyDataFromQueue 复制数据到用户缓冲区并更新计数,随后检查 xTasksWaitingToSend 列表,唤醒其中因队列满而阻塞的最高优先级任务(若存在),最后退出临界区并返回成功;若队列为空且未指定阻塞时间则直接返回队列空错误;若指定了阻塞时间,则配置超时结构并退出临界区,随后挂起调度器、锁定队列,并在循环中检查超时:若未超时且队列仍空,则将当前任务挂入 xTasksWaitingToReceive 列表等待数据,解锁队列并恢复调度器;若在此期间有数据入队,则重新尝试接收流程;若超时发生,则检查最终队列状态后返回相应结果。整个流程通过临界区保护、双等待列表协调及超时管理,实现了支持阻塞等待的队列数据接收机制。
BaseType_t xQueueReceive( QueueHandle_t xQueue, void * const pvBuffer, TickType_t xTicksToWait ) { BaseType_t xEntryTimeSet = pdFALSE; TimeOut_t xTimeOut; Queue_t * const pxQueue = xQueue; traceENTER_xQueueReceive( xQueue, pvBuffer, xTicksToWait ); /* Check the pointer is not NULL. */ configASSERT( ( pxQueue ) ); /* The buffer into which data is received can only be NULL if the data size * is zero (so no data is copied into the buffer). */ configASSERT( !( ( ( pvBuffer ) == NULL ) && ( ( pxQueue )->uxItemSize != ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) ) ); /* Cannot block if the scheduler is suspended. */ #if ( ( INCLUDE_xTaskGetSchedulerState == 1 ) || ( configUSE_TIMERS == 1 ) ) { configASSERT( !( ( xTaskGetSchedulerState() == taskSCHEDULER_SUSPENDED ) && ( xTicksToWait != 0 ) ) ); } #endif for( ; ; ) { taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { const UBaseType_t uxMessagesWaiting = pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting; /* Is there data in the queue now? To be running the calling task * must be the highest priority task wanting to access the queue. */ if( uxMessagesWaiting > ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) { /* Data available, remove one item. */ prvCopyDataFromQueue( pxQueue, pvBuffer ); traceQUEUE_RECEIVE( pxQueue ); pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting = ( UBaseType_t ) ( uxMessagesWaiting - ( UBaseType_t ) 1 ); /* There is now space in the queue, were any tasks waiting to * post to the queue? If so, unblock the highest priority waiting * task. */ if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToSend ) ) == pdFALSE ) { if( xTaskRemoveFromEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToSend ) ) != pdFALSE ) { queueYIELD_IF_USING_PREEMPTION(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceRETURN_xQueueReceive( pdPASS ); return pdPASS; } else { if( xTicksToWait == ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { /* The queue was empty and no block time is specified (or * the block time has expired) so leave now. */ taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceQUEUE_RECEIVE_FAILED( pxQueue ); traceRETURN_xQueueReceive( errQUEUE_EMPTY ); return errQUEUE_EMPTY; } else if( xEntryTimeSet == pdFALSE ) { /* The queue was empty and a block time was specified so * configure the timeout structure. */ vTaskInternalSetTimeOutState( &xTimeOut ); xEntryTimeSet = pdTRUE; } else { /* Entry time was already set. */ mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); /* Interrupts and other tasks can send to and receive from the queue * now the critical section has been exited. */ vTaskSuspendAll(); prvLockQueue( pxQueue ); /* Update the timeout state to see if it has expired yet. */ if( xTaskCheckForTimeOut( &xTimeOut, &xTicksToWait ) == pdFALSE ) { /* The timeout has not expired. If the queue is still empty place * the task on the list of tasks waiting to receive from the queue. */ if( prvIsQueueEmpty( pxQueue ) != pdFALSE ) { traceBLOCKING_ON_QUEUE_RECEIVE( pxQueue ); vTaskPlaceOnEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ), xTicksToWait ); prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); if( xTaskResumeAll() == pdFALSE ) { taskYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { /* The queue contains data again. Loop back to try and read the * data. */ prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } } else { /* Timed out. If there is no data in the queue exit, otherwise loop * back and attempt to read the data. */ prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); if( prvIsQueueEmpty( pxQueue ) != pdFALSE ) { traceQUEUE_RECEIVE_FAILED( pxQueue ); traceRETURN_xQueueReceive( errQUEUE_EMPTY ); return errQUEUE_EMPTY; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } }
3.2 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中实现中断服务程序从队列接收数据的核心函数 xQueueReceiveFromISR 的实现,它在完成中断优先级合法性断言后,通过 taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR 进入中断级临界区,然后检查队列中是否存在数据(uxMessagesWaiting > 0):若有数据,则调用 prvCopyDataFromQueue 将数据拷贝至调用者提供的缓冲区并更新队列计数;随后根据队列接收锁的状态(cRxLock)决定后续行为——若队列未锁定,则检查并尝试唤醒 xTasksWaitingToSend 列表中因队列满而阻塞的最高优先级任务,并通过 pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken 参数输出上下文切换请求;若队列已锁定,则递增接收锁计数以延迟执行唤醒操作;最终返回成功。若队列中无数据,则直接返回失败。整个函数在中断上下文中实现了非阻塞、线程安全的数据接收,并妥善处理了队列锁与任务唤醒的协调。
BaseType_t xQueueReceiveFromISR( QueueHandle_t xQueue, void * const pvBuffer, BaseType_t * const pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ) { BaseType_t xReturn; UBaseType_t uxSavedInterruptStatus; Queue_t * const pxQueue = xQueue; traceENTER_xQueueReceiveFromISR( xQueue, pvBuffer, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); configASSERT( pxQueue ); configASSERT( !( ( pvBuffer == NULL ) && ( pxQueue->uxItemSize != ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) ) ); /* RTOS ports that support interrupt nesting have the concept of a maximum * system call (or maximum API call) interrupt priority. Interrupts that are * above the maximum system call priority are kept permanently enabled, even * when the RTOS kernel is in a critical section, but cannot make any calls to * FreeRTOS API functions. If configASSERT() is defined in FreeRTOSConfig.h * then portASSERT_IF_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY_INVALID() will result in an assertion * failure if a FreeRTOS API function is called from an interrupt that has been * assigned a priority above the configured maximum system call priority. * Only FreeRTOS functions that end in FromISR can be called from interrupts * that have been assigned a priority at or (logically) below the maximum * system call interrupt priority. FreeRTOS maintains a separate interrupt * safe API to ensure interrupt entry is as fast and as simple as possible. * More information (albeit Cortex-M specific) is provided on the following * link: https://www.FreeRTOS.org/RTOS-Cortex-M3-M4.html */ portASSERT_IF_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY_INVALID(); /* MISRA Ref 4.7.1 [Return value shall be checked] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#dir-47 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_directive_4_7_violation] */ uxSavedInterruptStatus = ( UBaseType_t ) taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR(); { const UBaseType_t uxMessagesWaiting = pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting; /* Cannot block in an ISR, so check there is data available. */ if( uxMessagesWaiting > ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) { const int8_t cRxLock = pxQueue->cRxLock; traceQUEUE_RECEIVE_FROM_ISR( pxQueue ); prvCopyDataFromQueue( pxQueue, pvBuffer ); pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting = ( UBaseType_t ) ( uxMessagesWaiting - ( UBaseType_t ) 1 ); /* If the queue is locked the event list will not be modified. * Instead update the lock count so the task that unlocks the queue * will know that an ISR has removed data while the queue was * locked. */ if( cRxLock == queueUNLOCKED ) { if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToSend ) ) == pdFALSE ) { if( xTaskRemoveFromEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToSend ) ) != pdFALSE ) { /* The task waiting has a higher priority than us so * force a context switch. */ if( pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken != NULL ) { *pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { /* Increment the lock count so the task that unlocks the queue * knows that data was removed while it was locked. */ prvIncrementQueueRxLock( pxQueue, cRxLock ); } xReturn = pdPASS; } else { xReturn = pdFAIL; traceQUEUE_RECEIVE_FROM_ISR_FAILED( pxQueue ); } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR( uxSavedInterruptStatus ); traceRETURN_xQueueReceiveFromISR( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
2 . 互斥锁
前言 :在FreeRTOS构建的多任务嵌入式系统中,当多个任务并发访问共享资源时,若无适当保护机制,极易引发数据竞争与状态不一致的严重后果。为此,FreeRTOS不仅提供了基础的二进制与计数信号量,更引入了互斥锁这一核心同步原语。与简单信号量不同,互斥锁专为资源独占访问而设计,其内部集成优先级继承机制,能有效缓解低优先级任务持有锁时阻碍高优先级任务运行的“优先级反转”问题,从而保障系统实时性与可靠性。此外,FreeRTOS亦支持递归互斥锁,允许同一任务多次安全地获取同一锁,极大简化了嵌套函数调用或递归算法中的资源管理逻辑。这些精心设计的API共同构成了一个兼顾安全、效率与实时性的临界区守卫体系,是构建稳健并发程序的基石。
互斥锁创建 Step1 :描述互斥锁创建的过程
互斥锁释放 Step2 :任务/中断操作互斥锁释放的核心实现
互斥锁获取 Step3 :任务/中断操作互斥锁获取的核心实现
互斥锁与信号量共用同一套API,通过宏选择队列/锁/信号量
#define queueQUEUE_TYPE_BASE ( ( uint8_t ) 0U )
#define queueQUEUE_TYPE_SET ( ( uint8_t ) 0U )
#define queueQUEUE_TYPE_MUTEX ( ( uint8_t ) 1U )
#define queueQUEUE_TYPE_COUNTING_SEMAPHORE ( ( uint8_t ) 2U )
#define queueQUEUE_TYPE_BINARY_SEMAPHORE ( ( uint8_t ) 3U )
#define queueQUEUE_TYPE_RECURSIVE_MUTEX ( ( uint8_t ) 4U )
创建API:各不相同,分别有:
-
互斥锁:xSemaphoreCreateMutex()
-
递归互斥锁:xSemaphoreCreateRecursiveMutex()
-
二进制信号量:xSemaphoreCreateBinary()
-
计数型信号量:xSemaphoreCreateCounting()
获取API:对于互斥锁、二进制信号量和计数型信号量,都可以使用xSemaphoreTake(),但是递归互斥锁必须使用xSemaphoreTakeRecursive()。
释放API:对于互斥锁、二进制信号量和计数型信号量,都可以使用xSemaphoreGive(),但是递归互斥锁必须使用xSemaphoreGiveRecursive()。
-
互斥锁创建,描述 SemaphoreHandle_t xMutex;
xMutex = xSemaphoreCreateMutex();的内部过程;
1.1 :互斥锁创建的过程;以下代码清晰地展现了FreeRTOS中互斥锁的本质——一种特殊的队列实现。函数通过xQueueGenericCreate()创建了一个长度为1、数据项大小为0的队列骨架,这一设计表明互斥锁不承载实际数据传输,仅作为同步状态标志;随后调用prvInitialiseMutex()初始化互斥锁特有属性(如递归计数、持有者记录等),从而在队列基础设施之上构建出完整的互斥语义。这种实现方式巧妙复用了队列的阻塞等待机制,让任务在获取锁时能自然进入阻塞队列,释放时又能自动唤醒等待任务,体现了FreeRTOS模块间高度复用与分层抽象的设计哲学。
QueueHandle_t xQueueCreateMutex( const uint8_t ucQueueType ) { QueueHandle_t xNewQueue; const UBaseType_t uxMutexLength = ( UBaseType_t ) 1, uxMutexSize = ( UBaseType_t ) 0; traceENTER_xQueueCreateMutex( ucQueueType ); xNewQueue = xQueueGenericCreate( uxMutexLength, uxMutexSize, ucQueueType ); prvInitialiseMutex( ( Queue_t * ) xNewQueue ); traceRETURN_xQueueCreateMutex( xNewQueue ); return xNewQueue; }
