import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import optimize
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
class SmoothWaveguideDesign:
def __init__(self):
self.n_core = 1.51
self.n_clad = 1.45
self.lambda0 = 1550e-9
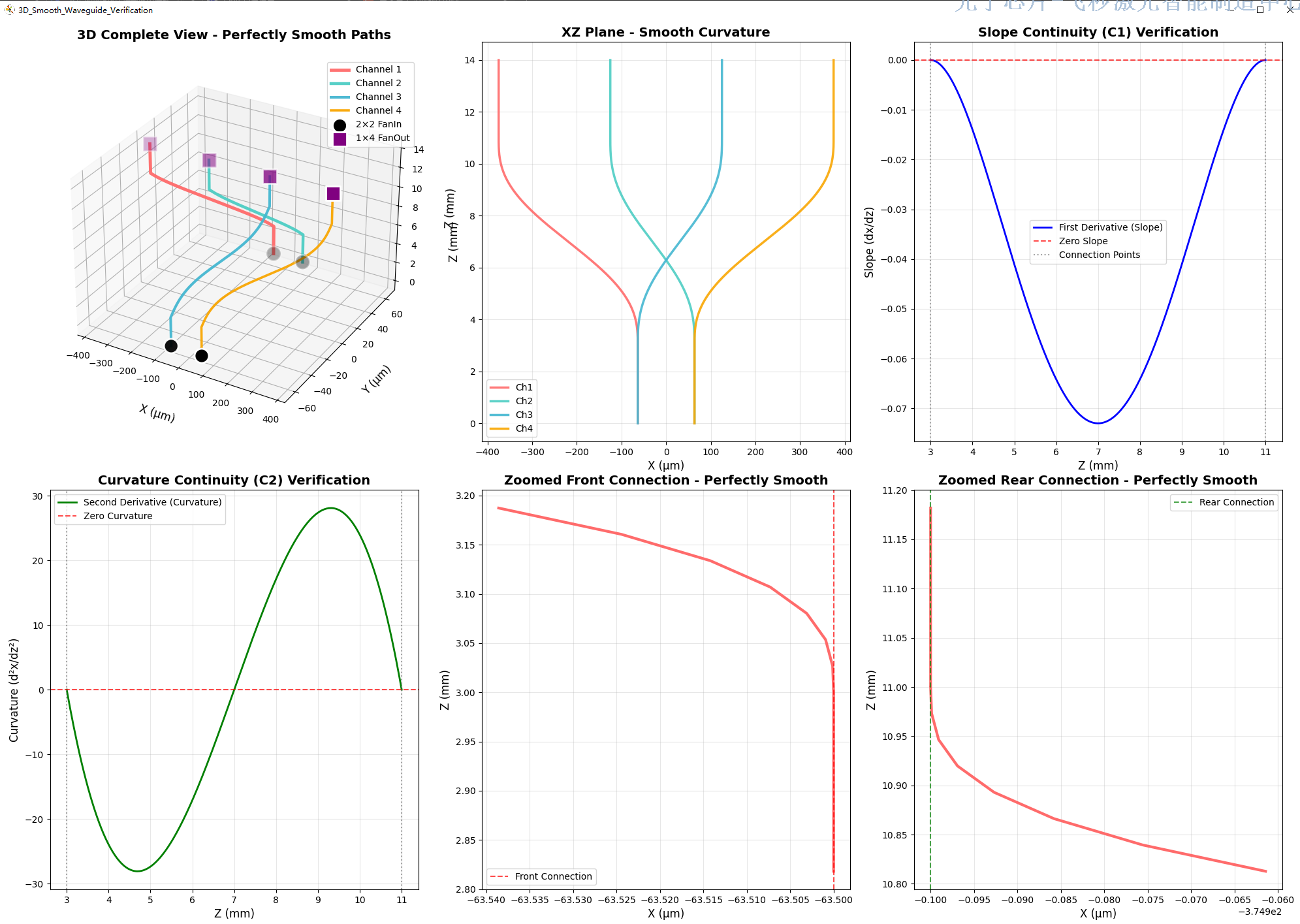
def calculate_smooth_transition(self, x_start, z_start, x_end, z_end, y_start, y_end, transition_length):
"""Calculate smooth transition with C2 continuity"""
# Use cubic polynomial for smooth transition
# f(z) = a*(z-z0)^3 + b*(z-z0)^2 + c*(z-z0) + d
z0 = z_start
z1 = z_end
# Boundary conditions for C2 continuity:
# f(z0) = x_start, f'(z0) = 0, f(z1) = x_end, f'(z1) = 0
# f''(z0) = 0, f''(z1) = 0
# Solve cubic polynomial coefficients
dz = z1 - z0
dx = x_end - x_start
# Cubic polynomial: f(z) = a*(z-z0)^3 + b*(z-z0)^2 + c*(z-z0) + d
# With boundary conditions: f(z0)=x_start, f'(z0)=0, f(z1)=x_end, f'(z1)=0
a = 2 * dx / (dz**3)
b = -3 * dx / (dz**2)
c = 0
d = x_start
z_transition = np.linspace(z0, z1, 200)
z_normalized = z_transition - z0
x_transition = a * z_normalized**3 + b * z_normalized**2 + c * z_normalized + d
# First derivative (slope)
dx_dz = 3 * a * z_normalized**2 + 2 * b * z_normalized + c
# Second derivative (curvature)
d2x_dz2 = 6 * a * z_normalized + 2 * b
# Y coordinate varies linearly
y_transition = y_start + (y_end - y_start) * (z_transition - z0) / dz
return x_transition, y_transition, z_transition, dx_dz, d2x_dz2
def generate_smooth_waveguide_paths(input_positions, output_positions):
"""Generate perfectly smooth waveguide paths with C2 continuity"""
num_channels = len(input_positions)
# Section lengths
straight_length = 3.0e-3
transition_length = 8.0e-3
total_length = straight_length * 2 + transition_length
paths = []
derivative_info = []
for i in range(num_channels):
x_in, y_in = inpu






 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1080
1080

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








