- 过拟合的判断:测试集和训练集同步打印指标
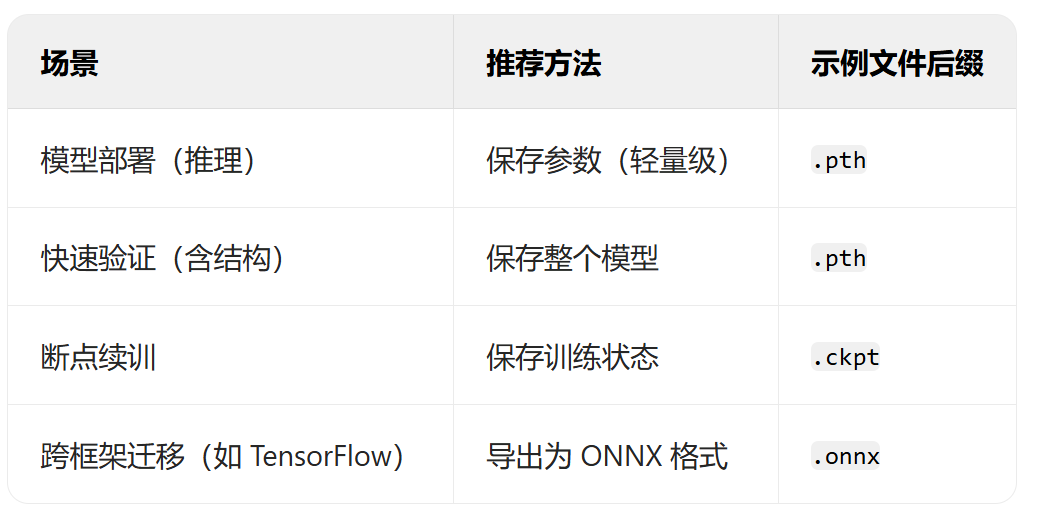
- 模型的保存和加载:仅保存权重;保存权重和模型;保存全部信息checkpoint,还包含训练状态;
- 早停策略
作业:对信贷数据集训练后保存权重,加载权重后继续训练50轮,并采取早停策略
模型的保存与加载
在深度学习中,模型保存与加载主要涉及参数(权重)和整个模型结构的存储,同时需兼顾训练状态(如优化器参数、轮次等)以支持断点续训。
在pytorch中使用torch.save()函数可执行保存功能,它主要提供了以下几种保存机制:
(1)仅保存模型参数
使用state_dict 将模型中所有可学习参数(权重、偏置)存储在字典中,适合于模型推理。
- 优点:文件小(不保存模型结构代码,仅参数),安全(不依赖具体类定义)
- 缺点:加载时需先定义模型结构(实例化与训练时相同的模型结构)
# 保存参数
torch.save(model.state_dict(),'model_weights.pth')
# 加载,需先定义模型结构
model = MLP() #先定义模型结构(与训练时相同)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_weights.pth')) # 加载参数
# model.eval() # 进入推理模型(2)保存整个模型
保存整个模型,包括结构和参数,适合于临时调试的场景
- 优点:加载时无需提前定义模型类
- 缺点:依赖 Python 类的具体定义;文件大;存在安全隐患(代码环境的一致性)
# 保存模型和参数
torch.save(model,'full_model.pth')
# 加载,无需提前定义类,但需确保环境一致
model = torch.load('full_model.pth') # 加载保存的模型
# model.eval() # 进入推理模型(3)保存训练状态
保存模型参数、优化器状态、当前 epoch、损失值等信息,适合于断点续训(长时间训练任务)。
训练 → 第99轮结束 → 保存 checkpoint(含 epoch=99)
↓
程序中断 / 重启
↓
加载 checkpoint
├─ 先定义模型结构,恢复模型参数
├─ 创建优化器,恢复优化器状态
├─ 获取 epoch=99, best_loss=0.123
↓
从 epoch=100 开始继续训练# 保存检查点
checking_point = {
'model_state':model.state_dict(), # 保存当前的可学习参数
'optimiser_state':optimizer.state_dict(), # 保存优化器状态
'epoch':epoch, # 当前已完成的训练轮数(用于知道从哪里继续)
'loss':best_loss, # 最佳损失值,用于早停策略或模型选择
}
torch.save(checking_point,'checking_point.pth') # 保存
# 加载
model = MLP() # 先定义模型结构,只保存了参数
optimiser = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.01) # 创建优化器
checking_point = torch.load('checking_point.pth') # 加载检查点
model.load_state_dict(checking_point['model_state']) # 加载参数
optimiser.load_state_dict(checking_point['optimiser_state']) # 加载优化器状态
start_epoch = checking_point['epoch'] + 1 # 加载epoch,从下一轮开始训练
best_loss = checking_point['loss'] # 加载loss值
# 继续训练
for epoch in range(start_epoch,num_epochs):
# 继续流程
pass
总结上述保存机制的适用场景:
过拟合(Overfitting)
过拟合:模型在训练集上表现非常好(完美拟合),但在新数据(验证集或测试集)上表现明显变差(泛化能力差)。具体表现为训练误差持续下降,但验证误差却在某个点后上升。
出现过拟合的原因:
- 模型太复杂:神经网络参数多、层数多
