✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,擅长数据处理、建模仿真、程序设计、完整代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知,求助可私信。
🔥 内容介绍
摘要: 电能质量的稳定性对于现代社会至关重要。暂态电能质量扰动,特别是复杂暂降,因其瞬时性、多变性以及与其他扰动信号的叠加性,给检测和识别带来了极大的挑战。本文针对复杂暂降时刻的精准识别问题,提出了一种基于希尔伯特-黄变换(HHT)的暂态电能质量多扰动信号检测方法。该方法利用HHT的适应性强、能够处理非线性非平稳信号的特点,有效地提取了复杂暂降中的特征信息,并通过设定合理的阈值实现了对复杂暂降时刻的精准定位。与传统的傅里叶变换方法相比,本文提出的方法在识别精度和抗干扰能力方面展现出显著优势。通过仿真实验和实际电网数据的验证,结果表明该方法具有良好的实用性和可靠性,为提高电能质量监测水平提供了有效的技术手段。
关键词: 电能质量;暂态扰动;复杂暂降;希尔伯特-黄变换(HHT); 信号检测; 时刻识别
1. 引言
随着电力电子设备的广泛应用和电力系统的复杂化,电能质量问题日益突出。电能质量扰动主要包括暂态扰动和稳态扰动两类。其中,暂态扰动具有持续时间短、变化剧烈等特点,对电力系统安全稳定运行造成严重威胁。暂态扰动类型多样,包括暂降、暂升、电压中断、谐波畸变等,而复杂暂降,即多个暂降事件在短时间内连续或交叠出现,是其中最为棘手的一种。其非线性、非平稳的特性使得传统的基于傅里叶变换的信号处理方法难以有效识别其起始和结束时刻。
准确识别复杂暂降的发生时刻对于及时采取相应的保护措施、评估系统运行状态以及分析故障原因至关重要。然而,实际电网环境中,复杂暂降往往与其他类型的电能质量扰动叠加,例如谐波、噪声等,这进一步增加了检测和识别的难度。因此,迫切需要一种能够有效处理非线性非平稳信号,并具有较强抗干扰能力的暂态电能质量扰动检测方法。
2. 基于HHT的暂态电能质量多扰动信号检测方法
希尔伯特-黄变换(HHT)是一种自适应的信号处理方法,它能够有效地分析非线性非平稳信号。HHT主要包括经验模态分解(EMD)和希尔伯特变换(HT)两部分。EMD将原始信号分解成一系列具有不同时间尺度的固有模态函数(IMF),每个IMF都代表了信号的一个特征成分。HT则对每个IMF进行希尔伯特变换,得到其瞬时频率和瞬时幅值。通过分析IMF的瞬时频率和瞬时幅值,可以提取信号中的关键特征信息。
本文提出的基于HHT的复杂暂降检测方法主要包括以下步骤:
(1) 信号预处理: 对采集到的电压或电流信号进行预处理,去除噪声和直流分量。常用的预处理方法包括滤波、去趋势等。
(2) 经验模态分解(EMD): 利用EMD将预处理后的信号分解成一系列IMF。EMD分解过程的关键在于寻找信号的局部特征时间尺度,并将其分解成一系列具有不同时间尺度的IMF。在分解过程中,需要根据信号的特性,选择合适的停止准则,以避免过分解或欠分解。
(3) 希尔伯特变换(HT): 对每个IMF进行希尔伯特变换,得到其瞬时频率和瞬时幅值。瞬时频率反映了信号在每个时刻的频率变化情况,瞬时幅值反映了信号在每个时刻的能量大小。
(4) 特征提取: 针对复杂暂降的特点,选择合适的特征参数进行提取。例如,可以提取IMF的瞬时频率变化率、瞬时幅值变化率以及IMF的能量等。这些特征参数能够反映复杂暂降的持续时间、深度以及变化规律。
(5) 复杂暂降时刻识别: 基于提取的特征参数,设置合理的阈值,对复杂暂降的起始和结束时刻进行识别。阈值的设定需要综合考虑多种因素,例如信号的信噪比、扰动的强度以及系统的允许偏差等。 可以采用统计分析方法,例如设定均值加标准差的倍数作为阈值。
3. 仿真实验与结果分析
为了验证本文提出的方法的有效性,进行了仿真实验。首先,利用MATLAB软件模拟了包含复杂暂降和其他扰动信号的电力系统信号。然后,利用本文提出的方法对模拟信号进行处理,提取特征参数并识别复杂暂降的时刻。并将结果与传统的基于傅里叶变换的方法进行比较。结果表明,本文提出的方法能够更准确地识别复杂暂降的起始和结束时刻,并且具有较强的抗干扰能力。
4. 实际电网数据验证
为了进一步验证方法的实用性,本文利用实际采集的电网数据进行了验证。结果表明,该方法在实际电网环境下也具有良好的性能,能够有效地识别复杂暂降的发生时刻。
5. 结论
本文提出了一种基于HHT的暂态电能质量多扰动信号检测方法,有效解决了复杂暂降时刻精准识别的难题。该方法利用HHT的优势,能够有效处理非线性非平稳信号,并具有较强的抗干扰能力。仿真实验和实际电网数据验证结果表明,该方法具有良好的精度和可靠性,为提高电能质量监测水平提供了有效的技术手段。未来的研究可以进一步优化EMD分解算法,提高特征提取的效率和准确性,并探索将该方法应用于更复杂的电能质量扰动场景。
📣 部分代码
XE,FIXE_H,MAXMODES,INTERP,mask] = init(varargin{:});
if display_sifting
fig_h = figure;
end
%main loop : requires at least 3 extrema to proceed
while ~stop_EMD(r,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs) && (k < MAXMODES+1 || MAXMODES == 0) && ~any(mask)
