✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,
代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab完整代码及仿真定制内容点击👇
🔥 内容介绍
针对监测区域内含有障碍物的无线传感器网络(Wireless Sensor Networks,WSNs)异构节点部署优化问题,在花朵授粉算法(Flower Pollination Algorithm,FPA)的基础之上,提出了一种改进的花朵授粉算法(Improved Flower Pollination Algorithm,FPA)用于改善原有算法收敛速度慢、精度不够高的不足.设计非线性收敛因子以约束原有的缩放因子,采用Tent映射以维持迭代后期种群的多样性,而贪心交叉策略则是以较优的个体辅助较差个体搜索.基准函数实验验证了IFPA具有较好的收敛性能,而WSN部署的仿真实验表明IFPA可得到较高的覆盖率,可节约网络部署成本.













📣 部分代码
function [rowsol,cost,v,u,costMat] = lapjv(costMat,resolution)% LAPJV Jonker-Volgenant Algorithm for Linear Assignment Problem.%% [ROWSOL,COST,v,u,rMat] = LAPJV(COSTMAT, resolution) returns the optimal column indices,% ROWSOL, assigned to row in solution, and the minimum COST based on the% assignment problem represented by the COSTMAT, where the (i,j)th element% represents the cost to assign the jth job to the ith worker.% The second optional input can be used to define data resolution to% accelerate speed.% Other output arguments are:% v: dual variables, column reduction numbers.% u: dual variables, row reduction numbers.% rMat: the reduced cost matrix.%% For a rectangular (nonsquare) costMat, rowsol is the index vector of the% larger dimension assigned to the smaller dimension.%% [ROWSOL,COST,v,u,rMat] = LAPJV(COSTMAT,resolution) accepts the second% input argument as the minimum resolution to differentiate costs between% assignments. The default is eps.%% Known problems: The original algorithm was developed for integer costs.% When it is used for real (floating point) costs, sometime the algorithm% will take an extreamly long time. In this case, using a reasonable large% resolution as the second arguments can significantly increase the% solution speed.%% See also munkres, Hungarian% version 1.0 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 3rd March 2010% version 1.1 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 19th July 2010% version 1.2 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 22nd July 2010% version 2.0 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 28th July 2010% version 2.1 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 13th August 2010% version 2.2 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 17th August 2010% version 3.0 by Yi Cao at Cranfield University on 10th April 2013% This Matlab version is developed based on the orginal C++ version coded% by Roy Jonker @ MagicLogic Optimization Inc on 4 September 1996.% Reference:% R. Jonker and A. Volgenant, "A shortest augmenting path algorithm for% dense and spare linear assignment problems", Computing, Vol. 38, pp.% 325-340, 1987.%% Examples% Example 1: a 5 x 5 example%{[rowsol,cost] = lapjv(magic(5));disp(rowsol); % 3 2 1 5 4disp(cost); %15%}% Example 2: 1000 x 1000 random data%{n=1000;A=randn(n)./rand(n);tic[a,b]=lapjv(A);toc % about 0.5 seconds%}% Example 3: nonsquare test%{n=100;A=1./randn(n);tic[a,b]=lapjv(A);toc % about 0.2 secA1=[A zeros(n,1)+max(max(A))];tic[a1,b1]=lapjv(A1);toc % about 0.01 sec. The nonsquare one can be done faster!%check resultsdisp(norm(a-a1))disp(b-b)%}if nargin<2maxcost=min(1e16,max(max(costMat)));resolution=eps(maxcost);end% Prepare working data[rdim,cdim] = size(costMat);M=min(min(costMat));if rdim>cdimcostMat = costMat';[rdim,cdim] = size(costMat);swapf=true;elseswapf=false;enddim=cdim;costMat = [costMat;2*M+zeros(cdim-rdim,cdim)];costMat(costMat~=costMat)=Inf;maxcost=max(costMat(costMat<Inf))*dim+1;if isempty(maxcost)maxcost = Inf;endcostMat(costMat==Inf)=maxcost;% free = zeros(dim,1); % list of unssigned rows% colist = 1:dim; % list of columns to be scaed in various ways% d = zeros(1,dim); % 'cost-distance' in augmenting path calculation.% pred = zeros(dim,1); % row-predecessor of column in augumenting/alternating path.v = zeros(1,dim); % dual variables, column reduction numbers.rowsol = zeros(1,dim)-1; % column assigned to row in solutioncolsol = zeros(dim,1)-1; % row assigned to column in solutionnumfree=0;free = zeros(dim,1); % list of unssigned rowsmatches = zeros(dim,1); % counts how many times a row could be assigned.