module softmax_data_memory (
input wire clk,
input wire rst_n,
// PORTA
input wire [11:0]BRAM_PORTA_1_addr,
input wire [31:0]BRAM_PORTA_1_din,
output wire [31:0]BRAM_PORTA_1_dout,
input wire BRAM_PORTA_1_en,
input wire BRAM_PORTA_1_rst,
input wire [3:0]BRAM_PORTA_1_we,
// PORTB
input wire [31:0] mem_addr,
input wire read_req,
output reg read_ack,
output wire [31:0] read_data,
input wire write_req,
input wire write_we,
input wire [31:0] write_data,
output reg write_ack
);
// 参数定义
parameter DATA_WIDTH = 32;
parameter MEMORY_SIZE = 2**11; // 内存大小(以32位为单位)
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 11; // 地址位宽 (2^32 )
parameter MEM_PRIMITIVE = "auto" ; //自动选择 Block/Distributed RAM
parameter MEM_INIT_FILE = "none" ;
parameter READ_LATENCY_A = 1 ;
parameter READ_LATENCY_B = 1 ;
// 地址转换(字节地址转换为字地址)
wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] word_addrb = mem_addr[ADDR_WIDTH+1:2];
// 原语控制信号
wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] doutb;
wire ena = BRAM_PORTA_1_en;
wire enb = write_req || read_req;
wire [0:0] wea = |BRAM_PORTA_1_we; //单bit 写使能
wire [0:0] web = write_we; //单bit 写使能
// 应答逻辑(独立于原语)
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
read_ack <= 1'b0;
write_ack <= 1'b0;
end else begin
read_ack <= read_req; //读延迟1周期
write_ack <= write_req & write_we; //写延迟1周期
end
end
// xpm_memory_tdpram: True Dual Port RAM
// Xilinx Parameterized Macro, version 2021.2
//PORTA-CPU; PORTB-SOFTMAX
xpm_memory_tdpram #(
.ADDR_WIDTH_A(ADDR_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.ADDR_WIDTH_B(ADDR_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.AUTO_SLEEP_TIME(0), // DECIMAL
.BYTE_WRITE_WIDTH_A(DATA_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.BYTE_WRITE_WIDTH_B(DATA_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.CASCADE_HEIGHT(0), // DECIMAL
.CLOCKING_MODE("common_clock"), // String
.ECC_MODE("no_ecc"), // String
.MEMORY_INIT_FILE(MEM_INIT_FILE), // String
.MEMORY_INIT_PARAM("0"), // String
.MEMORY_OPTIMIZATION("true"), // String
.MEMORY_PRIMITIVE(MEM_PRIMITIVE), // String
.MEMORY_SIZE(MEMORY_SIZE*DATA_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.MESSAGE_CONTROL(0), // DECIMAL
.READ_DATA_WIDTH_A(DATA_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.READ_DATA_WIDTH_B(DATA_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.READ_LATENCY_A(READ_LATENCY_A), // DECIMAL
.READ_LATENCY_B(READ_LATENCY_B), // DECIMAL
.READ_RESET_VALUE_A("0"), // String
.READ_RESET_VALUE_B("0"), // String
.RST_MODE_A("SYNC"), // String
.RST_MODE_B("SYNC"), // String
.SIM_ASSERT_CHK(1), // DECIMAL; 0=disable simulation messages, 1=enable simulation messages
.USE_EMBEDDED_CONSTRAINT(0), // DECIMAL
.USE_MEM_INIT(1), // DECIMAL
.USE_MEM_INIT_MMI(0), // DECIMAL
.WAKEUP_TIME("disable_sleep"), // String
.WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_A(DATA_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_B(DATA_WIDTH), // DECIMAL
.WRITE_MODE_A("no_change"), // String
.WRITE_MODE_B("no_change"), // String
.WRITE_PROTECT(1) // DECIMAL
)
xpm_memory_tdpram_inst (
.dbiterra(), // 1-bit output: Status signal to indicate double bit error occurrence
// on the data output of port A.
.dbiterrb(), // 1-bit output: Status signal to indicate double bit error occurrence
// on the data output of port A.
.douta(BRAM_PORTA_1_dout), // READ_DATA_WIDTH_A-bit output: Data output for port A read operations.
.doutb(read_data), // READ_DATA_WIDTH_B-bit output: Data output for port B read operations.
.sbiterra(), // 1-bit output: Status signal to indicate single bit error occurrence
// on the data output of port A.
