
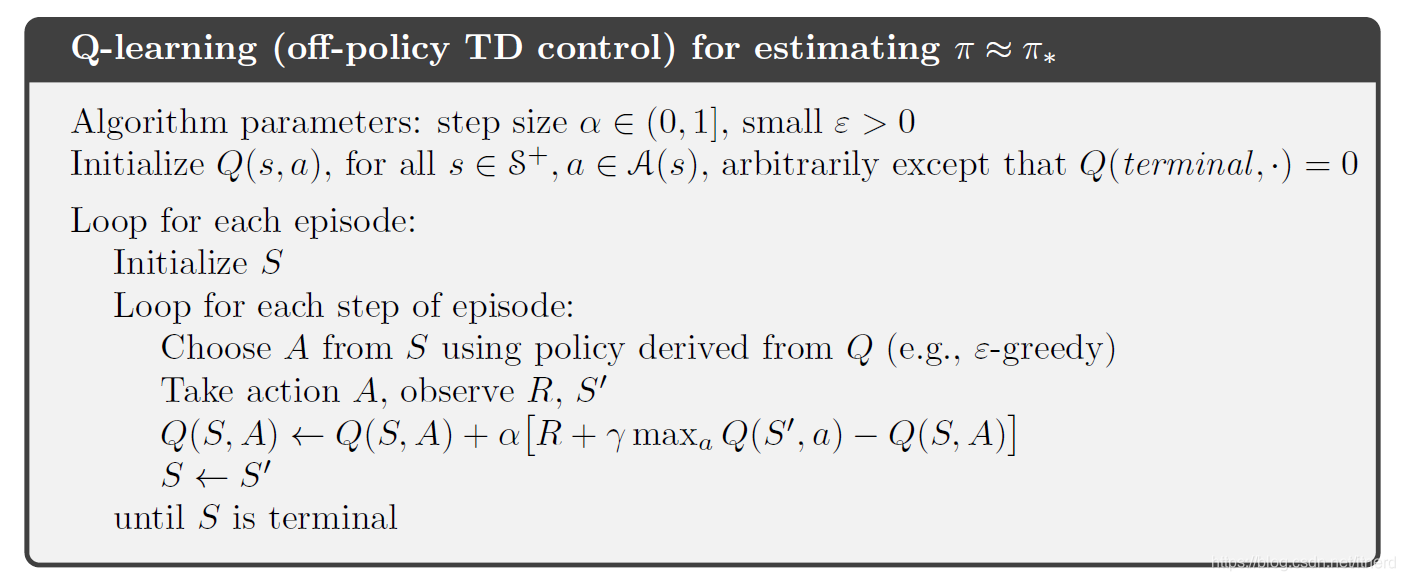
import random
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
#%matplotlib inline
import gym
env = gym.make('Taxi-v1')
env.render()
print(env.observation_space.n)
print(env.action_space.n)
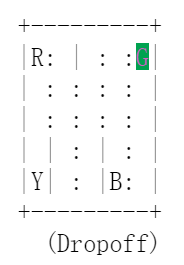
500
6
q = {}
for s in range(env.observation_space.n):
for a in range(env.action_space.n):
q[(s,a)] = 0.0
def update_q_table(prev_state, action, reward, nextstate, alpha, gamma):
qa = max([q[(nextstate, a)] for a in range(env.action_space.n)])
q[(prev_state,action)] += alpha * (reward + gamma * qa - q[(prev_state,action)])
def epsilon_greedy_policy(state, epsilon):
if random.uniform(0,1) < epsilon:
return env.action_space.sample()
else:
return max(list(range(env.action_space.n)), key = lambda x: q[(state,x)])
alpha = 0.4
gamma = 0.999
epsilon = 0.017
rewards = []
for i in range(800):
r = 0
prev_state = env.reset()
while True:
env.render()
# In each state, we select the action by epsilon-greedy policy
action = epsilon_greedy_policy(prev_state, epsilon)
# then we perform the action and move to the next state, and receive the reward
nextstate, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
# Next we update the Q value using our update_q_table function
# which updates the Q value by Q learning update rule
update_q_table(prev_state, action, reward, nextstate, alpha, gamma)
# Finally we update the previous state as next state
prev_state = nextstate
# Store all the rewards obtained
r += reward
#we will break the loop, if we are at the terminal state of the episode
if done:
break
#print("total reward: ", r)
rewards.append(r)
env.close()
plt.plot(rewards)
plt.show()
从 800 个 episode 训练的结果来看,agent 已经学到了合理的策略:reward 从负到正。实际上,400次试验后已经稳定。
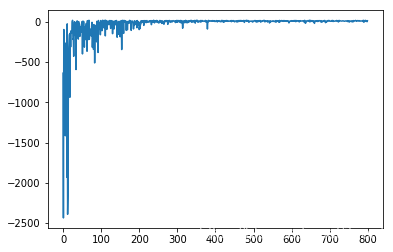





 本文通过Python实现Q学习算法解决Taxi-v1环境问题,详细展示了如何使用epsilon-greedy策略进行智能体训练,并通过图表展示800轮训练后奖励的变化趋势。
本文通过Python实现Q学习算法解决Taxi-v1环境问题,详细展示了如何使用epsilon-greedy策略进行智能体训练,并通过图表展示800轮训练后奖励的变化趋势。

















 2859
2859

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










