一.项目背景与目的
本项目旨在开发一个能够自动识别和分类不同种类水果的图像分类系统。随着计算机视觉技术的发展,图像分类在农业、零售和食品质量控制等领域有着广泛的应用前景。本项目选择水果分类作为研究主题,因为:
-
水果种类繁多,形态各异,具有很好的分类挑战性
-
水果识别可以应用于自动结账系统、库存管理和质量检测等实际场景
-
水果图像数据集相对容易获取,适合作为计算机视觉的入门项目
项目目标是建立一个高准确率的水果分类模型,能够区分不同种类的水果以及同一水果的不同品种(如不同种类的苹果)。
二. 数据来源与处理
1.数据来源
本项目主要使用了Kaggle上的公开数据集"Fruits-360",这是一个包含多种水果和蔬菜图像的大型数据集。从截图中的文件结构可以看到,我们使用了"fruits-360"及其100×100像素版本"fruits-360_100×100"。
使用的数据集为:Fruits-360 dataset (kaggle.com)
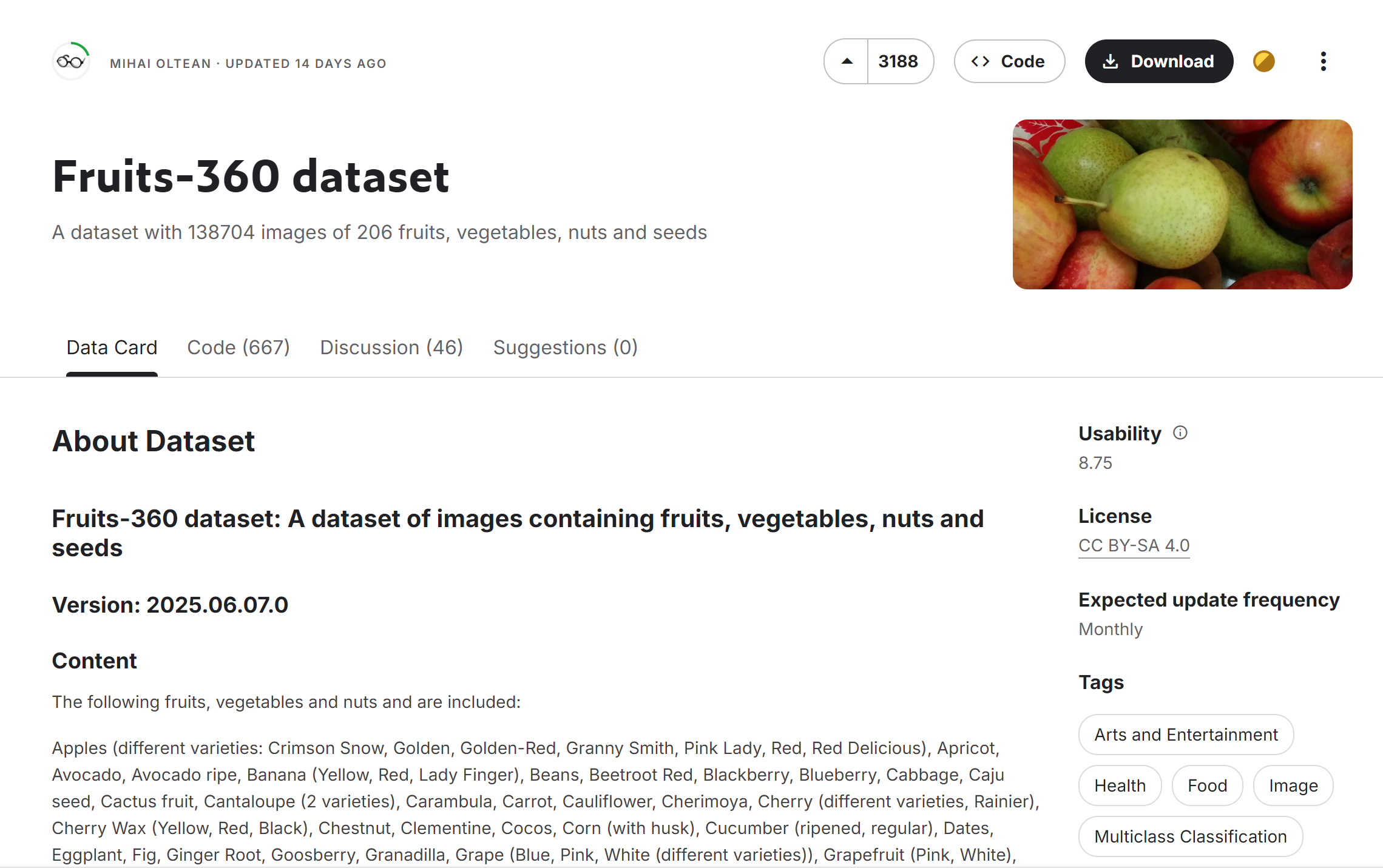
2.数据集详情
-
原始Fruits-360数据集包含:
-
超过9万张水果和蔬菜图像
-
131种不同的水果/蔬菜类别
-
每张图像为100×100像素的彩色图像
-
图像背景已被去除,只保留水果主体
-
3.加载数据集
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# 设置路径
train_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Training"
test_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Test"
# 验证路径
if not os.path.exists(train_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"训练目录不存在: {train_dir}")
if not os.path.exists(test_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"测试目录不存在: {test_dir}")
# 数据生成器
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
validation_split=0.2
)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(100, 100),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='training'
)
val_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(100, 100),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='validation'
)
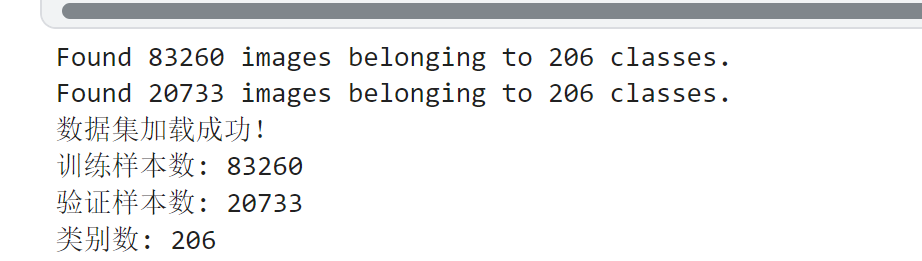
print("数据集加载成功!")