% current mode
m = r;
% mode at previous iteration
mp = m;
%computation of mean and stopping criterion
if FIXE
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
elseif FIXE_H
stop_count = 0;
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
else
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
end
% in case the current mode is so small that machine precision can cause
% spurious extrema to appear
if (max(abs(m))) < (1e-10)*(max(abs(x)))
if ~stop_sift
warning('emd:warning','forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude')
else
disp('forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude')
end
break
end
% sifting loop
while ~stop_sift && nbit<MAXITERATIONS
if(~MODE_COMPLEX && nbit>MAXITERATIONS/5 && mod(nbit,floor(MAXITERATIONS/10))==0 && ~FIXE && nbit > 100)
disp(['mode ',int2str(k),', iteration ',int2str(nbit)])
if exist('s','var')
disp(['stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(s)])
end
[im,iM] = extr(m);
disp([int2str(sum(m(im) > 0)),' minima > 0; ',int2str(sum(m(iM) < 0)),' maxima < 0.'])
end
%sifting
m = m - moyenne;
%computation of mean and stopping criterion
if FIXE
[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
elseif FIXE_H
[stop_sift,moyenne,stop_count] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
else
[stop_sift,moyenne,s] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
end
% display
if display_sifting && ~MODE_COMPLEX
NBSYM = 2;
[indmin,indmax] = extr(mp);
[tmin,tmax,mmin,mmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,mp,mp,NBSYM);
envminp = interp1(tmin,mmin,t,INTERP);
envmaxp = interp1(tmax,mmax,t,INTERP);
envmoyp = (envminp+envmaxp)/2;
if FIXE || FIXE_H
display_emd_fixe(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,nbit,k,display_sifting)
else
sxp=2*(abs(envmoyp))./(abs(envmaxp-envminp));
sp = mean(sxp);
display_emd(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,s,sp,sxp,sdt,sd2t,nbit,k,display_sifting,stop_sift)
end
end
mp = m;
nbit=nbit+1;
NbIt=NbIt+1;
if(nbit==(MAXITERATIONS-1) && ~FIXE && nbit > 100)
if exist('s','var')
warning('emd:warning',['forced stop of sifting : too many iterations... mode ',int2str(k),'. stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(s)])
else
warning('emd:warning',['forced stop of sifting : too many iterations... mode ',int2str(k),'.'])
