今日任务:
- 尝试找到一个kaggle或者其他地方的结构化数据集,用之前的内容完成一个全新的项目。
- 探索开源的数据网站
今天主要是将之前所学的内容进行回顾,自己选择一个数据集将机器学习的完整流程进行实践。首先简要回顾完整流程:
- 数据获取:明确研究的问题(回归 or 分类),确定标签和特征
- 数据查看:明确数据的基本信息
- 数据预处理:缺失值填充、异常值处理、数据类型转换(标签编码和独热编码)、连续特征处理(特征尺度统一,标准化与归一化)。若为分类问题,考虑不平衡数据的处理,使用过采样、权重设置和阈值调整等方法
- 描述性统计分析:数据初步可视化,探索特征分布、特征间的关系等
- 特征工程:删除不重要的特征和创造新的特征
- 模型训练与评估:划分数据集后,对比多模型进行训练,使用评估指标进行评估。选择其中效果好的模型进行超参数调整(贝叶斯优化,网格搜索)
- 对训练的结果进行可解释性分析(SHAP)
开源数据网站:
Kaggle:https://www.kaggle.com/datasets
UCI Machine Learning Repository: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
阿里云天池:天池数据集_阿里系唯一对外开放数据分享平台-阿里云天池
和鲸社区:数据集 - Heywhale.com
除了上述所列,还有许多,比如政府开放数据、学术数据共享等等
选择Entrepreneurial Competency in University Students进行分析,地址为:https://www.kaggle.com/namanmanchanda/entrepreneurial-competency-in-university-students
数据总共219行,17列。下面是列的说明:
| 列名 | 含义 |
| EducationSector | 教育部门(8个类别) |
| IndividualProject | 个人项目 Yes/No |
| Age | 学生年龄 (17-26) |
| Gender | 学生性别 Male/Female |
| City | 是否在城市 Yes/No |
| Influenced | 影响 Yes/No |
| Perseverance | 毅力(1,2,3,4,5) |
| DesireToTakeInitiative | 积极主动的愿望(1,2,3,4,5) |
| Competitiveness | 竞争力(1,2,3,4,5) |
| SelfReliance | 自力更生(1,2,3,4,5) |
| StrongNeedToAchieve | 强烈的实现需求(1,2,3,4,5) |
| SelfConfidence | 自信心(1,2,3,4,5) |
| GoodPhysicalHealth | 良好的身体健康等级(1,2,3,4,5) |
| MentalDisorder | 是否有精神障碍 Yes/No |
| KeyTraits | 学生的主要特征(5个类别) |
| ReasonsForLack | 缺乏的原因(各种各样) |
