✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,
代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab完整代码及仿真定制内容点击👇
🔥 内容介绍
信号去噪一直是语音信号处理领域的重要研究方向之一。在实际应用中,由于环境噪声和其他干扰因素的存在,语音信号常常受到严重的干扰,降低了语音信号的质量和可理解性。因此,开发高效的信号去噪算法对于提高语音信号的清晰度和准确性至关重要。
近年来,随着机器学习和优化算法的快速发展,许多新的方法被提出来用于信号去噪。其中,变分模态分解(VMD)是一种有效的信号分解方法,可以将信号分解为多个模态分量。然后,通过选择性地去除噪声模态分量,可以实现对信号的去噪。
然而,传统的VMD方法在实际应用中存在一些问题。首先,它对于不同类型的信号和噪声的适应性较差。其次,由于VMD是一种迭代优化算法,其收敛速度较慢,需要较长的计算时间。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种基于全局搜索策略的鲸鱼算法优化变分模态分解(GSWOA-VMD)的信号去噪方法。
鲸鱼算法是一种基于自然界鲸鱼行为的优化算法,具有全局搜索能力和快速收敛速度。在GSWOA-VMD方法中,我们首先将语音信号分解为多个模态分量。然后,利用鲸鱼算法对每个模态分量进行优化,以选择性地去除噪声分量。最后,将去噪后的模态分量重构为去噪信号。
与传统的VMD方法相比,GSWOA-VMD方法具有以下优点。首先,鲸鱼算法能够全局搜索最优解,从而提高了去噪效果。其次,由于鲸鱼算法的快速收敛性,GSWOA-VMD方法具有更短的计算时间。此外,GSWOA-VMD方法还具有较好的适应性,可以应用于各种类型的信号和噪声。
为了评估GSWOA-VMD方法的性能,我们进行了一系列实验。实验结果表明,GSWOA-VMD方法在不同类型的信号和噪声下都能取得较好的去噪效果。与传统的VMD方法相比,GSWOA-VMD方法在去噪效果和计算时间方面都取得了显著的改善。
综上所述,本文提出了一种基于全局搜索策略的鲸鱼算法优化变分模态分解的信号去噪方法。该方法通过选择性地去除噪声模态分量,提高了语音信号的清晰度和准确性。实验结果表明,GSWOA-VMD方法在去噪效果和计算时间方面都具有明显的优势。未来,我们将进一步研究和改进该方法,以提高其在实际应用中的性能和稳定性。
📣 部分代码
function [u, u_hat, omega] = VMD(signal, alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol)%%% Input and Parameters:% ---------------------% signal - the time domain signal (1D) to be decomposed% alpha - the balancing parameter of the data-fidelity constraint% tau - time-step of the dual ascent ( pick 0 for noise-slack )% K - the number of modes to be recovered% DC - true if the first mode is put and kept at DC (0-freq)% init - 0 = all omegas start at 0% 1 = all omegas start uniformly distributed% 2 = all omegas initialized randomly% tol - tolerance of convergence criterion; typically around 1e-6%% Output:% -------% u - the collection of decomposed modes% u_hat - spectra of the modes% omega - estimated mode