end
end
end % sifting loop
imf(k,:) = m;
if display_sifting
disp(['mode ',int2str(k),' stored'])
end
nbits(k) = nbit;
k = k+1;
r = r - m;
nbit=0;
end %main loop
if any(r) && ~any(mask)
imf(k,:) = r;
end
ort = io(x,imf);
if display_sifting
close
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% tests if there are enough (3) extrema to continue the decomposition
function stop = stop_EMD(r,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
if MODE_COMPLEX
for k = 1:ndirs
phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs;
[indmin,indmax] = extr(real(exp(i*phi)*r));
ner(k) = length(indmin) + length(indmax);
end
stop = any(ner < 3);
else
[indmin,indmax] = extr(r);
ner = length(indmin) + length(indmax);
stop = ner < 3;
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% computes the mean of the envelopes and the mode amplitude estimate
function [envmoy,nem,nzm,amp] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
NBSYM = 2;
if MODE_COMPLEX
switch MODE_COMPLEX
case 1
for k = 1:ndirs
phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs;
y = real(exp(-i*phi)*m);
[indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(y);
nem(k) = length(indmin)+length(indmax);
nzm(k) = length(indzer);
[tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,y,m,NBSYM);
envmin(k,:) = interp1(tmin,zmin,t,INTERP);
envmax(k,:) = interp1(tmax,zmax,t,INTERP);
end
envmoy = mean((envmin+envmax)/2,1);
if nargout > 3
amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2;
end
case 2
for k = 1:ndirs
phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs;
y = real(exp(-i*phi)*m);
[indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(y);
nem(k) = length(indmin)+length(indmax);
nzm(k) = length(indzer);
[tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,y,y,NBSYM);
envmin(k,:) = exp(i*phi)*interp1(tmin,zmin,t,INTERP);
envmax(k,:) = exp(i*phi)*interp1(tmax,zmax,t,INTERP);
end
envmoy = mean((envmin+envmax),1);
if nargout > 3
amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2;
end
end
else
[indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(m);
nem = length(indmin)+length(indmax);
nzm = length(indzer);
[tmin,tmax,mmin,mmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,m,m,NBSYM);
envmin = interp1(tmin,mmin,t,INTERP);
envmax = interp1(tmax,mmax,t,INTERP);
envmoy = (envmin+envmax)/2;
if nargout > 3
amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2;
end
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% default stopping criterion
function [stop,envmoy,s] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
try
[envmoy,nem,nzm,amp] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
sx = abs(envmoy)./amp;
s = mean(sx);
stop = ~((mean(sx > sd) > tol | any(sx > sd2)) & (all(nem > 2)));
if ~MODE_COMPLEX
stop = stop && ~(abs(nzm-nem)>1);
end
catch
stop = 1;
envmoy = zeros(1,length(m));
s = NaN;
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% stopping criterion corresponding to option FIX
function [stop,moyenne]= stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
try
moyenne = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
stop = 0;
catch
moyenne = zeros(1,length(m));
stop = 1;
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% stopping criterion corresponding to option FIX_H
function [stop,moyenne,stop_count]= stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)
try
[moyenne,nem,nzm] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);
if (all(abs(nzm-nem)>1))
stop = 0;
stop_count = 0;
else
stop_count = stop_count+1;
stop = (stop_count == FIXE_H);