| y | 学生是否成为企业家 0/1 |
导入库
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,precision_score,recall_score,f1_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,classification_report
import shap
import numpy as np
#绘图中中文显示问题
#绘图中负号显示问题
数据查看
data = pd.read_csv(r'university_students.csv')
data.info()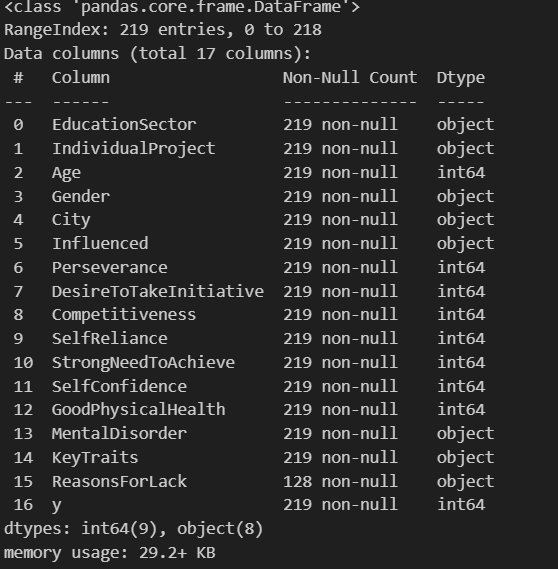
data.info()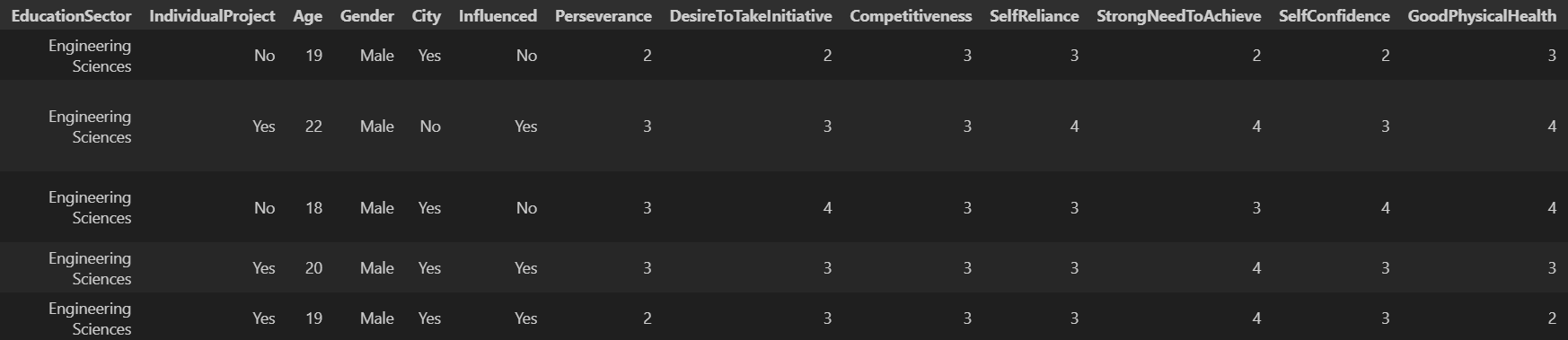
数据预处理
通过概览信息的查看,可以得到数据无缺失值。异常值先不考虑。对于16个特征中,有8个属于obejct类型,其中ReasonsForLack列的内容太杂,暂时删去。剩下的有4个列均为‘Yes/No’型和1个‘男/女’,采用标签编码映射;2个为多类别的无序特征,选择使用独热编码。
#离散特征和连续特征
#continous_features = data.select_dtypes(include=['float64','int64']).columns.tolist()
#discrete_features = data.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns.tolist()
#编码
#1-标签编码,0-1映射
mapping_dict = {
'IndividualProject':{
'No':0,
'Yes':1
},
'City':{
'No':0,
'Yes':1
},
'Influenced':{
'No':0,
'Yes':1
},
'MentalDisorder':{
'No':0,
'Yes':1
},
'Gender':{
'Female':0,
'Male':1
}
}
for key,value in mapping_dict.items():
data[key] = data[key].map(value)
data.rename(columns={'Gender': 'Male'}, inplace=True) # 重命名列,0-1映射
#2-独热编码
data = pd.get_dummies(data,columns=['EducationSector','KeyTraits'])
data_1 = pd.read_csv(r'university_students.csv')
new_features = []
for i in data:
if i not in data_1:
new_features.append(i)
for j in new_features:
data[j] = data[j].astype(int)