-
互斥锁释放,描述 xSemaphoreGive( xSemaphore ) 的内部过程;
2.1 :以下这段代码可以看出信号量释放本质上是队列的特殊应用。通过将信号量句柄强制转换为队列句柄,并调用xQueueGenericSend()这一底层队列操作,传递NULL数据、零阻塞时间和队尾发送标志,实现了信号量的释放操作。这种设计将信号量的"给予"抽象为向长度为1的空队列发送虚拟项,巧妙利用队列内置的阻塞/唤醒机制管理等待任务,体现了FreeRTOS通过队列基础设施统一构建高层同步原语的设计哲学,确保了内核代码的高度复用和一致性。
#define xSemaphoreGive( xSemaphore ) xQueueGenericSend( ( QueueHandle_t ) ( xSemaphore ), NULL, semGIVE_BLOCK_TIME, queueSEND_TO_BACK )
-
互斥锁 BaseType_t xQueueSemaphoreTake( QueueHandle_t xQueue,
TickType_t xTicksToWait ) 的内部过程;
3.1 :这段代码是FreeRTOS信号量获取操作的核心实现,展现了信号量作为零长度队列的深层统一性。函数通过循环机制不断尝试获取信号量:若当前计数(队列中消息数)大于0,则直接递减计数并唤醒可能等待发送的任务;若计数为0且指定了阻塞时间,则任务会进入阻塞状态并挂入等待接收列表。特别对于互斥锁类型,代码实现了动态优先级继承机制——当高优先级任务因等待互斥锁而阻塞时,会临时提升持有者任务的优先级;若等待超时,则进行优先级解除继承。整个过程通过临界区保护与调度器挂起确保原子性,完美复用了队列的阻塞/唤醒基础设施,体现了信号量机制在队列抽象上的精巧构建。
BaseType_t xQueueSemaphoreTake( QueueHandle_t xQueue, TickType_t xTicksToWait ) { BaseType_t xEntryTimeSet = pdFALSE; TimeOut_t xTimeOut; Queue_t * const pxQueue = xQueue; #if ( configUSE_MUTEXES == 1 ) BaseType_t xInheritanceOccurred = pdFALSE; #endif traceENTER_xQueueSemaphoreTake( xQueue, xTicksToWait ); /* Check the queue pointer is not NULL. */ configASSERT( ( pxQueue ) ); /* Check this really is a semaphore, in which case the item size will be * 0. */ configASSERT( pxQueue->uxItemSize == 0 ); /* Cannot block if the scheduler is suspended. */ #if ( ( INCLUDE_xTaskGetSchedulerState == 1 ) || ( configUSE_TIMERS == 1 ) ) { configASSERT( !( ( xTaskGetSchedulerState() == taskSCHEDULER_SUSPENDED ) && ( xTicksToWait != 0 ) ) ); } #endif for( ; ; ) { taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { /* Semaphores are queues with an item size of 0, and where the * number of messages in the queue is the semaphore's count value. */ const UBaseType_t uxSemaphoreCount = pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting; /* Is there data in the queue now? To be running the calling task * must be the highest priority task wanting to access the queue. */ if( uxSemaphoreCount > ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) { traceQUEUE_RECEIVE( pxQueue ); /* Semaphores are queues with a data size of zero and where the * messages waiting is the semaphore's count. Reduce the count. */ pxQueue->uxMessagesWaiting = ( UBaseType_t ) ( uxSemaphoreCount - ( UBaseType_t ) 1 ); #if ( configUSE_MUTEXES == 1 ) { if( pxQueue->uxQueueType == queueQUEUE_IS_MUTEX ) { /* Record the information required to implement * priority inheritance should it become necessary. */ pxQueue->u.xSemaphore.xMutexHolder = pvTaskIncrementMutexHeldCount(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* configUSE_MUTEXES */ /* Check to see if other tasks are blocked waiting to give the * semaphore, and if so, unblock the highest priority such task. */ if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToSend ) ) == pdFALSE ) { if( xTaskRemoveFromEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToSend ) ) != pdFALSE ) { queueYIELD_IF_USING_PREEMPTION(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceRETURN_xQueueSemaphoreTake( pdPASS ); return pdPASS; } else { if( xTicksToWait == ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { /* The semaphore count was 0 and no block time is specified * (or the block time has expired) so exit now. */ taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceQUEUE_RECEIVE_FAILED( pxQueue ); traceRETURN_xQueueSemaphoreTake( errQUEUE_EMPTY ); return errQUEUE_EMPTY; } else if( xEntryTimeSet == pdFALSE ) { /* The semaphore count was 0 and a block time was specified * so configure the timeout structure ready to block. */ vTaskInternalSetTimeOutState( &xTimeOut ); xEntryTimeSet = pdTRUE; } else { /* Entry time was already set. */ mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); /* Interrupts and other tasks can give to and take from the semaphore * now the critical section has been exited. */ vTaskSuspendAll(); prvLockQueue( pxQueue ); /* Update the timeout state to see if it has expired yet. */ if( xTaskCheckForTimeOut( &xTimeOut, &xTicksToWait ) == pdFALSE ) { /* A block time is specified and not expired. If the semaphore * count is 0 then enter the Blocked state to wait for a semaphore to * become available. As semaphores are implemented with queues the * queue being empty is equivalent to the semaphore count being 0. */ if( prvIsQueueEmpty( pxQueue ) != pdFALSE ) { traceBLOCKING_ON_QUEUE_RECEIVE( pxQueue ); #if ( configUSE_MUTEXES == 1 ) { if( pxQueue->uxQueueType == queueQUEUE_IS_MUTEX ) { taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { xInheritanceOccurred = xTaskPriorityInherit( pxQueue->u.xSemaphore.xMutexHolder ); } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* if ( configUSE_MUTEXES == 1 ) */ vTaskPlaceOnEventList( &( pxQueue->xTasksWaitingToReceive ), xTicksToWait ); prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); if( xTaskResumeAll() == pdFALSE ) { taskYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { /* There was no timeout and the semaphore count was not 0, so * attempt to take the semaphore again. */ prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } } else { /* Timed out. */ prvUnlockQueue( pxQueue ); ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); /* If the semaphore count is 0 exit now as the timeout has * expired. Otherwise return to attempt to take the semaphore that is * known to be available. As semaphores are implemented by queues the * queue being empty is equivalent to the semaphore count being 0. */ if( prvIsQueueEmpty( pxQueue ) != pdFALSE ) { #if ( configUSE_MUTEXES == 1 ) { /* xInheritanceOccurred could only have be set if * pxQueue->uxQueueType == queueQUEUE_IS_MUTEX so no need to * test the mutex type again to check it is actually a mutex. */ if( xInheritanceOccurred != pdFALSE ) { taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { UBaseType_t uxHighestWaitingPriority; /* This task blocking on the mutex caused another * task to inherit this task's priority. Now this task * has timed out the priority should be disinherited * again, but only as low as the next highest priority * task that is waiting for the same mutex. */ uxHighestWaitingPriority = prvGetDisinheritPriorityAfterTimeout( pxQueue ); /* vTaskPriorityDisinheritAfterTimeout uses the uxHighestWaitingPriority * parameter to index pxReadyTasksLists when adding the task holding * mutex to the ready list for its new priority. Coverity thinks that * it can result in out-of-bounds access which is not true because * uxHighestWaitingPriority, as returned by prvGetDisinheritPriorityAfterTimeout, * is capped at ( configMAX_PRIORITIES - 1 ). */ /* coverity[overrun] */ vTaskPriorityDisinheritAfterTimeout( pxQueue->u.xSemaphore.xMutexHolder, uxHighestWaitingPriority ); } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } } #endif /* configUSE_MUTEXES */ traceQUEUE_RECEIVE_FAILED( pxQueue ); traceRETURN_xQueueSemaphoreTake( errQUEUE_EMPTY ); return errQUEUE_EMPTY; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } }
3 . 事件组
前言 : FreeRTOS事件组是一种轻量级、高效率的多任务同步与通信机制,它专为应对多事件复杂等待场景而设计。与队列的点对点、顺序性数据传递不同,事件组的核心思想是 “状态标志” 和 “广播通知” 。它将多个独立的事件抽象为一个整型变量中的不同二进制位,允许任务等待一个或多个指定事件位的任意组合(“或”等待任一发生,“与”等待全部发生),并且任何任务或中断都可以设置或清除事件位。当一个事件位被设置时,内核可以同时唤醒所有正在等待该事件位的任务,实现高效的“一对多”广播式通知。这种设计使得事件组在处理多个松散事件源、实现复杂同步逻辑以及减少系统轮询开销方面具有独特优势,其源码实现围绕事件位的原子操作、多任务等待列表的高效管理以及从任务与中断的安全访问等核心环节展开。
事件组创建 Step1 :描述事件组创建与初始的过程
事件组发送 Step2 :任务/中断操作事件组发送的核心实现
事件组接收 Step3 :任务/中断操作事件组接收的核心实现
跳转置顶
-
事件组创建,描述 EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup = xEventGroupCreate();的内部过程;
1.1 :事件组创建和初始的过程;
1.1 :以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 中动态创建事件组的核心函数 xEventGroupCreate 的实现,它首先调用 pvPortMalloc 动态分配一个 EventGroup_t 结构体所需的内存空间;若分配成功,则对该事件组进行关键初始化:将核心状态变量 uxEventBits(存储所有事件位)清零,初始化用于管理阻塞任务的链表 xTasksWaitingForBits,并根据配置设置动态分配标志 ucStaticallyAllocated,最终返回该事件组的句柄;若内存分配失败,则记录失败信息并返回 NULL。此过程为事件组机制构建了基础状态容器和任务同步框架。
EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroupCreate( void ) { EventGroup_t * pxEventBits; traceENTER_xEventGroupCreate(); /* MISRA Ref 11.5.1 [Malloc memory assignment] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-115 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_5_violation] */ pxEventBits = ( EventGroup_t * ) pvPortMalloc( sizeof( EventGroup_t ) ); if( pxEventBits != NULL ) { pxEventBits->uxEventBits = 0; vListInitialise( &( pxEventBits->xTasksWaitingForBits ) ); #if ( configSUPPORT_STATIC_ALLOCATION == 1 ) { /* Both static and dynamic allocation can be used, so note this * event group was allocated statically in case the event group is * later deleted. */ pxEventBits->ucStaticallyAllocated = pdFALSE; } #endif /* configSUPPORT_STATIC_ALLOCATION */ traceEVENT_GROUP_CREATE( pxEventBits ); } else { traceEVENT_GROUP_CREATE_FAILED(); } traceRETURN_xEventGroupCreate( pxEventBits ); return pxEventBits; }
-
事件组设置,描述任务/中断设置事件组的内部过程;
2.1 :任务设置事件组的核心实现
2.2 :中断设置事件组的核心实现2.1 : 以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 事件组中用于设置事件位并触发任务同步的核心函数 xEventGroupSetBits 的实现。它在挂起任务调度器进入临界区后,通过位或操作将指定的事件位合并到事件组的状态变量 uxEventBits 中;随后遍历事件组的等待任务列表 xTasksWaitingForBits,针对其中每个任务,根据其等待模式(等待任意一位或所有位)和当前事件位状态进行匹配判断。若匹配成功,则根据任务的控制标志决定是否在退出时清除对应事件位,并将该任务从等待列表移至就绪列表,同时为其标记“因事件位匹配而解除阻塞”的状态;遍历完成后,统一清除所有需要清理的事件位,最后恢复任务调度并返回更新后的事件组状态。此过程以原子操作完成了事件位的设置、多任务条件匹配与唤醒,以及事件位清理的协同,是实现高效广播式任务同步的关键。
