C1. Potions (Easy Version)/(Hard Version)
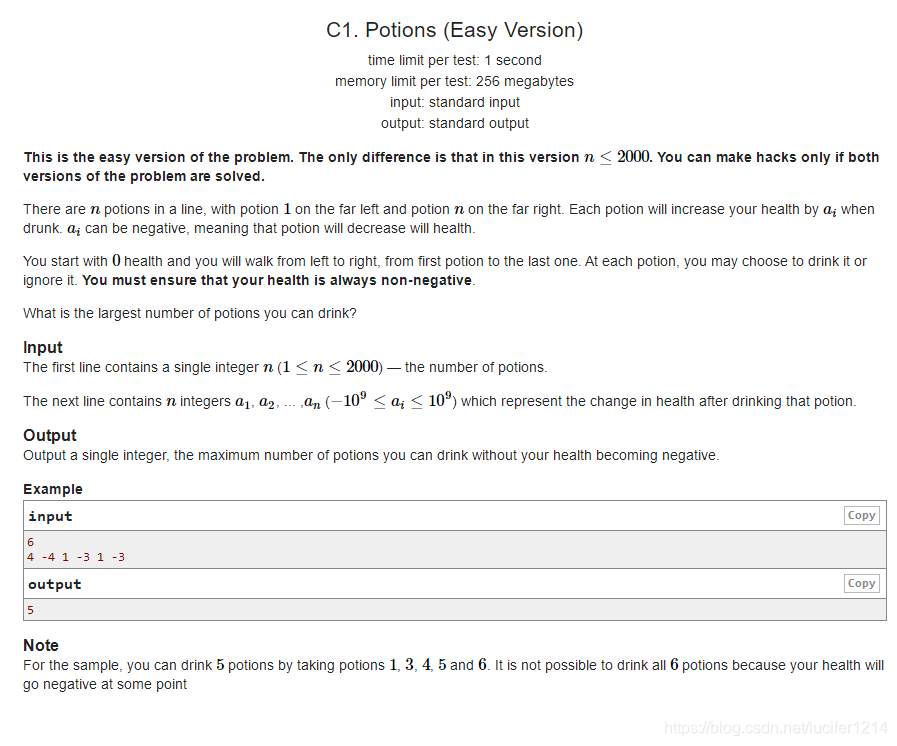
题目大意:
给定一串饮品,你的初始健康值为0,喝下对应饮品后会使得你的健康值改变,对于每个饮品你都可以选择喝或者不喝,请问在健康值不为负数的情况下,最多喝几个饮品。
思路:
首先,如果饮品的健康值为正数时,那我们肯定是要喝的。
其次,当饮品的健康值为负数时,如果当前健康值减去该健康值不小于0的话,我们也喝下他,但是同时,我们要将他记入到一个小根堆中,方便我们以后进行后悔。
当我们的健康值减去对应饮品的健康值后,小于0,那么我们就要看一看,在先前喝下的负健康值的饮品中最小的一个所需的代价是不是比该饮品大,如果大,那么我们就将它“吐”出来,其实就是反悔,我们不喝他了,改成喝当前这个饮品,最后输出计数即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int p = 1e9 + 7;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int N = 1e6+10;
bool st[N];
ll a[N];
int main() {
ll n;
cin >> n;
ll h = 0, cnt = 0;
priority_queue<ll, vector<ll>, greater<ll>>heap;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
if (a[i] >= 0)h += a[i],cnt++;
else {
if (h + a[i] >= 0) {
h += a[i], cnt++;
heap.push(a[i]);
}
else {
if (!heap.empty()&&a[i] > heap.top()) {//这里需要注意,要把堆是否为空放在前,否则当堆为空时,如果先取顶端值就会RE
h -= heap.top();
heap.pop(), heap.push(a[i]);
h += a[i];
}
}
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
简单版本和困难版本都可AC





 本文介绍了如何使用动态规划策略解决在确保健康值不为负数的前提下,最多能喝多少饮品的问题。通过建立小根堆来处理负值饮品,实现后悔操作,从而找到最佳饮品组合。代码实现包括对负值饮品的处理逻辑,最终输出可以喝下的饮品数量。
本文介绍了如何使用动态规划策略解决在确保健康值不为负数的前提下,最多能喝多少饮品的问题。通过建立小根堆来处理负值饮品,实现后悔操作,从而找到最佳饮品组合。代码实现包括对负值饮品的处理逻辑,最终输出可以喝下的饮品数量。
















 692
692

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