- 训练数据少或代表性差:样本不足以让模型学习到泛化的规律,侧重了细节
- 训练时间长:epoch太多(学了太多遍),可能会死记硬背
既然要看模型在训练集和测试集上的表现差异,那么可以同步打印两者的loss值,来判断是否出现了过拟合现象。通过对两者变化的同步性,来判断过拟合。
注意:由于在某些层中,训练和评估时的行为是不同的。因此在训练中途,若手动进入推理模式(测试)后,要记得切换回训练模式。
在训练部分做修改,其它部分不变:
# 训练
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.01)
epoch_num = 20000
train_losses = []
test_losses = []
epochs = []
start_time = time.time()
with tqdm(total=epoch_num) as pbar:
for epoch in range(epoch_num):
# 训练集
train_output = model(X_train)
train_loss = criterion(train_output,y_train)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
train_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 记录
if (epoch + 1) % 200 == 0:
# 测试集的loss,后续可视化
model.eval() # 进入推理模式
with torch.no_grad():
test_output = model(X_test)
test_loss = criterion(test_output,y_test)
model.train() # 切换回训练模式
# 存储
train_losses.append(train_loss.item())
test_losses.append(test_loss.item())
epochs.append(epoch + 1)
pbar.set_postfix({'Train Loss': f'{train_loss.item():.4f}', 'Test Loss': f'{test_loss.item():.4f}'})
# 更新进度条
if (epoch + 1) % 1000 == 0:
pbar.update(1000)
# 补全进度条
if pbar.n < epoch_num:
pbar.update(epoch_num - pbar.n)
end_time = time.time()
print(print(f'Training time: {end_time-start_time:.2f} seconds'))
# 可视化损失曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(epochs, train_losses,label='Train Loss')
plt.plot(epochs, test_losses,label='Test Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss over Epochs')
plt.legend() # 图例显示
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()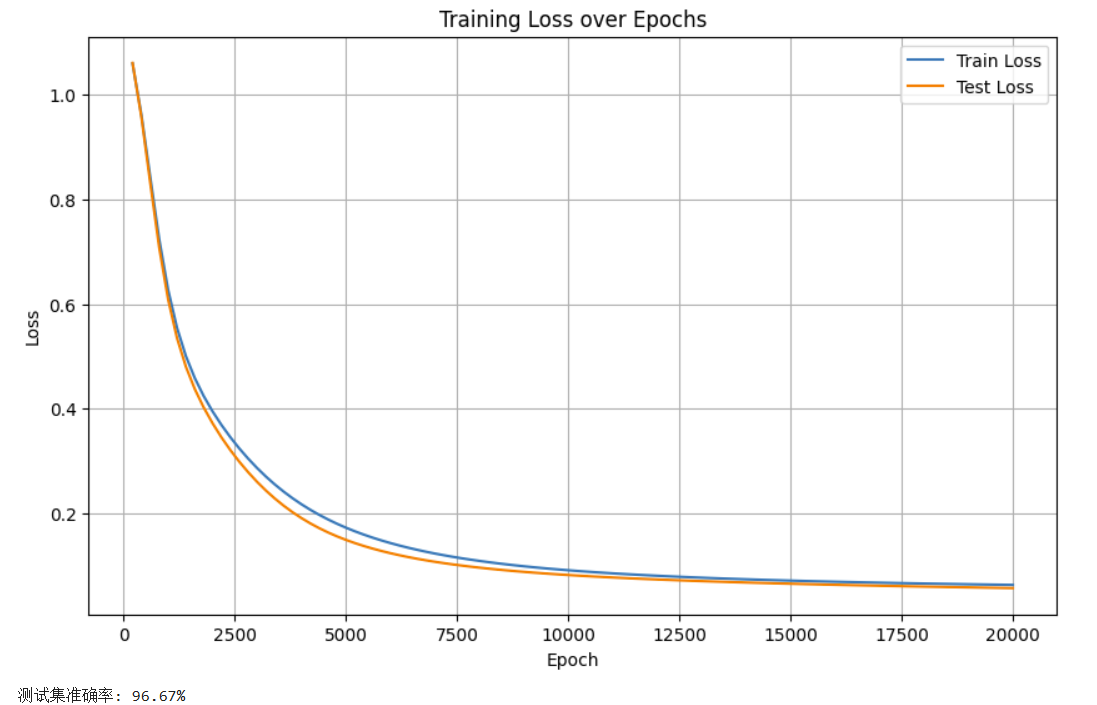
早停策略(Early Stopping)
防止过拟合的策略有很多,比如正则化、dropout(随机关闭部分神经元)、早停策略等。下面介绍早停策略,它的核心思想是:在验证误差不再改善时提前停止训练。
具体的流程:
- 数据划分:分为训练集、验证集和测试集。
- 开始训练:在每个训练周期(Epoch)结束后,同时在训练集和验证集上评估模型性能(例如,计算损失或准确率),并持续监控验证集上的性能指标(通常是验证损失)。
- 设定耐心值(正整数patience):允许验证集性能在连续 patience个周期内不再提升。
- 保存最佳模型:每当在验证集上取得一个新的最佳性能时,就保存当前模型的权重。
- 判断停止:如果在连续的 patience个训练周期内,验证集性能都没有超过之前保存的最佳性能,则触发早停,训练终止。
- 恢复模型:训练结束后,丢弃最后一次训练的模型权重,加载之前保存的性能最佳的那个模型权重。
