1、简介
区域生长分割(Region Growing Segmentation)
定义:
区域生长分割是一种基于相似性准则的图像分割方法,通过从种子点开始,逐步合并邻近像素或点,形成具有相似属性的区域。
步骤:
- 选择种子点:手动或自动选择初始种子点。
- 定义相似性准则:如颜色、强度、法线等。
- 区域生长:从种子点出发,合并符合相似性准则的邻近像素或点。
- 终止条件:当没有更多符合准则的像素或点时,停止生长。
主要应用场景:
- 医学图像分割:用于分割器官、肿瘤等。
- 遥感图像分析:用于土地分类、植被检测等。
- 三维点云处理:用于物体识别、场景理解等。
- 计算机视觉:用于目标检测、图像分割等。
总结:
区域生长分割是一种有效的图像和点云分割方法,广泛应用于医学、遥感和计算机视觉等领域。PCL提供了便捷的实现工具。
2、代码实现
2.1 region_growing_segmentation.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/search/search.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/filters/filter_indices.h> // for pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud
#include <pcl/segmentation/region_growing.h>
int main ()
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if ( pcl::io::loadPCDFile <pcl::PointXYZ> ("yourpcd.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
std::cout << "Cloud reading failed." << std::endl;
return (-1);
}
pcl::search::Search<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>);
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> normal_estimator;
normal_estimator.setSearchMethod (tree);
normal_estimator.setInputCloud (cloud);
normal_estimator.setKSearch (50);
normal_estimator.compute (*normals);
pcl::IndicesPtr indices (new std::vector <int>);
pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*cloud, *indices);
pcl::RegionGrowing<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> reg;
reg.setMinClusterSize (50);
reg.setMaxClusterSize (1000000);
reg.setSearchMethod (tree);
reg.setNumberOfNeighbours (30);
reg.setInputCloud (cloud);
reg.setIndices (indices);
reg.setInputNormals (normals);
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold (3.0 / 180.0 * M_PI);
reg.setCurvatureThreshold (1.0);
std::vector <pcl::PointIndices> clusters;
reg.extract (clusters);
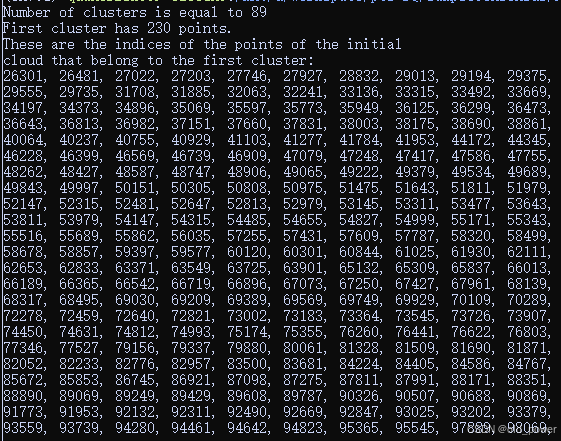
std::cout << "Number of clusters is equal to " << clusters.size () << std::endl;
std::cout << "First cluster has " << clusters[0].indices.size () << " points." << std::endl;
std::cout << "These are the indices of the points of the initial" <<
std::endl << "cloud that belong to the first cluster:" << std::endl;
std::size_t counter = 0;
while (counter < clusters[0].indices.size ())
{
std::cout << clusters[0].indices[counter] << ", ";
counter++;
if (counter % 10 == 0)
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr colored_cloud = reg.getColoredCloud ();
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer ("Cluster viewer");
viewer.showCloud(colored_cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped ())
{
}
return (0);
}
2.2 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5 FATAL_ERROR)
project(region_growing_segmentation)
find_package(PCL 1.5 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
add_executable (region_growing_segmentation region_growing_segmentation.cpp)
target_link_libraries (region_growing_segmentation ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
2.3 运行结果
- 编译运行
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
./region_growing_segmentation
- 结果
3、代码分析
这段代码主要分为数据的加载、法线估计、区域生长分割以及可视化。以下是对代码的详细解释:
3.1 头文件引入
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/search/search.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/filters/filter_indices.h> // for pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud
#include <pcl/segmentation/region_growing.h>
- iostream: 用于标准输入输出。
- vector: 用于存储点云索引等数据。
- pcl/point_types.h: 定义了PCL中的点类型(如
pcl::PointXYZ)。 - pcl/io/pcd_io.h: 提供了点云数据的读写功能。
- pcl/search/search.h 和 pcl/search/kdtree.h: 提供了点云搜索功能,使用KD树进行最近邻搜索。
- pcl/features/normal_3d.h: 用于估计点云中每个点的法线。
- pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h: 用于点云的可视化。
- pcl/filters/filter_indices.h: 提供了点云滤波功能,如去除无效点(NaN点)。
- pcl/segmentation/region_growing.h: 提供了区域生长分割算法。
3.2 主函数
int main ()
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if ( pcl::io::loadPCDFile <pcl::PointXYZ> ("yourpcd.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
std::cout << "Cloud reading failed." << std::endl;
return (-1);
}
- pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZ::Ptr cloud: 定义一个指向
pcl::PointXYZ类型点云的智能指针。 - pcl::io::loadPCDFile: 从PCD文件中加载点云数据。如果加载失败,程序返回-1并输出错误信息。
3.3 法线估计
pcl::search::Search<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>);
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> normal_estimator;
normal_estimator.setSearchMethod (tree);
normal_estimator.setInputCloud (cloud);
normal_estimator.setKSearch (50);
normal_estimator.compute (*normals);
- pcl::search::Searchpcl::PointXYZ::Ptr tree: 定义一个KD树用于最近邻搜索。
- pcl::PointCloud pcl::Normal::Ptr normals: 定义一个存储法线的点云。
- pcl::NormalEstimation: 法线估计器,用于计算点云中每个点的法线。
- setSearchMethod: 设置搜索方法为KD树。
- setInputCloud: 设置输入点云。
- setKSearch: 设置最近邻搜索的K值为50。
- compute: 计算法线并存储在
normals中。
3.4 去除无效点
pcl::IndicesPtr indices (new std::vector <int>);
pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*cloud, *indices);
- pcl::IndicesPtr indices: 定义一个存储有效点索引的向量。
- pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud: 去除点云中的无效点(NaN点),并返回有效点的索引。
3.5 区域生长分割
pcl::RegionGrowing<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> reg;
reg.setMinClusterSize (50);
reg.setMaxClusterSize (1000000);
reg.setSearchMethod (tree);
reg.setNumberOfNeighbours (30);
reg.setInputCloud (cloud);
reg.setIndices (indices);
reg.setInputNormals (normals);
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold (3.0 / 180.0 * M_PI);
reg.setCurvatureThreshold (1.0);
std::vector <pcl::PointIndices> clusters;
reg.extract (clusters);
- pcl::RegionGrowing: 区域生长分割器,用于将点云分割成多个簇。
- setMinClusterSize: 设置最小簇的大小为50。
- setMaxClusterSize: 设置最大簇的大小为1000000。
- setSearchMethod: 设置搜索方法为KD树。
- setNumberOfNeighbours: 设置每个点的邻居数量为30。
- setInputCloud: 设置输入点云。
- setIndices: 设置有效点的索引。
- setInputNormals: 设置输入法线。
- setSmoothnessThreshold: 设置平滑度阈值(3度转换为弧度)。
- setCurvatureThreshold: 设置曲率阈值为1.0。
- reg.extract: 执行区域生长分割,并将结果存储在
clusters中。
3.6 输出分割结果
std::cout << "Number of clusters is equal to " << clusters.size () << std::endl;
std::cout << "First cluster has " << clusters[0].indices.size () << " points." << std::endl;
std::cout << "These are the indices of the points of the initial" <<
std::endl << "cloud that belong to the first cluster:" << std::endl;
std::size_t counter = 0;
while (counter < clusters[0].indices.size ())
{
std::cout << clusters[0].indices[counter] << ", ";
counter++;
if (counter % 10 == 0)
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
- 输出分割后的簇的数量。
- 输出第一个簇中的点的数量。
- 输出第一个簇中点的索引,每10个索引换行。
3.7 可视化分割结果
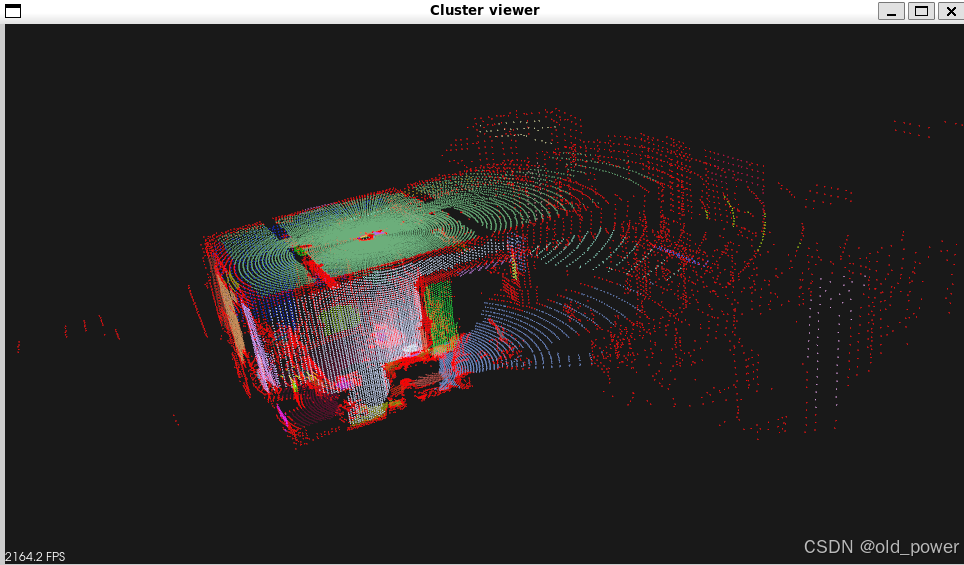
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr colored_cloud = reg.getColoredCloud ();
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer ("Cluster viewer");
viewer.showCloud(colored_cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped ())
{
}
return (0);
}
- reg.getColoredCloud: 获取带有颜色信息的点云,不同簇的点被赋予不同的颜色。
- pcl::visualization::CloudViewer: 创建一个点云查看器。
- viewer.showCloud: 显示带有颜色信息的点云。
- while (!viewer.wasStopped): 保持查看器窗口打开,直到用户关闭窗口。
总结
这段代码的主要功能是:
- 加载点云数据。
- 估计点云中每个点的法线。
- 使用区域生长算法对点云进行分割。
- 输出分割结果并可视化带有颜色信息的点云。
区域生长分割算法基于点云的法线和曲率信息,将点云分割成多个簇,每个簇代表一个平滑的表面区域。






















 40万+
40万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