.sbiterrb(), // 1-bit output: Status signal to indicate single bit error occurrence
// on the data output of port B.
.addra(BRAM_PORTA_1_addr), // ADDR_WIDTH_A-bit input: Address for port A write and read operations.
.addrb(word_addrb), // ADDR_WIDTH_B-bit input: Address for port B write and read operations.
.clka(clk), // 1-bit input: Clock signal for port A. Also clocks port B when
// parameter CLOCKING_MODE is "common_clock".
.clkb(clk), // 1-bit input: Clock signal for port B when parameter CLOCKING_MODE is
// "independent_clock". Unused when parameter CLOCKING_MODE is
// "common_clock".
.dina(BRAM_PORTA_1_din), // WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_A-bit input: Data input for port A write operations.
.dinb(write_data), // WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_B-bit input: Data input for port B write operations.
.ena(ena), // 1-bit input: Memory enable signal for port A. Must be high on clock
// cycles when read or write operations are initiated. Pipelined
// internally.
.enb(enb), // 1-bit input: Memory enable signal for port B. Must be high on clock
// cycles when read or write operations are initiated. Pipelined
// internally.
.injectdbiterra(1'b0), // 1-bit input: Controls double bit error injection on input data when
// ECC enabled (Error injection capability is not available in
// "decode_only" mode).
.injectdbiterrb(1'b0), // 1-bit input: Controls double bit error injection on input data when
// ECC enabled (Error injection capability is not available in
// "decode_only" mode).
.injectsbiterra(1'b0), // 1-bit input: Controls single bit error injection on input data when
// ECC enabled (Error injection capability is not available in
// "decode_only" mode).
.injectsbiterrb(1'b0), // 1-bit input: Controls single bit error injection on input data when
// ECC enabled (Error injection capability is not available in
// "decode_only" mode).
.regcea(1'b1), // 1-bit input: Clock Enable for the last register stage on the output
// data path.
.regceb(1'b1), // 1-bit input: Clock Enable for the last register stage on the output
// data path.
.rsta(~rst_n), // 1-bit input: Reset signal for the final port A output register stage.
// Synchronously resets output port douta to the value specified by
// parameter READ_RESET_VALUE_A.
.rstb(~rst_n), // 1-bit input: Reset signal for the final port B output register stage.
// Synchronously resets output port doutb to the value specified by
// parameter READ_RESET_VALUE_B.
.sleep(1'b0), // 1-bit input: sleep signal to enable the dynamic power saving feature.
.wea(wea), // WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_A/BYTE_WRITE_WIDTH_A-bit input: Write enable vector
// for port A input data port dina. 1 bit wide when word-wide writes are
// used. In byte-wide write configurations, each bit controls the
// writing one byte of dina to address addra. For example, to
// synchronously write only bits [15-8] of dina when WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_A
// is 32, wea would be 4'b0010.
.web(web) // WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_B/BYTE_WRITE_WIDTH_B-bit input: Write enable vector
// for port B input data port dinb. 1 bit wide when word-wide writes are
// used. In byte-wide write configurations, each bit controls the
// writing one byte of dinb to address addrb. For example, to
// synchronously write only bits [15-8] of dinb when WRITE_DATA_WIDTH_B
// is 32, web would be 4'b0010.
