目录
一、简介
ILRuntime 项目为基于C#的平台(例如Unity)提供了一个纯C#实现,快速、方便且可靠的IL运行时,使得能够在不支持JIT的硬件环境(如iOS)能够实现代码的热更新
ILRuntime 的优势
同市面上的其他热更方案相比,ILRuntime主要有以下优点:
无缝访问C#工程的现成代码,无需额外抽象脚本API
直接使用VS2015进行开发,ILRuntime的解译引擎支持.Net 4.6编译的DLL
执行效率是L#的10-20倍
选择性的CLR绑定使跨域调用更快速,绑定后跨域调用的性能能达到slua的2倍左右(从脚本调用GameObject之类的接口)
支持跨域继承
完整的泛型支持
拥有Visual Studio的调试插件,可以实现真机源码级调试。支持Visual Studio 2015 Update3、Visual Studio 2017、Visual Studio 2019和Visual Studio 2022
支持VS Code源码级调试,支持Mac OSX
最新的2.0版引入的寄存器模式将数学运算性能进行了大幅优化。
官方地址:
ILRuntime 目前只支持 Unity 5.x 到 Unity 2020.x,Unity 2018 - 2020 版本是最合适的。
二、环境搭建
创建一个 Unity 项目,我用的 Unity 版本是 Unity 2020.3.48f1c1
打开你项目的 Packages 文件夹
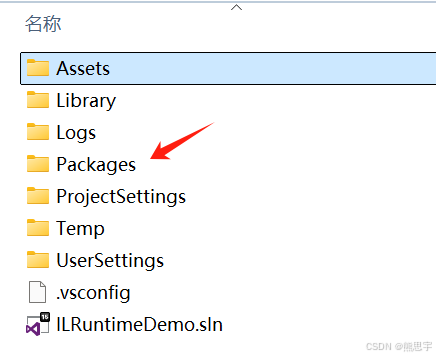
打开 manifest.json 文件

添加下面 Json 字符串:
"scopedRegistries": [
{
"name": "ILRuntime",
"url": "https://registry.npmjs.org",
"scopes": [
"com.ourpalm"
]
}
],添加完成后为这样:
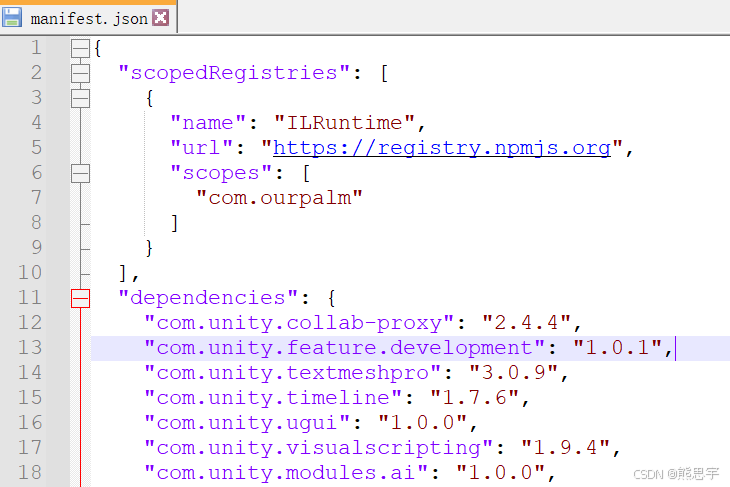
如果是第一次导入,会弹出下面的界面,点 Close
在 Unity 2022 和 2023 是不支持 ILRuntime,这么操作会报错,而且包管理器根本无法刷新。
将 Enable Preview Packages(启用预览包)和 Show Dependencies()
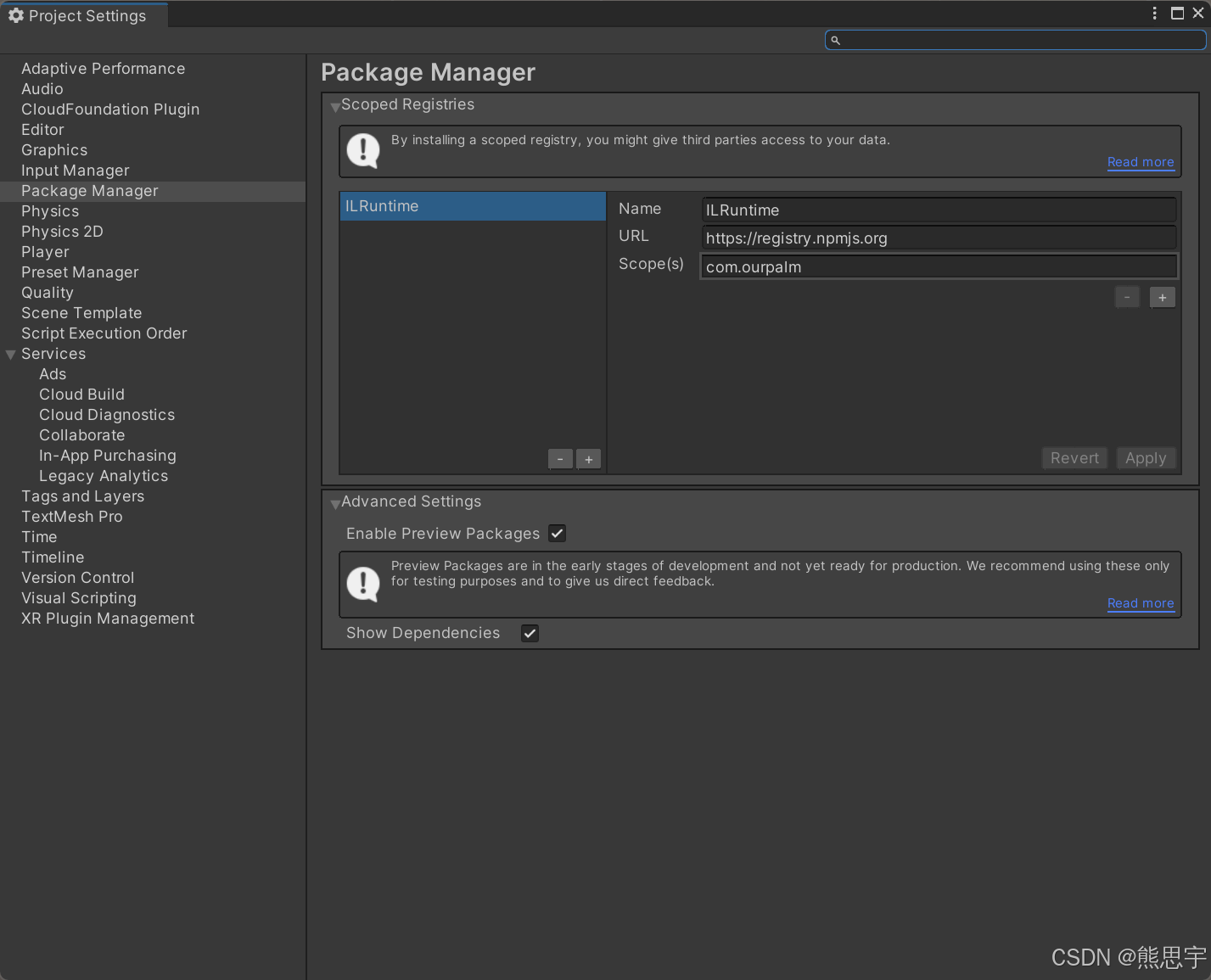
打开包管理器
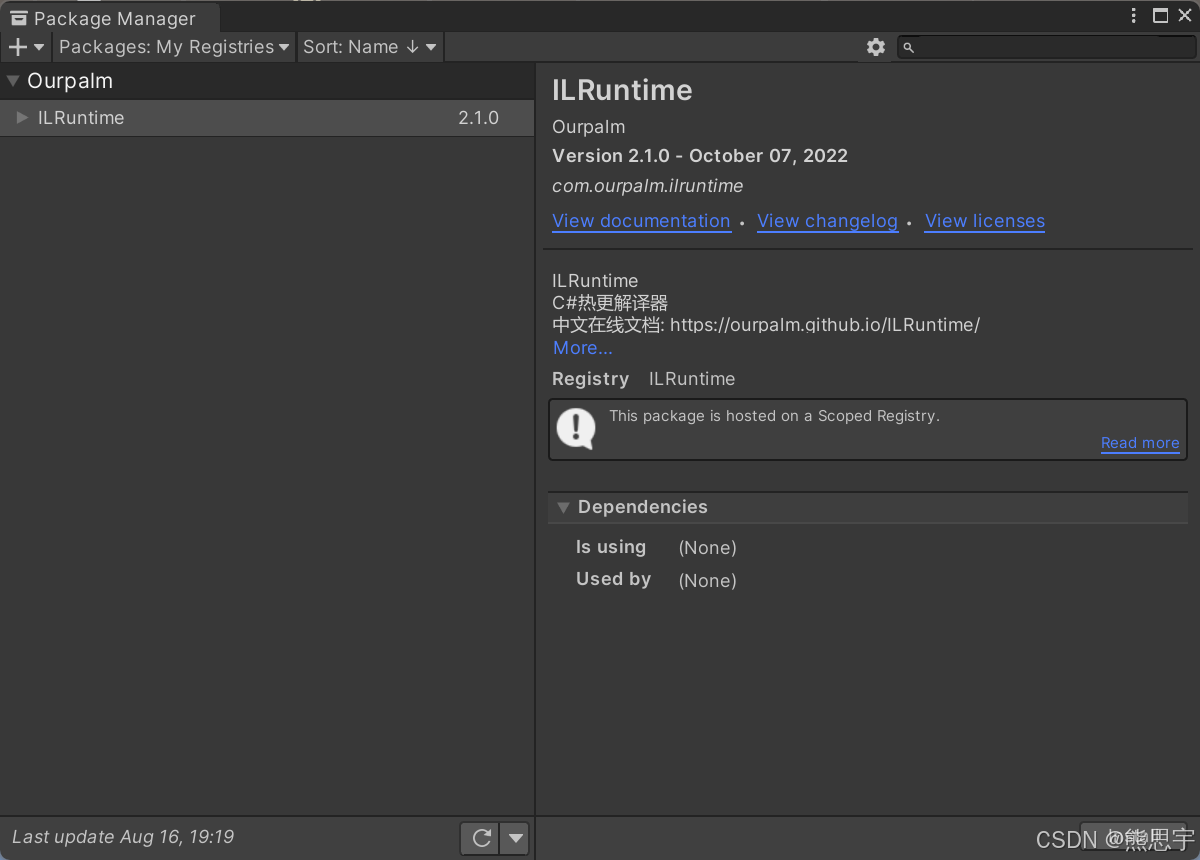
安装完成后,点击导入 Demo
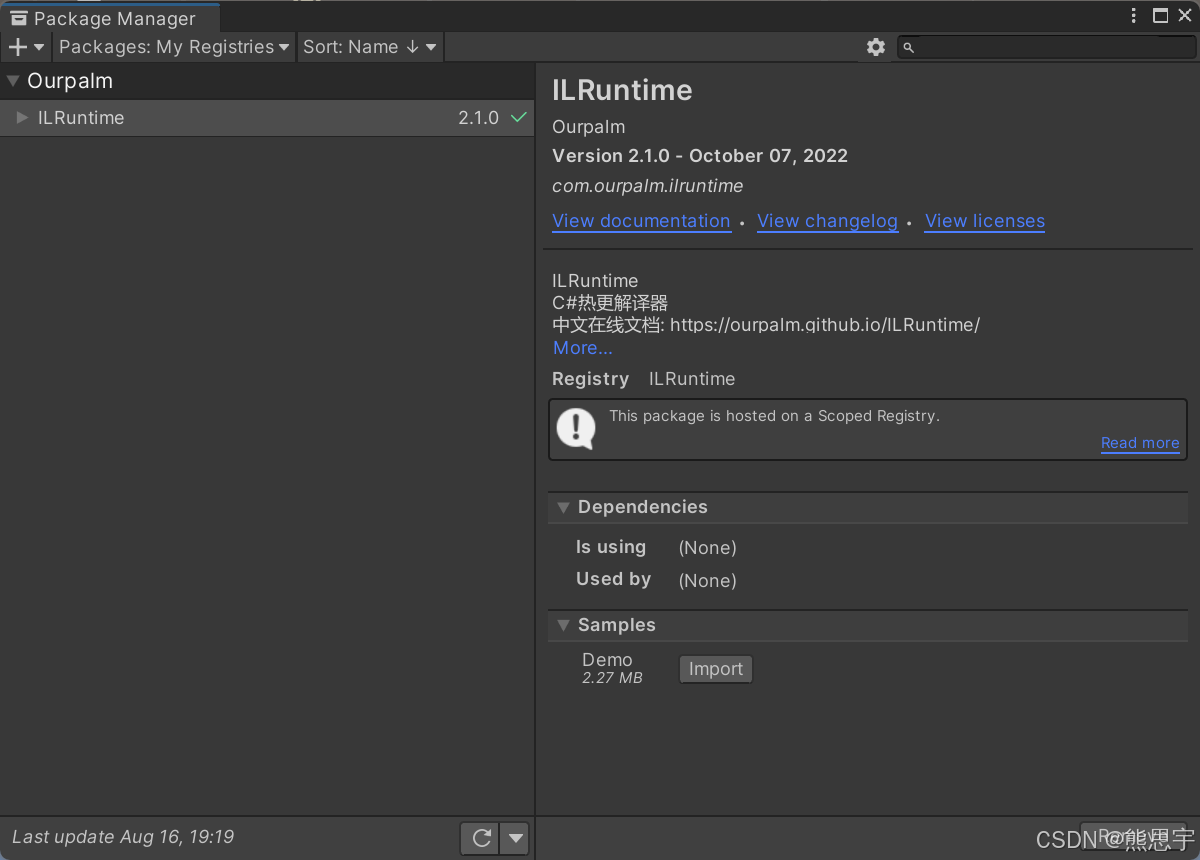
这时候发现控制台报了一堆的错误,这主要是因为 ILRuntime 中的不安全代码导致的
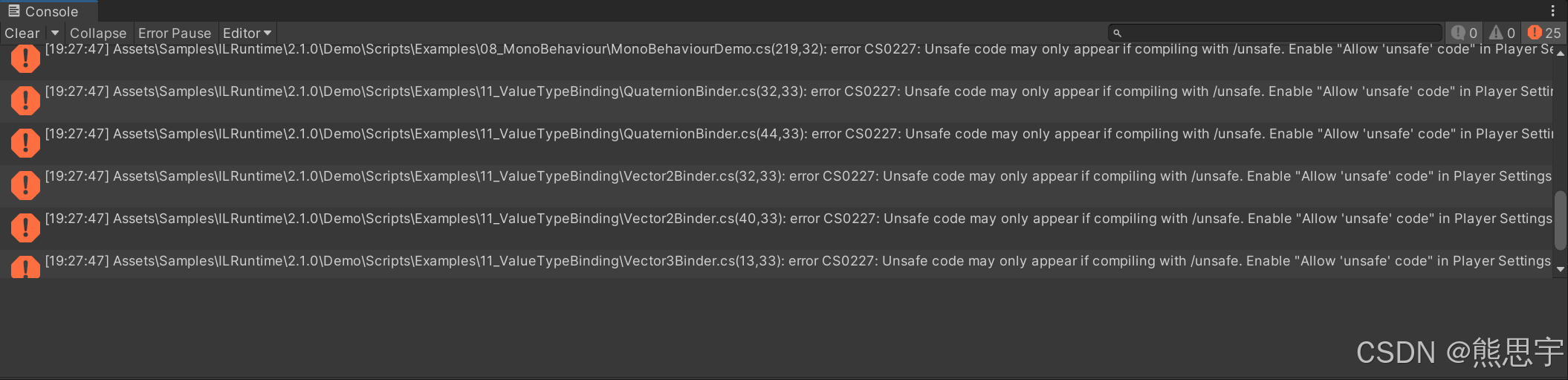
在 Project Settings 中搜索 Allow unsafe Code,并将勾打上,等加载完了,就没有这个错误了。
这时先别急着关闭,把 Api Compatibility Level 设置为 .Net 4.x 。
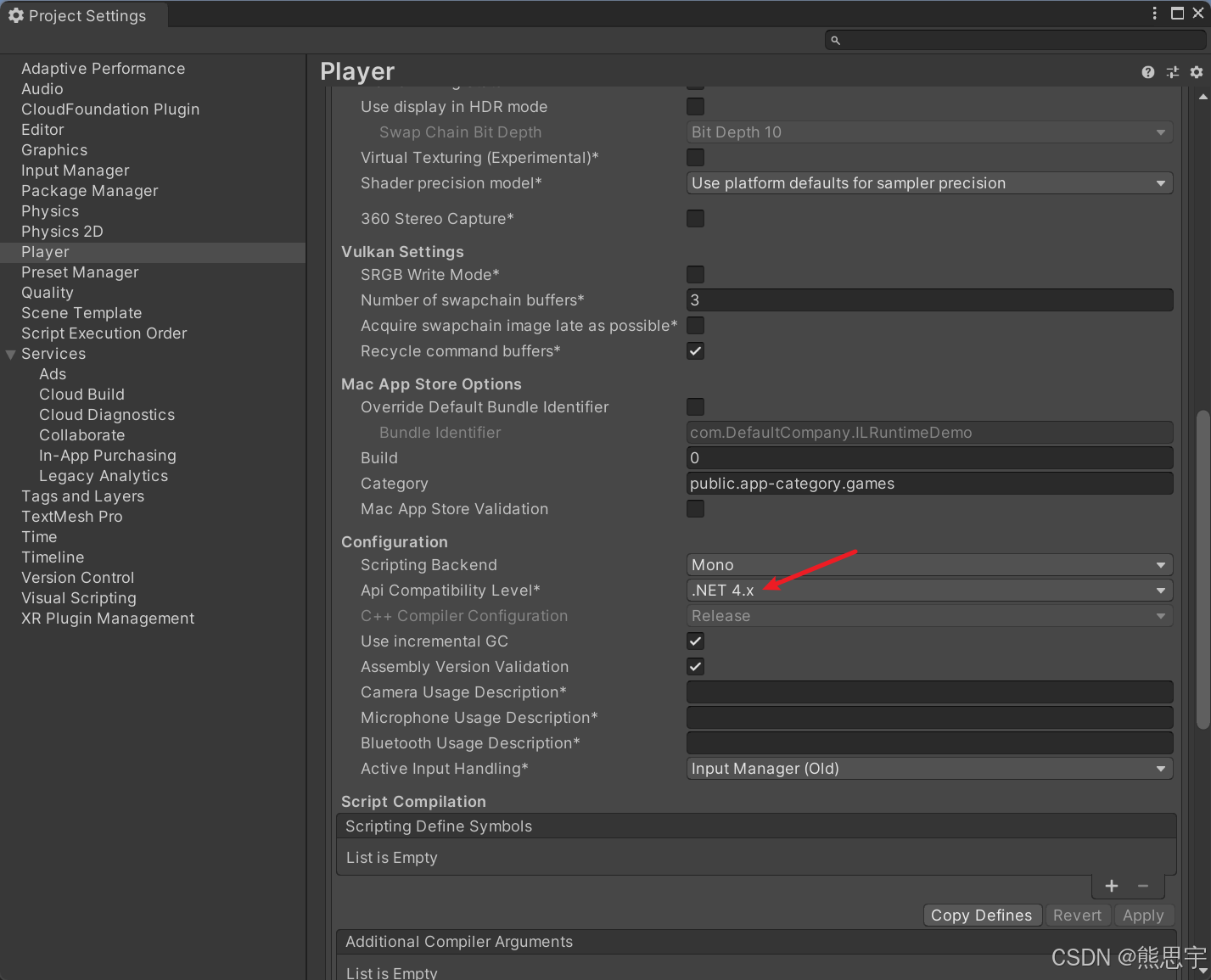
我们打开第一个Demo场景,
直接运行会报错
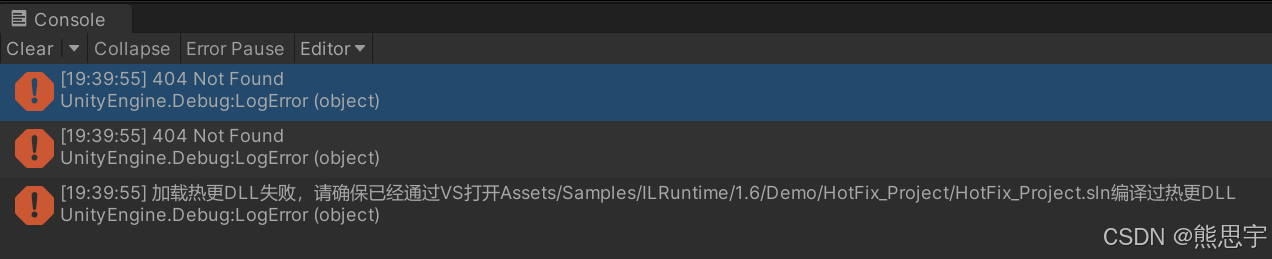
根据提示,找到 HotFix_Project~ 文件夹下 HotFix_Project.sln
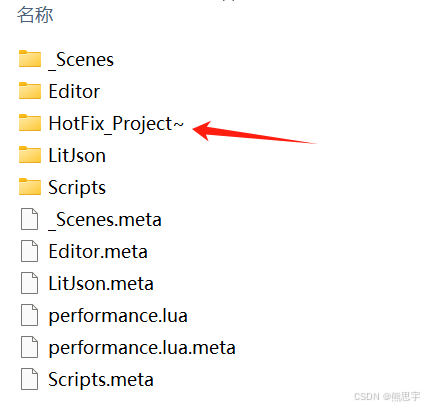
用 Visual Studio 2022 打开项目,查看代码是否有错误,如果没有错误,直接右键生成即可,最好是生成 Release 模式,执行的效率会比 Debug 模式要快几倍。
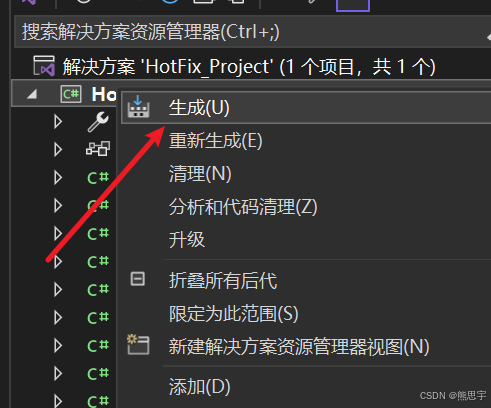
现实 生成 1 成功表示准备工作就可以了
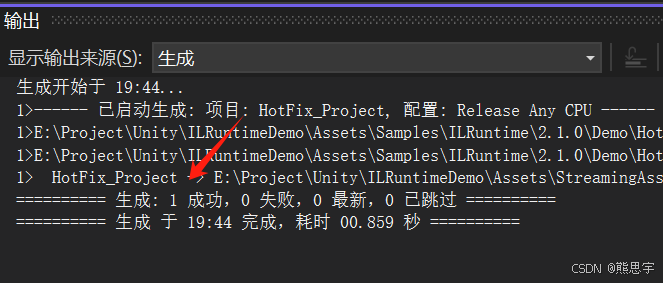
此时,可以看到,项目中多了一个 StreamingAssets 文件夹,并且里面有两个文件

再次运行项目,如果出现了 !!! InstanceClass.StaticFunTest() 的打印,就说明你的环境搭建已经成功了。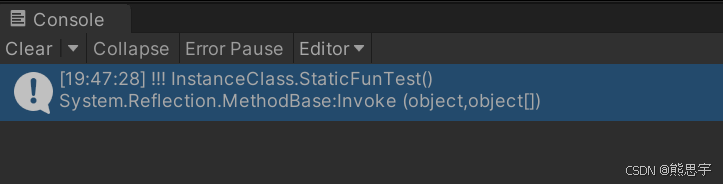
三、常用案例