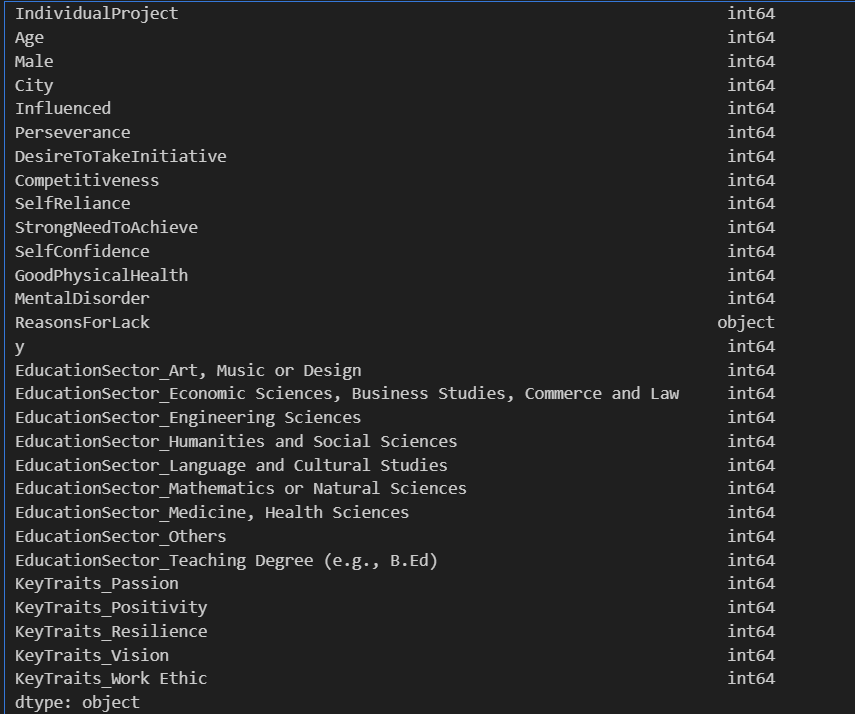
data.dtypes
查看标签的分布情况,两种类别比例在1.41:1,不平衡问题较轻
data['y'].value_counts()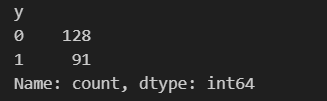
不进行过采样处理,但简单回顾处理方法:
#不平衡数据的处理,对训练集进行处理
#导入库
from sklearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
#SMOTE过采样
smote = SMOTE(random_state=42)
X_smote,y_smote = smote.fit_resample(X_train,y_train)
描述性分析
之前学习的图形主要有直方图、箱形图、小提琴图、计数图和热图。此外还知道了绘制子图的方法。
#描述性统计
continuous_features = data.select_dtypes(include=['int64']).columns.to_list()
#设置画布
fig,axes = plt.subplots(3,3,figsize=(12,12))
axes = axes.flatten()
for index,value in enumerate(continuous_features[:9]): #查看前9个
sns.countplot(data=data,x=value,ax=axes[index])
axes[index].set_xlabel(value)
axes[index].set_title(f'The Countplot of {value}')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()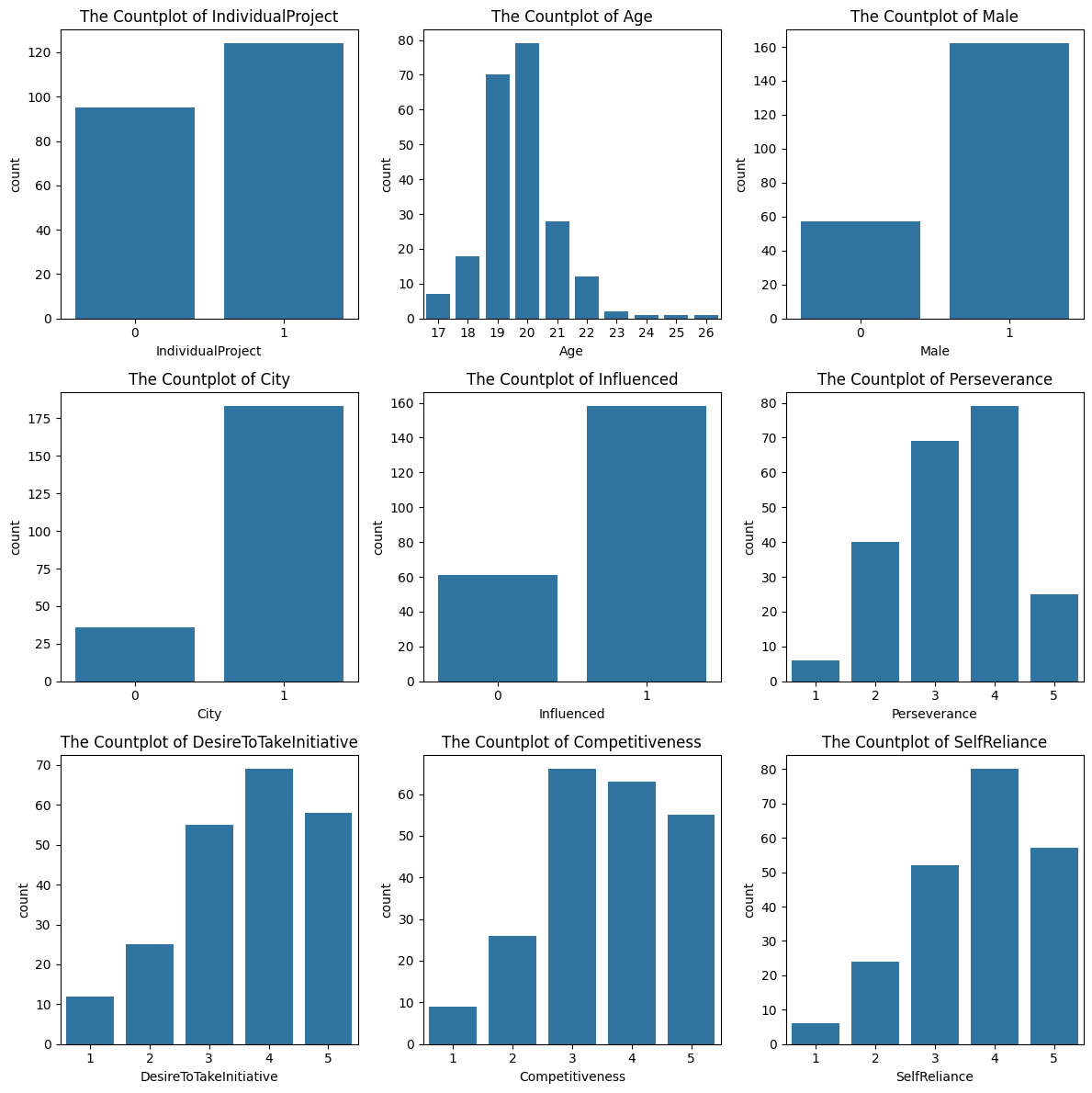
建模与训练
#设置标签和特征
X = data.drop(['y','ReasonsForLack'],axis=1) #由于ReasonsForLack列的东西太杂,选择删去
y = data['y']
#数据集的划分
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,train_size=0.8,random_state=42)
#确定少数类
counts = np.bincount(y)
minority_class = np.argmin(counts)
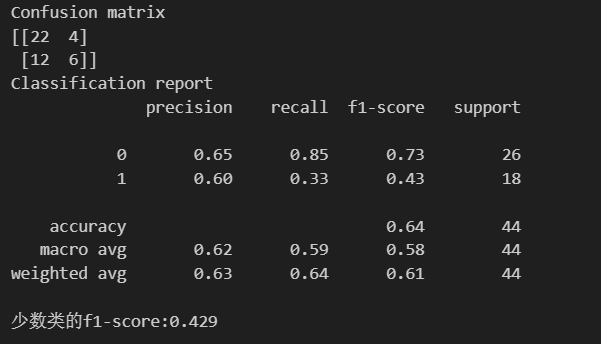
随机森林
#导入模型训练
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
#核心三行代码
rf_model = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42) #实例化
rf_model.fit(X_train,y_train) #训练,此处未考虑过采样
rf_pred = rf_model.predict(X_test) #预测