具体代码的实现:
# 1-加入验证集
# 加载数据
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X_train,X_temp,y_train,y_temp = train_test_split(X,y,train_size=0.8,random_state=42)
X_val,X_test,y_val,y_test = train_test_split(X_temp,y_temp,train_size=0.5,random_state=42)
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print('使用的设备:{}'.format(device))
# 数据预处理
# 归一化
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_val = scaler.transform(X_val)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 张量转换
X_train = torch.FloatTensor(X_train).to(device)
y_train = torch.LongTensor(y_train).to(device)
X_val = torch.FloatTensor(X_val).to(device)
y_val = torch.LongTensor(y_val).to(device)
X_test = torch.FloatTensor(X_test).to(device)
y_test = torch.LongTensor(y_test).to(device)# 2-训练部分加入早停逻辑
#-------早停策略参数添加-----------
patience = 50
best_loss = float('inf') # 初始值设为无穷大,方便比较
best_epoch = 0 # best_loss 对应的epoch
count = 0 # 开始上升的次数
early_stopping = False # 是否早停标志
#---------------------------------
start_time = time.time()
with tqdm(total=epoch_num) as pbar:
for epoch in range(epoch_num):
# 训练集
train_output = model(X_train)
train_loss = criterion(train_output,y_train)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
train_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 记录
if (epoch + 1) % 200 == 0:
# 测试集的loss,后续可视化
model.eval() # 进入推理模式
with torch.no_grad():
val_output = model(X_val)
val_loss = criterion(val_output,y_val)
model.train() # 切换回训练模式
# 存储
train_losses.append(train_loss.item())
val_losses.append(val_loss.item())
epochs.append(epoch + 1)
pbar.set_postfix({'Train Loss': f'{train_loss.item():.4f}', 'Val Loss': f'{val_loss.item():.4f}'})
#-------早停逻辑添加-----------
if val_loss.item() < best_loss:
best_loss = val_loss.item()
best_epoch = epoch + 1
count = 0 # 清零(只要在耐心值范围内,出现loss值下降的情况,就清零重来)
# 保存模型参数,便于后续加载、评估
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_model.pth')
else:
count += 1