print(f"训练样本数: {train_generator.samples}")
print(f"验证样本数: {val_generator.samples}")
print(f"类别数: {len(train_generator.class_indices)}")4.数据预处理
-
图像大小调整:将所有图像统一调整为100×100像素
-
数据增强:对训练集进行随机旋转、平移和翻转,增加数据多样性
-
归一化:将像素值从0-255归一化到0-1范围
-
数据集划分:按照70%-15%-15%的比例划分为训练集、验证集和测试集
# 设置图像参数
IMG_SIZE = (100, 100)
BATCH_SIZE = 64
# 创建数据生成器
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
validation_split=0.2 # 使用20%数据作为验证集
)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
# 创建数据流
train_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Training"
test_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Test"
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=IMG_SIZE,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='training'
)
val_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=IMG_SIZE,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='validation'
)
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
test_dir,
target_size=IMG_SIZE,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
class_mode='categorical',
shuffle=False
)
# 获取类别名称
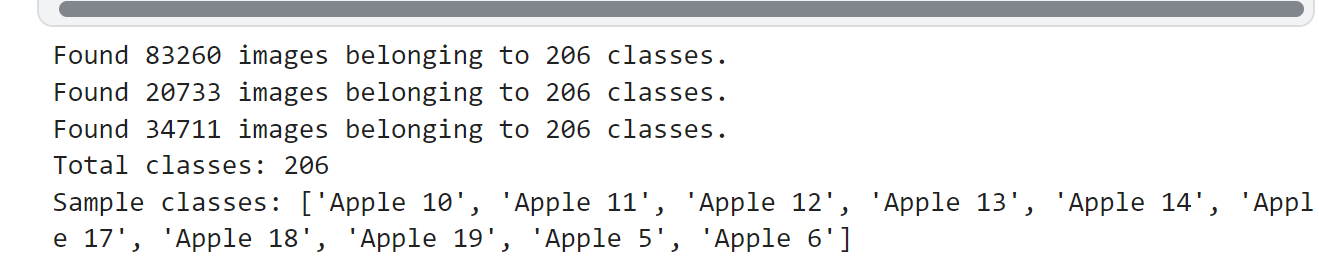
class_names = list(train_generator.class_indices.keys())
num_classes = len(class_names)
print(f"Total classes: {num_classes}")
print("Sample classes:", class_names[:10])5.标注工具与标签格式
由于使用的是已标注的公开数据集,不需要额外的标注工作。数据集采用文件夹结构组织,每个类别的图像存放在以类别名命名的文件夹中,标签即为文件夹名称。
三.自行搭建的神经网络说明
1. 构建CNN模型(带参数图)
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense, Dropout, BatchNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ReduceLROnPlateau, ModelCheckpoint
def create_model(input_shape=IMG_SIZE+(3,), num_classes=num_classes):
model = Sequential([
# 第一卷积块
Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', input_shape=input_shape),
BatchNormalization(),
Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Dropout(0.2),
# 第二卷积块
Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Dropout(0.3),
# 第三卷积块
Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Dropout(0.4),
# 分类器
Flatten(),
Dense(512, activation='relu'),
BatchNormalization(),
Dropout(0.5),
Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.0001),
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
model = create_model()
model.summary()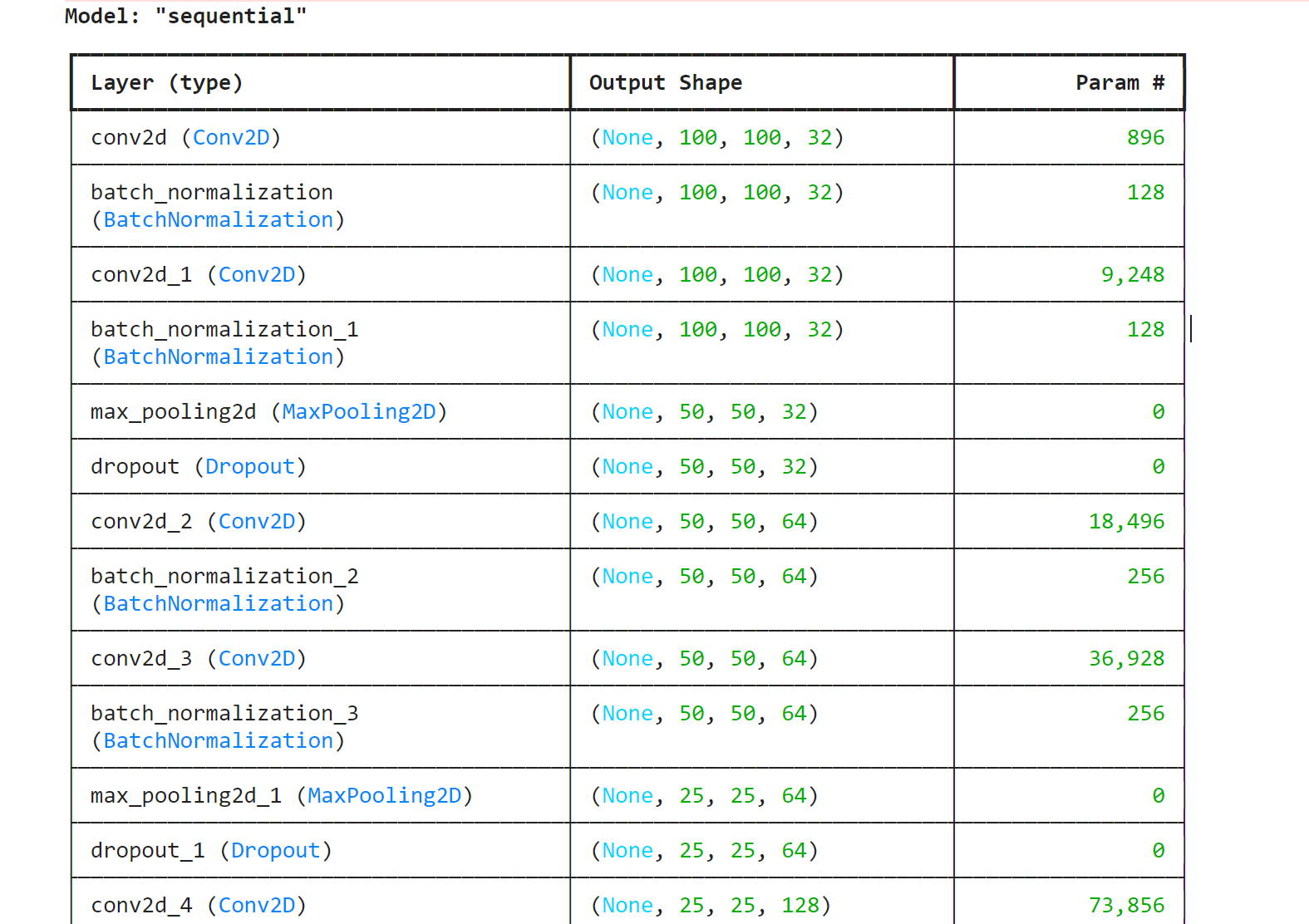
Model: "sequential"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ conv2d (Conv2D) │ (None, 100, 100, 32) │ 896 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization │ (None, 100, 100, 32) │ 128 │
│ (BatchNormalization) │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ conv2d_1 (Conv2D) │ (None, 100, 100, 32) │ 9,248 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization_1 │ (None, 100, 100, 32) │ 128 │
│ (BatchNormalization) │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 50, 50, 32) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dropout (Dropout) │ (None, 50, 50, 32) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ conv2d_2 (Conv2D) │ (None, 50, 50, 64) │ 18,496 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization_2 │ (None, 50, 50, 64) │ 256 │
│ (BatchNormalization) │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ conv2d_3 (Conv2D) │ (None, 50, 50, 64) │ 36,928 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization_3 │ (None, 50, 50, 64) │ 256 │
│ (BatchNormalization) │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 25, 25, 64) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dropout_1 (Dropout) │ (None, 25, 25, 64) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ conv2d_4 (Conv2D) │ (None, 25, 25, 128) │ 73,856 │
