✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
⛄ 内容介绍
Engine failures are a large cause of concern for mission planners when dealing with the operation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). This is primarily due to the lack of a skilled pilot on-board who can deal with the resulting loss of control by assessing the environment around them to perform an emergency landing. This has recently become a growing issue due to the fact UAVs are seeing a huge rise in use ranging from a plethora of civilian and military applications. With more UAVs in operation, the chances of a crash landing or collision from a loss of control increase. Therefore an autonomous system which will allow the vehicle to land safely is highly desirable. The challenge is to produce dynamically feasible routes for the unpowered UAV, which consider spatial constraints from a complex obstacle space, as well as temporal constraints for landing in pre-defifined safety zones. This chapter will begin with the motivation and inherent diffiffifficulty in solving such a problem, followed by a brief description of the proposed solution.

⛄ 部分代码
%% generateRoadmap.m
function [nodes, distMatrix, heuristic] = generate_roadmap(npoints,radius,init,final,obs,radius_obstacle,zone)
nodes = [init,final,zone];
distMatrix = zeros(npoints);
heuristic = zeros(1,npoints);
heuristic(1) = norm(final-init);
heuristic(2) = 0;
offset = 2+length(zone);
for i = 1 : npoints-offset
while true
new = init(1)+(final(1)-init(1))*abs(rand(2,1));
if collision_test(new,obs,radius_obstacle)
break;
end
end
heuristic(i+offset) = norm(new-final);
nodes = [nodes, new];
[idx, D] = rangesearch(nodes', new', radius);
idx = idx{1};
if length(idx) == 1
continue;
end
D = D{1};
for k = 2 : length(idx)
if edge_test(new,nodes(:,idx(k)),obs,radius_obstacle);
plot([nodes(1,end), nodes(1,idx(k))], [nodes(2,end), nodes(2,idx(k))], 'c', 'linewidth', 0.5); % plot the edge
distMatrix(length(nodes),idx(k)) = D(k); % add in symmetric positions in distMatrix
distMatrix(idx(k),length(nodes)) = D(k);
end
end
end
end
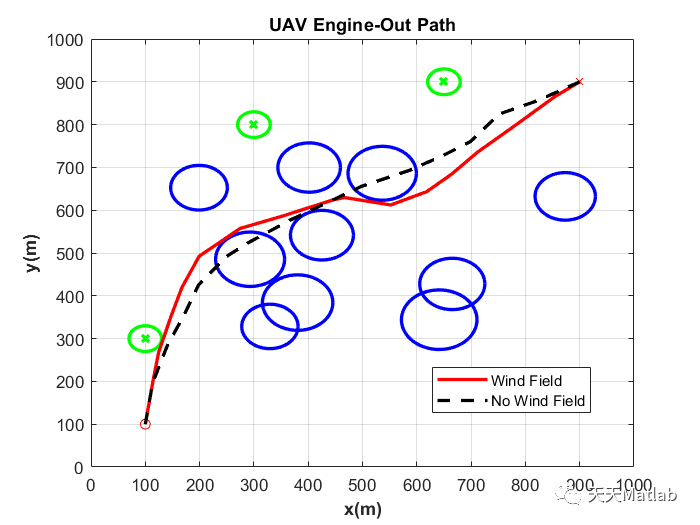
⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
⛳️ 代码获取关注我
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料





 文章探讨了无人机(UAVs)在发动机故障时面临的控制问题,由于缺乏飞行员进行应急着陆,这是一个日益严重的问题。随着UAVs在民用和军事领域的广泛应用,自动安全着陆系统的需求增加。文章提出了一种动态路径规划方法,考虑复杂障碍空间和预定义的安全着陆区,以解决无动力UAV的着陆挑战。此外,还展示了Matlab代码片段,用于生成路线图。
文章探讨了无人机(UAVs)在发动机故障时面临的控制问题,由于缺乏飞行员进行应急着陆,这是一个日益严重的问题。随着UAVs在民用和军事领域的广泛应用,自动安全着陆系统的需求增加。文章提出了一种动态路径规划方法,考虑复杂障碍空间和预定义的安全着陆区,以解决无动力UAV的着陆挑战。此外,还展示了Matlab代码片段,用于生成路线图。

















 143
143

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