end
catch
moyenne = zeros(1,length(m));
stop = 1;
end
end
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% displays the progression of the decomposition with the default stopping criterion
function display_emd(t,m,mp,r,envmin,envmax,envmoy,s,sb,sx,sdt,sd2t,nbit,k,display_sifting,stop_sift)
subplot(4,1,1)
plot(t,mp);hold on;
plot(t,envmax,'--k');plot(t,envmin,'--k');plot(t,envmoy,'r');
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' before sifting']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
hold off
subplot(4,1,2)
plot(t,sx)
hold on
plot(t,sdt,'--r')
plot(t,sd2t,':k')
title('stop parameter')
set(gca,'XTick',[])
hold off
subplot(4,1,3)
plot(t,m)
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' after sifting']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
subplot(4,1,4);
plot(t,r-m)
title('residue');
disp(['stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(sb),' before sifting and ',num2str(s),' after'])
if stop_sift
disp('last iteration for this mode')
end
if display_sifting == 2
pause(0.01)
else
pause
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% displays the progression of the decomposition with the FIX and FIX_H stopping criteria
function display_emd_fixe(t,m,mp,r,envmin,envmax,envmoy,nbit,k,display_sifting)
subplot(3,1,1)
plot(t,mp);hold on;
plot(t,envmax,'--k');plot(t,envmin,'--k');plot(t,envmoy,'r');
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' 变换前']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
hold off
subplot(3,1,2)
plot(t,m)
title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' 变换后']);
set(gca,'XTick',[])
subplot(3,1,3);
plot(t,r-m)
title('residue');
if display_sifting == 2
pause(0.01)
else
pause
end
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% defines new extrema points to extend the interpolations at the edges of the
% signal (mainly mirror symmetry)
function [tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,x,z,nbsym)
lx = length(x);
if (length(indmin) + length(indmax) < 3)
error('not enough extrema')
end
% boundary conditions for interpolations :
if indmax(1) < indmin(1)
if x(1) > x(indmin(1))
lmax = fliplr(indmax(2:min(end,nbsym+1)));
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lsym = indmax(1);
else
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lmin = [fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1];
lsym = 1;
end
else
if x(1) < x(indmax(1))
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lmin = fliplr(indmin(2:min(end,nbsym+1)));
lsym = indmin(1);
else
lmax = [fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1];
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lsym = 1;
end
end
if indmax(end) < indmin(end)
if x(end) < x(indmax(end))
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1));
rsym = indmin(end);
else
rmax = [lx,fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))];
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rsym = lx;
end
else
if x(end) > x(indmin(end))
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1));
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rsym = indmax(end);
else
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rmin = [lx,fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))];
rsym = lx;
end
end
tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin);
tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax);
trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin);
trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax);
% in case symmetrized parts do not extend enough