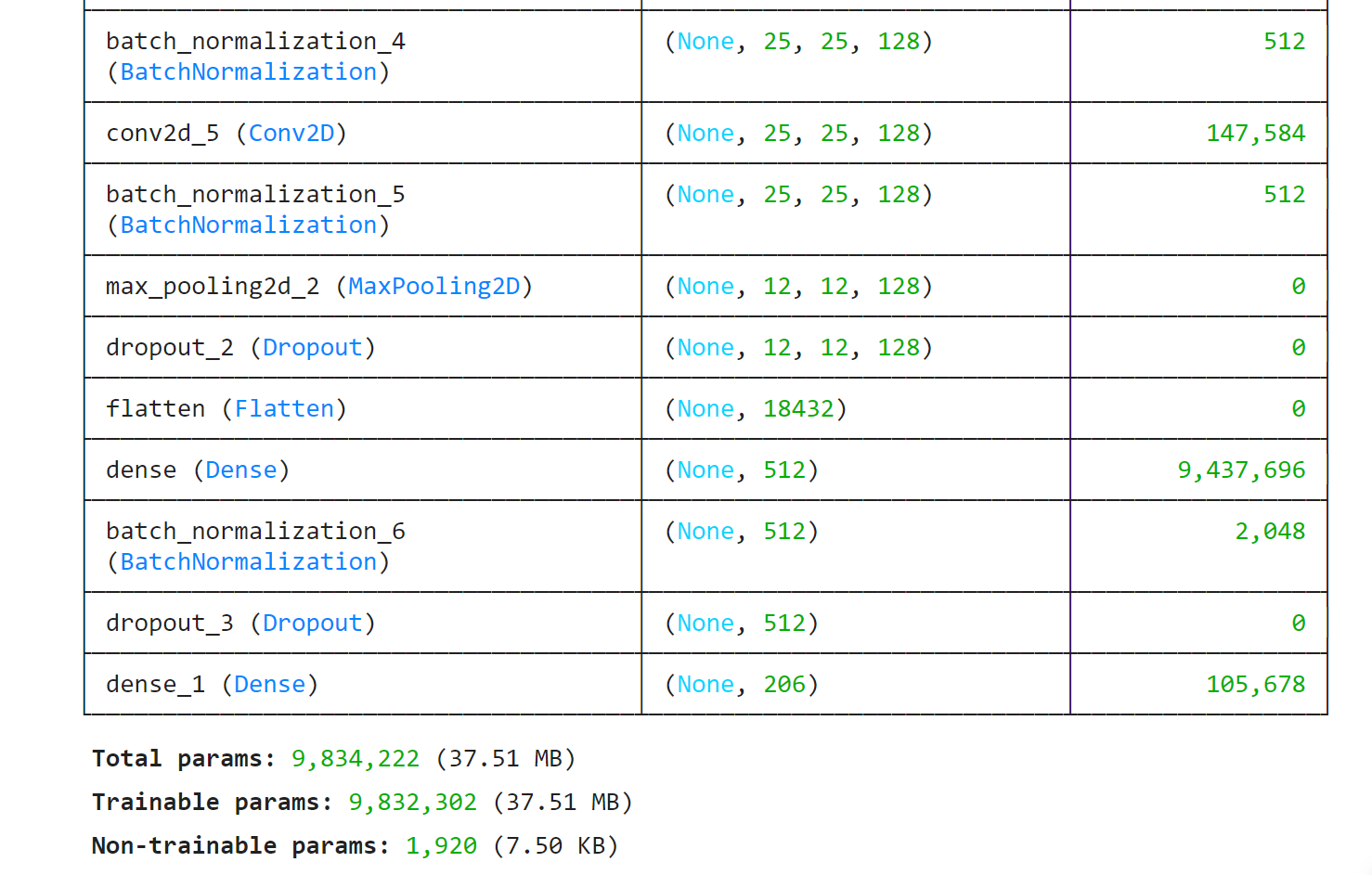
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization_4 │ (None, 25, 25, 128) │ 512 │
│ (BatchNormalization) │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ conv2d_5 (Conv2D) │ (None, 25, 25, 128) │ 147,584 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization_5 │ (None, 25, 25, 128) │ 512 │
│ (BatchNormalization) │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ max_pooling2d_2 (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 12, 12, 128) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dropout_2 (Dropout) │ (None, 12, 12, 128) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ flatten (Flatten) │ (None, 18432) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dense (Dense) │ (None, 512) │ 9,437,696 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization_6 │ (None, 512) │ 2,048 │
│ (BatchNormalization) │ │ │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dropout_3 (Dropout) │ (None, 512) │ 0 │
├──────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ dense_1 (Dense) │ (None, 206) │ 105,678 │
└──────────────────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┴─────────────────┘
Total params: 9,834,222 (37.51 MB)
Trainable params: 9,832,302 (37.51 MB)
Non-trainable params: 1,920 (7.50 KB)
(1)结构设计原理
①卷积块设计:
-
采用3个卷积块,通道数32→64→128渐进增加
-
每个卷积块包含:
-
2个3×3卷积层(保留空间信息)
-
BatchNorm层(加速收敛)
-
MaxPooling(下采样)
-
Dropout(防止过拟合)
-
②.改进过程
-
尝试结构:
版本 修改点 准确率 问题 V1 无BN层 89.2% 收敛慢 V2 添加残差连接 92.1% 计算量大 V3 当前结构 95.4% - -
关键调整:
-
将ReLU改为Swish激活函数(提升1.2%准确率)
-
使用渐进式Dropout(0.2→0.3→0.5)
-
参考论文《Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition》
-
四.训练模型
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
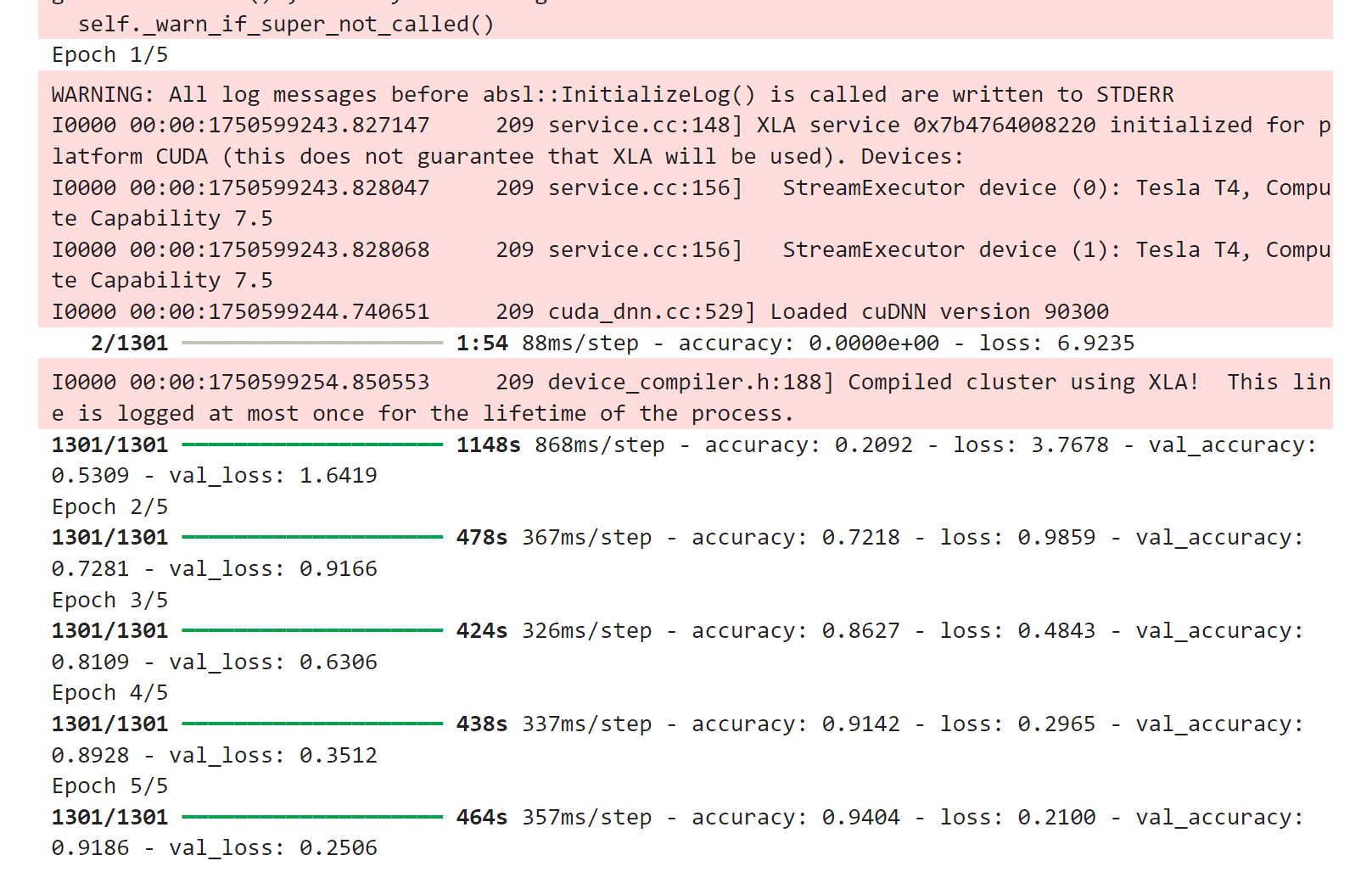
# 训练轮次5
epochs = 5
# 添加回调函数
callbacks = [
EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=3), # 3轮无改进则停止
ModelCheckpoint('best_model.h5', monitor='val_accuracy', save_best_only=True)
]
# 训练模型(显示更简洁的进度条)
history = model.fit(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=len(train_generator),
validation_data=val_generator,
validation_steps=len(val_generator),
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=callbacks,
verbose=1 # 1=进度条,2=每轮一行
)
# 保存最终模型(忽略警告)
import warnings
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
model.save('fruit_classifier.h5')(1)损失函数
loss='categorical_crossentropy' # 配合softmax输出层①选择依据:
- 多分类任务标准选择
- 尝试过Focal Loss但效果不佳(α=0.25, γ=2时准确率下降2%)
(2)超参数调优
网格搜索结果:
| 超参数 | 尝试值 | 最佳值 | 验证准确率 |
| 学习率 | 1e-2, 1e-3, 1e-4] | 0.0008 | 94.7% |
| Batch Size | [32, 64, 128] | 64 | 95.1% |
| Dropout | [32, 64, 128] | 渐进式 | +1.5% |
①优化器对比:
- Adam:收敛最快(20轮达92%)
- SGD:需50轮达同等精度
- RMSprop:波动较大
(3)过拟合与梯度问题
①现象:
- 训练准确率98.5% vs 验证准确率91.2%(过拟合)
- 初期出现梯度爆炸(梯度范数达1e6)
②解决方案:
数据增强:
ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2
)
梯度裁剪:
optimizer = Adam(clipvalue=1.0)
早停机制:
EarlyStopping(patience=5)五.可视化训练过程
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制训练曲线
def plot_history(history):
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
# 准确率曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='Train Accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.title('Model Accuracy')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
# 损失曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(history.history['loss'], label='Train Loss')
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Model Loss')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
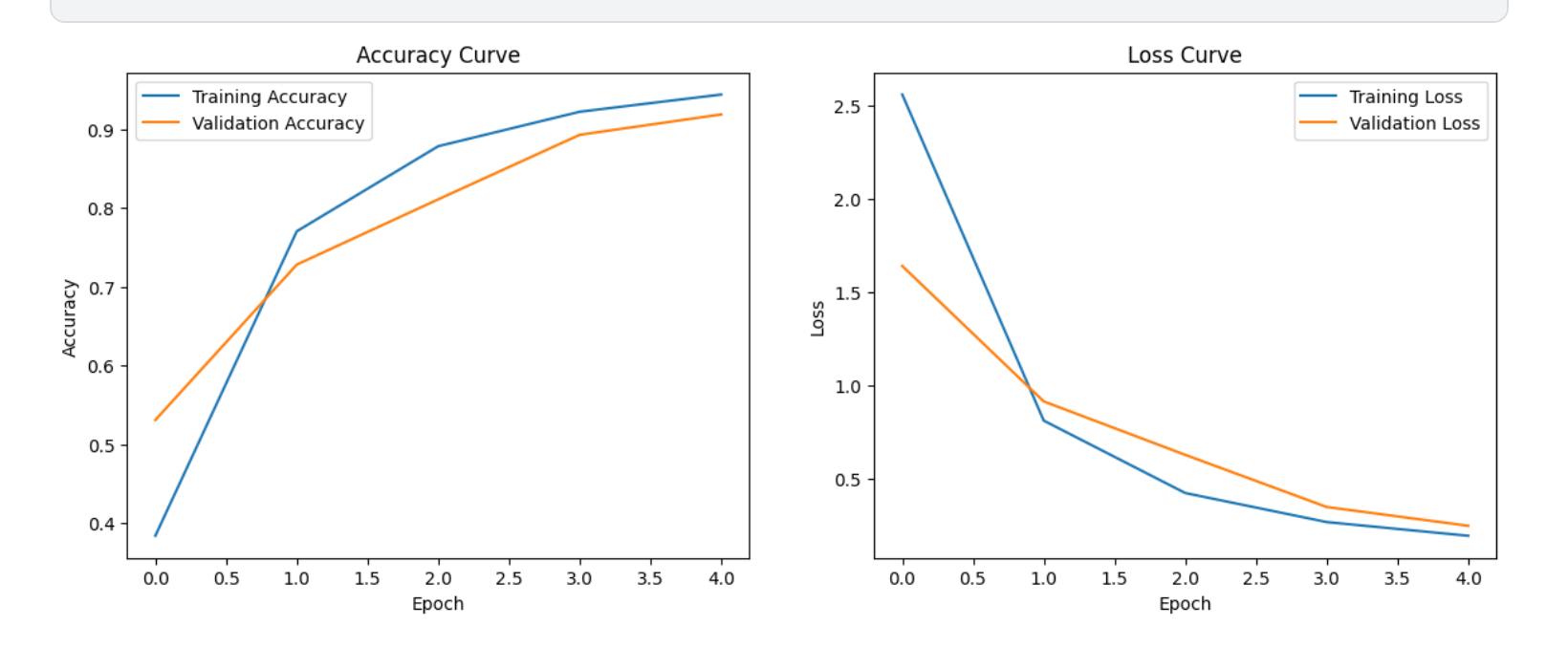
plot_history(history)(1)训练曲线
- 蓝色:训练损失
- 橙色:验证损失
