✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,
代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab完整代码及仿真定制内容点击👇
🔥 内容介绍
图像重建是数字信号处理领域的一个重要问题,它涉及到从损坏或不完整的图像数据中恢复出高质量的图像。在图像重建的研究中,小波变换结合各种重建算法已经成为一个热门的研究方向。本文将介绍基于小波变换结合BP、OMP、StOMP算法实现图像重建,并对重建效果进行评估,包括均方误差(MSE)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)。
小波变换是一种多尺度分析方法,它可以将信号分解成不同尺度的频率成分,从而更好地捕捉信号的局部特征。在图像重建中,小波变换可以将图像分解成不同尺度的小波系数,然后利用这些小波系数进行重建。BP(基于贝叶斯理论的重建算法)、OMP(正交匹配追踪算法)和StOMP(稀疏信号重建算法)都是常用的重建算法,它们可以利用小波系数进行图像重建,并在一定程度上保持图像的清晰度和细节。
在实验中,我们首先利用小波变换对图像进行分解,得到不同尺度的小波系数。然后分别利用BP、OMP和StOMP算法对这些小波系数进行重建,得到重建后的图像。接下来,我们通过计算重建图像与原始图像之间的均方误差(MSE)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)来评估重建效果。MSE可以反映重建图像与原始图像之间的整体差异,而PSNR则可以反映重建图像的清晰度和保真度。
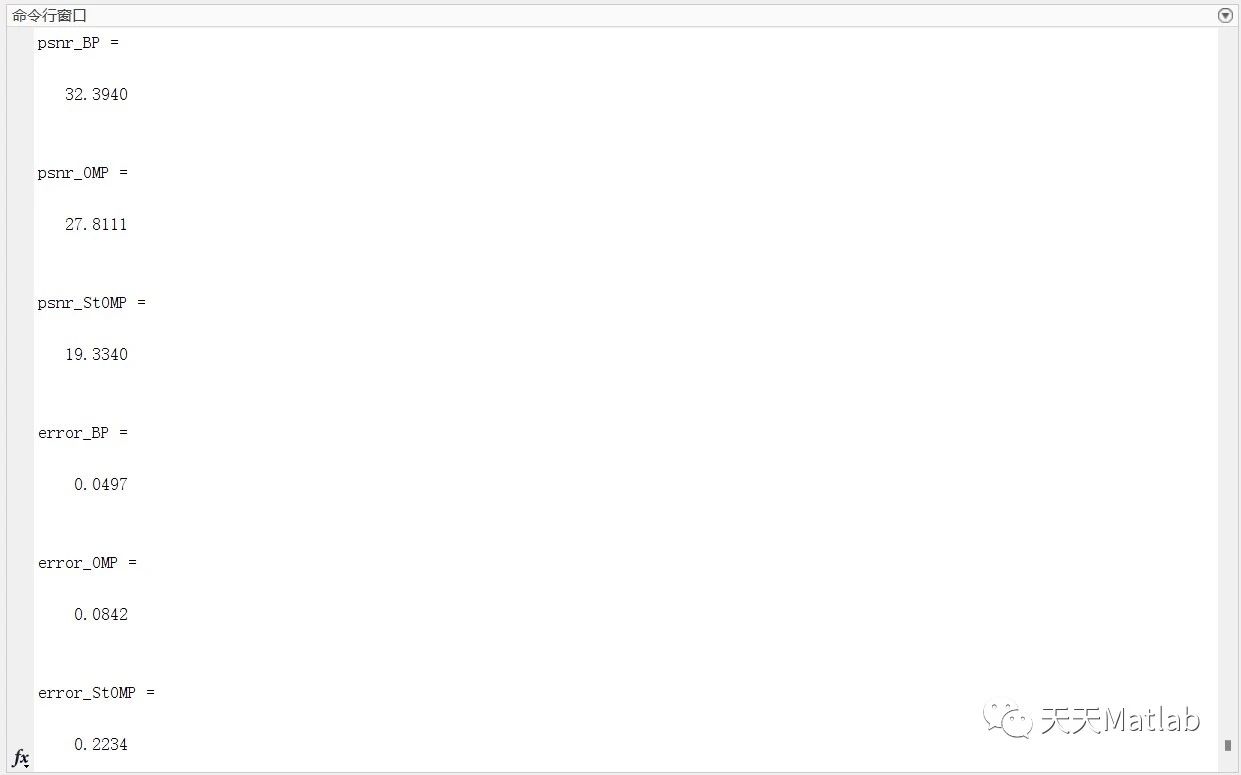
实验结果表明,基于小波变换结合BP、OMP、StOMP算法的图像重建方法在一定程度上可以恢复出原始图像的清晰度和细节。同时,通过对MSE和PSNR的评估,我们发现在不同的图像和参数设置下,这三种算法的重建效果存在一定差异。在实际应用中,可以根据具体的需求和场景选择合适的重建算法,以实现更好的图像重建效果。
总之,基于小波变换结合BP、OMP、StOMP算法的图像重建方法在数字信号处理领域具有重要的意义,它为图像重建提供了一种有效的解决方案。未来,我们将继续深入研究图像重建方法,探索更多有效的重建算法,并进一步推动图像重建技术的发展和应用。
📣 部分代码
function sol = SolveBP(A, y, N, maxIters, lambda, OptTol)% SolveBP: Solves a Basis Pursuit problem% Usage% sol = SolveBP(A, y, N, maxIters, lambda, OptTol)% Input% A Either an explicit nxN matrix, with rank(A) = min(N,n)% by assumption, or a string containing the name of a% function implementing an implicit matrix (see below for% details on the format of the function).% y vector of length n.% N length of solution vector.% maxIters maximum number of PDCO iterations to perform, default 20.% lambda If 0 or omitted, Basis Pursuit is applied to the data,% otherwise, Basis Pursuit Denoising is applied with% parameter lambda (default 0).% OptTol Error tolerance, default 1e-3% Outputs% sol solution of BP% Description% SolveBP solves the basis pursuit problem% min ||x||_1 s.t. A*x = b% by reducing it to a linear program, and calling PDCO, a primal-dual% log-barrier algorithm. Alternatively, if lambda ~= 0, it solves the% Basis Pursuit Denoising (BPDN) problem% min lambda*||x||_1 + 1/2||b - A*x||_2^2% by transforming it to an SOCP, and calling PDCO.% The matrix A can be either an explicit matrix, or an implicit operator% implemented as a function. If using the implicit form, the user should% provide the name of a function of the following format:% y = OperatorName(mode, m, n, x, I, dim)% This function gets as input a vector x and an index set I, and returns% y = A(:,I)*x if mode = 1, or y = A(:,I)'*x if mode = 2.