EventBits_t xEventGroupSetBits( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup, const EventBits_t uxBitsToSet ) { ListItem_t * pxListItem; ListItem_t * pxNext; ListItem_t const * pxListEnd; List_t const * pxList; EventBits_t uxBitsToClear = 0, uxBitsWaitedFor, uxControlBits; EventGroup_t * pxEventBits = xEventGroup; BaseType_t xMatchFound = pdFALSE; traceENTER_xEventGroupSetBits( xEventGroup, uxBitsToSet ); /* Check the user is not attempting to set the bits used by the kernel * itself. */ configASSERT( xEventGroup ); configASSERT( ( uxBitsToSet & eventEVENT_BITS_CONTROL_BYTES ) == 0 ); pxList = &( pxEventBits->xTasksWaitingForBits ); pxListEnd = listGET_END_MARKER( pxList ); vTaskSuspendAll(); { traceEVENT_GROUP_SET_BITS( xEventGroup, uxBitsToSet ); pxListItem = listGET_HEAD_ENTRY( pxList ); /* Set the bits. */ pxEventBits->uxEventBits |= uxBitsToSet; /* See if the new bit value should unblock any tasks. */ while( pxListItem != pxListEnd ) { pxNext = listGET_NEXT( pxListItem ); uxBitsWaitedFor = listGET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( pxListItem ); xMatchFound = pdFALSE; /* Split the bits waited for from the control bits. */ uxControlBits = uxBitsWaitedFor & eventEVENT_BITS_CONTROL_BYTES; uxBitsWaitedFor &= ~eventEVENT_BITS_CONTROL_BYTES; if( ( uxControlBits & eventWAIT_FOR_ALL_BITS ) == ( EventBits_t ) 0 ) { /* Just looking for single bit being set. */ if( ( uxBitsWaitedFor & pxEventBits->uxEventBits ) != ( EventBits_t ) 0 ) { xMatchFound = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else if( ( uxBitsWaitedFor & pxEventBits->uxEventBits ) == uxBitsWaitedFor ) { /* All bits are set. */ xMatchFound = pdTRUE; } else { /* Need all bits to be set, but not all the bits were set. */ } if( xMatchFound != pdFALSE ) { /* The bits match. Should the bits be cleared on exit? */ if( ( uxControlBits & eventCLEAR_EVENTS_ON_EXIT_BIT ) != ( EventBits_t ) 0 ) { uxBitsToClear |= uxBitsWaitedFor; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* Store the actual event flag value in the task's event list * item before removing the task from the event list. The * eventUNBLOCKED_DUE_TO_BIT_SET bit is set so the task knows * that is was unblocked due to its required bits matching, rather * than because it timed out. */ vTaskRemoveFromUnorderedEventList( pxListItem, pxEventBits->uxEventBits | eventUNBLOCKED_DUE_TO_BIT_SET ); } /* Move onto the next list item. Note pxListItem->pxNext is not * used here as the list item may have been removed from the event list * and inserted into the ready/pending reading list. */ pxListItem = pxNext; } /* Clear any bits that matched when the eventCLEAR_EVENTS_ON_EXIT_BIT * bit was set in the control word. */ pxEventBits->uxEventBits &= ~uxBitsToClear; } ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); traceRETURN_xEventGroupSetBits( pxEventBits->uxEventBits ); return pxEventBits->uxEventBits; }
2.2 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中事件组在中断服务程序(ISR)内设置事件位的核心函数 xEventGroupSetBitsFromISR 的实现,它并不直接操作事件组,而是通过调用 xTimerPendFunctionCallFromISR 函数,将实际设置事件位的工作(即调用 vEventGroupSetBitsCallback 回调函数)连同事件组句柄和待设置的事件位值,作为延迟函数调用(Deferred Function Call)请求,安全地提交给高优先级的定时器服务任务(Daemon Task) 去异步执行,从而保证了中断服务程序本身的快速响应与退出;此函数同时会通过 pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken 参数返回一个标志,指示该延迟操作是否可能唤醒了一个优先级高于当前被中断任务的、从而需要在中断退出时请求一次上下文切换。这种设计巧妙地将中断上下文中的复杂逻辑(如遍历任务等待列表、执行条件匹配与唤醒)延迟到任务上下文中完成,是FreeRTOS实现中断安全与系统实时性平衡的经典范例。
BaseType_t xEventGroupSetBitsFromISR( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup, const EventBits_t uxBitsToSet, BaseType_t * pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ) { BaseType_t xReturn; traceENTER_xEventGroupSetBitsFromISR( xEventGroup, uxBitsToSet, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); traceEVENT_GROUP_SET_BITS_FROM_ISR( xEventGroup, uxBitsToSet ); xReturn = xTimerPendFunctionCallFromISR( vEventGroupSetBitsCallback, ( void * ) xEventGroup, ( uint32_t ) uxBitsToSet, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); traceRETURN_xEventGroupSetBitsFromISR( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
-
事件组接收,描述任务/中断响应事件组的内部过程;
3.1 :任务接收事件组的核心实现
3.2 :中断接收事件组的核心实现
3.1 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中事件组等待函数 xEventGroupWaitBits 的核心实现,它首先挂起任务调度器进入临界区,并立即检查当前事件位是否已满足任务指定的等待条件(全部位或任意位):若条件已满足,则根据 xClearOnExit 参数决定是否清除相应事件位,然后直接返回当前事件值;若条件未满足但阻塞时间为零,则直接返回当前事件值并标记超时;若需要阻塞等待,则将任务的等待条件(包括待等待的位、清除标志及等待模式)组合后存入任务的事件列表项,并将任务挂入事件组的等待列表 xTasksWaitingForBits,随后恢复调度器并主动执行任务切换使任务进入阻塞态。当任务因事件位被设置或超时而解除阻塞后,函数会从任务的事件列表项中取出结果:若因事件位匹配而唤醒,则返回匹配时的事件值并已自动处理清除标志;若因超时而唤醒,则再次进入临界区,重新检查事件位状态(防止在解除阻塞到再次运行期间事件位被修改)并做相应处理,最终返回超时时刻的事件值。此函数完整实现了事件组中任务的复杂条件等待、高效阻塞与唤醒机制,涵盖了条件即时满足、零阻塞返回、主动阻塞及超时处理等所有场景。
EventBits_t xEventGroupWaitBits( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup, const EventBits_t uxBitsToWaitFor, const BaseType_t xClearOnExit, const BaseType_t xWaitForAllBits, TickType_t xTicksToWait ) { EventGroup_t * pxEventBits = xEventGroup; EventBits_t uxReturn, uxControlBits = 0; BaseType_t xWaitConditionMet, xAlreadyYielded; BaseType_t xTimeoutOccurred = pdFALSE; traceENTER_xEventGroupWaitBits( xEventGroup, uxBitsToWaitFor, xClearOnExit, xWaitForAllBits, xTicksToWait ); /* Check the user is not attempting to wait on the bits used by the kernel * itself, and that at least one bit is being requested. */ configASSERT( xEventGroup ); configASSERT( ( uxBitsToWaitFor & eventEVENT_BITS_CONTROL_BYTES ) == 0 ); configASSERT( uxBitsToWaitFor != 0 ); #if ( ( INCLUDE_xTaskGetSchedulerState == 1 ) || ( configUSE_TIMERS == 1 ) ) { configASSERT( !( ( xTaskGetSchedulerState() == taskSCHEDULER_SUSPENDED ) && ( xTicksToWait != 0 ) ) ); } #endif vTaskSuspendAll(); { const EventBits_t uxCurrentEventBits = pxEventBits->uxEventBits; /* Check to see if the wait condition is already met or not. */ xWaitConditionMet = prvTestWaitCondition( uxCurrentEventBits, uxBitsToWaitFor, xWaitForAllBits ); if( xWaitConditionMet != pdFALSE ) { /* The wait condition has already been met so there is no need to * block. */ uxReturn = uxCurrentEventBits; xTicksToWait = ( TickType_t ) 0; /* Clear the wait bits if requested to do so. */ if( xClearOnExit != pdFALSE ) { pxEventBits->uxEventBits &= ~uxBitsToWaitFor; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else if( xTicksToWait == ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { /* The wait condition has not been met, but no block time was * specified, so just return the current value. */ uxReturn = uxCurrentEventBits; xTimeoutOccurred = pdTRUE; } else { /* The task is going to block to wait for its required bits to be * set. uxControlBits are used to remember the specified behaviour of * this call to xEventGroupWaitBits() - for use when the event bits * unblock the task. */ if( xClearOnExit != pdFALSE ) { uxControlBits |= eventCLEAR_EVENTS_ON_EXIT_BIT; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } if( xWaitForAllBits != pdFALSE ) { uxControlBits |= eventWAIT_FOR_ALL_BITS; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* Store the bits that the calling task is waiting for in the * task's event list item so the kernel knows when a match is * found. Then enter the blocked state. */ vTaskPlaceOnUnorderedEventList( &( pxEventBits->xTasksWaitingForBits ), ( uxBitsToWaitFor | uxControlBits ), xTicksToWait ); /* This is obsolete as it will get set after the task unblocks, but * some compilers mistakenly generate a warning about the variable * being returned without being set if it is not done. */ uxReturn = 0; traceEVENT_GROUP_WAIT_BITS_BLOCK( xEventGroup, uxBitsToWaitFor ); } } xAlreadyYielded = xTaskResumeAll(); if( xTicksToWait != ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { if( xAlreadyYielded == pdFALSE ) { taskYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* The task blocked to wait for its required bits to be set - at this * point either the required bits were set or the block time expired. If * the required bits were set they will have been stored in the task's * event list item, and they should now be retrieved then cleared. */ uxReturn = uxTaskResetEventItemValue(); if( ( uxReturn & eventUNBLOCKED_DUE_TO_BIT_SET ) == ( EventBits_t ) 0 ) { taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { /* The task timed out, just return the current event bit value. */ uxReturn = pxEventBits->uxEventBits; /* It is possible that the event bits were updated between this * task leaving the Blocked state and running again. */ if( prvTestWaitCondition( uxReturn, uxBitsToWaitFor, xWaitForAllBits ) != pdFALSE ) { if( xClearOnExit != pdFALSE ) { pxEventBits->uxEventBits &= ~uxBitsToWaitFor; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } xTimeoutOccurred = pdTRUE; } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } else { /* The task unblocked because the bits were set. */ } /* The task blocked so control bits may have been set. */ uxReturn &= ~eventEVENT_BITS_CONTROL_BYTES; } traceEVENT_GROUP_WAIT_BITS_END( xEventGroup, uxBitsToWaitFor, xTimeoutOccurred ); /* Prevent compiler warnings when trace macros are not used. */ ( void ) xTimeoutOccurred; traceRETURN_xEventGroupWaitBits( uxReturn ); return uxReturn; }
3.2 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中供中断服务程序(ISR)安全读取事件组当前状态的核心函数 xEventGroupGetBitsFromISR 的实现,它通过调用 taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR 进入一个极短的中断级临界区,在此保护下直接获取事件组结构体中 uxEventBits 成员的当前值并保存为返回值,随后立即退出临界区并返回该值。此函数以完全非阻塞且线程安全的方式,为中断上下文提供了对共享事件组状态的瞬时“快照”式读取,确保在可能的多任务及中断并发访问下数据的一致性,并且由于其执行快速、不会引起任务切换,完美契合了中断服务程序对确定性与执行时效的严格要求。
EventBits_t xEventGroupGetBitsFromISR( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup ) { UBaseType_t uxSavedInterruptStatus; EventGroup_t const * const pxEventBits = xEventGroup; EventBits_t uxReturn; traceENTER_xEventGroupGetBitsFromISR( xEventGroup ); /* MISRA Ref 4.7.1 [Return value shall be checked] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#dir-47 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_directive_4_7_violation] */ uxSavedInterruptStatus = taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR(); { uxReturn = pxEventBits->uxEventBits; } taskEXIT_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR( uxSavedInterruptStatus ); traceRETURN_xEventGroupGetBitsFromISR( uxReturn ); return uxReturn; }
