Vehicle Motion Planning/Local Planner
T: 确定一系列行动以达到指定目标
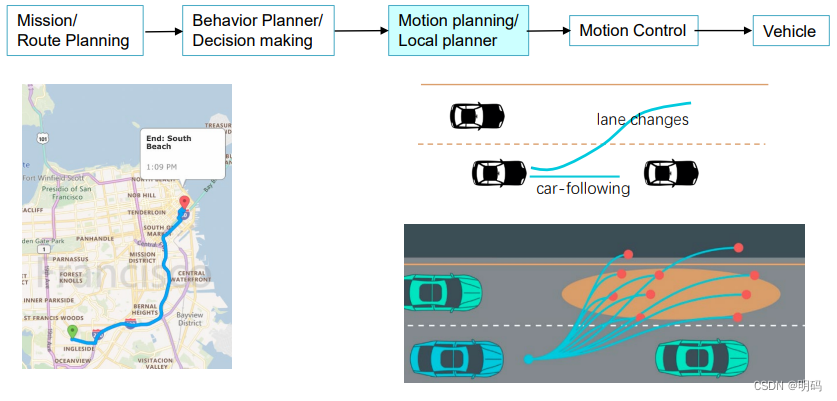
W: 搜索
• Functionality and Common method
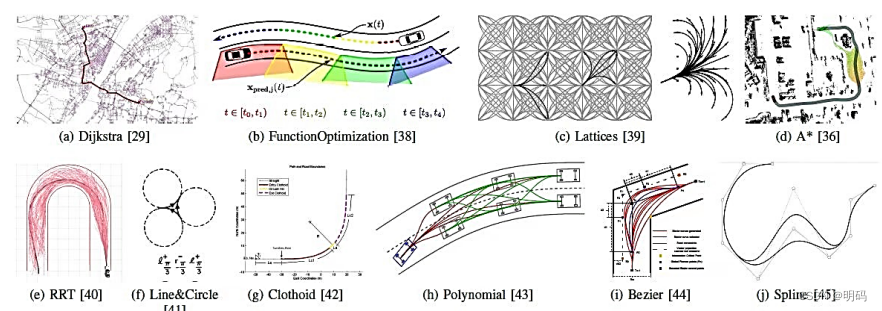
(a)Global path by Dijkastra.
(b) Trajectory optimization considering a vehicle in the other lane.
© Lattices and motion primitives. (d)Hybrid A* in DRAPA Junior. (e) RRT.
(f) Optimal path to turn the vehicle around. (g) Planning a turn from Stanford.
(h) Different motion states, planned with polynomial curves. (i) Evaluation of several Bezie curves. (j) Spline behaviour when a knot changes places
概括:
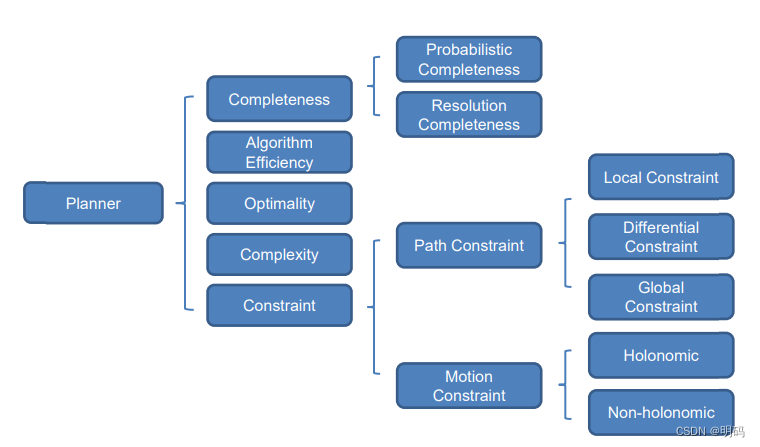
• Fundamental Concepts and Key terminology
Completeness: 只要有路;就能找到路
• Ability to find a solution if one exists,
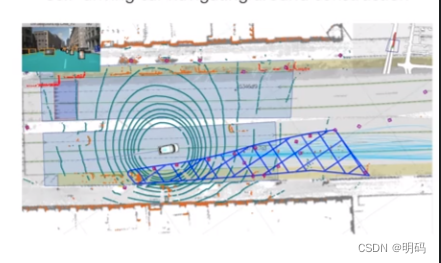
• Narrow Gap Problem Examples
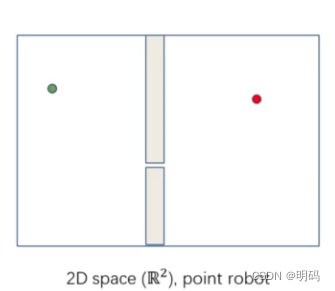
Self-driving car navigating around construction
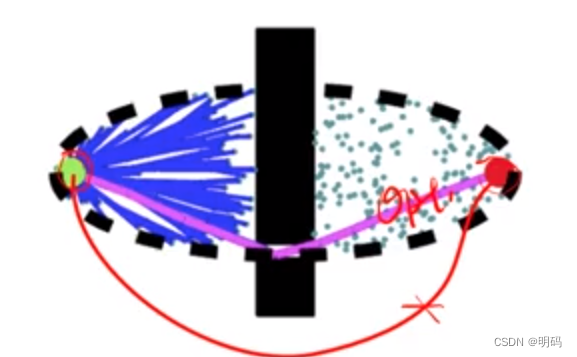
Probabilistic Completeness: 主要针对采样,如果存在路,只要有足够时间,就能找到路
Probability of finding a solution (when one exists) increases as computational time spent on the problem increases
**Resolution Completeness:**如果在状态和/或控制空间的离散化中使用足够精细的分辨率,能够找到路
Ability to find a solution if one exists AND using fine enough resolution in discretization of the state and/or control space
Algorithmic efficiency: 算法如何解决时间与输入数据大小成比例的问题,描述采用大O标记法,也就是算法中常用于描述复杂度的方法。How an algorithm solve time scales proportionally with respect to size of the input data,
