💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
钠核磁共振是一种重要的生物医学成像技术,可以用于研究生物体内部的结构和功能。为了模拟钠核磁共振序列,可以使用密度算符、超算符、利维尔演化和不可约张量分解等方法进行模拟研究。
首先,可以使用密度算符来描述钠核磁共振系统的量子态。密度算符是描述量子系统的一个重要工具,可以用来描述系统的量子态和动力学演化。通过密度算符,可以计算钠核磁共振系统在不同时间点的量子态演化情况。
其次,可以使用超算符来描述钠核磁共振系统的演化动力学。超算符是描述量子系统演化的数学工具,可以用来描述系统在外部干扰下的演化过程。通过超算符,可以模拟钠核磁共振系统在外部磁场和射频脉冲的作用下的演化情况。
利维尔演化是描述量子系统的时间演化的一种重要方法,可以用来模拟钠核磁共振系统在不同时间点的量子态演化情况。利维尔演化可以帮助研究人员了解钠核磁共振系统在外部干扰下的动力学行为。
最后,可以使用不可约张量分解来分解钠核磁共振系统的密度算符,从而得到系统的量子态信息。不可约张量分解是一种重要的量子信息处理方法,可以用来分解多体量子系统的密度算符,从而得到系统的量子态信息和量子相干性信息。
综合利用密度算符、超算符、利维尔演化和不可约张量分解等方法,可以对钠核磁共振系统进行全面的模拟研究,从而深入了解钠核磁共振技术的原理和应用。这对于优化钠核磁共振成像技术,提高成像质量和分辨率,具有重要的理论和实际意义。
使用密度算符演化模拟钠核磁共振是一种重要的研究方法,可以帮助我们更深入地了解钠核磁共振技术的原理和应用。在这个模拟中,我们可以利用密度算符、超算符、利维尔演化和不可约张量分解等方法,来模拟钠核磁共振系统的量子态演化和动力学行为。