ILRuntime 主要还是用在 Unity 中的,为了方便测试,我将源代码复制到了 Winform 中,所以下面的代码有些是用控制台输出的。
ILRuntime Demo 场景文件的路径:
ILRuntime Demo 脚本文件的路径:
实例化 ILRuntime 内部的类
ILRuntime 内代码:
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string SayHi()
{
return "hello";
}
public Program() { }
public Program(string name)
{
this.Name = name;
}
}
}方式1
ILTypeInstance instance = appdomain.Instantiate("HotFix_Project.Program");
IMethod sayHiMethod = instance.Type.GetMethod("SayHi");
object res = appdomain.Invoke(sayHiMethod, instance, null);
Console.WriteLine(res);运行:

如果构造函数需要传入参数,可以这么写:
ILTypeInstance instance = appdomain.Instantiate("HotFix_Project.Program", new object[] { "张三" });方式2
IType type = appdomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Program"];
ILTypeInstance instance = ((ILType)type).Instantiate();
IMethod sayHiMethod = instance.Type.GetMethod("SayHi");
object res = appdomain.Invoke(sayHiMethod, instance, null);
Console.WriteLine(res);运行结果一样
获取/设置 ILRuntime 的属性值
获取属性值
ILRuntime 内代码:
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public Program(string name)
{
this.Name = name;
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
var obj = appdomain.Instantiate("HotFix_Project.Program", new object[] { "张三" });
var res = appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Program", "get_Name", obj, null);
Console.WriteLine(res);获取属性值和调用方法差不多,只不过要在属性名字前面加上 "get_",参考上面的代码,如果直接写 "Name" 是获取不到属性值的。
设置属性值
ILRuntime 内代码:
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}Unity 内代码:
var obj = appdomain.Instantiate("HotFix_Project.Program");
appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Program", "set_Name", obj, "张三");
var res = appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Program", "get_Name", obj, null);
Console.WriteLine(res);调用 ILRuntime 的方法
在其他的几个章节中,已经有很多案例用到调用方法了,调用 ILRuntime 方法在传参数的时候,大部分的参数都是没问题的,比如值类型,引用类型,但也有些类型是不能传的,比如存在跨域继承的类,需要手动去写适配器。
调用静态方法