if count >= patience:
print(f"早停触发!在第{epoch+1}轮,测试集损失已有{patience}轮未改善。")
print(f"最佳测试集损失出现在第{best_epoch}轮,损失值为{best_loss:.4f}")
early_stopping = True
break #手动中止循环
#---------------------------------
# 更新进度条
if (epoch + 1) % 1000 == 0:
pbar.update(1000)
# 补全进度条
if pbar.n < epoch_num:
pbar.update(epoch_num - pbar.n)
end_time = time.time()
print(f'Training time: {end_time-start_time:.2f} seconds')
#-------加载最终模型来评估-----------
if early_stopping:
print(f"加载第{best_epoch}轮的最佳模型进行最终评估...")
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('best_model.pth'))
#---------------------------------作业
作业:对信贷数据集训练后保存权重,加载权重后继续训练50轮,并采取早停策略
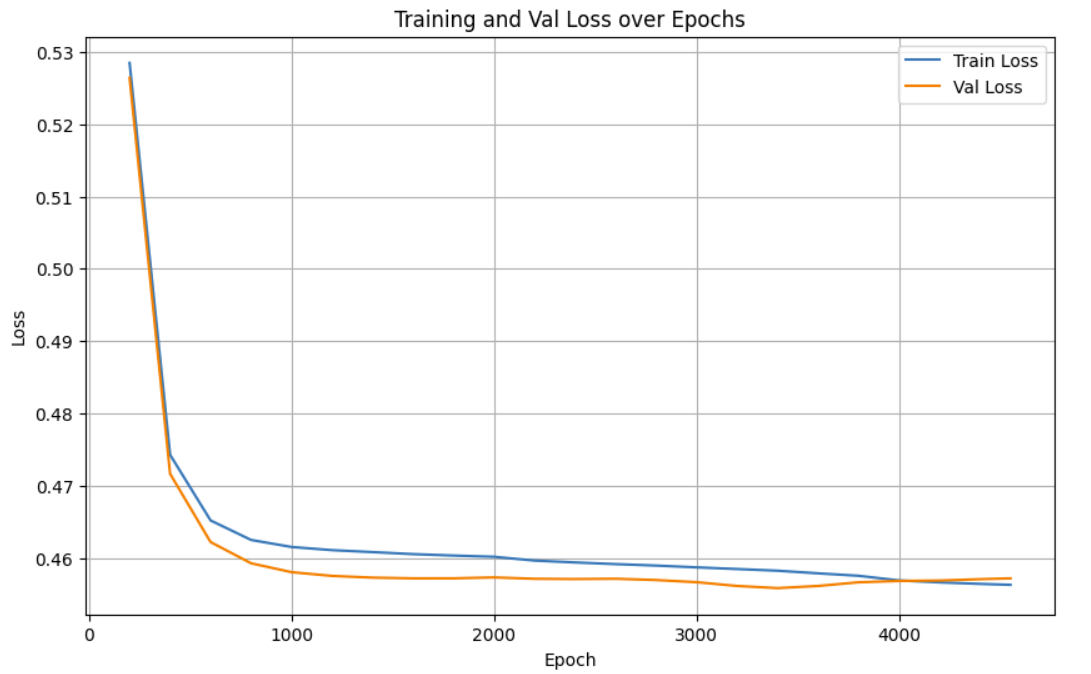
一开始层数设置的比较大加上epoch值也比较大,虽然触发了早停策略,但是从曲线上可以看出在后期验证损失高于训练损失,存在明显的过拟合,后续需尝试调整参数、加入正则化等措施优化。
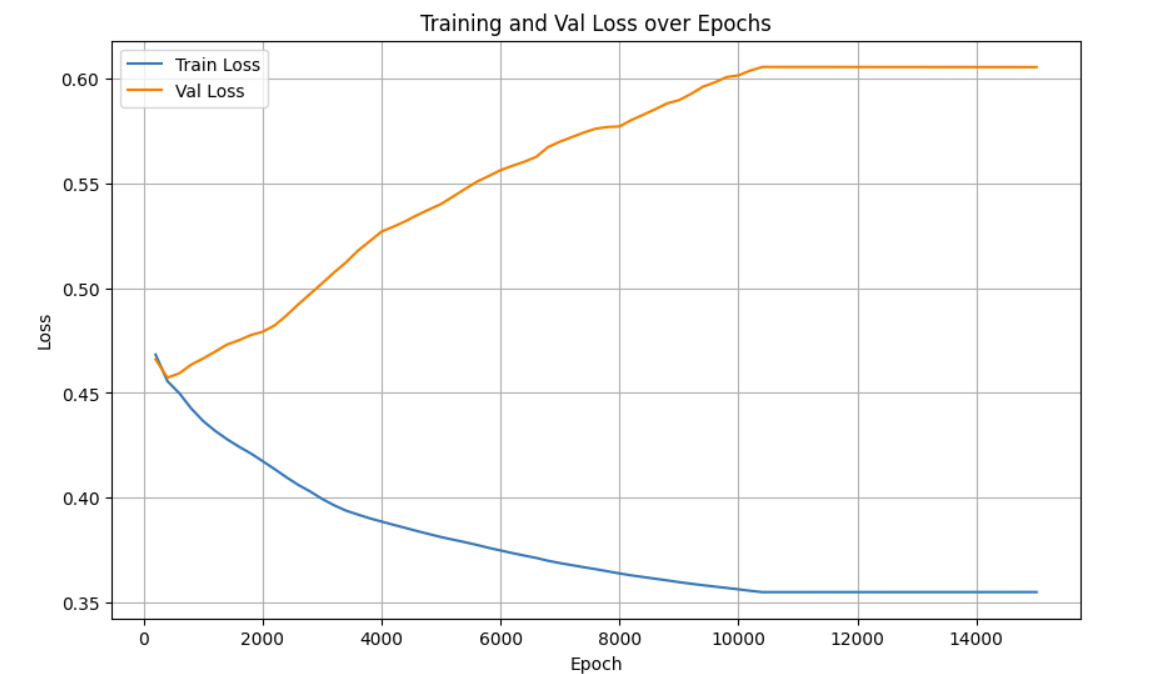
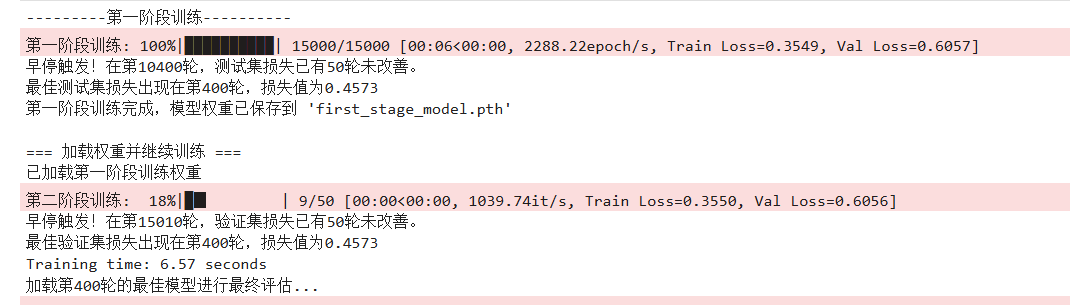
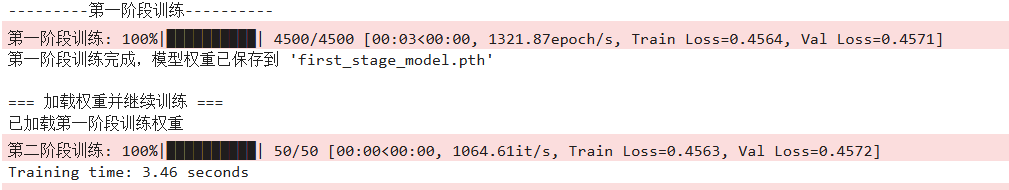
调整隐藏层层数为8,最终准确率:76.93%,epoch跑了4500+50,没有触发早停,训练集和验证集的loss曲线比较接近,过拟合程度较小。
完整代码:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim # 优化器
from tqdm import tqdm # 进度条
import time
# 数据导入
data = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
# 数据预处理-1
# 离散特征编码
mapping_dict = {
'Home Ownership':{
'Own Home':0,
'Rent':1,
'Home Mortgage':2,
'Have Mortgage':3
},
'Years in current job':{
'< 1 year': 0,
'1 year': 1,
'2 years': 2,
'3 years': 3,
'4 years': 4,
'5 years': 5,
'6 years': 6,
'7 years': 7,
'8 years': 8,
'9 years': 9,
'10+ years': 10
},
'Term':{
'Short Term':0,
'Long Term':1
}
} # 映射字典
data['Home Ownership'] = data['Home Ownership'].map(mapping_dict['Home Ownership'])
data['Years in current job'] = data['Years in current job'].map(mapping_dict['Years in current job'])
data['Term'] = data['Term'].map(mapping_dict['Term']) # 0-1映射
data.rename(columns={'Term':'Long Term'},inplace=True) # 重命名列
df = pd.get_dummies(data,columns=['Purpose']) # 独热编码
new_features = [] # 编码后的新特征
for i in df.columns:
if i not in data.columns:
