某些项目,在某些特殊场合,有一代码段混合了耗时代码和Unity api。如下面这种情况
MainFunction
{
//这个函数会进行大量文件读写操作
DownloadFile1
(
)
;
//这个函数是unity函数
UnityFunction1
(
)
;
DownloadFile2
(
)
;
UnityFunction2
(
)
;
DownloadFile3
(
)
;
UnityFunction3
(
)
;
..
..
..
}
如果必须保证LoadLocalFile() 不“假死”,不管是使用带参回调,或事件注册,都会导致代码难以编写和阅读。 参考Loom,网上的代码五花八门,甚至还有错误的,我做了一些修改,核心思路是把主线程需要执行的任务放在待消费列表中。 实际项目中可以在MainThreadTask结构中定义自己的各种调度排序策略(类似操作系统进程调度)
using
UnityEngine
;
using
System
.
Collections
;
using
System
.
Collections
.
Generic
;
using
System
;
using
System
.
Threading
;
using
System
.
Linq
;
public
class
Loom
:
MonoBehaviour
{
public
struct
MainThreadTask
{
//何时运行该函数
public
System
.
DateTime
time
;
public
Action
action
;
}
public
static
int
maxThreads
=
8
;
private
int
hasThreadCount
;
private
static
Loom
current
;
private
static
void
CheckInit
(
)
{
if
(
current
==
null
)
{
var
g
=
new
GameObject
(
"Loom"
)
;
current
=
g
.
AddComponent
<
Loom
>
(
)
;
UnityEngine
.
Object
.
DontDestroyOnLoad
(
g
)
;
}
}
public
static
void
RunOnMainThread
(
Action
action
,
float
time
=
0
)
{
CheckInit
(
)
;
if
(
time
<
0
)
{
Debug
.
LogError
(
"time参数错误 函数不会被执行"
)
;
return
;
}
if
(
time
!=
0
)
{
lock
(
current
.
allDelayed
)
{
current
.
allDelayed
.
Add
(
new
MainThreadTask
{
time
=
System
.
DateTime
.
Now
.
AddSeconds
(
time
)
,
action
=
action
}
)
;
}
}
else
{
lock
(
current
.
allNoDelayed
)
{
current
.
allNoDelayed
.
Add
(
new
MainThreadTask
{
time
=
System
.
DateTime
.
Now
,
action
=
action
}
)
;
}
}
}
public
static
void
RunOnAsync
(
Action
active
)
{
CheckInit
(
)
;
while
(
current
.
hasThreadCount
>=
maxThreads
)
{
Thread
.
Sleep
(
100
)
;
}
Interlocked
.
Increment
(
ref
current
.
hasThreadCount
)
;
ThreadPool
.
QueueUserWorkItem
(
RunAction
,
active
)
;
}
private
static
void
RunAction
(
object
action
)
{
try
{
(
(
Action
)
action
)
(
)
;
}
catch
(
Exception
e
)
{
Debug
.
LogError
(
e
.
ToString
(
)
)
;
}
finally
{
Interlocked
.
Decrement
(
ref
current
.
hasThreadCount
)
;
}
}
//延时和不延时区分开来的目的是保证不延时的函数立即执行 且减少linq查询
private
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
allDelayed
=
new
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
(
)
;
private
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
currentDelayed
=
new
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
(
)
;
private
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
allNoDelayed
=
new
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
(
)
;
private
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
currentNoDelayed
=
new
List
<
MainThreadTask
>
(
)
;
// 消费主线程任务
private
void
Update
(
)
{
if
(
allNoDelayed
.
Count
>
0
)
{
lock
(
allNoDelayed
)
{
currentNoDelayed
.
Clear
(
)
;
currentNoDelayed
.
AddRange
(
allNoDelayed
)
;
allNoDelayed
.
Clear
(
)
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
currentNoDelayed
.
Count
;
i
++
)
{
currentNoDelayed
[
i
]
.
action
(
)
;
}
}
if
(
allDelayed
.
Count
>
0
)
{
lock
(
allDelayed
)
{
currentDelayed
.
Clear
(
)
;
currentDelayed
.
AddRange
(
allDelayed
.
Where
(
d
=>
d
.
time
<=
System
.
DateTime
.
Now
)
)
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
currentDelayed
.
Count
;
i
++
)
{
allDelayed
.
Remove
(
currentDelayed
[
i
]
)
;
}
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
currentDelayed
.
Count
;
i
++
)
{
currentDelayed
[
i
]
.
action
(
)
;
}
}
}
}
使用方式
void
Start
(
)
{
Loom
.
RunOnAsync
(
MainFun
)
;
}
public
void
MainFun
(
)
{
Loom
.
RunOnMainThread
(
FirstTest
)
;
Thread
.
Sleep
(
100
)
;
Loom
.
RunOnMainThread
(
(
)
=>
{
Test
(
"2"
)
;
}
)
;
Thread
.
Sleep
(
100
)
;
Loom
.
RunOnMainThread
(
(
)
=>
{
Test
(
"4"
)
;
}
,
1f
)
;
Loom
.
RunOnMainThread
(
(
)
=>
{
Test
(
"3"
)
;
}
)
;
}
private
void
FirstTest
(
)
{
Debug
.
Log
(
"1:"
+
gameObject
.
name
)
;
}
private
void
Test
(
string
time
)
{
Debug
.
Log
(
time
+
":"
+
gameObject
.
name
)
;
}
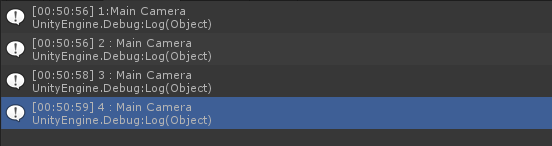
执行结果




 本文介绍了一种在Unity中优化多线程调用的方法,通过将主线程任务放入待消费列表并采用Loom类实现,有效避免了耗时代码与UnityAPI混合导致的“假死”现象。文中详细解释了如何使用Loom类的RunOnMainThread和RunOnAsync方法,并通过实例展示了如何在主线程和子线程间高效调度任务。
本文介绍了一种在Unity中优化多线程调用的方法,通过将主线程任务放入待消费列表并采用Loom类实现,有效避免了耗时代码与UnityAPI混合导致的“假死”现象。文中详细解释了如何使用Loom类的RunOnMainThread和RunOnAsync方法,并通过实例展示了如何在主线程和子线程间高效调度任务。
















 2450
2450

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