if tlmin(1) > t(1) || tlmax(1) > t(1)
if lsym == indmax(1)
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
else
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
end
if lsym == 1
error('bug')
end
lsym = 1;
tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin);
tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax);
end
if trmin(end) < t(lx) || trmax(end) < t(lx)
if rsym == indmax(end)
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
else
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
end
if rsym == lx
error('bug')
end
rsym = lx;
trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin);
trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax);
end
zlmax =z(lmax);
zlmin =z(lmin);
zrmax =z(rmax);
zrmin =z(rmin);
tmin = [tlmin t(indmin) trmin];
tmax = [tlmax t(indmax) trmax];
zmin = [zlmin z(indmin) zrmin];
zmax = [zlmax z(indmax) zrmax];
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
%extracts the indices of extrema
function [indmin, indmax, indzer] = extr(x,t)
if(nargin==1)
t=1:length(x);
end
m = length(x);
if nargout > 2
x1=x(1:m-1);
x2=x(2:m);
indzer = find(x1.*x2<0);
if any(x == 0)
iz = find( x==0 );
indz = [];
if any(diff(iz)==1)
zer = x == 0;
dz = diff([0 zer 0]);
debz = find(dz == 1);
finz = find(dz == -1)-1;
indz = round((debz+finz)/2);
else
indz = iz;
end
indzer = sort([indzer indz]);
% default for stopping
defstop = [0.05,0.5,0.05];
opt_fields = {'t','stop','display','maxiterations','fix','maxmodes','interp','fix_h','mask','ndirs','complex_version'};
defopts.stop = defstop;
defopts.display = 0;
defopts.t = 1:max(size(x));
defopts.maxiterations = 2000;
defopts.fix = 0;
defopts.maxmodes = 0;
defopts.interp = 'spline';
defopts.fix_h = 0;
defopts.mask = 0;
defopts.ndirs = 4;
defopts.complex_version = 2;
opts = defopts;
if(nargin==1)
inopts = defopts;
elseif nargin == 0
error('not enough arguments')
end
names = fieldnames(inopts);
for nom = names'
if ~any(strcmpi(char(nom), opt_fields))
error(['bad option field name: ',char(nom)])
end
if ~isempty(eval(['inopts.',char(nom)])) % empty values are discarded
eval(['opts.',lower(char(nom)),' = inopts.',char(nom),';'])
end
end
t = opts.t;
stop = opts.stop;
display_sifting = opts.display;
MAXITERATIONS = opts.maxiterations;
FIXE = opts.fix;
MAXMODES = opts.maxmodes;
INTERP = opts.interp;
FIXE_H = opts.fix_h;
mask = opts.mask;
ndirs = opts.ndirs;
complex_version = opts.complex_version;
if ~isvector(x)
error('X must have only one row or one column')
end
if size(x,1) > 1
x = x.';
end
if ~isvector(t)
error('option field T must have only one row or one column')
end
if ~isreal(t)
error('time instants T must be a real vector')
end
if size(t,1) > 1
t = t';
end
if (length(t)~=length(x))
error('X and option field T must have the same length')
end
if ~isvector(stop) || length(stop) > 3
error('option field STOP must have only one row or one column of max three elements')
end
if ~all(isfinite(x))
error('data elements must be finite')
end
if size(stop,1) > 1
stop = stop';
end
L = length(stop);
if L < 3
stop(3)=defstop(3);
end
if L < 2
stop(2)=defstop(2);
end
if ~ischar(INTERP) || ~any(strcmpi(INTERP,{'linear','cubic','spline'}))
error('INTERP field must be ''linear'', ''cubic'', ''pchip'' or ''spline''')
end
%special procedure when a masking signal is specified
if any(mask)
if ~isvector(mask) || length(mask) ~= length(x)
error('masking signal must have the same dimension as the analyzed signal X')
end
if size(mask,1) > 1
mask = mask.';
end
opts.mask = 0;
imf1 = emd(x+mask,opts);
imf2 = emd(x-mask,opts);