ILRuntime 内代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("你好");
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Program", "Main", null, null);调用无参数的方法
ILRuntime 内代码:
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public static string SayHi()
{
return "hello";
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
//获取类
IType type = appdomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Program"];
//获取方法
//参数1 方法名
//参数2 这个方法参数的个数
IMethod method = type.GetMethod("SayHi", 0);
//执行方法
object res = appdomain.Invoke(method, null, null);
Console.WriteLine(res);调用有参数的方法
ILRuntime 内代码:
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public static void SayHi(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine("[SayHi]{0}", msg);
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
IType type = appdomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Program"];
IMethod method = type.GetMethod("SayHi", 1);
appdomain.Invoke(method, null, "恭喜发财");运行:

获取方法的返回值
ILRuntime 内代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public static string SayHi()
{
return "hello";
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
var result = appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Program", "SayHi", null, null);
Console.WriteLine(result);运行:

获取方法的元组返回值
ILRuntime 内代码:
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public static (int, string) GetUser()
{
return (25, "zhangsan");
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
var result = appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Program", "GetUser", null, null);
if (result != null)
{
var resultTuple = (ValueTuple<int, string>)result;
Console.WriteLine($"Result: {resultTuple.Item1}, {resultTuple.Item2}");
}运行:
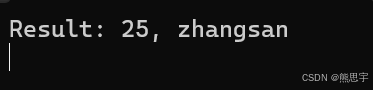
委托转换器
注册方法大概如下:
public delegate void TestDelegateMethod(int a);
public delegate string TestDelegateFunction(int a);
