右值引用和左值引用
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
void reference(std::string& str) {
std::cout << "lvalue" << std::endl;
}
void reference(std::string&& str) {
std::cout << "rvalue" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
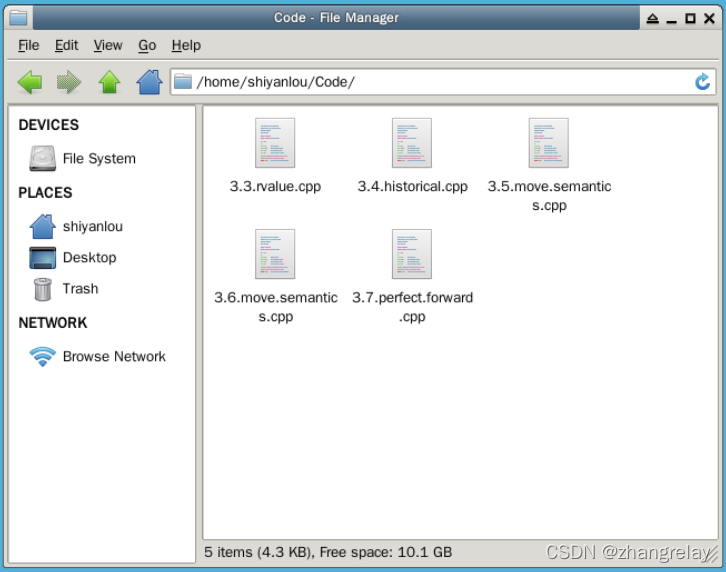
std::string lv1 = "string,"; // lv1 is a lvalue
// std::string&& r1 = lv1; // illegal, rvalue can't ref to lvalue
std::string&& rv1 = std::move(lv1); // legal, std::move can convert lvalue to rvalue
std::cout << rv1 << std::endl; // string,
const std::string& lv2 = lv1 + lv1; // legal, const lvalue reference can extend temp variable's lifecycle
// lv2 += "Test"; // illegal, const ref can't be modified
std::cout << lv2 << std::endl; // string,string
std::string&& rv2 = lv1 + lv2; // legal, rvalue ref extend lifecycle
rv2 += "string"; // legal, non-const reference can be modified
std::cout << rv2 << std::endl; // string,string,string,
reference(rv2); // output: lvalue
return 0;
}
一个很有趣的历史遗留问题
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// int &a = std::move(1); // illegal, non-const lvalue reference cannot ref rvalue
const int &b = std::move(1); // legal, const lvalue reference can
std::cout << b << std::endl;
}

#include <iostream>
class A {
public:
int *pointer;
A():pointer(new int(1)) {
std::cout << "construct" << pointer << std::endl;
}
A(A& a):pointer(new int(*a.pointer)) {
std::cout << "copy" << pointer << std::endl;
} // meaningless object copy
A(A&& a):pointer(a.pointer) {
a.pointer = nullptr;
std::cout << "move" << pointer << std::endl;
}
~A(){
std::cout << "destruct" << pointer << std::endl;
delete pointer;
}
};
// avoid compiler optimization
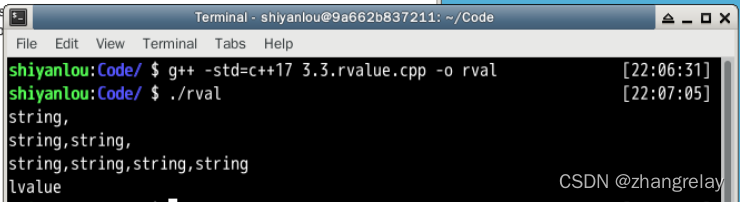
A return_rvalue(bool test) {
A a,b;
if(test) return a; // equal to static_cast<A&&>(a);
else return b; // equal to static_cast<A&&>(b);
}
int main() {
A obj = return_rvalue(false);
std::cout << "obj:" << std::endl;
std::cout << obj.pointer << std::endl;
std::cout << *obj.pointer << std::endl;
return 0;
}
移动语义
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <utility> // std::move
#include <vector> // std::vector
#include <string> // std::string
int main() {
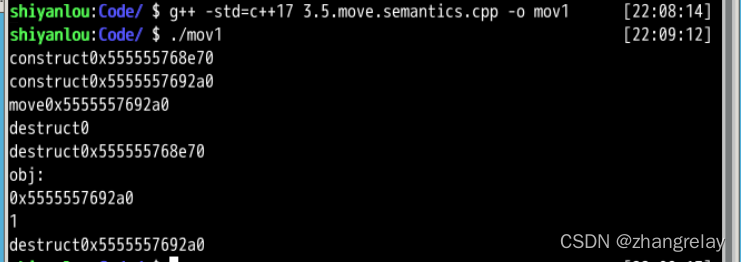
std::string str = "Hello world.";
std::vector<std::string> v;
// use push_back(const T&), copy
v.push_back(str);
// "str: Hello world."
std::cout << "str: " << str << std::endl;
// use push_back(const T&&), no copy
// the string will be moved to vector, and therefore std::move can reduce copy cost
v.push_back(std::move(str));
// str is empty now
std::cout << "str: " << str << std::endl;
return 0;
}
完美转发
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
void reference(int& v) {
std::cout << "lvalue reference" << std::endl;
}
void reference(int&& v) {
std::cout << "rvalue reference" << std::endl;
}
template <typename T>
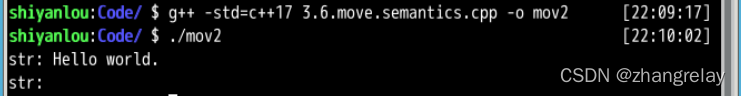
void pass(T&& v) {
std::cout << " normal param passing: ";
reference(v);
std::cout << " std::move param passing: ";
reference(std::move(v));
std::cout << " std::forward param passing: ";
reference(std::forward<T>(v));
std::cout << "static_cast<T&&> param passing: ";
reference(static_cast<T&&>(v));
}
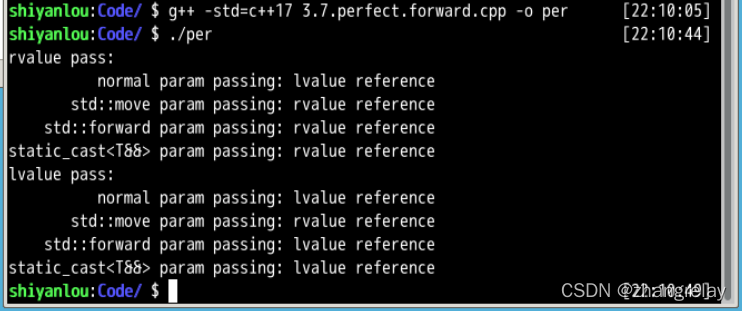
int main() {
std::cout << "rvalue pass:" << std::endl;
pass(1);
std::cout << "lvalue pass:" << std::endl;
int l = 1;
pass(l);
return 0;
}




 本文介绍了C++中的右值引用、移动语义和完美转发的概念及应用。通过示例代码展示了右值引用如何用于提高效率,移动构造函数和移动赋值操作符的使用,以及完美转发在函数模板中的作用,解释了如何正确传递参数以保留其原始性质。
本文介绍了C++中的右值引用、移动语义和完美转发的概念及应用。通过示例代码展示了右值引用如何用于提高效率,移动构造函数和移动赋值操作符的使用,以及完美转发在函数模板中的作用,解释了如何正确传递参数以保留其原始性质。

















 1059
1059

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