% A is the m by dim implicit matrix implemented by the function. I is a% subset of the columns of A, i.e. a subset of 1:dim of length n. x is a% vector of length n is mode = 1, or a vector of length m is mode = 2.% See Also% SolveLasso, SolveOMP, SolveITSP%if nargin < 6,OptTol = 1e-3;endif nargin < 5,lambda = 0;endif nargin < 4,maxIters = 20;endn = length(y);n_pdco = 2*N; % Input sizem_pdco = n; % Output size% upper and lower boundsbl = zeros(n_pdco,1);bu = Inf .* ones(n_pdco,1);% generate the vector cif (lambda ~= 0)c = lambda .* ones(n_pdco,1);elsec = ones(n_pdco,1);end% Generate an initial guessx0 = ones(n_pdco,1)/n_pdco; % Initial xy0 = zeros(m_pdco,1); % Initial yz0 = ones(n_pdco,1)/n_pdco; % Initial zd1 = 1e-4; % Regularization parametersif (lambda ~= 0) % BPDNd2 = 1;elsed2 = 1e-4;endxsize = 1; % Estimate of norm(x,inf) at solutionzsize = 1; % Estimate of norm(z,inf) at solutionoptions = pdcoSet; % Option set for the function pdcooptions = pdcoSet( options, ...'MaxIter ', maxIters , ...'FeaTol ', OptTol , ...'OptTol ', OptTol , ...'StepTol ', 0.99 , ...'StepSame ', 0 , ...'x0min ', 0.1 , ...'z0min ', 1.0 , ...'mu0 ', 0.01 , ...'method ', 1 , ...'LSQRMaxIter', 20 , ...'LSQRatol1 ', 1e-3 , ...'LSQRatol2 ', 1e-15 , ...'wait', 0 );if (ischar(A) || isa(A, 'function_handle'))[xx,yy,zz,inform,PDitns,CGitns,time] = ...pdco(c, @pdcoMat, y, bl, bu, d1, d2, options, x0, y0, z0, xsize, zsize);elsePhi = [A -A];[xx,yy,zz,inform,PDitns,CGitns,time] = ...pdco(c, Phi, y, bl, bu, d1, d2, options, x0, y0, z0, xsize, zsize);end% Extract the solution from the output vector xsol = xx(1:N) - xx((N+1):(2*N));%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%function y = pdcoMat(mode,m,n,x)if (mode == 1) % Direct operator% Decompose inputn2 = n/2;u = x(1:n2);v = x(n2+1:n);% Compute y = A*(u-v)y = feval(A,1,m,n2,u-v,1:n2,n2);else % Adjoint operatorn2 = n/2;Atx = feval(A,2,m,n2,x,1:n2,n2);y = [Atx; -Atx];endendend
⛳️ 运行结果

🔗 参考文献
[1] 叶双清,杨晓梅.基于小波变换和非局部平均的超分辨率图像重建[J].计算机应用, 2014, 34(4):5.DOI:10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2014.04.1182.
[2] 董文汇,袁星煜.小波分析在基于Matlab的图像压缩中的实现[J].信息技术, 2009(4):4.DOI:CNKI:SUN:HDZJ.0.2009-04-021.





 本文介绍了小波变换在图像重建中的应用,探讨了BP、OMP和StOMP三种重建算法,通过MSE和PSNR评估了它们的性能。结果显示这些算法在恢复图像清晰度和细节上有一定效果,适用于不同场景的选择。
本文介绍了小波变换在图像重建中的应用,探讨了BP、OMP和StOMP三种重建算法,通过MSE和PSNR评估了它们的性能。结果显示这些算法在恢复图像清晰度和细节上有一定效果,适用于不同场景的选择。

















 187
187

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