public static TestDelegateMethod TestMethodDelegate;
public static TestDelegateFunction TestFunctionDelegate;
//注册无返回值委托
appdomain.DelegateManager.RegisterMethodDelegate<int>();
//注册带返回值委托(返回string)
appdomain.DelegateManager.RegisterFunctionDelegate<int, string>();
//这里的 TestDelegateMethod 就是上面第一行定义的委托 TestDelegateMethod(int a)
appdomain.DelegateManager.RegisterDelegateConvertor<TestDelegateMethod>((action) =>
{
返回正确的委托,并且内部执行Action或Func
return new TestDelegateMethod((a) =>
{
((System.Action<int>)action)(a);
});
});案例1
在项目的开发中,委托的使用一般比较频繁的, 比如在 ILRuntime 内使用线程,用到了一个委托 ThreadStart :
我这里只是作为演示,重新加载热更DLL之前,记得把之前的线程关闭和释放,否则会两个线程一起在执行,线程不会因为你执行了热重载而主动销毁的,这点需要注意。
ILRuntime 内代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
// 创建并启动线程
Thread myThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(MethodToExecute));
myThread.IsBackground = true; // 设置为后台线程,程序退出时自动终止
myThread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("主线程正在运行...");
}
static void MethodToExecute()
{
while (true)
{
// 你的逻辑代码
Console.WriteLine("方法正在执行...");
// 睡眠1秒钟,避免过度消耗CPU资源
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
先注册委托转换器
appdomain.DelegateManager.RegisterDelegateConvertor<ThreadStart>((act) =>
{
return new ThreadStart(() =>
{
((Action)act)();
});
});调用:
appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Program", "Main", null, null);运行:

案例2
普通的委托 Action, Func 如果使用值类型直接用就行了,不需要委托转换器
ILRuntime 内代码:
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class Program
{
public static void Test(int a, int b, Action<int> action)
{
int res = a + b;
action?.Invoke(res);
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
//获取类
var type = appdomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Program"];
//获取方法,方法的参数有3个
IMethod method = type.GetMethod("Test", 3);
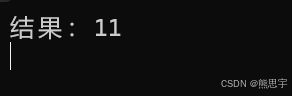
appdomain.Invoke(method, null, new object[] { 5, 6,
new Action<int>((result)=>{ Console.WriteLine("结果:{0}", result); })