4 . 任务通知
前言 : 任务通知是 FreeRTOS 中一种极致轻量、高效的任务间通信与同步机制。其核心思想是为每个任务控制块(TCB)内嵌一组专用的通知值和状态标志,从而省去了独立通信对象的创建开销。它支持多种操作模式(如置位、递增、覆写),允许一个任务直接向另一个任务发送事件信号或数据(一个32位值),并可通过阻塞等待机制实现同步。考虑到中断响应速度,其对应的 FromISR 版本能在中断中安全地更新通知值和唤醒等待任务,并通过优先级比较决定是否需要在中断退出时触发任务切换。任务通知巧妙地复用了任务控制块中的现有字段,实现了堪比二值/计数信号量、事件组的功能,但速度更快、内存占用更少,其源码实现围绕通知值的设置、等待与查询等核心操作展开。
任务通知发送 Step2 :任务/中断操作任务通知发送的核心实现
任务通知接收 Step3 :任务/中断操作任务通知接收的核心实现
跳转置顶
-
任务通知发送,描述任务/中断发送任务通知的内部过程;
2.1 :任务发送任务通知的核心实现
2.2 :中断发送任务通知的核心实现2.1 : 以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 中任务通知机制的核心函数 xTaskGenericNotify 的实现,它在临界区保护下直接操作目标任务的控制块(TCB):首先保存原始通知值(若调用者请求),然后根据指定的 eAction(如置位、递增、覆写等)更新任务的 ulNotifiedValue 字段,并将任务的通知状态标记为“已接收”(taskNOTIFICATION_RECEIVED);关键在于,若任务原本正处于“等待通知”的阻塞状态(taskWAITING_NOTIFICATION),则立即将其从阻塞列表中移除并置入就绪列表,同时根据其优先级判断是否需要触发任务切换;若尝试无覆盖写时任务已存有未处理通知,则返回失败。此函数以极低开销实现了任务间的直接、灵活通信。
#define xTaskNotify( xTaskToNotify, ulValue, eAction ) \ xTaskGenericNotify( ( xTaskToNotify ), ( tskDEFAULT_INDEX_TO_NOTIFY ), ( ulValue ), ( eAction ), NULL ) BaseType_t xTaskGenericNotify( TaskHandle_t xTaskToNotify, UBaseType_t uxIndexToNotify, uint32_t ulValue, eNotifyAction eAction, uint32_t * pulPreviousNotificationValue ) { TCB_t * pxTCB; BaseType_t xReturn = pdPASS; uint8_t ucOriginalNotifyState; traceENTER_xTaskGenericNotify( xTaskToNotify, uxIndexToNotify, ulValue, eAction, pulPreviousNotificationValue ); configASSERT( uxIndexToNotify < configTASK_NOTIFICATION_ARRAY_ENTRIES ); configASSERT( xTaskToNotify ); pxTCB = xTaskToNotify; taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { if( pulPreviousNotificationValue != NULL ) { *pulPreviousNotificationValue = pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ]; } ucOriginalNotifyState = pxTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToNotify ]; pxTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToNotify ] = taskNOTIFICATION_RECEIVED; switch( eAction ) { case eSetBits: pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] |= ulValue; break; case eIncrement: ( pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] )++; break; case eSetValueWithOverwrite: pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] = ulValue; break; case eSetValueWithoutOverwrite: if( ucOriginalNotifyState != taskNOTIFICATION_RECEIVED ) { pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] = ulValue; } else { /* The value could not be written to the task. */ xReturn = pdFAIL; } break; case eNoAction: /* The task is being notified without its notify value being * updated. */ break; default: /* Should not get here if all enums are handled. * Artificially force an assert by testing a value the * compiler can't assume is const. */ configASSERT( xTickCount == ( TickType_t ) 0 ); break; } traceTASK_NOTIFY( uxIndexToNotify ); /* If the task is in the blocked state specifically to wait for a * notification then unblock it now. */ if( ucOriginalNotifyState == taskWAITING_NOTIFICATION ) { listREMOVE_ITEM( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ); prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB ); /* The task should not have been on an event list. */ configASSERT( listLIST_ITEM_CONTAINER( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ) == NULL ); #if ( configUSE_TICKLESS_IDLE != 0 ) { /* If a task is blocked waiting for a notification then * xNextTaskUnblockTime might be set to the blocked task's time * out time. If the task is unblocked for a reason other than * a timeout xNextTaskUnblockTime is normally left unchanged, * because it will automatically get reset to a new value when * the tick count equals xNextTaskUnblockTime. However if * tickless idling is used it might be more important to enter * sleep mode at the earliest possible time - so reset * xNextTaskUnblockTime here to ensure it is updated at the * earliest possible time. */ prvResetNextTaskUnblockTime(); } #endif /* Check if the notified task has a priority above the currently * executing task. */ taskYIELD_ANY_CORE_IF_USING_PREEMPTION( pxTCB ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceRETURN_xTaskGenericNotify( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
2.2 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中任务通知机制在中断服务程序(ISR)中使用的核心函数 xTaskGenericNotifyFromISR 的实现,它在验证中断优先级合法性后,通过 taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR 进入中断级临界区,直接操作目标任务的控制块(TCB)来更新通知值(根据 eAction 执行置位、递增、覆写等操作)并将状态标记为“已接收”;其关键逻辑在于:若目标任务原本处于“等待通知”的阻塞态,则根据调度器是否被挂起,选择将其立即移入就绪列表或暂挂于待处理就绪列表;同时,通过判断被唤醒任务的优先级是否高于当前被中断任务的优先级,来设置 pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken 输出标志(若提供了该参数),以告知调用者中断退出时是否需要请求一次上下文切换。此函数实现了中断上下文下高效、安全的直接任务间通信与唤醒。
BaseType_t xTaskGenericNotifyFromISR( TaskHandle_t xTaskToNotify, UBaseType_t uxIndexToNotify, uint32_t ulValue, eNotifyAction eAction, uint32_t * pulPreviousNotificationValue, BaseType_t * pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ) { TCB_t * pxTCB; uint8_t ucOriginalNotifyState; BaseType_t xReturn = pdPASS; UBaseType_t uxSavedInterruptStatus; traceENTER_xTaskGenericNotifyFromISR( xTaskToNotify, uxIndexToNotify, ulValue, eAction, pulPreviousNotificationValue, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); configASSERT( xTaskToNotify ); configASSERT( uxIndexToNotify < configTASK_NOTIFICATION_ARRAY_ENTRIES ); /* RTOS ports that support interrupt nesting have the concept of a * maximum system call (or maximum API call) interrupt priority. * Interrupts that are above the maximum system call priority are keep * permanently enabled, even when the RTOS kernel is in a critical section, * but cannot make any calls to FreeRTOS API functions. If configASSERT() * is defined in FreeRTOSConfig.h then * portASSERT_IF_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY_INVALID() will result in an assertion * failure if a FreeRTOS API function is called from an interrupt that has * been assigned a priority above the configured maximum system call * priority. Only FreeRTOS functions that end in FromISR can be called * from interrupts that have been assigned a priority at or (logically) * below the maximum system call interrupt priority. FreeRTOS maintains a * separate interrupt safe API to ensure interrupt entry is as fast and as * simple as possible. More information (albeit Cortex-M specific) is * provided on the following link: * https://www.FreeRTOS.org/RTOS-Cortex-M3-M4.html */ portASSERT_IF_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY_INVALID(); pxTCB = xTaskToNotify; /* MISRA Ref 4.7.1 [Return value shall be checked] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#dir-47 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_directive_4_7_violation] */ uxSavedInterruptStatus = ( UBaseType_t ) taskENTER_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR(); { if( pulPreviousNotificationValue != NULL ) { *pulPreviousNotificationValue = pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ]; } ucOriginalNotifyState = pxTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToNotify ]; pxTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToNotify ] = taskNOTIFICATION_RECEIVED; switch( eAction ) { case eSetBits: pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] |= ulValue; break; case eIncrement: ( pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] )++; break; case eSetValueWithOverwrite: pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] = ulValue; break; case eSetValueWithoutOverwrite: if( ucOriginalNotifyState != taskNOTIFICATION_RECEIVED ) { pxTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToNotify ] = ulValue; } else { /* The value could not be written to the task. */ xReturn = pdFAIL; } break; case eNoAction: /* The task is being notified without its notify value being * updated. */ break; default: /* Should not get here if all enums are handled. * Artificially force an assert by testing a value the * compiler can't assume is const. */ configASSERT( xTickCount == ( TickType_t ) 0 ); break; } traceTASK_NOTIFY_FROM_ISR( uxIndexToNotify ); /* If the task is in the blocked state specifically to wait for a * notification then unblock it now. */ if( ucOriginalNotifyState == taskWAITING_NOTIFICATION ) { /* The task should not have been on an event list. */ configASSERT( listLIST_ITEM_CONTAINER( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ) == NULL ); if( uxSchedulerSuspended == ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) { listREMOVE_ITEM( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ); prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB ); } else { /* The delayed and ready lists cannot be accessed, so hold * this task pending until the scheduler is resumed. */ listINSERT_END( &( xPendingReadyList ), &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ); } #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) { if( pxTCB->uxPriority > pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority ) { /* The notified task has a priority above the currently * executing task so a yield is required. */ if( pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken != NULL ) { *pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdTRUE; } /* Mark that a yield is pending in case the user is not * using the "xHigherPriorityTaskWoken" parameter to an ISR * safe FreeRTOS function. */ xYieldPendings[ 0 ] = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #else /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ { #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) { prvYieldForTask( pxTCB ); if( xYieldPendings[ portGET_CORE_ID() ] == pdTRUE ) { if( pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken != NULL ) { *pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdTRUE; } } } #endif /* if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) */ } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL_FROM_ISR( uxSavedInterruptStatus ); traceRETURN_xTaskGenericNotifyFromISR( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