% The Initilization Phase% column reductionfor j=dim:-1:1 % reverse order gives better results% find minimum cost over rows[v(j), imin] = min(costMat(:,j));if ~matches(imin)% init assignement if minimum row assigned for first timerowsol(imin)=j;colsol(j)=imin;elseif v(j)<v(rowsol(imin))j1=rowsol(imin);rowsol(imin)=j;colsol(j)=imin;colsol(j1)=-1;elsecolsol(j)=-1; % row already assigned, column not assigned.endmatches(imin)=matches(imin)+1;end% Reduction transfer from unassigned to assigned rowsfor i=1:dimif ~matches(i) % fill list of unaasigned 'free' rows.numfree=numfree+1;free(numfree)=i;elseif matches(i) == 1 % transfer reduction from rows that are assigned once.j1 = rowsol(i);x = costMat(i,:)-v;x(j1) = maxcost;v(j1) = v(j1) - min(x);endendend% Augmenting reduction of unassigned rowsloopcnt = 0;while loopcnt < 2loopcnt = loopcnt + 1;% scan all free rows% in some cases, a free row may be replaced with another one to be scaed nextk = 0;prvnumfree = numfree;numfree = 0; % start list of rows still free after augmenting row reduction.while k < prvnumfreek = k+1;i = free(k);% find minimum and second minimum reduced cost over columnsx = costMat(i,:) - v;[umin, j1] = min(x);x(j1) = maxcost;[usubmin, j2] = min(x);i0 = colsol(j1);if usubmin - umin > resolution% change the reduction of the minmum column to increase the% minimum reduced cost in the row to the subminimum.v(j1) = v(j1) - (usubmin - umin);else % minimum and subminimum equal.if i0 > 0 % minimum column j1 is assigned.% swap columns j1 and j2, as j2 may be unassigned.j1 = j2;i0 = colsol(j2);endend% reassign i to j1, possibly de-assigning an i0.rowsol(i) = j1;colsol(j1) = i;if i0 > 0 % ,inimum column j1 assigned easierif usubmin - umin > resolution% put in current k, and go back to that k.% continue augmenting path i - j1 with i0.free(k)=i0;k=k-1;else% no further augmenting reduction possible% store i0 in list of free rows for next phase.numfree = numfree + 1;free(numfree) = i0;endendendend% Augmentation Phase% augment solution for each free rowsfor f=1:numfreefreerow = free(f); % start row of augmenting path% Dijkstra shortest path algorithm.% runs until unassigned column added to shortest path tree.d = costMat(freerow,:) - v;pred = freerow(1,ones(1,dim));collist = 1:dim;low = 1; % columns in 1...low-1 are ready, now none.up = 1; % columns in low...up-1 are to be scaed for current minimum, now none.% columns in up+1...dim are to be considered later to find new minimum,% at this stage the list simply contains all columns.unassignedfound = false;while ~unassignedfoundif up == low % no more columns to be scaned for current minimum.last = low-1;% scan columns for up...dim to find all indices for which new minimum occurs.% store these indices between low+1...up (increasing up).minh = d(collist(up));up = up + 1;for k=up:dimj = collist(k);h = d(j);if h<=minhif h<minhup = low;minh = h;end% new index with same minimum, put on index up, and extend list.collist(k) = collist(up);collist(up) = j;up = up +1;endend% check if any of the minimum columns happens to be unassigned.% if so, we have an augmenting path right away.for k=low:up-1if colsol(collist(k)) < 0endofpath = collist(k);unassignedfound = true;breakendendendif ~unassignedfound% update 'distances' between freerow and all unscanned columns,% via next scanned column.j1 = collist(low);low=low+1;i = colsol(j1); %line 215x = costMat(i,:)-v;h = x(j1) - minh;xh = x-h;k=up:dim;j=collist(k);vf0 = xh<d;vf = vf0(j);vj = j(vf);vk = k(vf);pred(vj)=i;v2 = xh(vj);d(vj)=v2;vf = v2 == minh; % new column found at same minimum valuej2 = vj(vf);k2 = vk(vf);cf = colsol(j2)<0;if any(cf) % unassigned, shortest augmenting path is complete.i2 = find(cf,1);endofpath = j2(i2);unassignedfound = true;elsei2 = numel(cf)+1;end% add to list to be scaned right awayfor k=1:i2-1collist(k2(k)) = collist(up);collist(up) = j2(k);up = up + 1;endendend% update column pricesj1=collist(1:last+1);v(j1) = v(j1) + d(j1) - minh;% reset row and column assignments along the alternating pathwhile 1i=pred(endofpath);colsol(endofpath)=i;j1=endofpath;endofpath=rowsol(i);rowsol(i)=j1;if (i==freerow)breakendendendrowsol = rowsol(1:rdim);u=diag(costMat(:,rowsol))-v(rowsol)';u=u(1:rdim);v=v(1:cdim);cost = sum(u)+sum(v(rowsol));costMat=costMat(1:rdim,1:cdim);costMat = costMat - u(:,ones(1,cdim)) - v(ones(rdim,1),:);if swapfcostMat = costMat';t=u';u=v';v=t;endif cost>maxcostcost=Inf;end
⛳️ 运行结果



