介绍stl里的map和string

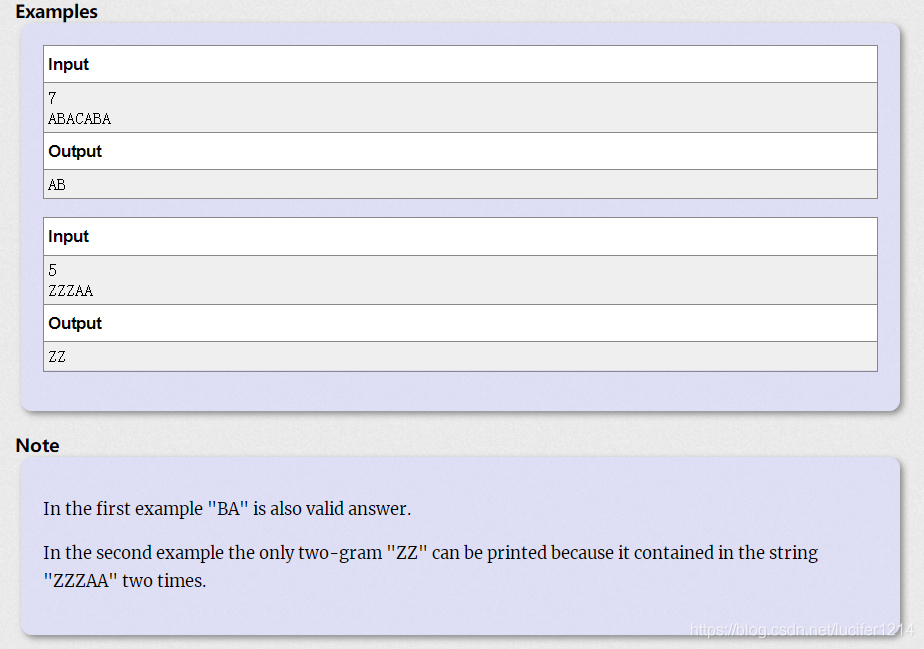
题意很简单,找出字符串中出现次数最多的长度为2的元素。由于数据不大,我们直接将所给字符串分解为两个两个一组并且存进map中。
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
map<string, int >mp;
int main() {
mp.clear();
int n;
cin >> n;
string a;
cin >> a;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
string b;
b =b + a[i] + a[i + 1];
mp[b]++;
}
int ans = -1;
map<string, int >::iterator it;
it = mp.begin(); string res;
for (it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++) {
if (it->second > ans) {
ans = it->second;
res = it->first;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
这里有一个知识,string的加法为string = string + char* , 不是string = char* + char* 或者char + char。
也就是上边代码中我们将字符串分成两个两个一组的部分b =b + a[i] + a[i + 1];需要这样写才行。
全部分离完成后,我们就要在map中寻找出现次数最多的串,这里就要用到一个叫迭代器的东西。
一般来说应用C++的map的时候,我们往往事先知道它有哪些key值,但偏偏有些问题我们事先并不知道。那么此时如何遍历出map的key值和val呢,那就只能用迭代器了。
用法如下 规定一个iter让他从map.begin()开始直到map.end()遍历。
map<string, int>::iterator iter;
iter = m.begin();
while(iter != m.end()){
string key = iter.first;//或是iter->first
int val = iter.second;//或是iter->second
iter++;
}
// for循环的写法
for(iter = m.begin();iter != m.end(); iter++){
string key = iter.first;//或是iter->first
int val = iter.second;//或是iter->second
}
//auto的写法
for (auto&& p : mp) {
int ans = p.second;
string res = p.first;
}
auto的原理就是根据后面的值,来自己推测前面的类型是什么。
auto的作用就是为了简化变量初始化,如果这个变量有一个很长很长的初始化类型,就可以用auto代替。

超级长的题干,其实就是问你每个字符串,出现的次数,占总数的百分比,结果保留四位小数。
直接上代码。
注意一下uva贼难受的输入格式。
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int t, sum;
map<string, int> mp;
int main()
{
scanf("%d\n", &t);
while (t--)
{
string op;
sum = 0;
mp.clear();
while (1)
{
getline(cin, op);
if (op[0] == '\0')
break;
sum++;
mp[op]++;
}
for (auto && p : mp)
{
cout << p.first << ' ';
printf("%.4lf\n",(p.second) * 100.0 / sum);
}
if (t!=0)
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
Prince Macaw is flying here and there and searching for food. Her Princess is waiting for him at home. But he stopped when he was flying near Shahbag. He saw millions of people gathered there for only one demand- death sentence of war crimes. They were giving slogans. If you are not familiar with slogans let me tell you, slogan has two parts. One part of the slogan is yelled by the leader and the rest part is chorused from the mass people. For example, when the leader says- “tomar amar thikana” then other say – “padma meghna jomuna”. Some of the slogans are listed below-
First Line
Second Line
ko te kader molla
tui rajakar tui rajakar
tumi ke ami ke
garo chakma bangali
Prince also joined with this mass people. When it was too late, Princess got worried about Prince. So she also went out. After some while, she found Prince on a tree at Shahbag yelling slogans in strong voice. Instead of getting mad, Princess asked Prince what are the slogans. So Prince told her a few slogans, first line and corresponding second line. So Princess got prepared. Given the list of the slogans and also the first lines Princess going to hear, print out the second line of the slogans.
Input
First line contains number of slogans, N (0 < N <=20) Prince is going to teach Princess. Hence follows N pairs of lines. First line of the pair contains first line of a slogan and the second line of the pair is corresponding second line of the slogan. Then another positive integer Q will be given (Q <= 100). Hence follows Q lines. Each line contains first line of a slogan. You may assume that the slogans will contain lower case English alphabet and/or space. Both the lines of slogan will contain at least one alphabet. No two first lines in the Prince’s slogan list will be same. Each slogan will be at most 100 characters long. All of the query first line will be in Prince’s list.
Output
For each of the first line of the slogan, you need to print out corresponding second line.
Sample Input
3
ko te kader molla
tui rajakar tui rajakar
tumi ke ami ke
garo chakma bangali
jalo re jalo
agun jalo
2
jalo re jalo
ko te kader molla
Output for Sample Input
agun jalo
tui rajakar tui rajakar
首先输入数据,每一句话对应一个答案,然后输入几个询问,输出对应的答案句子即可,用一个map来存储对应关系,用getline来读入带空格的字符串即可。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
map<string, string>mp;
int main() {
int n;
mp.clear();
scanf("%d\n", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
string a;
string b;
getline(cin , a);
getline(cin , b);
mp[a] = b;
}
int q;
scanf("%d\n", &q);
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
string c;
getline(cin, c);
cout << mp[c] << endl;
}
}
这就是map的基础用法啦!





 本文介绍了C++标准库中的map容器和string类型在编程中的使用。通过实例展示了如何利用map存储字符串对,并查找出现次数最多的长度为2的子串。此外,还讨论了迭代器在遍历map时的重要性。最后,提供了处理字符串出现频率并计算百分比的代码示例,以及解决特定问题的map实现。
本文介绍了C++标准库中的map容器和string类型在编程中的使用。通过实例展示了如何利用map存储字符串对,并查找出现次数最多的长度为2的子串。此外,还讨论了迭代器在遍历map时的重要性。最后,提供了处理字符串出现频率并计算百分比的代码示例,以及解决特定问题的map实现。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