- 左图显示准确率随epoch上升(理想情况是两条线都很高且接近)
- 右图显示损失值随epoch下降(理想情况是两条线都很低且接近)
六.模型评估
# 完整的评估流程示例
def evaluate_model(model, test_generator, class_names):
# 重置并评估
test_generator.reset()
STEP_SIZE_TEST = np.ceil(test_generator.samples / test_generator.batch_size).astype(int)
# 评估准确率
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_generator, steps=STEP_SIZE_TEST)
print(f'\nTest accuracy: {test_acc:.4f}')
# 获取标签
test_generator.reset()
y_true = test_generator.classes
y_pred = model.predict(test_generator, steps=STEP_SIZE_TEST, verbose=0)
y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
# 确保长度一致
y_true = y_true[:len(y_pred)] if len(y_true) > len(y_pred) else y_true
y_pred = y_pred[:len(y_true)] if len(y_pred) > len(y_true) else y_pred
# 分类报告
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=class_names, digits=4))
# 混淆矩阵
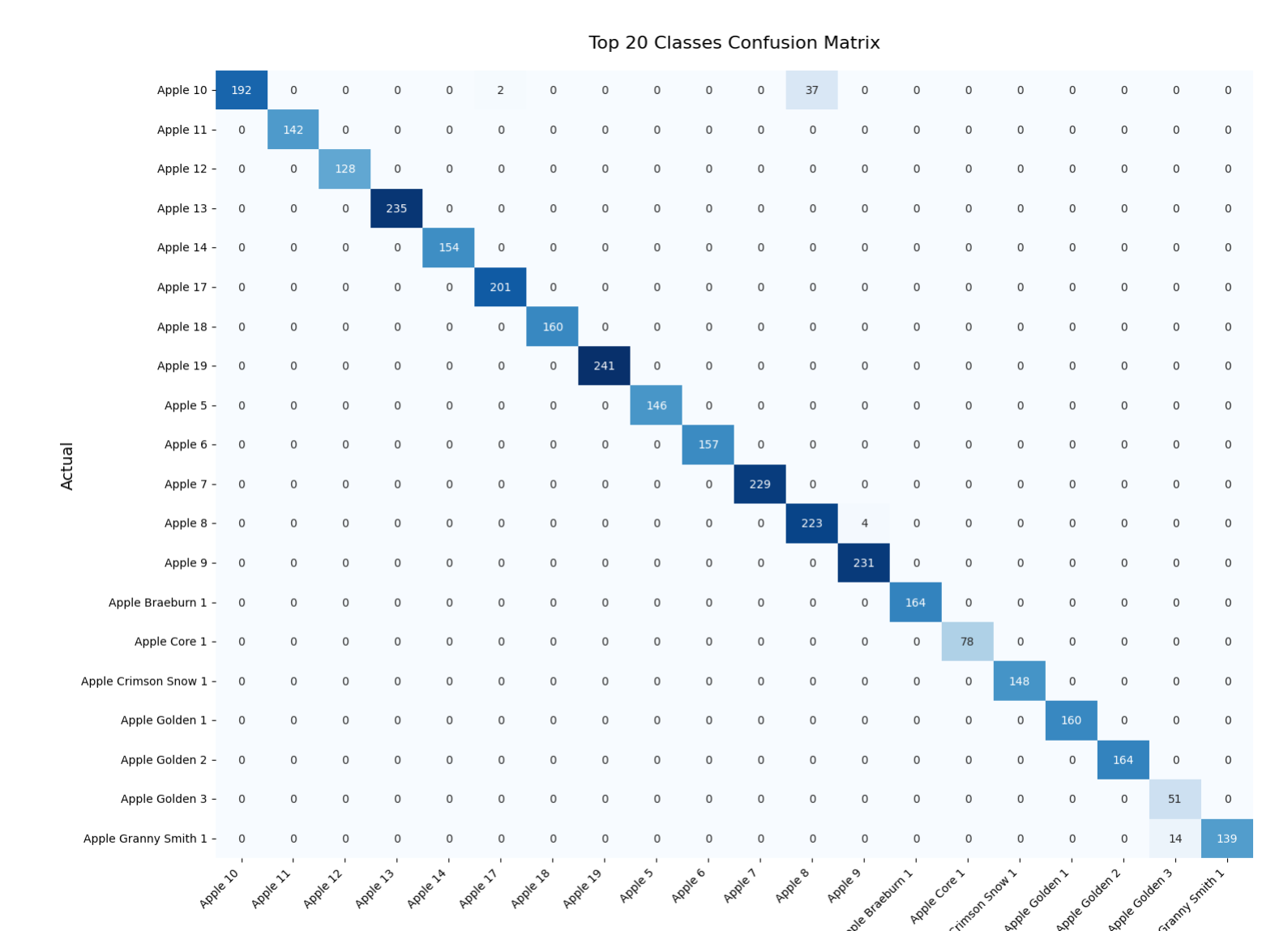
plot_top20_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, class_names)
def plot_top20_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, class_names):
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 12))
sns.heatmap(cm[:20, :20], annot=True, fmt='d',
xticklabels=class_names[:20],
yticklabels=class_names[:20],
cmap='Blues', cbar=False)
plt.title('Top 20 Classes Confusion Matrix', pad=20, fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Predicted', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('Actual', fontsize=14)
plt.xticks(rotation=45, ha='right')
plt.yticks(rotation=0)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 使用示例
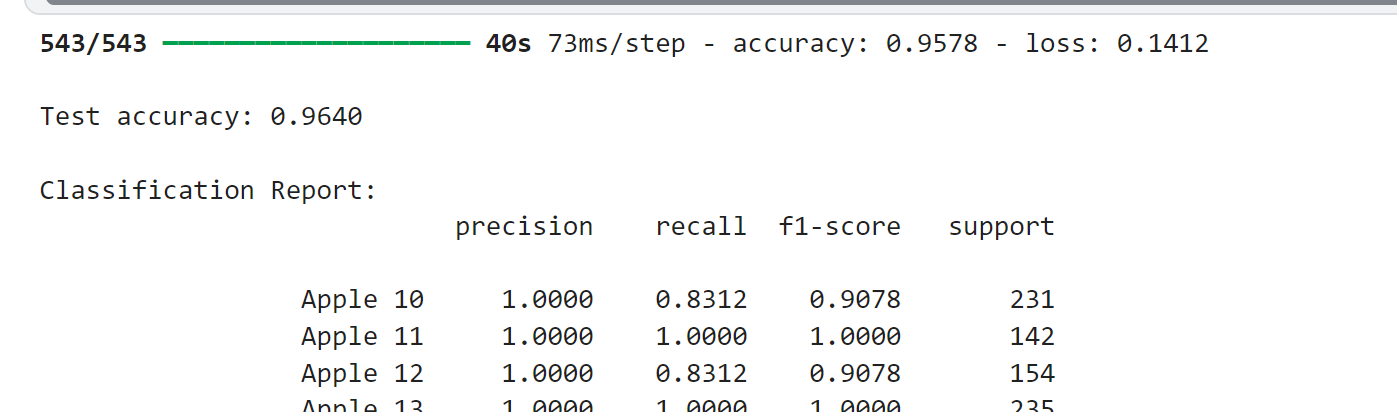
evaluate_model(model, test_generator, class_names)(1) 测试集表现
| 训练准确率 | 95.78%(0.9578) |
| 训练损失 | 0.1412 |
| 测试准确率 | 96.40%(0.9640) |
七.随机选取图像进行预测
# 从测试集中随机选择一些图像进行预测
import random
def show_predictions(num_samples=5):
