学习的程序如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <vector>
void foo(int *p, int len) {
for (int i = 0; i != len; ++i) {
std::cout << p[i] << std::endl;
}
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> v;
std::cout << "size:" << v.size() << std::endl; // output 0
std::cout << "capacity:" << v.capacity() << std::endl; // output 0
// As you can see, the storage of std::vector is automatically managed and
// automatically expanded as needed.
// But if there is not enough space, you need to redistribute more memory,
// and reallocating memory is usually a performance-intensive operation.
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
std::cout << "size:" << v.size() << std::endl; // output 3
std::cout << "capacity:" << v.capacity() << std::endl; // output 4
// The auto-expansion logic here is very similar to Golang's slice.
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
std::cout << "size:" << v.size() << std::endl; // output 5
std::cout << "capacity:" << v.capacity() << std::endl; // output 8
// As can be seen below, although the container empties the element,
// the memory of the emptied element is not returned.
v.clear();
std::cout << "size:" << v.size() << std::endl; // output 0
std::cout << "capacity:" << v.capacity() << std::endl; // output 8
// Additional memory can be returned to the system via the shrink_to_fit() call
v.shrink_to_fit();
std::cout << "size:" << v.size() << std::endl; // output 0
std::cout << "capacity:" << v.capacity() << std::endl; // output 0
std::array<int, 4> arr= {1,4,3,2};
//int len = 4;
//std::array<int, len> arr = {1,2,3,4}; // illegal, size of array must be constexpr
// C style parameter passing
// foo(arr, arr.size()); // illegal, cannot convert implicitly
foo(&arr[0], arr.size());
foo(arr.data(), arr.size());
// more usage
std::sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
for(auto &i : arr)
std::cout << i << std::endl;
return 0;
}
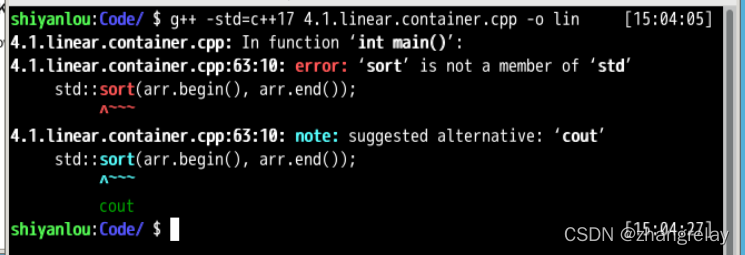
看了C++版本还是要更新支持到c++20才行。
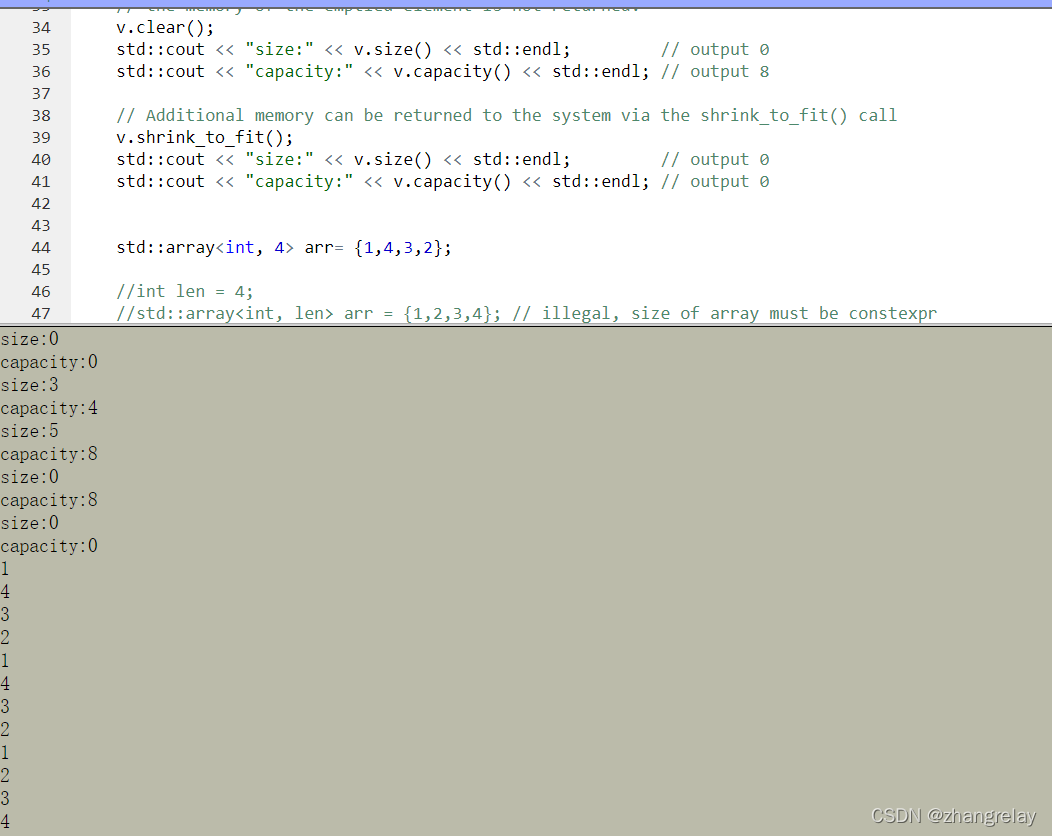




 本文探讨了C++中vector容器的内存管理机制,包括自动扩展、内存分配与回收,以及shrink_to_fit()的使用。通过实例展示了vector的动态增长和容量调整,并对比了其与C风格数组的差异。
本文探讨了C++中vector容器的内存管理机制,包括自动扩展、内存分配与回收,以及shrink_to_fit()的使用。通过实例展示了vector的动态增长和容量调整,并对比了其与C风格数组的差异。

















 1061
1061

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