-
任务通知接收,描述任务/中断接收任务通知的内部过程;
3.1 :任务接收任务通知的核心实现(任务通知主要通知对象是任务,因此无中断接收任务通知的函数)
3.1 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中任务等待通知的核心函数 xTaskGenericNotifyWait 的实现,它通过先挂起调度器再进入临界区的嵌套保护,检查当前任务的通知状态:若尚无通知待处理,则按参数清除指定的事件位,并将任务状态标记为“等待通知”;若指定了阻塞时间,则将任务置入阻塞态并启动超时计时。随后恢复调度器,任务可能因等待而让出CPU。当任务再次被调度(因收到通知或超时),函数在临界区内判断等待结果:若成功收到通知,则返回真并按参数清除退出位;若超时,则返回假。最后,无论结果如何,都将任务通知状态重置为“非等待”。此流程高效地实现了任务在指定通知位上的阻塞等待与同步。
#define xTaskNotifyWait( ulBitsToClearOnEntry, ulBitsToClearOnExit, pulNotificationValue, xTicksToWait ) \ xTaskGenericNotifyWait( tskDEFAULT_INDEX_TO_NOTIFY, ( ulBitsToClearOnEntry ), ( ulBitsToClearOnExit ), ( pulNotificationValue ), ( xTicksToWait ) ) BaseType_t xTaskGenericNotifyWait( UBaseType_t uxIndexToWaitOn, uint32_t ulBitsToClearOnEntry, uint32_t ulBitsToClearOnExit, uint32_t * pulNotificationValue, TickType_t xTicksToWait ) { BaseType_t xReturn, xAlreadyYielded, xShouldBlock = pdFALSE; traceENTER_xTaskGenericNotifyWait( uxIndexToWaitOn, ulBitsToClearOnEntry, ulBitsToClearOnExit, pulNotificationValue, xTicksToWait ); configASSERT( uxIndexToWaitOn < configTASK_NOTIFICATION_ARRAY_ENTRIES ); /* We suspend the scheduler here as prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList is a * non-deterministic operation. */ vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* We MUST enter a critical section to atomically check and update the * task notification value. If we do not do so, a notification from * an ISR will get lost. */ taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { /* Only block if a notification is not already pending. */ if( pxCurrentTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToWaitOn ] != taskNOTIFICATION_RECEIVED ) { /* Clear bits in the task's notification value as bits may get * set by the notifying task or interrupt. This can be used * to clear the value to zero. */ pxCurrentTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToWaitOn ] &= ~ulBitsToClearOnEntry; /* Mark this task as waiting for a notification. */ pxCurrentTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToWaitOn ] = taskWAITING_NOTIFICATION; if( xTicksToWait > ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { xShouldBlock = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); /* We are now out of the critical section but the scheduler is still * suspended, so we are safe to do non-deterministic operations such * as prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList. */ if( xShouldBlock == pdTRUE ) { traceTASK_NOTIFY_WAIT_BLOCK( uxIndexToWaitOn ); prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList( xTicksToWait, pdTRUE ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } xAlreadyYielded = xTaskResumeAll(); /* Force a reschedule if xTaskResumeAll has not already done so. */ if( ( xShouldBlock == pdTRUE ) && ( xAlreadyYielded == pdFALSE ) ) { taskYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { traceTASK_NOTIFY_WAIT( uxIndexToWaitOn ); if( pulNotificationValue != NULL ) { /* Output the current notification value, which may or may not * have changed. */ *pulNotificationValue = pxCurrentTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToWaitOn ]; } /* If ucNotifyValue is set then either the task never entered the * blocked state (because a notification was already pending) or the * task unblocked because of a notification. Otherwise the task * unblocked because of a timeout. */ if( pxCurrentTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToWaitOn ] != taskNOTIFICATION_RECEIVED ) { /* A notification was not received. */ xReturn = pdFALSE; } else { /* A notification was already pending or a notification was * received while the task was waiting. */ pxCurrentTCB->ulNotifiedValue[ uxIndexToWaitOn ] &= ~ulBitsToClearOnExit; xReturn = pdTRUE; } pxCurrentTCB->ucNotifyState[ uxIndexToWaitOn ] = taskNOT_WAITING_NOTIFICATION; } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceRETURN_xTaskGenericNotifyWait( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
5 . 流缓冲区
前言 :
- 流缓冲区是 FreeRTOS 中专门为面向字节流的单向异步数据传输而设计的通信机制。其数据结构核心是一个字节数组构成的环形缓冲区,通过读写位置指针来管理数据的流动,并记录缓冲区总容量及当前可用字节数。它允许任务在缓冲区空时阻塞等待数据到达,或在缓冲区满时阻塞等待空间释放,实现了生产者-消费者的流式同步。为适应中断环境,提供了中断安全版的发送与接收函数,确保了数据操作的原子性。流缓冲区的独特之处在于支持“触发级别” 设置,只有达到指定数据量时才唤醒等待任务,从而减少不必要的上下文切换。它通常与 “消息缓冲区” (在流缓冲区基础上增加了单条消息长度信息)配合使用,其源码实现围绕缓冲区的创建、字节流读写以及任务阻塞与唤醒等逻辑展开;
- FreeRTOS 中的流缓冲区机制采用了一种高度统一且可扩展的底层架构,其核心设计思想是:所有类型的缓冲区——普通流缓冲区、消息缓冲区和批处理缓冲区——都建立在同一套内部数据操作 API 之上(如 prvWriteMessageToBuffer 和 prvReadMessageFromBuffer),并通过在缓冲区控制结构体 StreamBuffer_t 中设置不同的标志位(ucFlags)和配置参数(如 xTriggerLevelBytes) 来实现行为的专项化。这种设计使得一个通用的环形缓冲区管理和字节流读写引擎,能够通过简单的条件分支和参数调整,分别服务于连续字节流传输、带长度的离散消息传递以及达到特定数据量才触发的批量处理这三种典型场景,从而在保证代码高度复用、维护一致接口与行为的基础上,以最小的运行时开销满足了多样化的通信需求。
流缓冲区创建 Step1 :描述流缓冲区创建与初始的过程
流缓冲区发送 Step2 :任务/中断操作流缓冲区发送的核心实现
流缓冲区接收 Step3 :任务/中断操作流缓冲区接收的核心实现
跳转置顶
-
流缓冲区创建,描述 StreamBufferHandle_t xStreamBufferCreate(size_t xBufferSizeBytes, size_t xTriggerLevelBytes); 的内部过程;
1.1 :流缓冲区创建的过程;
1.2 :流缓冲区初始的过程;
1.1 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS中流缓冲区通用创建函数xStreamBufferGenericCreate的核心实现,它首先根据缓冲区类型(流、消息或批处理)验证尺寸参数并设置标志位,然后对触发级别进行合理化处理(确保非零);在内存分配阶段,通过一次pvPortMalloc调用为流缓冲区控制结构StreamBuffer_t和实际存储区分配单块连续内存,并采用一个精妙的“尺寸加一”策略来确保后续报告的空闲空间与用户逻辑预期一致;若分配成功,则通过prvInitialiseNewStreamBuffer函数将控制结构置于内存块起始位置、存储区紧随其后,并完成读写指针、触发阈值、回调函数等核心成员的初始化,最终返回该流缓冲区句柄。
#define xStreamBufferCreate( xBufferSizeBytes, xTriggerLevelBytes ) \ xStreamBufferGenericCreate( ( xBufferSizeBytes ), ( xTriggerLevelBytes ), sbTYPE_STREAM_BUFFER, NULL, NULL ) StreamBufferHandle_t xStreamBufferGenericCreate( size_t xBufferSizeBytes, size_t xTriggerLevelBytes, BaseType_t xStreamBufferType, StreamBufferCallbackFunction_t pxSendCompletedCallback, StreamBufferCallbackFunction_t pxReceiveCompletedCallback ) { void * pvAllocatedMemory; uint8_t ucFlags; traceENTER_xStreamBufferGenericCreate( xBufferSizeBytes, xTriggerLevelBytes, xStreamBufferType, pxSendCompletedCallback, pxReceiveCompletedCallback ); /* In case the stream buffer is going to be used as a message buffer * (that is, it will hold discrete messages with a little meta data that * says how big the next message is) check the buffer will be large enough * to hold at least one message. */ if( xStreamBufferType == sbTYPE_MESSAGE_BUFFER ) { /* Is a message buffer but not statically allocated. */ ucFlags = sbFLAGS_IS_MESSAGE_BUFFER; configASSERT( xBufferSizeBytes > sbBYTES_TO_STORE_MESSAGE_LENGTH ); } else if( xStreamBufferType == sbTYPE_STREAM_BATCHING_BUFFER ) { /* Is a batching buffer but not statically allocated. */ ucFlags = sbFLAGS_IS_BATCHING_BUFFER; configASSERT( xBufferSizeBytes > 0 ); } else { /* Not a message buffer and not statically allocated. */ ucFlags = 0; configASSERT( xBufferSizeBytes > 0 ); } configASSERT( xTriggerLevelBytes <= xBufferSizeBytes ); /* A trigger level of 0 would cause a waiting task to unblock even when * the buffer was empty. */ if( xTriggerLevelBytes == ( size_t ) 0 ) { xTriggerLevelBytes = ( size_t ) 1; } /* A stream buffer requires a StreamBuffer_t structure and a buffer. * Both are allocated in a single call to pvPortMalloc(). The * StreamBuffer_t structure is placed at the start of the allocated memory * and the buffer follows immediately after. The requested size is * incremented so the free space is returned as the user would expect - * this is a quirk of the implementation that means otherwise the free * space would be reported as one byte smaller than would be logically * expected. */ if( xBufferSizeBytes < ( xBufferSizeBytes + 1U + sizeof( StreamBuffer_t ) ) ) { xBufferSizeBytes++; pvAllocatedMemory = pvPortMalloc( xBufferSizeBytes + sizeof( StreamBuffer_t ) ); } else { pvAllocatedMemory = NULL; } if( pvAllocatedMemory != NULL ) { /* MISRA Ref 11.5.1 [Malloc memory assignment] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-115 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_5_violation] */ prvInitialiseNewStreamBuffer( ( StreamBuffer_t * ) pvAllocatedMemory, /* Structure at the start of the allocated memory. */ /* MISRA Ref 11.5.1 [Malloc memory assignment] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-115 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_5_violation] */ ( ( uint8_t * ) pvAllocatedMemory ) + sizeof( StreamBuffer_t ), /* Storage area follows. */ xBufferSizeBytes, xTriggerLevelBytes, ucFlags, pxSendCompletedCallback, pxReceiveCompletedCallback ); traceSTREAM_BUFFER_CREATE( ( ( StreamBuffer_t * ) pvAllocatedMemory ), xStreamBufferType ); } else { traceSTREAM_BUFFER_CREATE_FAILED( xStreamBufferType ); } traceRETURN_xStreamBufferGenericCreate( pvAllocatedMemory ); /* MISRA Ref 11.5.1 [Malloc memory assignment] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-115 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_5_violation] */ return ( StreamBufferHandle_t ) pvAllocatedMemory; }
1.2 :以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 流缓冲区初始化函数 prvInitialiseNewStreamBuffer 的核心实现,它在调试模式下会先对存储缓冲区进行预填充以验证其可写性,随后将流缓冲区控制结构体 StreamBuffer_t 的内存清零,并依次设置其关键成员:指向独立存储区的指针 pucBuffer、总字节容量 xLength、唤醒阻塞任务的触发字节阈值 xTriggerLevelBytes、标识缓冲区类型(如消息缓冲区)的标志位 ucFlags、关联任务通知的索引 uxNotificationIndex,并根据系统配置选择性地设置发送与接收完成回调函数指针。此过程通过一次性地将控制结构与存储区关联并赋予初始状态,构建了一个完整就绪的流缓冲区操作基础。
