797.所有可能的路径
这个是一个典型的求路径的题(图论),也是递归方法/层序方法的实际应用,也就是我们常说的DFS和BFS在实际问题中的应用
给你一个有 n 个节点的 有向无环图(DAG),请你找出从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的所有路径并输出(不要求按特定顺序)
graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节点 i 到节点 graph[i][j]存在一条有向边)。
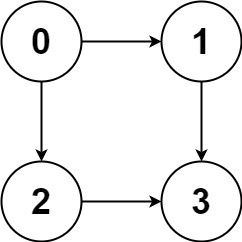
输入:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]]
输出:[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]]
解释:有两条路径 0 -> 1 -> 3 和 0 -> 2 -> 3
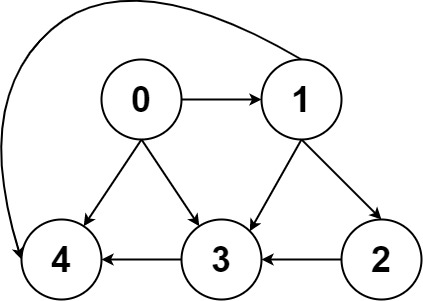
输入:graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]]
输出:[[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
有向无权图dfs搜索过程.需要用到回溯
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
result = []
current_path = []
target = len(graph) - 1 # 一定要先定好目标是什么
def dfs(current_node, current_path):
if (current_node == target):
result.append(current_path)
return
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
current_path.append(neighbor)
dfs(neighbor, current_path)
current_path.pop()
dfs(0, [0])
return result
咋一看好像没啥问题,但是其实答案永远都是输出0,这是为什么呢,因为对于result.append(curren_path)来说,存入的是current_path的引用,此时如果current_path变化,result也就会跟着变化,所以需要注意,我们再使用append装数组的时候,需要通过copy来存储副本:
result.append(current_path.copy()]
最终的解答为
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
result = []
current_path = []
target = len(graph) - 1 # 一定要先定好目标是什么
def dfs(current_node, current_path):
if (current_node == target):
result.append(current_path.copy)
return
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
current_path.append(neighbor)
dfs(neighbor, current_path)
current_path.pop()
dfs(0, [0])
return result
本质上就是一个二维数组的递归遍历,其实也是DFS的方法.还有一中更加简单的写法
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
self.result = []
self.path = []
self.target = len(graph)-1
self.traverse(graph, 0)
return self.result
def traverse(self, graph, current_node):
# 前序
self.path.append(current_node)
if current_node == self.target:
self.result.append(self.path.copy())
self.path.pop()
return
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
self.traverse(graph, neighbor)
# 后序
self.path.pop() # 移除节点s
如果要用BFS,那么可以这样实现
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
result = []
target = len(graph) - 1
current_path = [0]
q = deque()
q.append(current_path)
while q:
last_node = current_path[-1]
current_path = q.popleft()
if current_path[-1] == target:
result.append(current_path.copy())
continue
for neighbor in graph[last_node]:
new_path = current_path.copy()
new_path.append(neighbor)
q.append(new_path)
return result
这里唯一的注意点就是bfs找路,遍历的过程要用deque记录的是路径而不是节点,所以deque.popleft提取的是一条一条的路,直到这条路满足到达终点的硬性条件.





















 9186
9186

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