这种模拟方法不仅适用于特定类型的组织,而且还可以同时适用于多种组织。我们可以选择化学位移的高斯分布和残余四极相互作用,以及化学交换的选项(仅限两种组织之间),从而更加贴合实际情况。这样的模拟可以帮助我们更好地理解不同组织中钠核磁共振的特性和行为。
此外,我们还可以根据需要设计任何射频脉冲序列,从而模拟不同的钠核磁共振序列。这将有助于我们研究钠核磁共振系统在不同脉冲序列下的响应和演化情况,为钠核磁共振成像技术的优化和改进提供重要的理论支持。
综上,使用密度算符、超算符、利维尔演化和不可约张量分解等方法模拟钠核磁共振序列,可以帮助我们更全面地了解钠核磁共振技术的原理和应用,为该技术的进一步发展提供重要的理论指导和实践支持。
📚2 运行结果
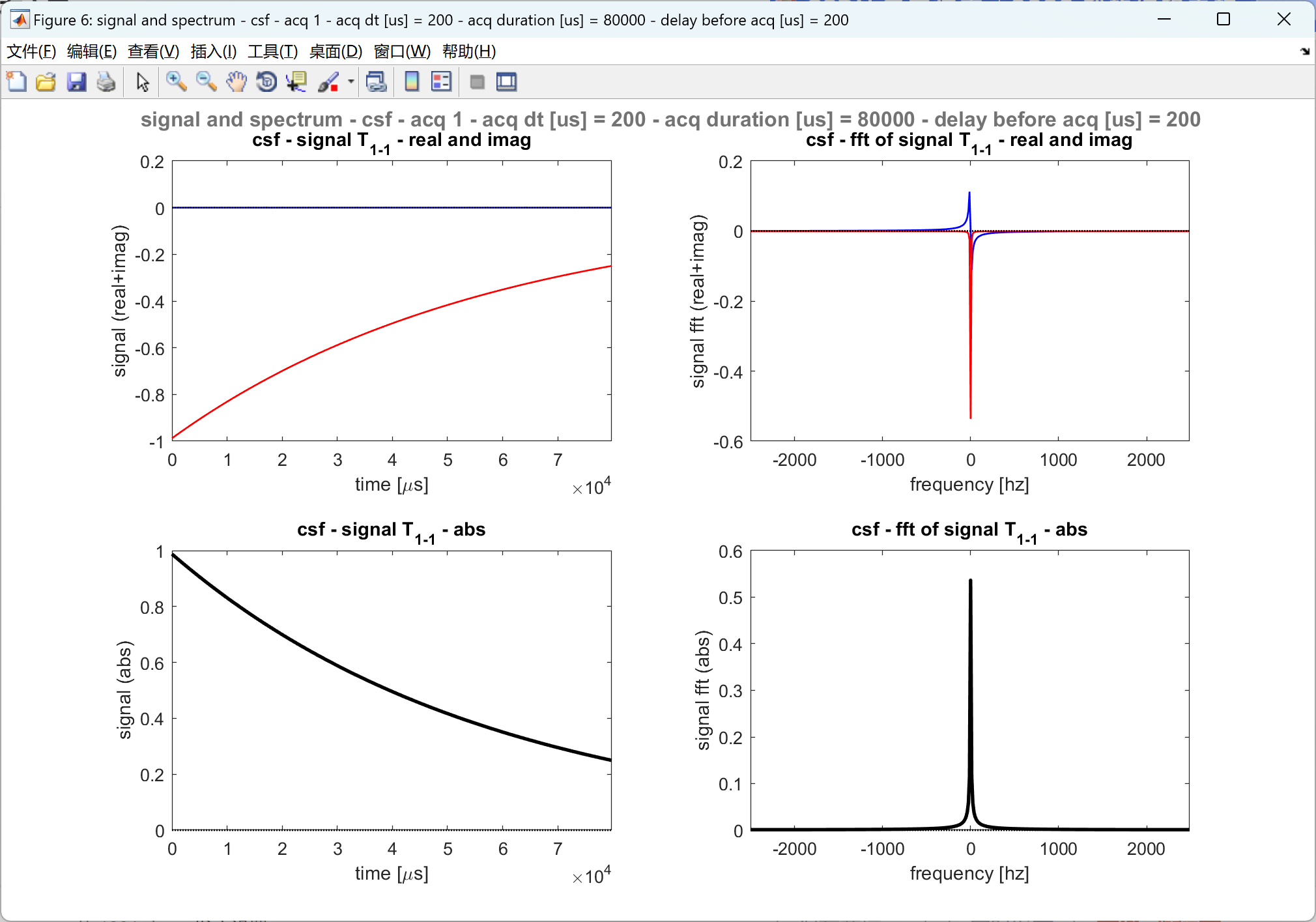
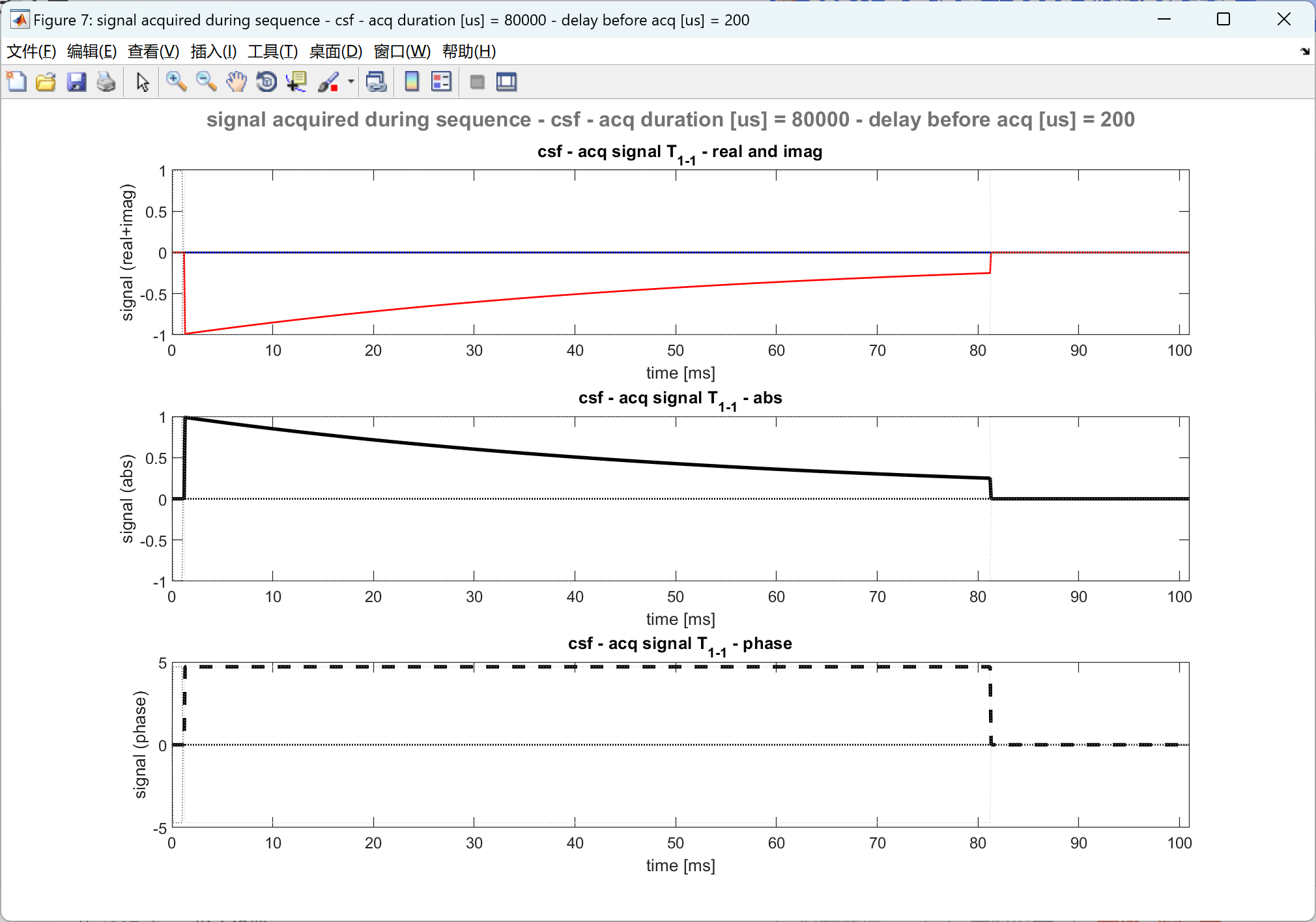
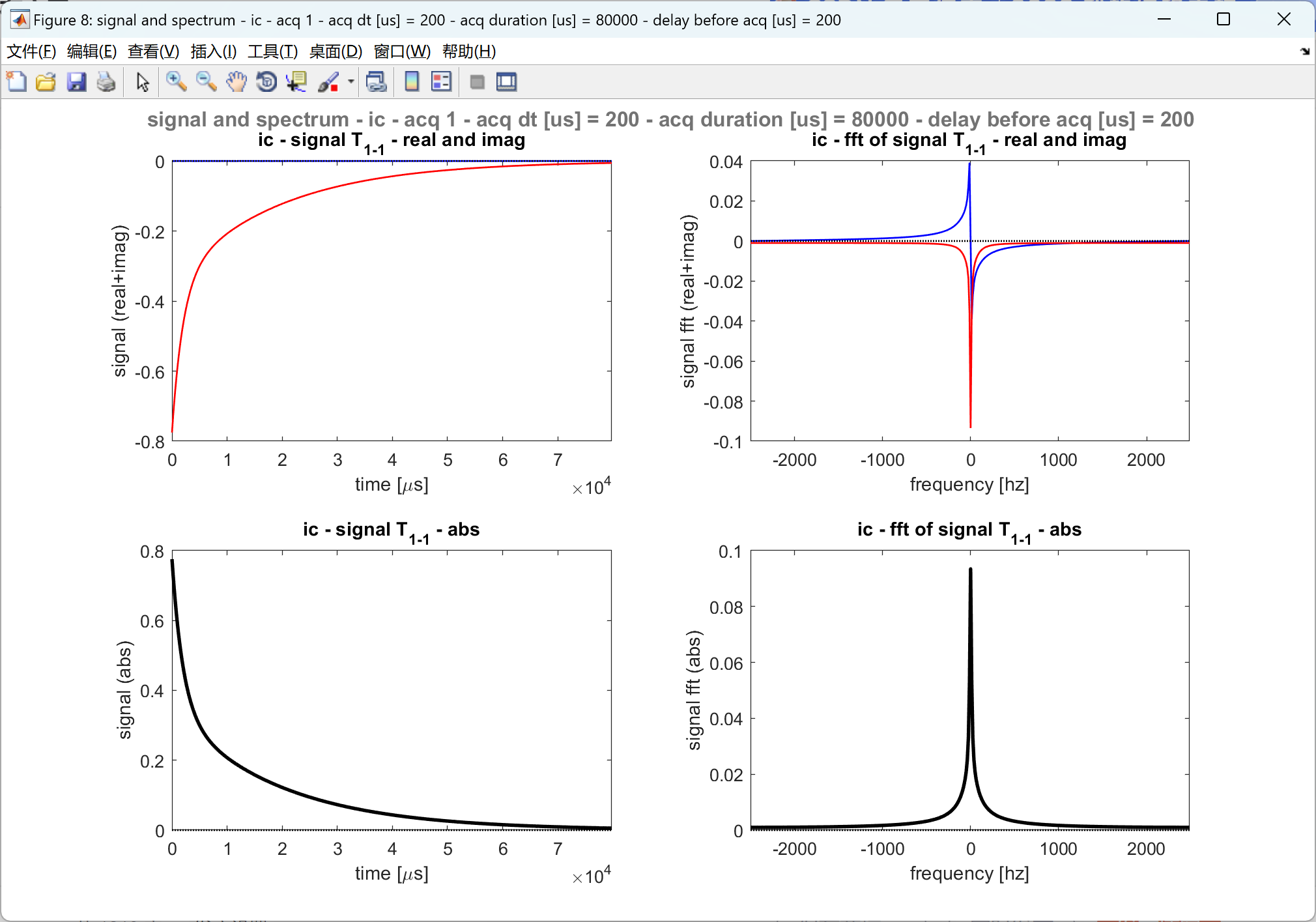
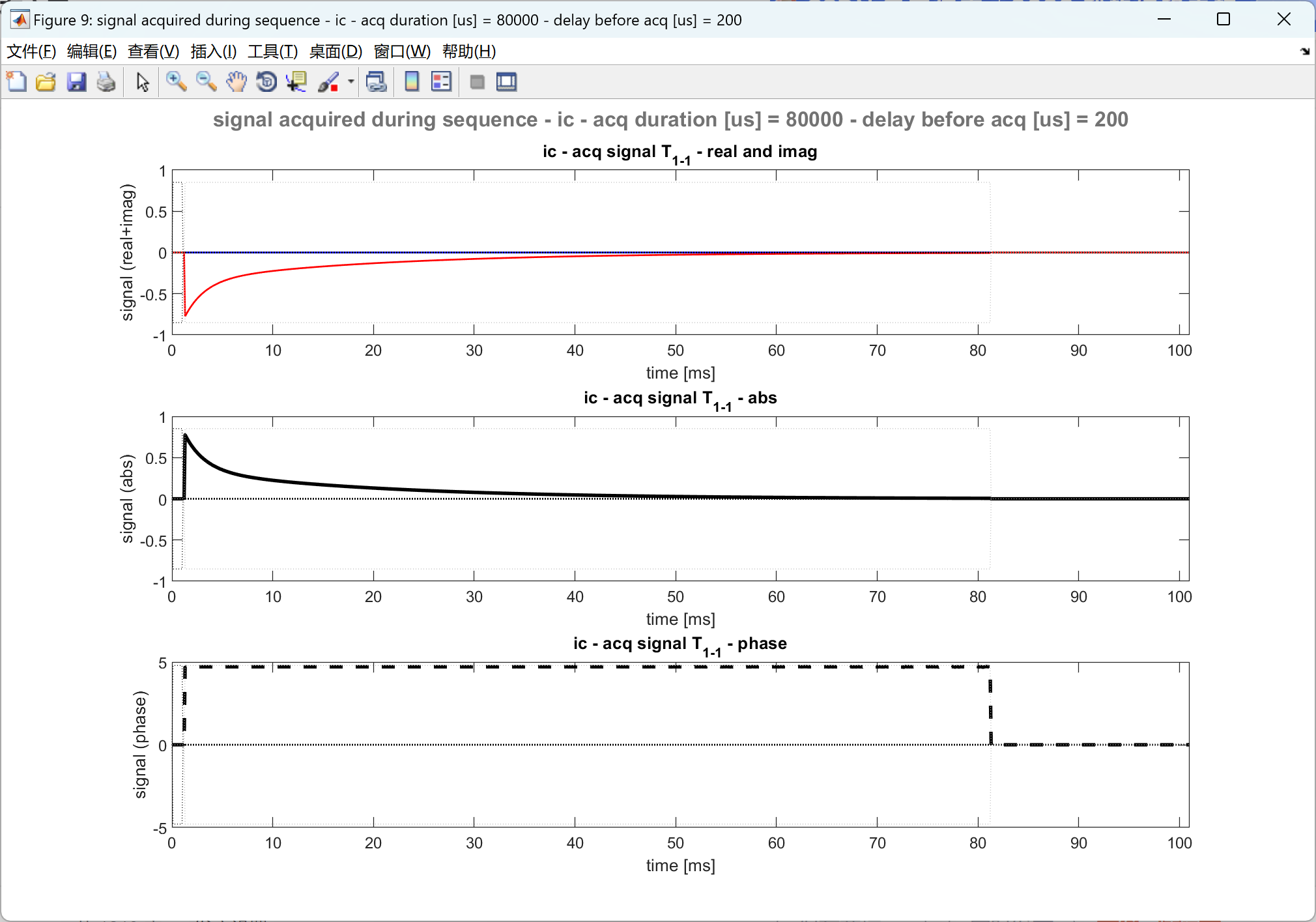
部分代码:
%% 1 - prepare simulation
% * prepare tissues to simulate and parameters of the simulation
% * prepare tissue relaxation times
% * prepare redfield relaxation matrix
% * prepare frequency offset (w)
% * prepare residual quadrupolar interaction (wq)
% * prepare superoperators for sodium spin 3/2
% * prepare rf pulse sequence parameters (number and types of pulses, delays, phases, ...)