new_features.append(i)
for j in new_features:
df[j] = df[j].astype(int) # 将bool型转换为int型
# 缺失值填充
for col in df.columns.tolist():
mode_value = df[col].mode()[0]
df[col] = df[col].fillna(mode_value)
# 设置设备
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print('使用的设备:{}'.format(device))
# 数据预处理-2
# 归一化
X = df.drop(columns=['Credit Default'],axis=1)
y = df['Credit Default']
X_train,X_temp,y_train,y_temp = train_test_split(X,y,train_size=0.8,random_state=42)
X_val,X_test,y_val,y_test = train_test_split(X_temp,y_temp,train_size=0.5,random_state=42)
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_val = scaler.transform(X_val)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 张量转换
X_train = torch.FloatTensor(X_train).to(device)
y_train = torch.LongTensor(y_train.to_numpy()).to(device)
X_val = torch.FloatTensor(X_val).to(device)
y_val = torch.LongTensor(y_val.to_numpy()).to(device)
X_test = torch.FloatTensor(X_test).to(device)
y_test = torch.LongTensor(y_test.to_numpy()).to(device)
# 模型框架
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MLP,self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(31,8)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
#self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.3) # 添加dropout防止过拟合
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(8,2)
def forward(self,x):
out = self.fc1(x)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
return out
model = MLP().to(device)
# 模型训练,单独提出为一部分
# 可视化损失曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(epochs, train_losses,label='Train Loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_losses,label='Val Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training and Val Loss over Epochs')
plt.legend() # 图例显示
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
# 模型评估
model.eval() # 进入评估模式
with torch.no_grad():
out = model(X_test) # 输入测试集,得到预测结果
_,predictions = torch.max(out,dim=1) # 获取概率最大值的索引,即预测的标签
