Genetics in geographically structured populations: defining, estimating and interpreting FST

Key Points
- Wright’s F-statistics, and especially FST, provide important insights into the evolutionary processes that influence the structure of genetic variation within and among populations, and they are among the most widely used descriptive statistics in
population and evolutionary genetics. - Wright’s F-statistics,特别是FST,为影响群体内和群体间遗传变异结构的进化过程提供重要见解,它们是
群体和进化遗传学中使用最广泛的描述性统计之一。 - FST is a property of the
distribution of allele frequencies among populations. It reflects the joint effects of drift, migration, mutation and selection on the distribution of genetic variation among populations. - FST是等
位基因频率在群体间分布的一个性质。它反映漂变、迁移、突变和选择对群体间遗传变异分布的共同影响。 - FST has a central role in
population and evolutionary geneticsand has wide applications in fields from disease association mapping to forensic science. - FST在群体和进化遗传学中发挥着核心作用,在从疾病关联制图到法医学等领域有着广泛的应用。
- FST can be used to describe the
distribution of genetic variation among any set of samples, but it ismost usefully applied when the samples represent discrete unitsrather than arbitrary divisions along a continuous distribution. - FST可以用来描述遗传变异在任何一组样本中的分布,但是当样本代表离散单位而不是沿着连续分布的任意划分时,它是最有用的。
- Statistics related to FST can be useful for haplotype or microsatellite data
if an appropriate measure of evolutionary distance among alleles is available. - 如果有合适的测量等位基因间进化距离的方法,FST相关的统计对单倍型或微卫星数据是有用的。
- Comparison of an
estimate of FST from marker datawith anestimate of QST from continuously varying trait datacan be used todetect selection, but the estimate of FST may depend on the choice of marker and the estimate of QST may differ from neutral expectations if there isa non-additive component(?)of genetic variance. - 比较来自marker 数据的FST估计值与来自连续变化的性状数据的QST估计值可以用来检测选择,但是FST的估计值可能取决于marker 的选择,如果存在遗传变异的非加性成分,QST的估计值可能与中性预期不同。
- Although the simple relationship between FST and migration rates in Wright’s island model makes it tempting to infer migration rates from FST, caution is needed if such an approach is to be used.
- 虽然Wright’s island model中FST和迁移率之间的简单关系使得从FST
推断迁移率很有吸引力,但如果要使用这种方法,则需要谨慎。 - If estimates of FST from many loci are available, it may be possible to
identify certain loci as 'outliers'that may have beensubject to different patterns of selectionor to different demographic processes. - 如果获得许多基因座的FST估计,则有可能
将某些基因座确定为“异常值”,这些基因座可能受到不同的选择模式或不同的群体统计过程的影响。 - Case–control studies for association-mapping studies must account for the possibility that population substructure accounts for an observed association between a marker and a disease. The genomic control method uses background estimates of FST to control for such substructure.
- 关联作图研究的Case–control 研究必须考虑到群体亚结构可能解释所观察到的marker 与疾病之间的关联。基因组控制方法使用FST的背景估计来控制这些子结构。
- In forensic applications, the probabilities of obtaining a match are sometimes calculated for subpopulations that lack specific allele frequency data. A θ correction, in which θ is FST, is used to calculate the probability of a match
using allele frequency information from a broader populationthat the subpopulation is part of. - 在法医应用中,有时会对缺乏特定等位基因频率数据的亚群计算获得匹配的概率。θ校正(其中θ为FST)用于使用来自该亚种群所属的更广泛种群的等位基因频率信息来计算匹配的概率。
- The massive amount of data that is being generated by population genomics projects can be understood fundamentally as
allelic variation at individual loci. We therefore expect F-statistics to be at least as useful in understanding these data sets as they have been in population and evolutionary genetics for most of the last century. - population genomics项目产生的大量数据可以从根本上理解为单个位点上的等位基因变异。因此,我们期望F统计在理解这些数据集方面至少能像在上个世纪的大部分时间里在人口和进化遗传学方面一样有用。
Definitions
Wright introduced FST as one of three interrelated parametersto describe the genetic structure of diploid populations. These parameters are:
FIT, the correlation between gametes within an individual relative to theentire population;FIS, the correlation between gametes within an individual relative to thesubpopulationto which that individual belongs;FST, the correlation between gametes chosen randomly from within the same subpopulation relative to the entire population.- We describe here how these parameters are defined in terms of the departure of genotype frequencies from Hardy–Weinberg proportions.