static void prvInitialiseNewStreamBuffer( StreamBuffer_t * const pxStreamBuffer, uint8_t * const pucBuffer, size_t xBufferSizeBytes, size_t xTriggerLevelBytes, uint8_t ucFlags, StreamBufferCallbackFunction_t pxSendCompletedCallback, StreamBufferCallbackFunction_t pxReceiveCompletedCallback ) { /* Assert here is deliberately writing to the entire buffer to ensure it can * be written to without generating exceptions, and is setting the buffer to a * known value to assist in development/debugging. */ #if ( configASSERT_DEFINED == 1 ) { /* The value written just has to be identifiable when looking at the * memory. Don't use 0xA5 as that is the stack fill value and could * result in confusion as to what is actually being observed. */ #define STREAM_BUFFER_BUFFER_WRITE_VALUE ( 0x55 ) configASSERT( memset( pucBuffer, ( int ) STREAM_BUFFER_BUFFER_WRITE_VALUE, xBufferSizeBytes ) == pucBuffer ); } #endif ( void ) memset( ( void * ) pxStreamBuffer, 0x00, sizeof( StreamBuffer_t ) ); pxStreamBuffer->pucBuffer = pucBuffer; pxStreamBuffer->xLength = xBufferSizeBytes; pxStreamBuffer->xTriggerLevelBytes = xTriggerLevelBytes; pxStreamBuffer->ucFlags = ucFlags; pxStreamBuffer->uxNotificationIndex = tskDEFAULT_INDEX_TO_NOTIFY; #if ( configUSE_SB_COMPLETED_CALLBACK == 1 ) { pxStreamBuffer->pxSendCompletedCallback = pxSendCompletedCallback; pxStreamBuffer->pxReceiveCompletedCallback = pxReceiveCompletedCallback; } #else { /* MISRA Ref 11.1.1 [Object type casting] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-111 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_1_violation] */ ( void ) pxSendCompletedCallback; /* MISRA Ref 11.1.1 [Object type casting] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-111 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_1_violation] */ ( void ) pxReceiveCompletedCallback; } #endif /* if ( configUSE_SB_COMPLETED_CALLBACK == 1 ) */ }
-
事件组发送,描述任务/中断发送事件组的内部过程;
2.1 :任务发送流缓冲区的核心实现
2.2 :中断发送流缓冲区的核心实现2.1 : 以下这段代码是FreeRTOS流缓冲区发送函数xStreamBufferSend的核心实现,它首先根据缓冲区类型(消息缓冲区或流缓冲区)计算所需空间并进行边界检查:对于消息缓冲区需额外包含长度信息且必须完整写入,对于流缓冲区则可部分写入。若指定了阻塞时间,函数会通过任务通知机制在临界区内循环检查可用空间,若空间不足则将当前任务记录为等待发送任务并进入阻塞态等待空间释放或超时。获得空间后,调用prvWriteMessageToBuffer执行实际的数据写入。若写入成功且缓冲区中的数据量达到了预设的触发水平(xTriggerLevelBytes),则通过prvSEND_COMPLETED唤醒等待接收的任务。最终函数返回实际写入的字节数,完整实现了支持阻塞等待、类型自适应及触发唤醒的流式数据发送机制。
size_t xStreamBufferSend( StreamBufferHandle_t xStreamBuffer, const void * pvTxData, size_t xDataLengthBytes, TickType_t xTicksToWait ) { StreamBuffer_t * const pxStreamBuffer = xStreamBuffer; size_t xReturn, xSpace = 0; size_t xRequiredSpace = xDataLengthBytes; TimeOut_t xTimeOut; size_t xMaxReportedSpace = 0; traceENTER_xStreamBufferSend( xStreamBuffer, pvTxData, xDataLengthBytes, xTicksToWait ); configASSERT( pvTxData ); configASSERT( pxStreamBuffer ); /* The maximum amount of space a stream buffer will ever report is its length * minus 1. */ xMaxReportedSpace = pxStreamBuffer->xLength - ( size_t ) 1; /* This send function is used to write to both message buffers and stream * buffers. If this is a message buffer then the space needed must be * increased by the amount of bytes needed to store the length of the * message. */ if( ( pxStreamBuffer->ucFlags & sbFLAGS_IS_MESSAGE_BUFFER ) != ( uint8_t ) 0 ) { xRequiredSpace += sbBYTES_TO_STORE_MESSAGE_LENGTH; /* Overflow? */ configASSERT( xRequiredSpace > xDataLengthBytes ); /* If this is a message buffer then it must be possible to write the * whole message. */ if( xRequiredSpace > xMaxReportedSpace ) { /* The message would not fit even if the entire buffer was empty, * so don't wait for space. */ xTicksToWait = ( TickType_t ) 0; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { /* If this is a stream buffer then it is acceptable to write only part * of the message to the buffer. Cap the length to the total length of * the buffer. */ if( xRequiredSpace > xMaxReportedSpace ) { xRequiredSpace = xMaxReportedSpace; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } if( xTicksToWait != ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { vTaskSetTimeOutState( &xTimeOut ); do { /* Wait until the required number of bytes are free in the message * buffer. */ taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { xSpace = xStreamBufferSpacesAvailable( pxStreamBuffer ); if( xSpace < xRequiredSpace ) { /* Clear notification state as going to wait for space. */ ( void ) xTaskNotifyStateClearIndexed( NULL, pxStreamBuffer->uxNotificationIndex ); /* Should only be one writer. */ configASSERT( pxStreamBuffer->xTaskWaitingToSend == NULL ); pxStreamBuffer->xTaskWaitingToSend = xTaskGetCurrentTaskHandle(); } else { taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); break; } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); traceBLOCKING_ON_STREAM_BUFFER_SEND( xStreamBuffer ); ( void ) xTaskNotifyWaitIndexed( pxStreamBuffer->uxNotificationIndex, ( uint32_t ) 0, ( uint32_t ) 0, NULL, xTicksToWait ); pxStreamBuffer->xTaskWaitingToSend = NULL; } while( xTaskCheckForTimeOut( &xTimeOut, &xTicksToWait ) == pdFALSE ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } if( xSpace == ( size_t ) 0 ) { xSpace = xStreamBufferSpacesAvailable( pxStreamBuffer ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } xReturn = prvWriteMessageToBuffer( pxStreamBuffer, pvTxData, xDataLengthBytes, xSpace, xRequiredSpace ); if( xReturn > ( size_t ) 0 ) { traceSTREAM_BUFFER_SEND( xStreamBuffer, xReturn ); /* Was a task waiting for the data? */ if( prvBytesInBuffer( pxStreamBuffer ) >= pxStreamBuffer->xTriggerLevelBytes ) { prvSEND_COMPLETED( pxStreamBuffer ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); traceSTREAM_BUFFER_SEND_FAILED( xStreamBuffer ); } traceRETURN_xStreamBufferSend( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
2.2 :以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 流缓冲区在中断服务程序中发送数据的核心函数 xStreamBufferSendFromISR 的实现,它在中断上下文中直接根据缓冲区类型(消息缓冲区需额外计入长度存储开销)计算所需空间并检查当前可用容量,随后调用 prvWriteMessageToBuffer 尝试执行非阻塞的数据写入操作。若写入成功且写入后缓冲区内的数据总量达到或超过了预设的触发水平(xTriggerLevelBytes),则通过 prvSEND_COMPLETE_FROM_ISR 函数唤醒可能正在等待接收数据的任务,并借助 pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken 参数输出上下文切换请求,最终返回实际写入的字节数,实现了中断环境下高效、无阻塞的流式数据传输与同步。
size_t xStreamBufferSendFromISR( StreamBufferHandle_t xStreamBuffer, const void * pvTxData, size_t xDataLengthBytes, BaseType_t * const pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ) { StreamBuffer_t * const pxStreamBuffer = xStreamBuffer; size_t xReturn, xSpace; size_t xRequiredSpace = xDataLengthBytes; traceENTER_xStreamBufferSendFromISR( xStreamBuffer, pvTxData, xDataLengthBytes, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); configASSERT( pvTxData ); configASSERT( pxStreamBuffer ); /* This send function is used to write to both message buffers and stream * buffers. If this is a message buffer then the space needed must be * increased by the amount of bytes needed to store the length of the * message. */ if( ( pxStreamBuffer->ucFlags & sbFLAGS_IS_MESSAGE_BUFFER ) != ( uint8_t ) 0 ) { xRequiredSpace += sbBYTES_TO_STORE_MESSAGE_LENGTH; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } xSpace = xStreamBufferSpacesAvailable( pxStreamBuffer ); xReturn = prvWriteMessageToBuffer( pxStreamBuffer, pvTxData, xDataLengthBytes, xSpace, xRequiredSpace ); if( xReturn > ( size_t ) 0 ) { /* Was a task waiting for the data? */ if( prvBytesInBuffer( pxStreamBuffer ) >= pxStreamBuffer->xTriggerLevelBytes ) { /* MISRA Ref 4.7.1 [Return value shall be checked] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#dir-47 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_directive_4_7_violation] */ prvSEND_COMPLETE_FROM_ISR( pxStreamBuffer, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceSTREAM_BUFFER_SEND_FROM_ISR( xStreamBuffer, xReturn ); traceRETURN_xStreamBufferSendFromISR( xReturn ); return xReturn; }
-
流缓冲区接收,描述任务/中断接收流缓冲区的内部过程;
3.1 :任务接收流缓冲区的核心实现
3.2 :中断接收流缓冲区的核心实现
3.1 :以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 流缓冲区接收函数 xStreamBufferReceive 的核心实现,它首先根据缓冲区类型确定需要提前满足的数据量阈值(消息缓冲区需包含长度信息,批处理缓冲区需达到触发水平),随后在指定阻塞时间的情况下,进入临界区检查当前数据量:若数据不足,则通过任务通知机制将当前任务记录为等待接收者并进入阻塞态,直至数据到达或超时。解除阻塞后,调用 prvReadMessageFromBuffer 执行实际数据读取。若读取成功,则通过 prvRECEIVE_COMPLETED 唤醒可能因缓冲区满而阻塞的发送任务。此函数完整实现了支持三种缓冲区类型、可阻塞等待及双向任务唤醒的流式数据接收机制。
size_t xStreamBufferReceive( StreamBufferHandle_t xStreamBuffer, void * pvRxData, size_t xBufferLengthBytes, TickType_t xTicksToWait ) { StreamBuffer_t * const pxStreamBuffer = xStreamBuffer; size_t xReceivedLength = 0, xBytesAvailable, xBytesToStoreMessageLength; traceENTER_xStreamBufferReceive( xStreamBuffer, pvRxData, xBufferLengthBytes, xTicksToWait ); configASSERT( pvRxData ); configASSERT( pxStreamBuffer ); /* This receive function is used by both message buffers, which store * discrete messages, and stream buffers, which store a continuous stream of * bytes. Discrete messages include an additional * sbBYTES_TO_STORE_MESSAGE_LENGTH bytes that hold the length of the * message. */ if( ( pxStreamBuffer->ucFlags & sbFLAGS_IS_MESSAGE_BUFFER ) != ( uint8_t ) 0 ) { xBytesToStoreMessageLength = sbBYTES_TO_STORE_MESSAGE_LENGTH; } else if( ( pxStreamBuffer->ucFlags & sbFLAGS_IS_BATCHING_BUFFER ) != ( uint8_t ) 0 ) { /* Force task to block if the batching buffer contains less bytes than * the trigger level. */ xBytesToStoreMessageLength = pxStreamBuffer->xTriggerLevelBytes; } else { xBytesToStoreMessageLength = 0; } if( xTicksToWait != ( TickType_t ) 0 ) { /* Checking if there is data and clearing the notification state must be * performed atomically. */ taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { xBytesAvailable = prvBytesInBuffer( pxStreamBuffer ); /* If this function was invoked by a message buffer read then * xBytesToStoreMessageLength holds the number of bytes used to hold * the length of the next discrete message. If this function was * invoked by a stream buffer read then xBytesToStoreMessageLength will * be 0. If this function was invoked by a stream batch buffer read * then xBytesToStoreMessageLength will be xTriggerLevelBytes value * for the buffer.*/ if( xBytesAvailable <= xBytesToStoreMessageLength ) { /* Clear notification state as going to wait for data. */ ( void ) xTaskNotifyStateClearIndexed( NULL, pxStreamBuffer->uxNotificationIndex ); /* Should only be one reader. */ configASSERT( pxStreamBuffer->xTaskWaitingToReceive == NULL ); pxStreamBuffer->xTaskWaitingToReceive = xTaskGetCurrentTaskHandle(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); if( xBytesAvailable <= xBytesToStoreMessageLength ) { /* Wait for data to be available. */ traceBLOCKING_ON_STREAM_BUFFER_RECEIVE( xStreamBuffer ); ( void ) xTaskNotifyWaitIndexed( pxStreamBuffer->uxNotificationIndex, ( uint32_t ) 0, ( uint32_t ) 0, NULL, xTicksToWait ); pxStreamBuffer->xTaskWaitingToReceive = NULL; /* Recheck the data available after blocking. */ xBytesAvailable = prvBytesInBuffer( pxStreamBuffer ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { xBytesAvailable = prvBytesInBuffer( pxStreamBuffer ); } /* Whether receiving a discrete message (where xBytesToStoreMessageLength * holds the number of bytes used to store the message length) or a stream of * bytes (where xBytesToStoreMessageLength is zero), the number of bytes * available must be greater than xBytesToStoreMessageLength to be able to * read bytes from the buffer. */ if( xBytesAvailable > xBytesToStoreMessageLength ) { xReceivedLength = prvReadMessageFromBuffer( pxStreamBuffer, pvRxData, xBufferLengthBytes, xBytesAvailable ); /* Was a task waiting for space in the buffer? */ if( xReceivedLength != ( size_t ) 0 ) { traceSTREAM_BUFFER_RECEIVE( xStreamBuffer, xReceivedLength ); prvRECEIVE_COMPLETED( xStreamBuffer ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { traceSTREAM_BUFFER_RECEIVE_FAILED( xStreamBuffer ); mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceRETURN_xStreamBufferReceive( xReceivedLength ); return xReceivedLength; }