});运行:
这里并没有添加委托转换器,要加的话,也是没有任何问题的,代码如下:
appdomain.DelegateManager.RegisterMethodDelegate<int>();
appdomain.DelegateManager.RegisterDelegateConvertor<Action<int>>((action) =>
{
return new Action<int>((a) =>
{
((Action<int>)action)(a);
});
});跨域继承
案例1
在 Unity 中,假设有这么一类 User,需要在 ILRuntime 内进行继承
using System;
public abstract class User
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public virtual string Password { get; set; }
public void SayHi()
{
Console.WriteLine("hello");
}
public virtual void SayHi2(string content)
{
Console.WriteLine("[SayHi2]{0}", content);
}
public abstract void TestAbs(string content);
}新建一个适配器 UserAdapter,让其继承 CrossBindingAdaptor,实现 CrossBindingAdaptor 的接口,代码就是这样子:
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment;
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Intepreter;
using System;
public class UserAdapter : CrossBindingAdaptor
{
public override Type BaseCLRType => throw new NotImplementedException();
public override Type AdaptorType => throw new NotImplementedException();
public override object CreateCLRInstance(ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain, ILTypeInstance instance)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}在 UserAdapter 类中,还需要创建一个新的类 Adapter,并让其继承 User, CrossBindingAdaptorType,并实现其接口,代码就是这样子:
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment;
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Intepreter;
using System;
public class UserAdapter : CrossBindingAdaptor
{
public override Type BaseCLRType => throw new NotImplementedException();
public override Type AdaptorType => throw new NotImplementedException();
public override object CreateCLRInstance(ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain, ILTypeInstance instance)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public class Adapter : User, CrossBindingAdaptorType
{