);
// End of xpm_memory_tdpram_inst instantiation
endmodule
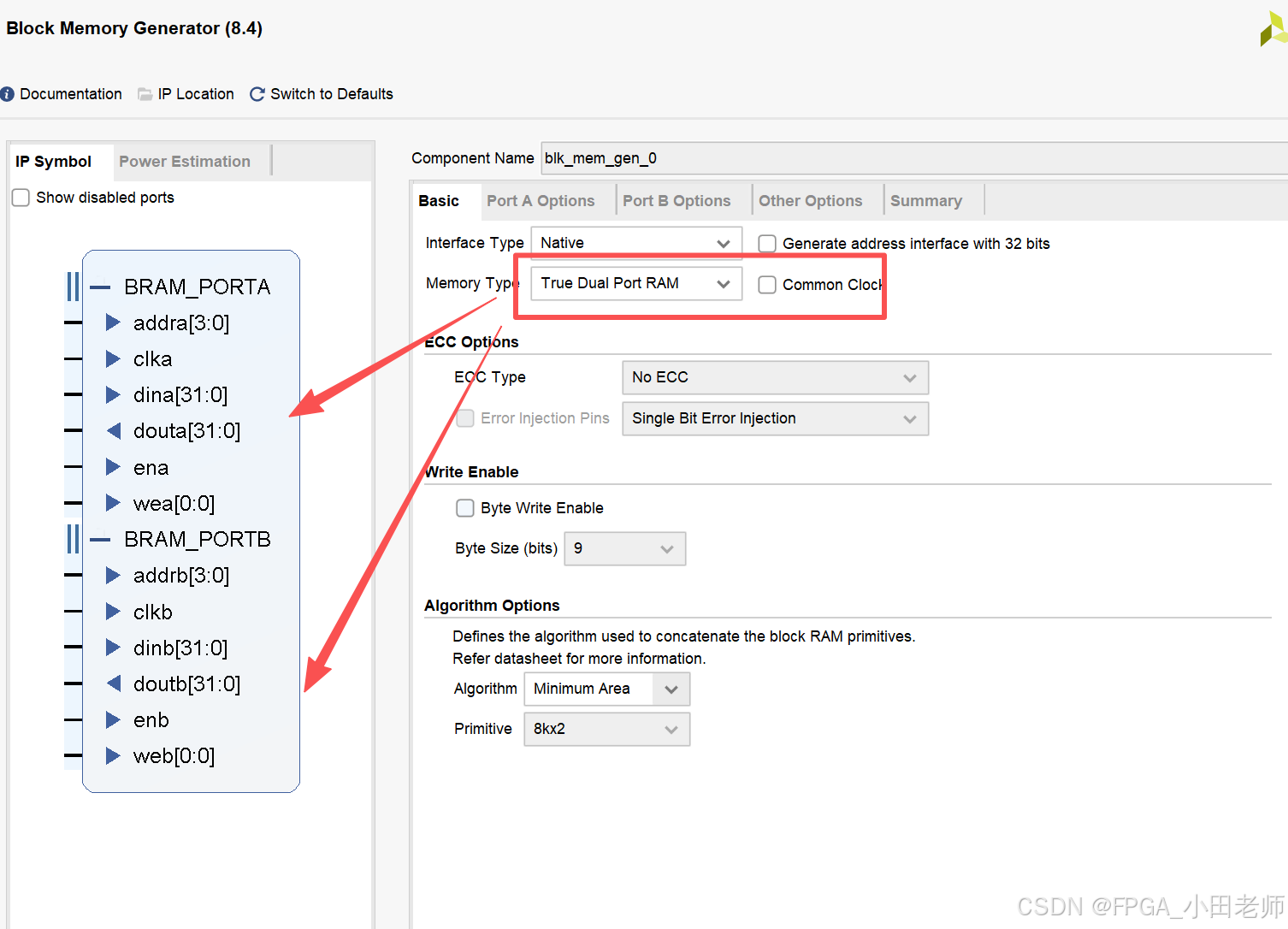