# 计算准确率
correct_num = (predictions == y_test).sum().item() #转换int
accuracy = correct_num / y_test.size(0)
print('Accuracy:{:.2f}%'.format(accuracy*100)) # 模型训练
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimiser = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.001)
epoch_num = 20000
train_losses = []
val_losses = []
epochs = []
#-------早停策略参数添加-----------
patience = 50
best_loss = float('inf') # 初始值设为无穷大,方便比较
best_epoch = 0 # best_loss 对应的epoch
count = 0 # 开始上升的次数
early_stopping = False # 是否早停标志
#---------------------------------
# 第一阶段
first_stage_epochs = 4500 # 第一阶段训练轮数
second_stage_epochs = 50 # 第二阶段训练轮数
#加入训练时间
start_time = time.time()
print('---------第一阶段训练----------')
with tqdm(total=first_stage_epochs,desc='第一阶段训练',unit='epoch') as pbar:
for epoch in range(first_stage_epochs):
# 训练集
train_output = model(X_train)
train_loss = criterion(train_output,y_train)
# 反向传播和优化
optimiser.zero_grad()
train_loss.backward()
optimiser.step()
# 记录
if (epoch + 1) % 200 == 0:
# 测试集的loss,后续可视化
model.eval() # 进入推理模式
with torch.no_grad():
val_output = model(X_val)
val_loss = criterion(val_output,y_val)
model.train() # 切换回训练模式
# 存储
train_losses.append(train_loss.item())
val_losses.append(val_loss.item())
epochs.append(epoch + 1)
pbar.set_postfix({'Train Loss': f'{train_loss.item():.4f}', 'Val Loss': f'{val_loss.item():.4f}'})
#-------早停逻辑添加-----------
if val_loss.item() < best_loss:
best_loss = val_loss.item()
best_epoch = epoch + 1
count = 0 # 清零(只要在耐心值范围内,出现loss值下降的情况,就清零重来)
# 保存模型参数,便于后续加载、评估
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_model.pth')
else:
count += 1
if count >= patience:
print(f"早停触发!在第{epoch+1}轮,测试集损失已有{patience}轮未改善。")
print(f"最佳测试集损失出现在第{best_epoch}轮,损失值为{best_loss:.4f}")
early_stopping = True
break #手动中止循环
#---------------------------------
# 更新进度条
if (epoch + 1) % 1000 == 0:
pbar.update(1000)
# 补全进度条
if pbar.n < first_stage_epochs:
pbar.update(first_stage_epochs - pbar.n)