public ILTypeInstance ILInstance => throw new NotImplementedException();
public override void TestAbs(string content)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}接下来将这些方法和接口完善
using ILRuntime.CLR.Method;
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment;
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Intepreter;
using System;
public class UserAdapter : CrossBindingAdaptor
{
//指定基类为 User
public override Type BaseCLRType { get => typeof(User); }
//指定适配器为 Adapter
public override Type AdaptorType { get => typeof(Adapter); }
//创建 CLR 实例
public override object CreateCLRInstance(ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain, ILTypeInstance instance)
{
return new Adapter(appdomain, instance);
}
public class Adapter : User, CrossBindingAdaptorType
{
#region 字段
//适配器的实例
public ILTypeInstance ILInstance { get => instance; }
private ILTypeInstance instance;
private ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain;
// 缓存方法,以提高性能
private IMethod mSayHi2;
private bool mSayHi2Got;
private IMethod mTestAbs;
private bool mTestAbsGot;
#endregion
#region 重写 User 方法和属性
// 重写 User 中虚属性 Password
public override string Password
{
get
{
var method = instance.Type.GetMethod("get_Password", 0);
if (method != null)
return (string)appdomain.Invoke(method, instance, null);
else
return base.Password;
}
set
{
var method = instance.Type.GetMethod("set_Password", 1);
if (method != null)
appdomain.Invoke(method, instance, value);
else
base.Password = value;
}
}
//重写 User 中的虚方法 SayHi2
public override void SayHi2(string content)
{
if (!mSayHi2Got)
{
mSayHi2 = instance.Type.GetMethod("SayHi2", 1);
mSayHi2Got = true;
}
if (mSayHi2 != null)
appdomain.Invoke(mSayHi2, instance, content);
else
base.SayHi2(content);
}
//实现 User 中的抽象方法 TestAbs
public override void TestAbs(string content)
{
if (!mTestAbsGot)
{
mTestAbs = instance.Type.GetMethod("TestAbs", 1);
mTestAbsGot = true;
}
if (mTestAbs != null)