#评估指标
print('Confusion matrix')
print('{}'.format(confusion_matrix(y_test,rf_pred)))
print('Classification report')
print('{}'.format(classification_report(y_test,rf_pred)))
#查看少数类的f1-score
print('少数类的f1-score:{:.3f}'.format(f1_score(y_test,rf_pred,pos_label=minority_class)))
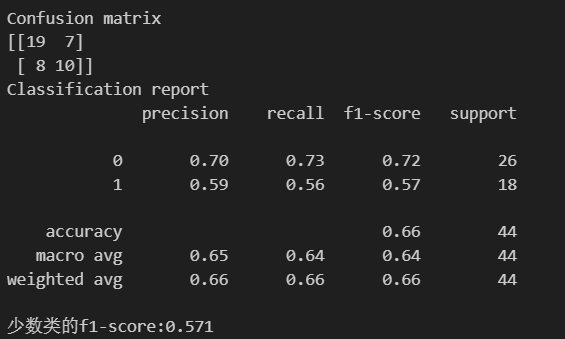
XGBoost
#导入模型训练
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
#核心三行代码
xgb_model = XGBClassifier(random_state=42) #实例化
xgb_model.fit(X_train,y_train) #训练,此处未考虑过采样
xgb_pred = xgb_model.predict(X_test) #预测
#评估指标
print('Confusion matrix')
print('{}'.format(confusion_matrix(y_test,xgb_pred)))
print('Classification report')
print('{}'.format(classification_report(y_test,xgb_pred)))
#查看少数类的f1-score
print('少数类的f1-score:{:.3f}'.format(f1_score(y_test,xgb_pred,pos_label=minority_class)))
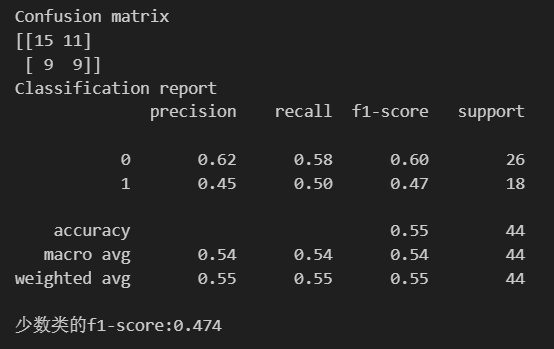
KNN
#导入模型训练
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
#核心三行代码
knn_model = KNeighborsClassifier() #实例化
knn_model.fit(X_train,y_train) #训练,此处未考虑过采样
knn_pred = knn_model.predict(X_test) #预测
#评估指标
print('Confusion matrix')
print('{}'.format(confusion_matrix(y_test,knn_pred)))
print('Classification report')
print('{}'.format(classification_report(y_test,knn_pred)))
#查看少数类的f1-score
print('少数类的f1-score:{:.3f}'.format(f1_score(y_test,knn_pred,pos_label=minority_class)))
超参数调整