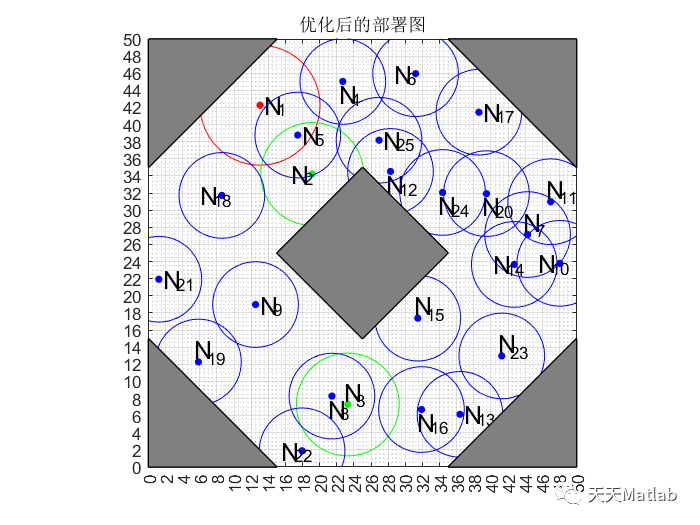


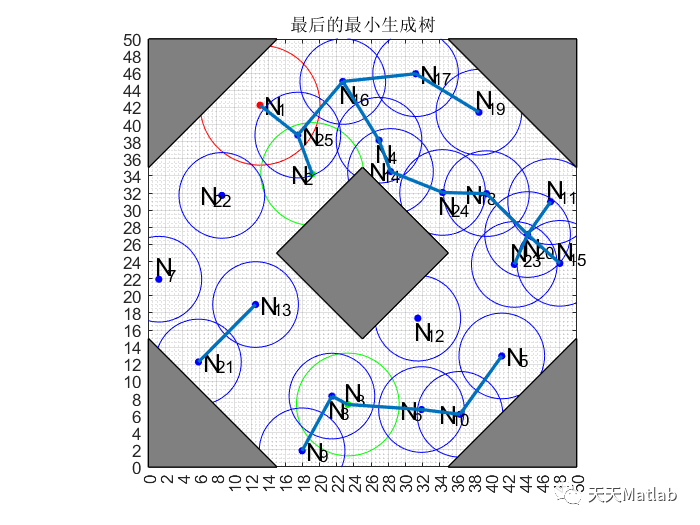
🔗 参考文献
本程序参考以下中文EI期刊,程序注释清晰,干货满满。
[1]王振东,谢华茂,胡中栋,et al.改进花朵授粉算法的无线传感器网络部署优化[J].系统仿真学报, 2021.DOI:10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.19-0580.





 本文介绍了一种改良的花朵授粉算法(IFPA),用于解决无线传感器网络部署中的优化问题,通过非线性收敛因子和Tent映射改进了原始算法。实验结果显示,IFPA在收敛性能和网络覆盖率上表现优秀,有助于降低部署成本。
本文介绍了一种改良的花朵授粉算法(IFPA),用于解决无线传感器网络部署中的优化问题,通过非线性收敛因子和Tent映射改进了原始算法。实验结果显示,IFPA在收敛性能和网络覆盖率上表现优秀,有助于降低部署成本。

















 1035
1035

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