# 保存第一阶段训练后的权重
torch.save(model.state_dict(),'first_stage_model.pth')
print("第一阶段训练完成,模型权重已保存到 'first_stage_model.pth'")
# ========== 加载权重并继续训练 ==========
print("\n=== 加载权重并继续训练 ===")
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('first_stage_model.pth'))
print("已加载第一阶段训练权重")
# 记录当前epoch数,用于可视化
current_epoch = len(epochs) if epochs else 0
# 第二阶段训练
with tqdm(total=second_stage_epochs, desc="第二阶段训练") as pbar:
for epoch in range(second_stage_epochs):
# 训练集
train_output = model(X_train)
train_loss = criterion(train_output, y_train)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
train_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 记录
current_epoch_total = first_stage_epochs + epoch + 1
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0: # 第二阶段记录更频繁
# 验证集的loss
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
val_output = model(X_val)
val_loss = criterion(val_output, y_val)
model.train()
# 存储
train_losses.append(train_loss.item())
val_losses.append(val_loss.item())
epochs.append(current_epoch_total)
pbar.set_postfix({'Train Loss': f'{train_loss.item():.4f}', 'Val Loss': f'{val_loss.item():.4f}'})
#-------早停逻辑(第二阶段继续生效)-----------
if val_loss.item() < best_loss:
best_loss = val_loss.item()
best_epoch = current_epoch_total
count = 0
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_model.pth')
else:
count += 1
if count >= patience:
print(f"早停触发!在第{current_epoch_total}轮,验证集损失已有{patience}轮未改善。")
print(f"最佳验证集损失出现在第{best_epoch}轮,损失值为{best_loss:.4f}")
early_stopping = True
break
#---------------------------------
# 更新进度条
pbar.update(1)
end_time = time.time()
print(f'Training time: {end_time:.2f} seconds')
#-------加载最终模型来评估-----------
if early_stopping:
print(f"加载第{best_epoch}轮的最佳模型进行最终评估...")
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('best_model.pth'))
#---------------------------------




















 1144
1144

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