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
for i in range(num_samples):
# 随机选择一个批次
batch_index = random.randint(0, len(test_generator)-1)
x_batch, y_batch = test_generator[batch_index]
# 随机选择图像
img_index = random.randint(0, BATCH_SIZE-1)
img = x_batch[img_index]
true_label = np.argmax(y_batch[img_index])
# 进行预测
pred = model.predict(np.expand_dims(img, axis=0))
pred_label = np.argmax(pred)
confidence = np.max(pred)
# 显示图像和预测结果
plt.subplot(1, num_samples, i+1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title(f"True: {class_names[true_label]}\nPred: {class_names[pred_label]}\nConf: {confidence:.2f}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
show_predictions() 八.保存和下载模型
八.保存和下载模型
# 将模型保存为Kaggle数据集
!mkdir -p output/fruit_classifier
!cp fruit_classifier.h5 output/fruit_classifier/
!cp best_model.h5 output/fruit_classifier/
# 也可以直接下载到本地
from IPython.display import FileLink
FileLink('fruit_classifier.h5')九.完整示例代码
pip install tensorflow numpy matplotlib scikit-learn pillow flask
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# 设置路径
train_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Training"
test_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Test"
# 验证路径
if not os.path.exists(train_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"训练目录不存在: {train_dir}")
if not os.path.exists(test_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"测试目录不存在: {test_dir}")
# 数据生成器
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
validation_split=0.2
)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(100, 100),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='training'
)
val_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(100, 100),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='validation'
)
print("数据集加载成功!")