appdomain.Invoke(mTestAbs, instance, content);
else
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
#endregion
#region 构造函数
public Adapter() { }
public Adapter(ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain, ILTypeInstance instance)
{
this.appdomain = appdomain;
this.instance = instance;
}
#endregion
}
}可以看到,写适配器非常的麻烦,这个类算简单的,就要写这么多代码,其中很多用法你可能不太理解,先不用管它,只要知道这么用就行了。
适配器只需要重写虚方法,虚属性,抽象方法就行了,其他正常的字段,方法可以不用管。
接下来在 ILRuntime 里面加入一个类 CustomUser,用来继承 User 类
using System;
namespace HotFix_Project
{
public class CustomUser : User
{
public override string Password { get; set; }
public override void SayHi2(string content)
{
Console.WriteLine("[CustomUser-SayHi2] {0}", content);
}
public override void TestAbs(string content)
{
Console.WriteLine("[CustomUser] {0}", content);
Console.WriteLine("=======================");
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0}", Name);
Console.WriteLine("Email:{0}", Email);
Console.WriteLine("Password:{0}", Password);
}
}
}在 Unity 中,注册这个适配器
//注册 User 的适配器
appdomain.RegisterCrossBindingAdaptor(new UserAdapter());调用:
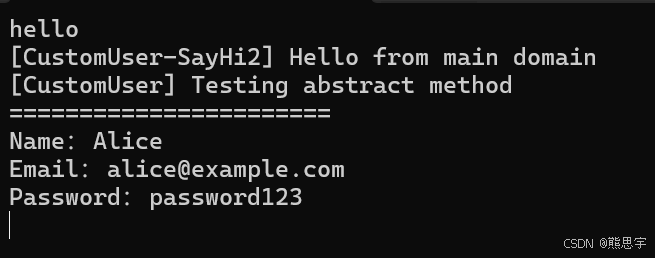
User user = appdomain.Instantiate<User>("HotFix_Project.CustomUser");
user.Name = "Alice";
user.Email = "alice@example.com";
user.Password = "password123";
user.SayHi(); // 调用基类方法
user.SayHi2("Hello from main domain"); // 调用子类重写方法
user.TestAbs("Testing abstract method"); // 调用子类实现的抽象方法注意这里,实例化的类是 HotFix_Project.CustomUser,然后用 User 接收的,就是一般的多态用法。
运行:
案例2
假设 Unity 中有一个类,没有使用任何的虚属性,虚方法,和抽象方法,是否需要写适配器?
只要 ILRuntime 中继承 Unity 中的类,都要适配器,它是不管这个类有没有虚属性,虚方法,和抽象方法,因为本来就是两个程序域。
Unity 内代码:
public class MyUnityClass
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
}新建一个类 MyUnityClassAdapter,用来作为适配器,这里面没有对原方法进行任何的重写
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment;
using ILRuntime.Runtime.Intepreter;
using System;
public class MyUnityClassAdapter : CrossBindingAdaptor
{