center-frequencies%---------- Preparations% Period and sampling frequency of input signalsave_T = length(signal);fs = 1/save_T;% extend the signal by mirroringT = save_T;f_mirror(1:T/2) = signal(T/2:-1:1);f_mirror(T/2+1:3*T/2) = signal;f_mirror(3*T/2+1:2*T) = signal(T:-1:T/2+1);f = f_mirror;% Time Domain 0 to T (of mirrored signal)T = length(f);t = (1:T)/T;% Spectral Domain discretizationfreqs = t-0.5-1/T;% Maximum number of iterations (if not converged yet, then it won't anyway)N = 500;% For future generalizations: individual alpha for each modeAlpha = alpha*ones(1,K);% Construct and center f_hatf_hat = fftshift((fft(f)));f_hat_plus = f_hat;f_hat_plus(1:T/2) = 0;% matrix keeping track of every iterant // could be discarded for memu_hat_plus = zeros(N, length(freqs), K);% Initialization of omega_komega_plus = zeros(N, K);switch initcase 1for i = 1:Komega_plus(1,i) = (0.5/K)*(i-1);endcase 2omega_plus(1,:) = sort(exp(log(fs) + (log(0.5)-log(fs))*rand(1,K)));otherwiseomega_plus(1,:) = 0;end% if DC mode imposed, set its omega to 0if DComega_plus(1,1) = 0;end% start with empty dual variableslambda_hat = zeros(N, length(freqs));% other initsuDiff = tol+eps; % update stepn = 1; % loop countersum_uk = 0; % accumulator% ----------- Main loop for iterative updateswhile ( uDiff > tol && n < N ) % not converged and below iterations limit% update first mode accumulatork = 1;sum_uk = u_hat_plus(n,:,K) + sum_uk - u_hat_plus(n,:,1);% update spectrum of first mode through Wiener filter of residualsu_hat_plus(n+1,:,k) = (f_hat_plus - sum_uk - lambda_hat(n,:)/2)./(1+Alpha(1,k)*(freqs - omega_plus(n,k)).^2);% update first omega if not held at 0if ~DComega_plus(n+1,k) = (freqs(T/2+1:T)*(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1, T/2+1:T, k)).