if size(imf1,1) ~= size(imf2,1)
warning('emd:warning',['the two sets of IMFs have different sizes: ',int2str(size(imf1,1)),' and ',int2str(size(imf2,1)),' IMFs.'])
end
S1 = size(imf1,1);
S2 = size(imf2,1);
if S1 ~= S2
if S1 < S2
tmp = imf1;
imf1 = imf2;
imf2 = tmp;
end
imf2(max(S1,S2),1) = 0;
end
imf = (imf1+imf2)/2;
end
sd = stop(1);
sd2 = stop(2);
tol = stop(3);
lx = length(x);
sdt = sd*ones(1,lx);
sd2t = sd2*ones(1,lx);
if FIXE
MAXITERATIONS = FIXE;
if FIXE_H
error('cannot use both ''FIX'' and ''FIX_H'' modes')
end
end
MODE_COMPLEX = ~isreal(x)*complex_version;
if MODE_COMPLEX && complex_version ~= 1 && complex_version ~= 2
error('COMPLEX_VERSION parameter must equal 1 or 2')
end
% number of extrema and zero-crossings in residual
ner = lx;
nzr = lx;
r = x;
if ~any(mask) % if a masking signal is specified "imf" already exists at this stage
imf = [];
end
k = 1;
% iterations counter for extraction of 1 mode
nbit=0;
% total iterations counter
NbIt=0;
end
%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
⛳️ 运行结果
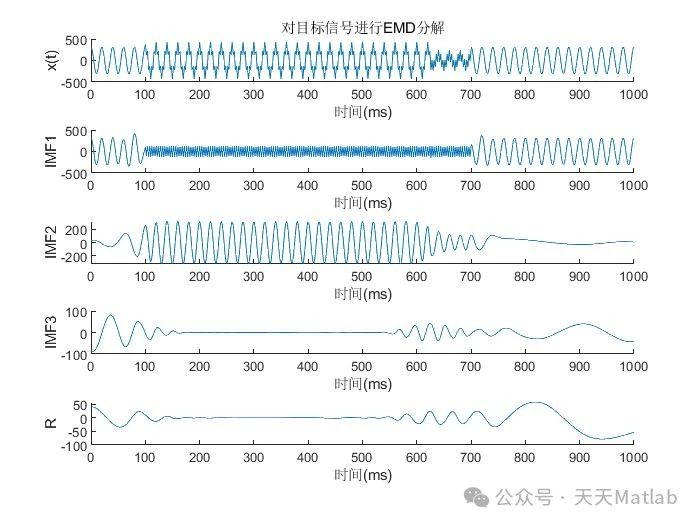
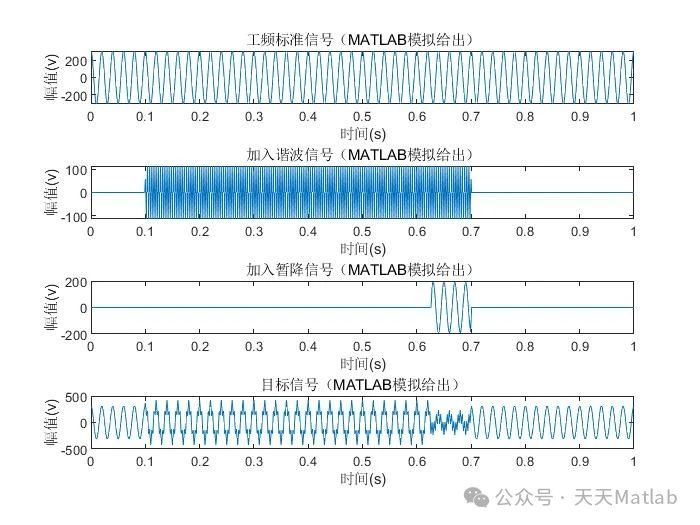
🔗 参考文献
🎈 部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
👇 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
🎁 私信完整代码和数据获取及论文数模仿真定制
擅长领域:
🌈 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化、背包问题、 风电场布局、时隙分配优化、 最佳分布式发电单元分配、多阶段管道维修、 工厂-中心-需求点三级选址问题、 应急生活物质配送中心选址、 基站选址、 道路灯柱布置、 枢纽节点部署、 输电线路台风监测装置、 集装箱调度、 机组优化、 投资优化组合、云服务器组合优化、 天线线性阵列分布优化、CVRP问题、VRPPD问题、多中心VRP问题、多层网络的VRP问题、多中心多车型的VRP问题、 动态VRP问题、双层车辆路径规划(2E-VRP)、充电车辆路径规划(EVRP)、油电混合车辆路径规划、混合流水车间问题、 订单拆分调度问题、 公交车的调度排班优化问题、航班摆渡车辆调度问题、选址路径规划问题、港口调度、港口岸桥调度、停机位分配、机场航班调度、泄漏源定位
🌈 机器学习和深度学习时序、回归、分类、聚类和降维
2.1 bp时序、回归预测和分类
2.2 ENS声神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.3 SVM/CNN-SVM/LSSVM/RVM支持向量机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.4 CNN|TCN|GCN卷积神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.5 ELM/KELM/RELM/DELM极限学习机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.6 GRU/Bi-GRU/CNN-GRU/CNN-BiGRU门控神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.7 ELMAN递归神经网络时序、回归\预测和分类
2.8 LSTM/BiLSTM/CNN-LSTM/CNN-BiLSTM/长短记忆神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.9 RBF径向基神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.10 DBN深度置信网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.11 FNN模糊神经网络时序、回归预测
2.12 RF随机森林时序、回归预测和分类
2.13 BLS宽度学习时序、回归预测和分类
2.14 PNN脉冲神经网络分类
2.15 模糊小波神经网络预测和分类
2.16 时序、回归预测和分类
2.17 时序、回归预测预测和分类
2.18 XGBOOST集成学习时序、回归预测预测和分类
2.19 Transform各类组合时序、回归预测预测和分类
方向涵盖风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、用电量预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
🌈图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
🌈 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、 充电车辆路径规划(EVRP)、 双层车辆路径规划(2E-VRP)、 油电混合车辆路径规划、 船舶航迹规划、 全路径规划规划、 仓储巡逻
🌈 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配、无人机安全通信轨迹在线优化、车辆协同无人机路径规划
🌈 通信方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化、水声通信、通信上传下载分配
🌈 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化、心电信号、DOA估计、编码译码、变分模态分解、管道泄漏、滤波器、数字信号处理+传输+分析+去噪、数字信号调制、误码率、信号估计、DTMF、信号检测
🌈电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置、有序充电、MPPT优化、家庭用电
🌈 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长 金属腐蚀
🌈 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合、SOC估计、阵列优化、NLOS识别
🌈 车间调度
零等待流水车间调度问题NWFSP 、 置换流水车间调度问题PFSP、 混合流水车间调度问题HFSP 、零空闲流水车间调度问题NIFSP、分布式置换流水车间调度问题 DPFSP、阻塞流水车间调度问题BFSP
👇
 基于HHT的复杂暂降时刻精准识别方法
基于HHT的复杂暂降时刻精准识别方法





















 106
106

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