Optimality:
Optimal is able to find the lowest cost solution of all possible options,
• Suboptimal of a lower cost solution exists,
• Asymptotically optimal if guaranteed to converge to the optimal solution given increasing computational time spent on the problem.
Complexity
Space dimensionality
• configuration space is a
R
3
ℝ^3
R3 for rigid body. But for the multi-bodies track, bicycle mode is not accurate enough to capture all the constraints.比如柔性机器人;
Geometric complexity
• How bounding box and bounding box interact;
• How to detect a path between polygons and interact with another obstacles;
…
There are three types of Path Constraints:
Local Constraints
• Avoid collision with static obstacles
Differential constraints
• Bounded curvature, limited steering angle for vehicle
Global constraints
• Find the shortest path by A
Holonomic vs non-holonomic motion constraints
Holonomic:控制的自由度=机器人总的自由度 如全向车
Cars are non-holonomic since control throttle and steering (2 DOF), but move in 𝑆E(2) (𝑥, 𝑦, 𝜃)
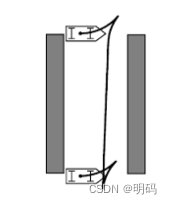
Local Planning
Find higher precision “good” (near optimal w.r.t. cost function) path to execute.
where to search
质点模型->Configuration Space Parameterization Options
● Workspace (direct physical environment, traditional)
- Control Space (e.g. velocity space, see link)
- Only saves effort in simple problems
● Belief Space (POMDP)
How to search?