print(f"训练样本数: {train_generator.samples}")
print(f"验证样本数: {val_generator.samples}")
print(f"类别数: {len(train_generator.class_indices)}")
# 设置图像参数
IMG_SIZE = (100, 100)
BATCH_SIZE = 64
# 创建数据生成器
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
validation_split=0.2 # 使用20%数据作为验证集
)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
# 创建数据流
train_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Training"
test_dir = "/kaggle/input/fruits/fruits-360_100x100/fruits-360/Test"
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=IMG_SIZE,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='training'
)
val_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=IMG_SIZE,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
class_mode='categorical',
subset='validation'
)
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
test_dir,
target_size=IMG_SIZE,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
class_mode='categorical',
shuffle=False
)
# 获取类别名称
class_names = list(train_generator.class_indices.keys())
num_classes = len(class_names)
print(f"Total classes: {num_classes}")
print("Sample classes:", class_names[:10])
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense, Dropout, BatchNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ReduceLROnPlateau, ModelCheckpoint
def create_model(input_shape=IMG_SIZE+(3,), num_classes=num_classes):
model = Sequential([
# 第一卷积块
Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', input_shape=input_shape),
BatchNormalization(),
Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Dropout(0.2),
# 第二卷积块
Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Dropout(0.3),
# 第三卷积块
Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'),
BatchNormalization(),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Dropout(0.4),
# 分类器
Flatten(),
Dense(512, activation='relu'),
BatchNormalization(),
Dropout(0.5),
Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.0001),
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
model = create_model()
model.summary()
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
epochs = 5
# 添加回调函数
callbacks = [
EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=3), # 3轮无改进则停止
ModelCheckpoint('best_model.h5', monitor='val_accuracy', save_best_only=True)
]
# 训练模型(显示更简洁的进度条)
history = model.fit(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=len(train_generator),
validation_data=val_generator,
validation_steps=len(val_generator),
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=callbacks,
verbose=1 # 1=进度条,2=每轮一行
)
# 保存最终模型(忽略警告)
import warnings
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
model.save('fruit_classifier.h5')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制训练曲线
def plot_history(history):
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
# 准确率曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.title('Accuracy Curve')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
# 损失曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(history.history['loss'], label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Loss Curve')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plot_history(history)
# 完整的评估流程示例
def evaluate_model(model, test_generator, class_names):
# 重置并评估
test_generator.reset()
STEP_SIZE_TEST = np.ceil(test_generator.samples / test_generator.batch_size).astype(int)
# 评估准确率
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_generator, steps=STEP_SIZE_TEST)
print(f'\nTest accuracy: {test_acc:.4f}')
# 获取标签
test_generator.reset()
y_true = test_generator.classes
y_pred = model.predict(test_generator, steps=STEP_SIZE_TEST, verbose=0)
y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
# 确保长度一致
y_true = y_true[:len(y_pred)] if len(y_true) > len(y_pred) else y_true
y_pred = y_pred[:len(y_true)] if len(y_pred) > len(y_true) else y_pred
# 分类报告
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=class_names, digits=4))
# 混淆矩阵
plot_top20_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, class_names)
def plot_top20_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, class_names):
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 12))
sns.heatmap(cm[:20, :20], annot=True, fmt='d',
xticklabels=class_names[:20],
yticklabels=class_names[:20],
cmap='Blues', cbar=False)
plt.title('Top 20 Classes Confusion Matrix', pad=20, fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Predicted', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('Actual', fontsize=14)
plt.xticks(rotation=45, ha='right')
plt.yticks(rotation=0)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 使用示例
evaluate_model(model, test_generator, class_names)
# 从测试集中随机选择一些图像进行预测
import random
def show_predictions(num_samples=5):
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
for i in range(num_samples):
# 随机选择一个批次
batch_index = random.randint(0, len(test_generator)-1)
x_batch, y_batch = test_generator[batch_index]
# 随机选择图像
img_index = random.randint(0, BATCH_SIZE-1)
img = x_batch[img_index]
true_label = np.argmax(y_batch[img_index])
# 进行预测
pred = model.predict(np.expand_dims(img, axis=0))
pred_label = np.argmax(pred)
confidence = np.max(pred)
# 显示图像和预测结果
plt.subplot(1, num_samples, i+1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title(f"True: {class_names[true_label]}\nPred: {class_names[pred_label]}\nConf: {confidence:.2f}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
show_predictions()
# 将模型保存为Kaggle数据集
!mkdir -p output/fruit_classifier
!cp fruit_classifier.h5 output/fruit_classifier/
!cp best_model.h5 output/fruit_classifier/
# 也可以直接下载到本地
from IPython.display import FileLink
FileLink('fruit_classifier.h5')



















 491
491

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