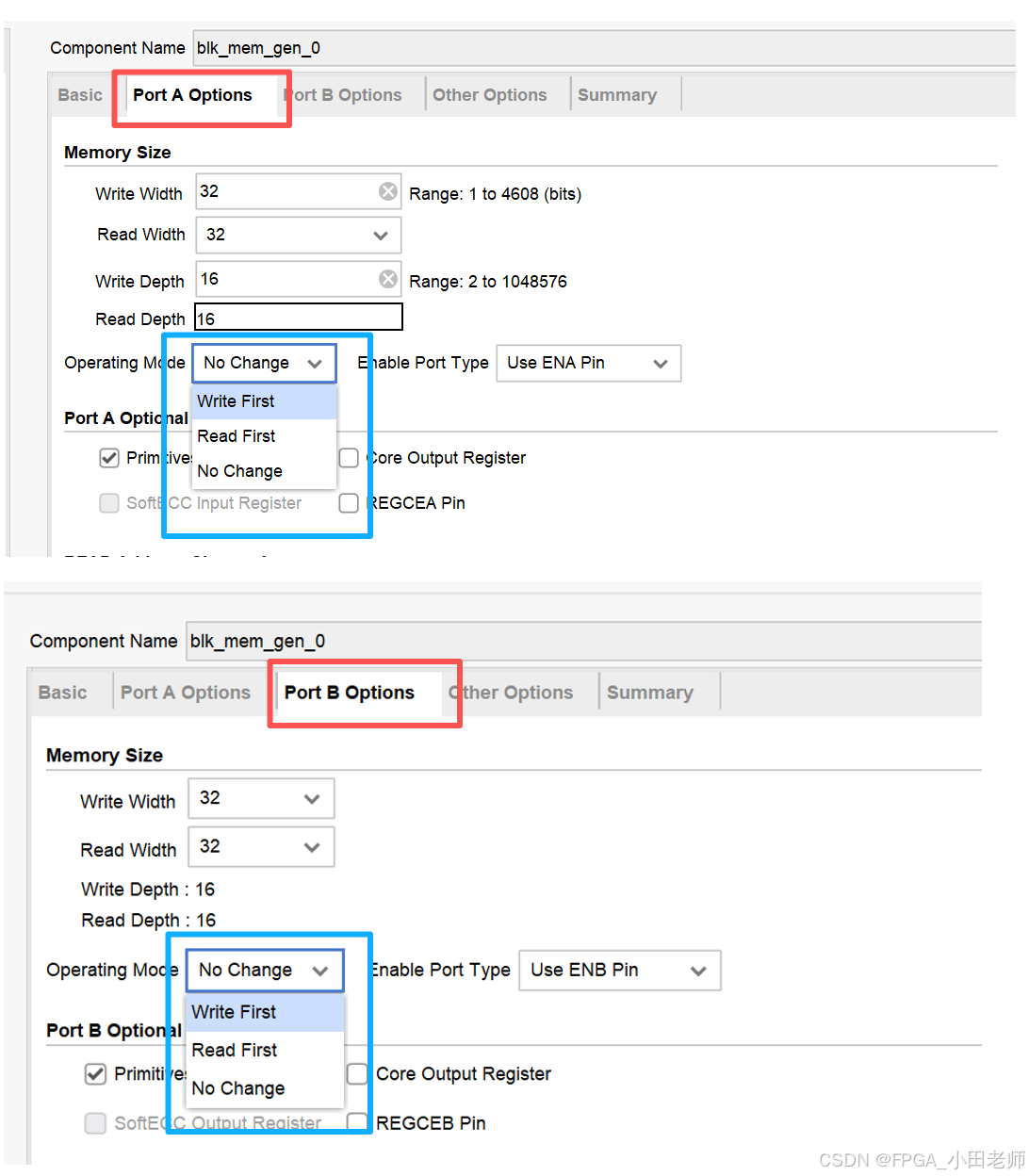
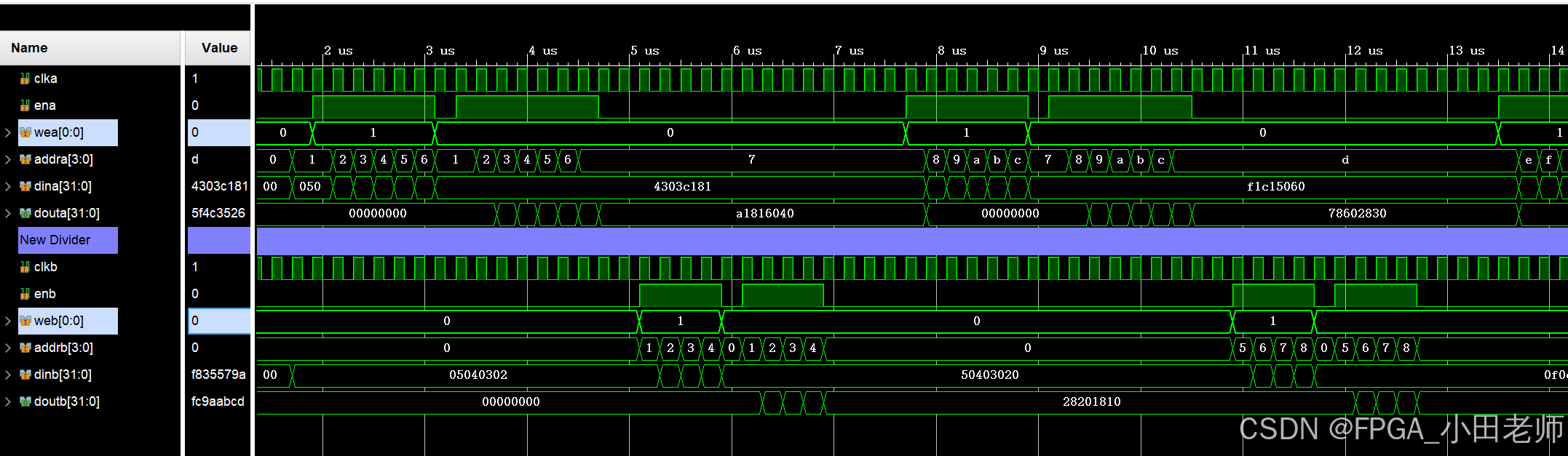
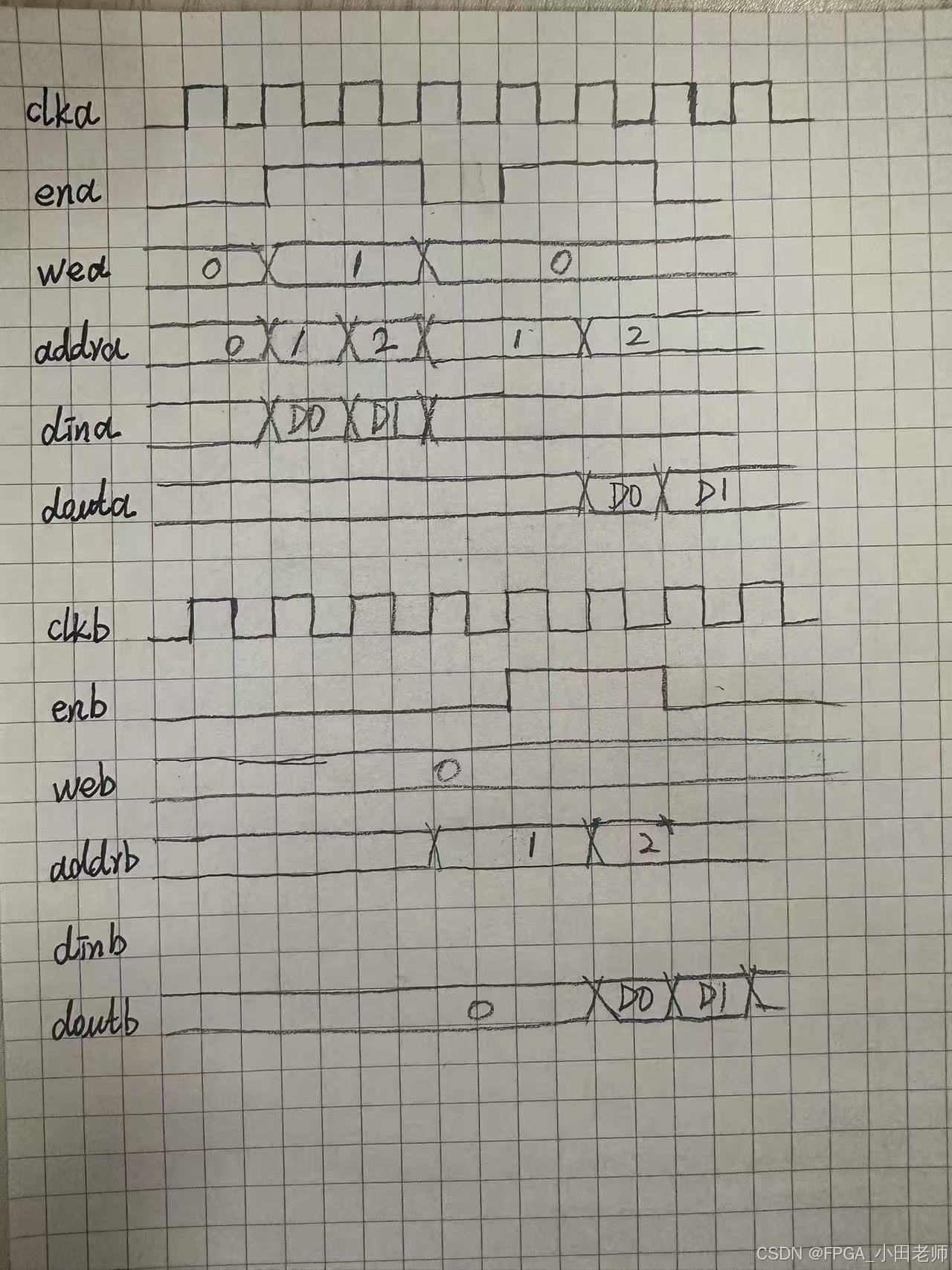
这是同一块RAM,分地址真双端口独立访问吗,一共定义了几块ram
























 2836
2836

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