-
Combinatorial methods (exact complete solution, e.g. visibility graph )
Rarely exists to find optimal solution to complex problems 起始点连线存在障碍物,最优解往往贴着障碍物,增加了碰撞的风险
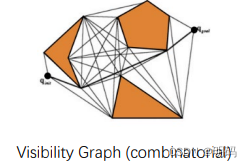
-
Sampling-based methods
• Deterministic (resolution complete), e.g. uniform grid or road structure graph, repeatable
• Stochastic (probabilistic completeness), e.g. random sampling
May need some smoothing/post-process to improve quality of solution
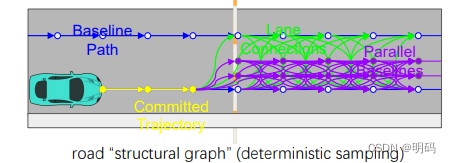
Stochastic Sampling Methods
obstacle avoidance
- 对于圆近似处理

- polygon
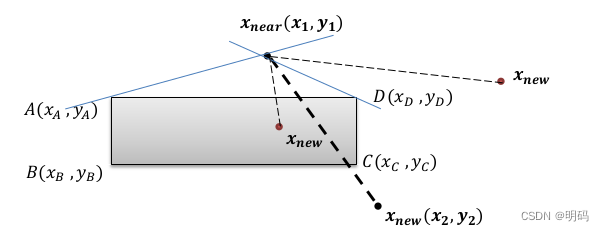
两步
1.如果 x_near和x_new在障碍物的同一边: 那么与障碍物没有碰撞
2.如果不在同一边;那么判断x_new 是否在障碍物中,如果在那么一定发生碰撞
如果不在那么需要连接两点做检查
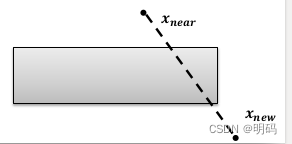
通过连接边界点线的斜率来判断
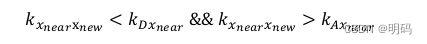
where k is the slope of line
Improvements may come through focus on any of those steps individually, e.g.:
•
Connect with edges of desirable properties
Dubins for shortest length w/fixed turn radius 只能往前走,Dubins曲线是在满足曲率约束和规定的始端和末端的切线方向的条件下,连接两个二维平面(即X-Y平面)的最短路径
Reeds-Shepp for forward/backward w/fixed turn radius,可以向后退
Spline, clothoid, Bezier for continuous curvature
Reference
深蓝学院
State Space Sampling of Feasible Motions for High-Performance Mobile Robot Navigation in Complex Environments,Thomas M. Howard, Colin J. Green, and Alonzo Kelly
Frenet坐标推导过程整理










 本文深入探讨了自动驾驶车辆的路径规划,包括全局路径规划(如Dijkstra算法、Hybrid A*)和局部规划(如RRT、Dubins曲线)。讨论了算法的完备性、概率完备性和分辨率完备性,并强调了在复杂环境下的寻路挑战,如避障和多体系统的几何约束。同时,提到了不同运动状态下的轨迹优化,如贝塞尔曲线的评估和样条行为。文章还涵盖了控制空间、局部和全局约束以及非完整运动约束(如汽车的转向限制)。局部规划的目标是找到高精度的近最优路径,采用粒子模型、配置空间参数化和采样方法进行搜索。最后,讨论了各种改进策略,如通过优化连接属性来提升路径质量。
本文深入探讨了自动驾驶车辆的路径规划,包括全局路径规划(如Dijkstra算法、Hybrid A*)和局部规划(如RRT、Dubins曲线)。讨论了算法的完备性、概率完备性和分辨率完备性,并强调了在复杂环境下的寻路挑战,如避障和多体系统的几何约束。同时,提到了不同运动状态下的轨迹优化,如贝塞尔曲线的评估和样条行为。文章还涵盖了控制空间、局部和全局约束以及非完整运动约束(如汽车的转向限制)。局部规划的目标是找到高精度的近最优路径,采用粒子模型、配置空间参数化和采样方法进行搜索。最后,讨论了各种改进策略,如通过优化连接属性来提升路径质量。
















 897
897

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