3.2 :以下这段代码是 FreeRTOS 流缓冲区在中断服务程序中接收数据的核心函数 xStreamBufferReceiveFromISR 的实现,它首先根据缓冲区类型标识判断本次读取是否需考虑消息长度开销,随后直接获取当前缓冲区中的数据总量;若数据量足以满足读取条件(对于消息缓冲区需包含长度信息),则调用 prvReadMessageFromBuffer 执行非阻塞的数据读取。读取成功后,通过 prvRECEIVE_COMPLETED_FROM_ISR 函数检查并唤醒可能因缓冲区满而等待的发送任务,并借助 pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken 参数传递上下文切换请求,最终返回实际读取的字节数,实现了在中断环境下高效、安全的数据消费与任务同步。
size_t xStreamBufferReceiveFromISR( StreamBufferHandle_t xStreamBuffer, void * pvRxData, size_t xBufferLengthBytes, BaseType_t * const pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ) { StreamBuffer_t * const pxStreamBuffer = xStreamBuffer; size_t xReceivedLength = 0, xBytesAvailable, xBytesToStoreMessageLength; traceENTER_xStreamBufferReceiveFromISR( xStreamBuffer, pvRxData, xBufferLengthBytes, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); configASSERT( pvRxData ); configASSERT( pxStreamBuffer ); /* This receive function is used by both message buffers, which store * discrete messages, and stream buffers, which store a continuous stream of * bytes. Discrete messages include an additional * sbBYTES_TO_STORE_MESSAGE_LENGTH bytes that hold the length of the * message. */ if( ( pxStreamBuffer->ucFlags & sbFLAGS_IS_MESSAGE_BUFFER ) != ( uint8_t ) 0 ) { xBytesToStoreMessageLength = sbBYTES_TO_STORE_MESSAGE_LENGTH; } else { xBytesToStoreMessageLength = 0; } xBytesAvailable = prvBytesInBuffer( pxStreamBuffer ); /* Whether receiving a discrete message (where xBytesToStoreMessageLength * holds the number of bytes used to store the message length) or a stream of * bytes (where xBytesToStoreMessageLength is zero), the number of bytes * available must be greater than xBytesToStoreMessageLength to be able to * read bytes from the buffer. */ if( xBytesAvailable > xBytesToStoreMessageLength ) { xReceivedLength = prvReadMessageFromBuffer( pxStreamBuffer, pvRxData, xBufferLengthBytes, xBytesAvailable ); /* Was a task waiting for space in the buffer? */ if( xReceivedLength != ( size_t ) 0 ) { /* MISRA Ref 4.7.1 [Return value shall be checked] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#dir-47 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_directive_4_7_violation] */ prvRECEIVE_COMPLETED_FROM_ISR( pxStreamBuffer, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceSTREAM_BUFFER_RECEIVE_FROM_ISR( xStreamBuffer, xReceivedLength ); traceRETURN_xStreamBufferReceiveFromISR( xReceivedLength ); return xReceivedLength; }
七. 源码 : 调度细节
1 . 临界区
-
vTaskSuspendAll () 与 xTaskResumeAll()实现与意义
1.1 :挂起调度器里面其实记录临界区嵌套的深度,嵌套计数器的本质意义:提供了一种可靠的所有权模型,确保调度器的恢复时机完全由最外层的调用者控制,从而保护复杂的、多层次的临界区代码,避免了因模块间协作不当而导致的调度器过早恢复问题。void vTaskSuspendAll( void ) { portSOFTWARE_BARRIER(); //关闭中断 uxSchedulerSuspended = ( UBaseType_t ) ( uxSchedulerSuspended + 1U ); //重点,调度 portMEMORY_BARRIER(); //打开中断 }1.2 :以下这是FreeRTOS中恢复调度器的核心函数,主要完成三项关键操作:首先递减调度器挂起计数器,当计数器归零时真正恢复调度;然后处理挂起期间积累的待就绪任务,将它们从挂起就绪列表移动到适当的就绪列表;最后处理挂起期间累积的系统节拍中断,更新系统时间和延迟任务状态。如果这些操作导致更高优先级的任务就绪,则会触发任务切换,确保系统恢复正常调度运行,总而言之恢复临界区这段时间积累在xPendingReadyList上的任务,处理Tick的积累,若是其中有优先级高的任务则立即切换,调度切换回来后 xAlreadyYielded 为Ture,告知上层我已切换任务调度过。
BaseType_t xTaskResumeAll( void ) { TCB_t * pxTCB = NULL; BaseType_t xAlreadyYielded = pdFALSE; traceENTER_xTaskResumeAll(); #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) if( xSchedulerRunning != pdFALSE ) #endif { /* It is possible that an ISR caused a task to be removed from an event * list while the scheduler was suspended. If this was the case then the * removed task will have been added to the xPendingReadyList. Once the * scheduler has been resumed it is safe to move all the pending ready * tasks from this list into their appropriate ready list. */ taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { BaseType_t xCoreID; xCoreID = ( BaseType_t ) portGET_CORE_ID(); /* If uxSchedulerSuspended is zero then this function does not match a * previous call to vTaskSuspendAll(). */ configASSERT( uxSchedulerSuspended != 0U ); uxSchedulerSuspended = ( UBaseType_t ) ( uxSchedulerSuspended - 1U ); portRELEASE_TASK_LOCK(); if( uxSchedulerSuspended == ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) { if( uxCurrentNumberOfTasks > ( UBaseType_t ) 0U ) { /* Move any readied tasks from the pending list into the * appropriate ready list. */ while( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( &xPendingReadyList ) == pdFALSE ) { /* MISRA Ref 11.5.3 [Void pointer assignment] */ /* More details at: https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel/blob/main/MISRA.md#rule-115 */ /* coverity[misra_c_2012_rule_11_5_violation] */ pxTCB = listGET_OWNER_OF_HEAD_ENTRY( ( &xPendingReadyList ) ); listREMOVE_ITEM( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ); portMEMORY_BARRIER(); listREMOVE_ITEM( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ); prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB ); #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) { /* If the moved task has a priority higher than the current * task then a yield must be performed. */ if( pxTCB->uxPriority > pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority ) { xYieldPendings[ xCoreID ] = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #else /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ { /* All appropriate tasks yield at the moment a task is added to xPendingReadyList. * If the current core yielded then vTaskSwitchContext() has already been called * which sets xYieldPendings for the current core to pdTRUE. */ } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ } if( pxTCB != NULL ) { /* A task was unblocked while the scheduler was suspended, * which may have prevented the next unblock time from being * re-calculated, in which case re-calculate it now. Mainly * important for low power tickless implementations, where * this can prevent an unnecessary exit from low power * state. */ prvResetNextTaskUnblockTime(); } /* If any ticks occurred while the scheduler was suspended then * they should be processed now. This ensures the tick count does * not slip, and that any delayed tasks are resumed at the correct * time. * * It should be safe to call xTaskIncrementTick here from any core * since we are in a critical section and xTaskIncrementTick itself * protects itself within a critical section. Suspending the scheduler * from any core causes xTaskIncrementTick to increment uxPendedCounts. */ { TickType_t xPendedCounts = xPendedTicks; /* Non-volatile copy. */ if( xPendedCounts > ( TickType_t ) 0U ) { do { if( xTaskIncrementTick() != pdFALSE ) { /* Other cores are interrupted from * within xTaskIncrementTick(). */ xYieldPendings[ xCoreID ] = pdTRUE; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } --xPendedCounts; } while( xPendedCounts > ( TickType_t ) 0U ); xPendedTicks = 0; } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } if( xYieldPendings[ xCoreID ] != pdFALSE ) { #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION != 0 ) { xAlreadyYielded = pdTRUE; } #endif /* #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION != 0 ) */ #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) { taskYIELD_TASK_CORE_IF_USING_PREEMPTION( pxCurrentTCB ); } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } traceRETURN_xTaskResumeAll( xAlreadyYielded ); return xAlreadyYielded; }
2 . 管理任务
-
管理任务
2.1 :vTaskSuspend(TaskHandle); 以下这段代码实现了FreeRTOS中挂起任务的核心功能:首先获取要挂起任务的控制块,然后将其从就绪/延迟列表中移除并插入挂起任务列表,同时如果任务正在等待事件或通知也会进行清理;在多核环境下还需确保任务从运行核心上被驱逐,最后根据是否挂起的是当前运行任务来决定是否触发任务切换,以维护系统调度的正确性