^2)')/sum(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1,T/2+1:T,k)).^2);end% update of any other modefor k=2:K% accumulatorsum_uk = u_hat_plus(n+1,:,k-1) + sum_uk - u_hat_plus(n,:,k);% mode spectrumu_hat_plus(n+1,:,k) = (f_hat_plus - sum_uk - lambda_hat(n,:)/2)./(1+Alpha(1,k)*(freqs - omega_plus(n,k)).^2);% center frequenciesomega_plus(n+1,k) = (freqs(T/2+1:T)*(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1, T/2+1:T, k)).^2)')/sum(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1,T/2+1:T,k)).^2);end% Dual ascentlambda_hat(n+1,:) = lambda_hat(n,:) + tau*(sum(u_hat_plus(n+1,:,:),3) - f_hat_plus);% loop countern = n+1;% converged yet?uDiff = eps;for i=1:KuDiff = uDiff + 1/T*(u_hat_plus(n,:,i)-u_hat_plus(n-1,:,i))*conj((u_hat_plus(n,:,i)-u_hat_plus(n-1,:,i)))';enduDiff = abs(uDiff);end%------ Postprocessing and cleanup% discard empty space if converged earlyN = min(N,n);omega = omega_plus(1:N,:);% Signal reconstructionu_hat = zeros(T, K);u_hat((T/2+1):T,:) = squeeze(u_hat_plus(N,(T/2+1):T,:));u_hat((T/2+1):-1:2,:) = squeeze(conj(u_hat_plus(N,(T/2+1):T,:)));u_hat(1,:) = conj(u_hat(end,:));u = zeros(K,length(t));for k = 1:Ku(k,:)=real(ifft(ifftshift(u_hat(:,k))));end% remove mirror partu = u(:,T/4+1:3*T/4);% recompute spectrumclear u_hat;for k = 1:Ku_hat(:,k)=fftshift(fft(u(k,:)))';endend
⛳️ 运行结果
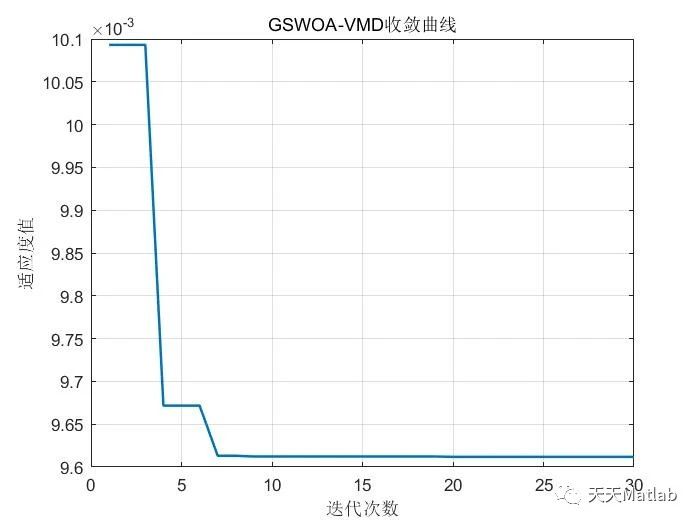
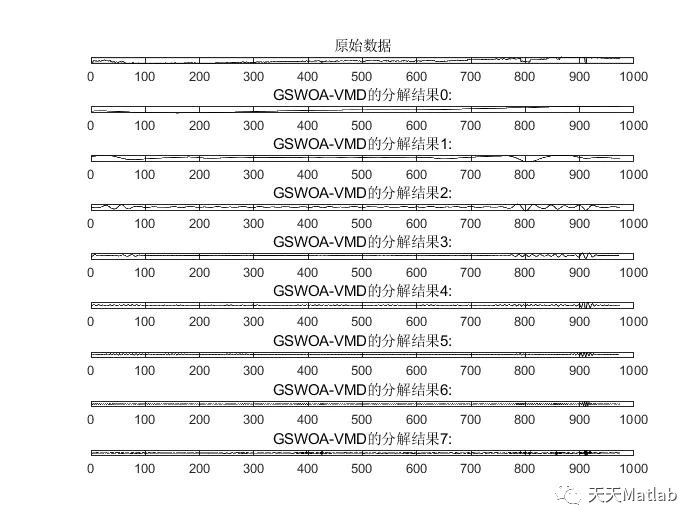
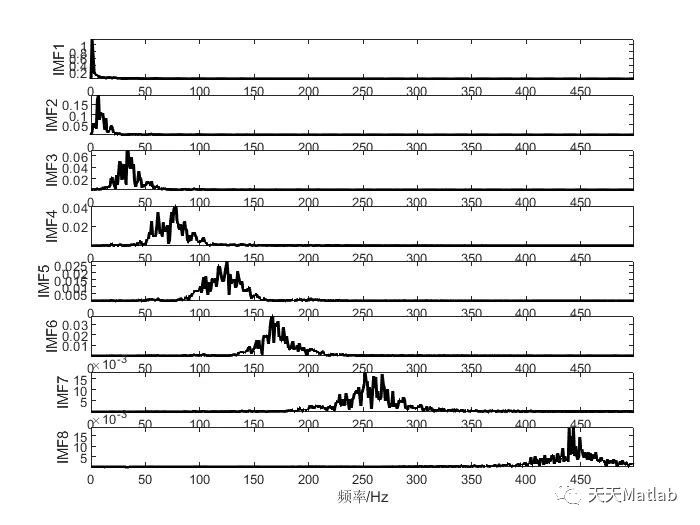
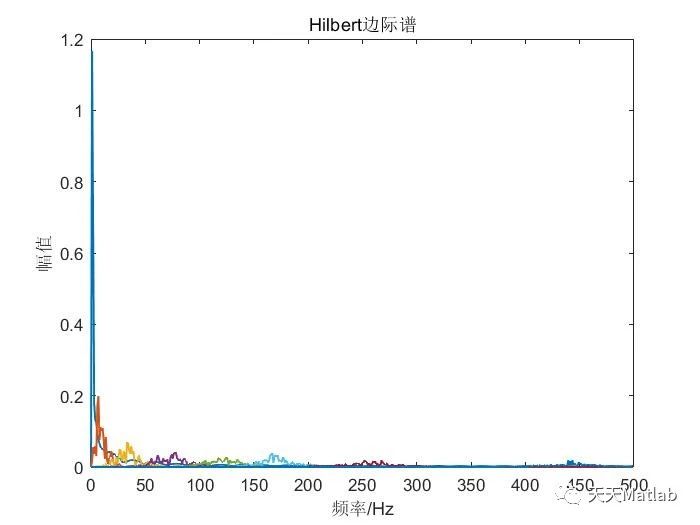
🔗 参考文献
[1] 李曼.在Matlab中实现基于LMS算法语音信号去噪[J].电脑知识与技术, 2014(11X):3.DOI:CNKI:SUN:DNZS.0.2014-32-035.
[2] 李志鹏,张智瀚,王睿,等.基于变分模态分解和改进鲸鱼算法优化的模糊神经网络风速预测模型[J]. 2022(3).
[3] 杨海马,陈嘉慈,徐笑寒,等.基于鲸鱼优化算法的VMD-NLM脉搏信号滤波算法研究[J].上海理工大学学报, 2022, 44(6):553-561.






















 806
806

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