根据F1-Score作为评估标准,选择XGBoost进行超参数调参(贝叶斯优化)
#导入库
from skopt import BayesSearchCV
from skopt.space import Integer
import time
start_time = time.time()
#设置参数空间
search_spaces = {
'n_estimators':Integer(50,200),
'max_depth':Integer(10,30),
'min_samples_split':Integer(2,10),
"min_sampls_leaf":Integer(1,4)
}
#实例化
bayes_search = BayesSearchCV(
estimator=XGBClassifier(random_state=42),
search_spaces=search_spaces,
n_iter=25,
cv=5,
n_jobs=-1,
scoring='f1' #使用f1分数评估
)
#训练
bayes_search.fit(X_train,y_train)
end_time = time.time()
print('调参所需时间:{:.4f}s'.format(end_time-start_time))
#获取最佳模型、参数,训练
best_xgb_model = bayes_search.best_estimator_
best_xgb_pred = best_xgb_model.predict(X_test)
#评估指标
print('Confusion matrix')
print('{}'.format(confusion_matrix(y_test,best_xgb_pred)))
print('Classification report')
print('{}'.format(classification_report(y_test,best_xgb_pred)))
可解释性分析
#初始化解释器
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(xgb_model)
#计算shap值
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(X_test)
#查看shap_value数组的尺寸(44,27),表示每个特征对预测为正类的对数几率的贡献
#绘制图形,查看特征重要性
shap.summary_plot(shap_values, X_test, plot_type='bar',feature_names=X_test.columns.tolist())
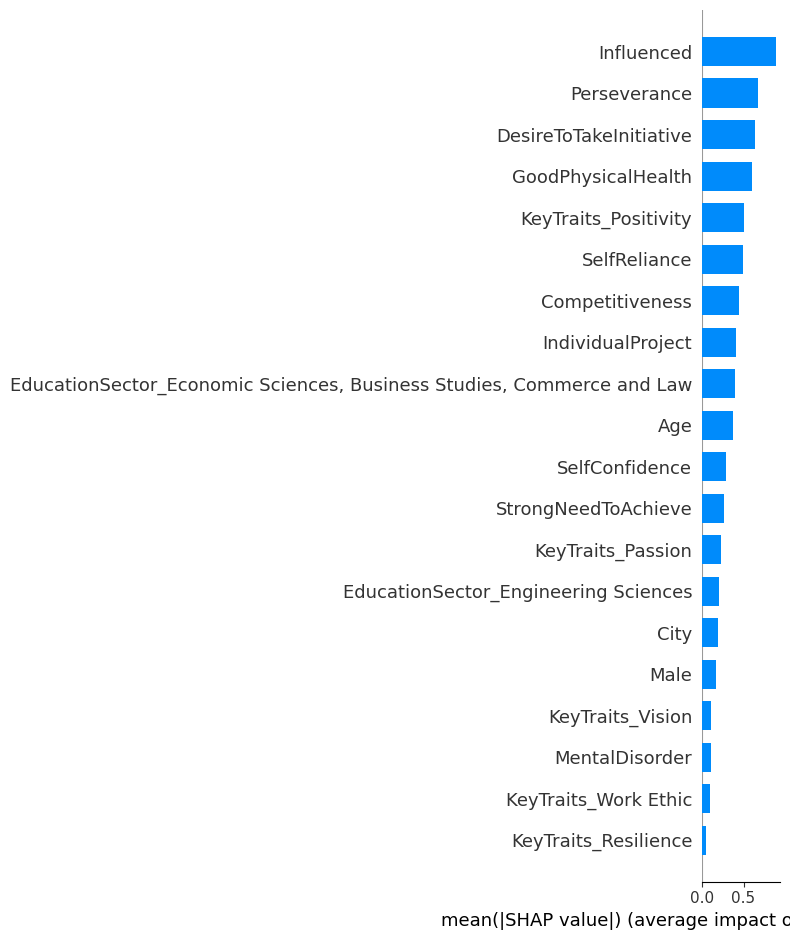
通过今日的练习,将之前所学的内容,基本都有回顾和操作。但是对于这个数据的分析是十分粗糙的,在很多地方需要优化,来挖掘数据的价值。





















 1165
1165

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