% * prepare rf pulse sequence
% * functions used: 'prepare_[name]_0201'
disp(' prepare simulation...'); tic;
% 1.1 - prepare parameters for the simulation => you can change simulation parameters in this file (tissues, choice of sequence, dwell time, offset frequency, etc.)
[sim] = prepare_parameters_0201();
% 1.2 - prepare simulation
[sim] = prepare_simulation_0201(sim);
% 1.3 - prepare tissue relaxation times + optimal tau (for mqf) => you can change relaxation times in this file
[sim] = prepare_tissue_relaxation_times_0201(sim);
% 1.4 - prepare redfield relaxation superoperator
[sim] = prepare_redfield_relaxation_0201(sim);
% 1.5 - prepare frequency offset (chemical shift) -> variable w
[sim] = prepare_w_0201(sim);
% 1.6 - prepare residual quadrupolar interaction (rqi) -> variable wq
[sim] = prepare_wq_0201(sim);
% 1.7 - prepare superoperators Ix, Iy, Iz (for spin 3/2) and initial vector
[sim] = prepare_superoperator_0201(sim);
% 1.8 - prepare rf pulse sequence parameters (pulses and delays) => you can change specific sequence parameters in this file
[sim] = prepare_sequence_parameters_0201(sim);
% 1.9 - prepare rf pulse sequence
[sim] = prepare_sequence_0201(sim);
%% 2 - simulation of superoperator evolution
% * evolution of superoperators during the rf pulse sequence
% * decomposition in spherical tensors
% * functions used: 'simulate_[name]_0201' and 'calculate_[name]_0201' (within 'simulate_[name]_0201')
disp( ' run simulation...'); tic;
% 2.1 - superoperator evolution
[sim] = simulate_evolution_superoperator_0201(sim);