public override Type BaseCLRType { get => typeof(MyUnityClass); }
public override Type AdaptorType { get => typeof(Adapter); }
public override object CreateCLRInstance(ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain, ILTypeInstance instance)
{
return new Adapter(appdomain, instance);
}
public class Adapter : MyUnityClass, CrossBindingAdaptorType
{
private ILTypeInstance instance;
private ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain;
public ILTypeInstance ILInstance { get => instance; }
public Adapter()
{
}
public Adapter(ILRuntime.Runtime.Enviorment.AppDomain appdomain, ILTypeInstance instance)
{
this.appdomain = appdomain;
this.instance = instance;
}
}
}ILRuntime 内代码:
using System;
namespace HotFix_Project
{
internal class MyILRuntimeClass : MyUnityClass
{
public void Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("=======================");
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0}", Name);
Console.WriteLine("Email:{0}", Email);
Console.WriteLine("Password:{0}", Password);
Console.WriteLine("=======================");
}
public MyILRuntimeClass() { }
public MyILRuntimeClass(string name, string email, string password)
{
this.Name = name;
this.Email = email;
this.Password = password;
}
}
}Unity 内代码:
对适配器进行注册
appdomain.RegisterCrossBindingAdaptor(new MyUnityClassAdapter());调用 ILRuntime 内方法,由于 MyUnityClass 没有使用多态的写法,这里只能使用反射去调用。
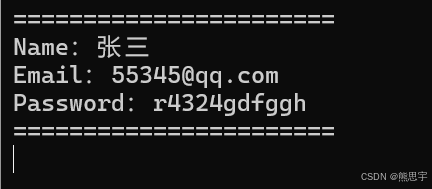
object[] parameter = new object[] { "张三", "55345@qq.com", "r4324gdfggh" };
var obj = appdomain.Instantiate("HotFix_Project.MyILRuntimeClass", parameter);
appdomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.MyILRuntimeClass", "Test", obj, null);运行:
我尝试用设置属性的方法赋值,发现根本赋值不了,这个问题暂时还不知道怎么解决,有知道的可以留言告诉我
另外,CLR 绑定和 CLR 重定向 就没有继续写了,有兴趣的可以去官网看看。
结束
如果这个帖子对你有所帮助,欢迎 关注 + 点赞 + 留言
end


























 41
41

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