void vTaskSuspend( TaskHandle_t xTaskToSuspend ) { TCB_t * pxTCB; traceENTER_vTaskSuspend( xTaskToSuspend ); taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { /* If null is passed in here then it is the running task that is * being suspended. */ pxTCB = prvGetTCBFromHandle( xTaskToSuspend ); traceTASK_SUSPEND( pxTCB ); /* Remove task from the ready/delayed list and place in the * suspended list. */ if( uxListRemove( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ) == ( UBaseType_t ) 0 ) { taskRESET_READY_PRIORITY( pxTCB->uxPriority ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } /* Is the task waiting on an event also? */ if( listLIST_ITEM_CONTAINER( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ) != NULL ) { ( void ) uxListRemove( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } vListInsertEnd( &xSuspendedTaskList, &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ); #if ( configUSE_TASK_NOTIFICATIONS == 1 ) { BaseType_t x; for( x = ( BaseType_t ) 0; x < ( BaseType_t ) configTASK_NOTIFICATION_ARRAY_ENTRIES; x++ ) { if( pxTCB->ucNotifyState[ x ] == taskWAITING_NOTIFICATION ) { /* The task was blocked to wait for a notification, but is * now suspended, so no notification was received. */ pxTCB->ucNotifyState[ x ] = taskNOT_WAITING_NOTIFICATION; } } } #endif /* if ( configUSE_TASK_NOTIFICATIONS == 1 ) */ /* In the case of SMP, it is possible that the task being suspended * is running on another core. We must evict the task before * exiting the critical section to ensure that the task cannot * take an action which puts it back on ready/state/event list, * thereby nullifying the suspend operation. Once evicted, the * task won't be scheduled before it is resumed as it will no longer * be on the ready list. */ #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) { if( xSchedulerRunning != pdFALSE ) { /* Reset the next expected unblock time in case it referred to the * task that is now in the Suspended state. */ prvResetNextTaskUnblockTime(); if( taskTASK_IS_RUNNING( pxTCB ) == pdTRUE ) { if( pxTCB->xTaskRunState == ( BaseType_t ) portGET_CORE_ID() ) { /* The current task has just been suspended. */ configASSERT( uxSchedulerSuspended == 0 ); vTaskYieldWithinAPI(); } else { prvYieldCore( pxTCB->xTaskRunState ); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) */ } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) { UBaseType_t uxCurrentListLength; if( xSchedulerRunning != pdFALSE ) { /* Reset the next expected unblock time in case it referred to the * task that is now in the Suspended state. */ taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { prvResetNextTaskUnblockTime(); } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } if( pxTCB == pxCurrentTCB ) { if( xSchedulerRunning != pdFALSE ) { /* The current task has just been suspended. */ configASSERT( uxSchedulerSuspended == 0 ); portYIELD_WITHIN_API(); } else { /* The scheduler is not running, but the task that was pointed * to by pxCurrentTCB has just been suspended and pxCurrentTCB * must be adjusted to point to a different task. */ /* Use a temp variable as a distinct sequence point for reading * volatile variables prior to a comparison to ensure compliance * with MISRA C 2012 Rule 13.2. */ uxCurrentListLength = listCURRENT_LIST_LENGTH( &xSuspendedTaskList ); if( uxCurrentListLength == uxCurrentNumberOfTasks ) { /* No other tasks are ready, so set pxCurrentTCB back to * NULL so when the next task is created pxCurrentTCB will * be set to point to it no matter what its relative priority * is. */ pxCurrentTCB = NULL; } else { vTaskSwitchContext(); } } } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) */ traceRETURN_vTaskSuspend(); }2.2 :vTaskResume(TaskHandle); 以下这段代码实现了FreeRTOS中恢复挂起任务的功能:首先验证要恢复的任务句柄有效且不是当前运行的任务,然后进入临界区检查该任务是否确实处于挂起状态;如果是,则将其从挂起任务列表中移除并添加到就绪列表中,最后根据情况触发任务切换以保证调度器能正确响应任务状态变化。
void vTaskResume( TaskHandle_t xTaskToResume ) { TCB_t * const pxTCB = xTaskToResume; traceENTER_vTaskResume( xTaskToResume ); /* It does not make sense to resume the calling task. */ configASSERT( xTaskToResume ); #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES == 1 ) /* The parameter cannot be NULL as it is impossible to resume the * currently executing task. */ if( ( pxTCB != pxCurrentTCB ) && ( pxTCB != NULL ) ) #else /* The parameter cannot be NULL as it is impossible to resume the * currently executing task. It is also impossible to resume a task * that is actively running on another core but it is not safe * to check their run state here. Therefore, we get into a critical * section and check if the task is actually suspended or not. */ if( pxTCB != NULL ) #endif { taskENTER_CRITICAL(); { if( prvTaskIsTaskSuspended( pxTCB ) != pdFALSE ) { traceTASK_RESUME( pxTCB ); /* The ready list can be accessed even if the scheduler is * suspended because this is inside a critical section. */ ( void ) uxListRemove( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) ); prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB ); /* This yield may not cause the task just resumed to run, * but will leave the lists in the correct state for the * next yield. */ taskYIELD_ANY_CORE_IF_USING_PREEMPTION( pxTCB ); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } traceRETURN_vTaskResume(); }2.3 :以下这段代码是FreeRTOS空闲任务的完整实现,它在一个无限循环中执行多项关键后台管理功能:首先清理已终止任务的资源,然后在非抢占模式下主动让出CPU确保任务切换;在可抢占配置下,如果同优先级有其他就绪任务则执行优先级让步;接着调用用户自定义的空闲钩子函数以支持低功耗或后台处理;当启用Tickless低功耗模式时,会精确计算预期的空闲时间,挂起调度器后调用平台特定的低功耗进入函数使系统进入睡眠状态;最后在多核系统中还可能执行被动空闲钩子管理核心活动。整个设计使得空闲任务不仅作为CPU空闲时的占位符,更成为系统资源回收、功耗管理和多核协调的核心枢纽;FreeRTOS的低功耗简而言之就是看下一个任务多久到来,若时间充足则看有没有比空闲任务优先级高的任务在运行/就绪,若没有则调用低功耗API(用户自己实现) ,如果用户长时间休眠的情况下还可以手动关闭Tick中断,然后用外部中断来唤醒,至于中间损失掉的时间计数看用户要不要加RTC来补偿计数,或者不管它这样,若是补偿则唤醒后用户手动叠加Tick,但是要考虑Tick溢出的相关逻辑处理,通过WFI()/WFE()休眠; WFE通过中断或__SEV();手动设置事件唤醒对应的核,一般用WFI();
static portTASK_FUNCTION( prvIdleTask, pvParameters ) { /* Stop warnings. */ ( void ) pvParameters; /** THIS IS THE RTOS IDLE TASK - WHICH IS CREATED AUTOMATICALLY WHEN THE * SCHEDULER IS STARTED. **/ /* In case a task that has a secure context deletes itself, in which case * the idle task is responsible for deleting the task's secure context, if * any. */ portALLOCATE_SECURE_CONTEXT( configMINIMAL_SECURE_STACK_SIZE ); #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) { /* SMP all cores start up in the idle task. This initial yield gets the application * tasks started. */ taskYIELD(); } #endif /* #if ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) */ for( ; configCONTROL_INFINITE_LOOP(); ) { /* See if any tasks have deleted themselves - if so then the idle task * is responsible for freeing the deleted task's TCB and stack. */ prvCheckTasksWaitingTermination(); #if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 0 ) { /* If we are not using preemption we keep forcing a task switch to * see if any other task has become available. If we are using * preemption we don't need to do this as any task becoming available * will automatically get the processor anyway. */ taskYIELD(); } #endif /* configUSE_PREEMPTION */ #if ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configIDLE_SHOULD_YIELD == 1 ) ) { /* When using preemption tasks of equal priority will be * timesliced. If a task that is sharing the idle priority is ready * to run then the idle task should yield before the end of the * timeslice. * * A critical region is not required here as we are just reading from * the list, and an occasional incorrect value will not matter. If * the ready list at the idle priority contains one more task than the * number of idle tasks, which is equal to the configured numbers of cores * then a task other than the idle task is ready to execute. */ if( listCURRENT_LIST_LENGTH( &( pxReadyTasksLists[ tskIDLE_PRIORITY ] ) ) > ( UBaseType_t ) configNUMBER_OF_CORES ) { taskYIELD(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configIDLE_SHOULD_YIELD == 1 ) ) */ #if ( configUSE_IDLE_HOOK == 1 ) { /* Call the user defined function from within the idle task. */ vApplicationIdleHook(); } #endif /* configUSE_IDLE_HOOK */ /* This conditional compilation should use inequality to 0, not equality * to 1. This is to ensure portSUPPRESS_TICKS_AND_SLEEP() is called when * user defined low power mode implementations require * configUSE_TICKLESS_IDLE to be set to a value other than 1. */ #if ( configUSE_TICKLESS_IDLE != 0 ) { TickType_t xExpectedIdleTime; /* It is not desirable to suspend then resume the scheduler on * each iteration of the idle task. Therefore, a preliminary * test of the expected idle time is performed without the * scheduler suspended. The result here is not necessarily * valid. */ xExpectedIdleTime = prvGetExpectedIdleTime(); if( xExpectedIdleTime >= ( TickType_t ) configEXPECTED_IDLE_TIME_BEFORE_SLEEP ) { vTaskSuspendAll(); { /* Now the scheduler is suspended, the expected idle * time can be sampled again, and this time its value can * be used. */ configASSERT( xNextTaskUnblockTime >= xTickCount ); xExpectedIdleTime = prvGetExpectedIdleTime(); /* Define the following macro to set xExpectedIdleTime to 0 * if the application does not want * portSUPPRESS_TICKS_AND_SLEEP() to be called. */ configPRE_SUPPRESS_TICKS_AND_SLEEP_PROCESSING( xExpectedIdleTime ); if( xExpectedIdleTime >= ( TickType_t ) configEXPECTED_IDLE_TIME_BEFORE_SLEEP ) { traceLOW_POWER_IDLE_BEGIN(); portSUPPRESS_TICKS_AND_SLEEP( xExpectedIdleTime ); traceLOW_POWER_IDLE_END(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } ( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); } else { mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); } } #endif /* configUSE_TICKLESS_IDLE */ #if ( ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) && ( configUSE_PASSIVE_IDLE_HOOK == 1 ) ) { /* Call the user defined function from within the idle task. This * allows the application designer to add background functionality * without the overhead of a separate task. * * This hook is intended to manage core activity such as disabling cores that go idle. * * NOTE: vApplicationPassiveIdleHook() MUST NOT, UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES, * CALL A FUNCTION THAT MIGHT BLOCK. */ vApplicationPassiveIdleHook(); } #endif /* #if ( ( configNUMBER_OF_CORES > 1 ) && ( configUSE_PASSIVE_IDLE_HOOK == 1 ) ) */ } }
八 :总结
总结 :看完整篇文章,大家可以手戳一个RTOS了,FreeRTOS作为一个可裁剪的实时操作系统内核,其核心设计围绕任务调度展开:系统通过xTaskCreate动态创建任务,为每个任务分配独立的TCB控制块和栈空间,并依据优先级将任务组织就绪列表、延迟列表、挂起列表等多维度数据结构;vTaskStartScheduler启动调度后,系统依托Systick中断驱动时钟节拍,结合基于优先级的抢占式调度和时间片轮转机制,通过PendSV实现高效任务切换;系统提供多种内存分配策略管理堆空间,并通过队列、信号量、事件组等通信机制实现任务同步;其调度细节充分考虑了实时性需求,包括嵌套调度器支持、延迟列表的溢出处理、临界区保护及任务状态的无缝转换,最终构建了一个兼具高效性、可靠性和可配置性的嵌入式实时任务调度框架。
技术交流群: 745662457
技术探讨,项目研究























 4705
4705

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