Wright引入FST作为描述二倍体群体遗传结构的三个相关参数之一。
- FIT,个体内配子相对于整个群体的相关性;
- FIS,个体内配子与该个体所属亚群之间的相关性;
- FST,从同一亚种群中随机选择的配子相对于整个种群之间的相关性。
- 我们在这里描述如何根据
基因型频率偏离Hardy-Weinberg比例来定义这些参数。
1. 文档1 Fst Pi
https://www.jianshu.com/p/cb1772e7f449
1.1 选择信号分析—Fst
1.1.1 Fst概念
- Fst:群体间遗传分化指数,是种群分化和遗传距离的一种衡量方法,
分化指数越大,差异越大。适用于亚群体间多样性的比较。 - 用于衡量种群分化程度,取值从0到1,为
0则认为两个种群间是随机交配,基因型完全相似;为1则表示是完全隔离,完全不相似。它往往从基因的多样性来估计,比如SNP或者microsatellites(串联重复序列一种,长度小于等于10bp)。是一种以哈温平衡为前提的种群遗传学统计方法。 两个种群之间遗传差异的基本测量是统计量FST。在遗传学中,F一词通常代表“近亲繁殖”,它倾向于减少群体中的遗传变异。遗传变异可以用杂合度来衡量,所以F一般表示群体中杂合性的减少。 FST是与它们所属的总群体相比,亚群体中杂合性的减少量。
具体可以下面的公式表示:
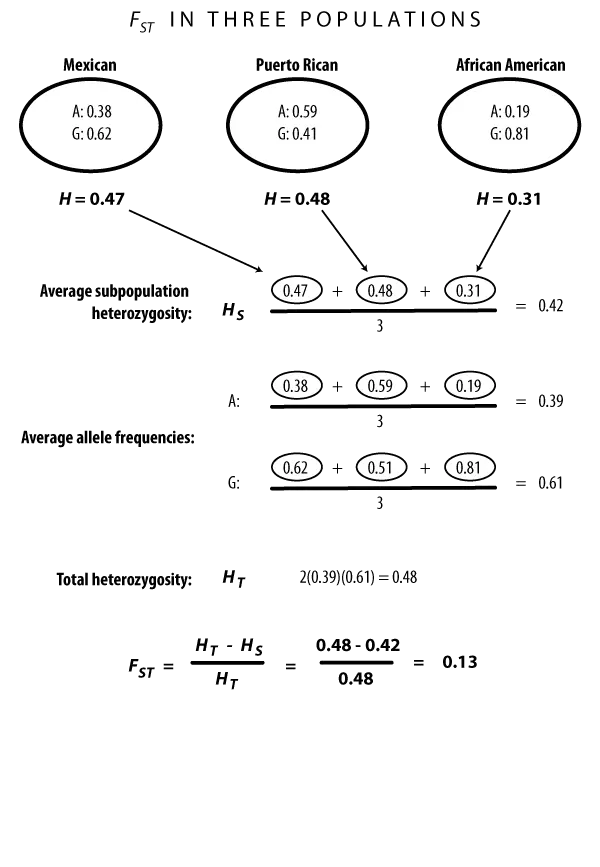
Fst= (Ht-Hs)/ Ht
Hs:亚群体中的平均杂合度
Ht:复合群体中的平均杂合度
Fst
理论上计算Fst的步骤
理论上要估算FST,需要以下步骤:
找出每个亚群的等位基因频率。
查找复合群体的平均等位基因频率
计算每个亚群的杂合度(2pq)
计算这些亚群杂合度的平均值,这是HS。
根据总体等位基因频率计算杂合度,这是HT。
最后,计算FST =(HT-HS)/ HT
1.1.2 Fst 图解
H=2pq
- FST(遗传分化指数):计算使用
vcftools,可视化分为箱线图和散点图,单组比较使用在染色体上的散点图,多组比较使用箱线图。 - FST的原理,计算方法,可视化的方法 https://www.jianshu.com/p/bb0beec0ed63
http





 本文详细介绍了FST和π在群体遗传学中的关键概念、计算方法和应用。FST是衡量群体间遗传分化的重要指标,而π则表示群体内的遗传多样性。文章通过实例探讨了如何利用vcftools等工具计算FST,并讨论了FST在检测选择信号和群体分化中的作用。此外,Tajima's D作为另一种统计量,用于评估群体的中性演化假说。通过结合FST、π和Tajima's D的分析,可以有效地识别出选择消除的区域,从而深入理解群体的进化历史和选择压力。
本文详细介绍了FST和π在群体遗传学中的关键概念、计算方法和应用。FST是衡量群体间遗传分化的重要指标,而π则表示群体内的遗传多样性。文章通过实例探讨了如何利用vcftools等工具计算FST,并讨论了FST在检测选择信号和群体分化中的作用。此外,Tajima's D作为另一种统计量,用于评估群体的中性演化假说。通过结合FST、π和Tajima's D的分析,可以有效地识别出选择消除的区域,从而深入理解群体的进化历史和选择压力。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 9233
9233