% 2.2 - spherical tensor decomposition
[sim] = simulate_spherical_tensor_decomposition_0201(sim);
disp([' timing [s] = ' num2str(toc)]);
%% 3 - data acquisition and spectra
% * acquire nmr signal and apply fft (as in a spectrometer)
% * functions used: 'acquire_[name]_0201'
disp( ' acquire signal...');
% 3.1 - acquire signal and apply fft (spectrum)
[sim] = acquire_signal_spectrum_0201(sim);
%% 4 - figures
% * plot w and wq distributions for each tissue
% * plot evolution spherical tensors for each tissue
% * plot evolution magnetization for each tissue
% * plot acquired signal and spectrum
% * plot rf pulse sequence
% * functions used: 'plot_[name]_0201'
disp( ' plot figures...');
% 4.1 - plot w and wq distributions for each tissue (individual figure for each tissue)
[sim] = plot_distributions_w_wq_0201(sim);
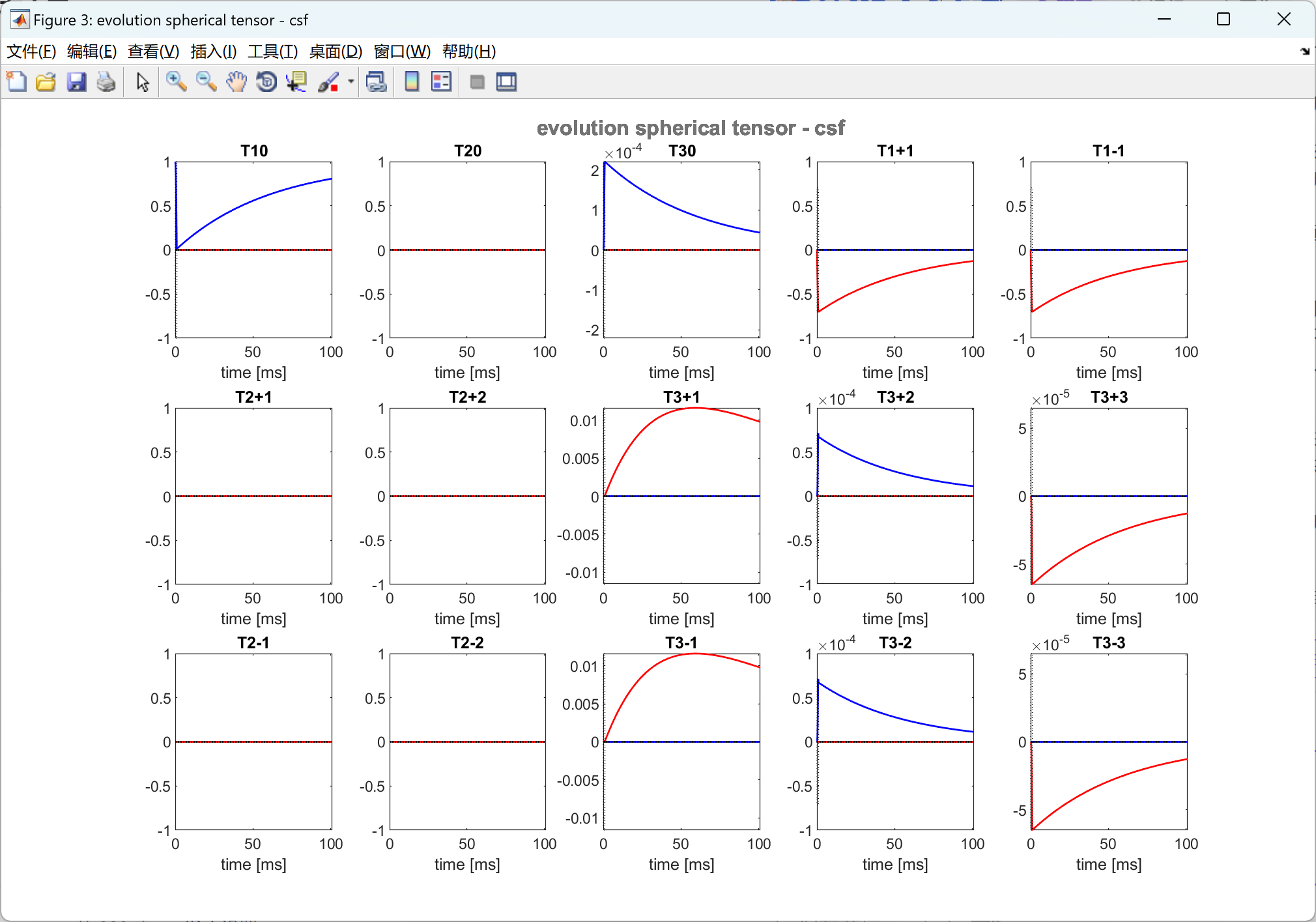
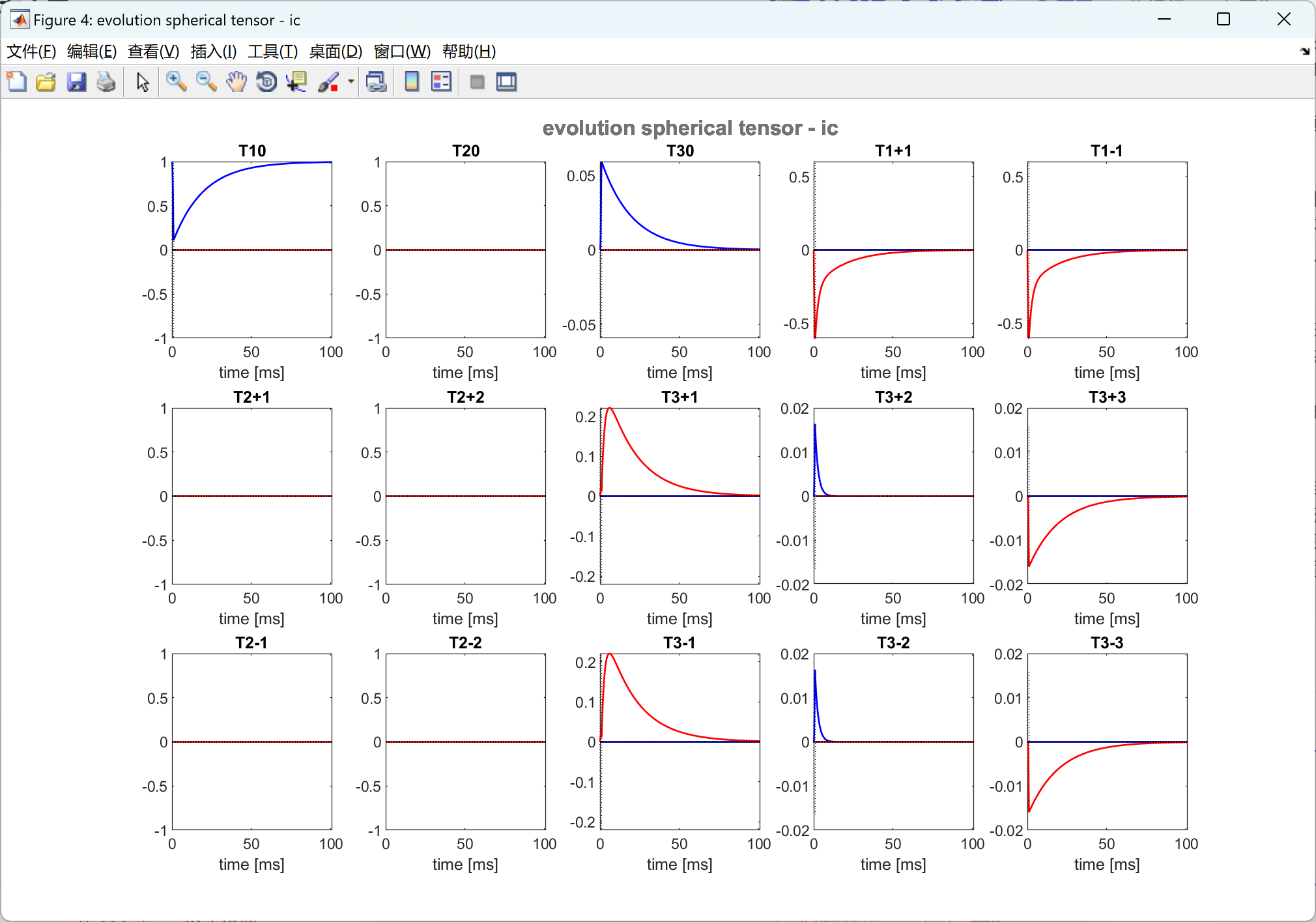
% 4.2 - plot evolution spherical tensors for each tissue (individual figure for each tissue)
[sim] = plot_evolution_spherical_tensor_0201(sim);
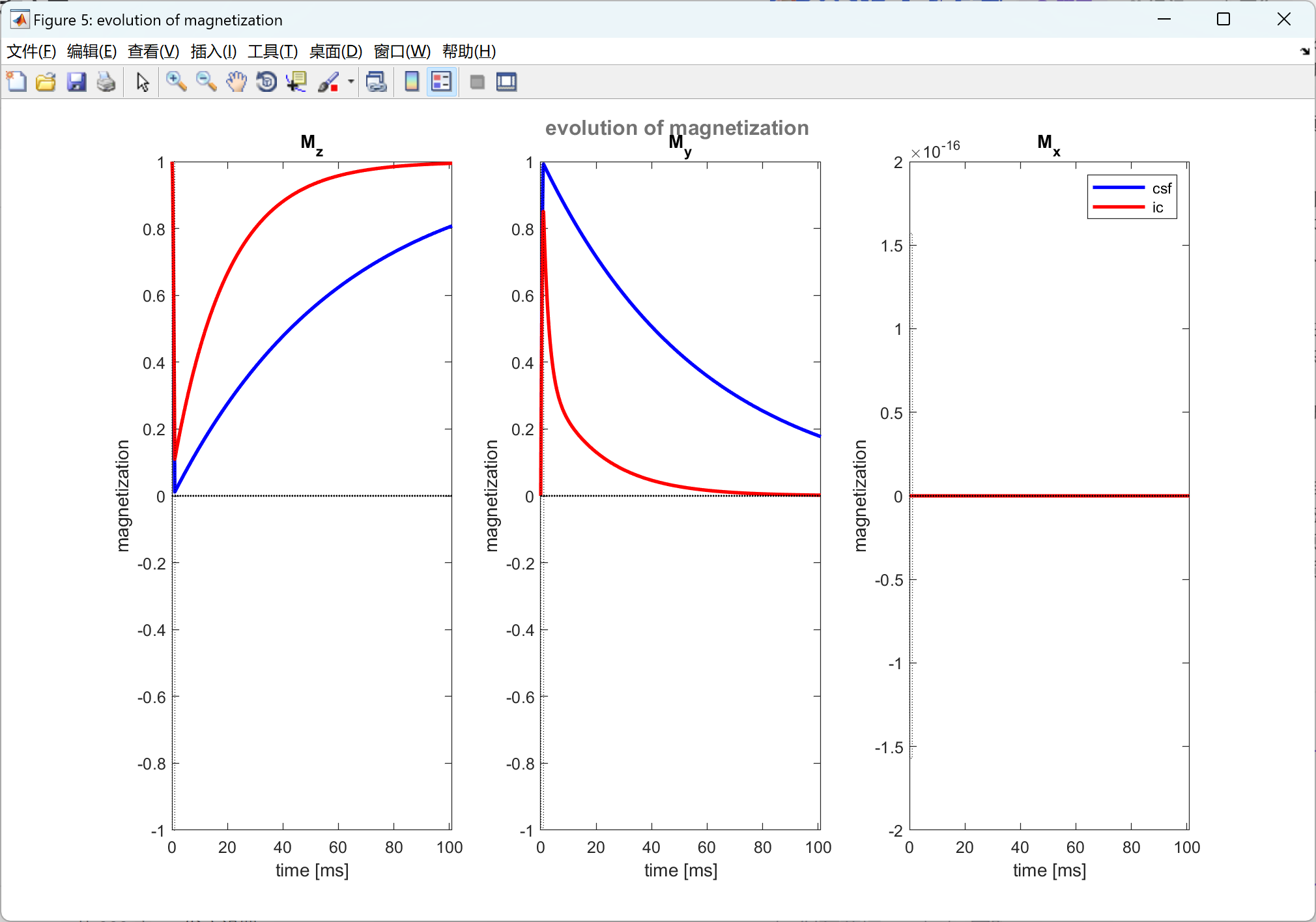
% 4.3 - plot evolution magnetization for all tissues (all tissues in same figure)
[sim] = plot_evolution_magnetization_0201(sim);
% 4.4 - plot acquired signal (T1-1) and spectrum (fft)
[sim] = plot_acquired_signal_spectrum_0201(sim);
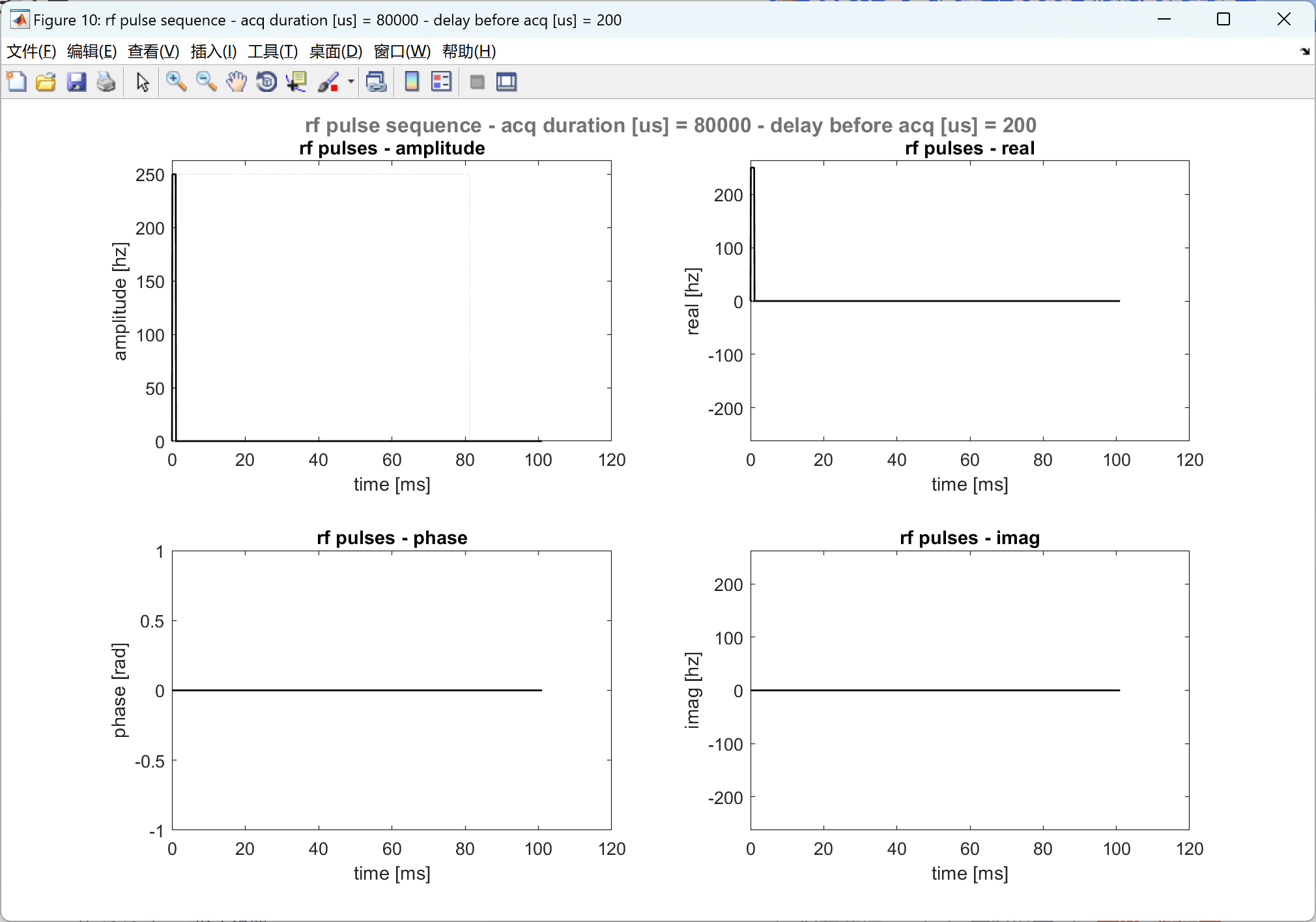
% 4.5 - plot rf pulse sequence
[sim] = plot_rf_pulse_sequence_0201(sim);
%% 5 - display simulation information
% * display information on the simulation parameters and results
% * functions used: 'display_[name]_0201'
disp( ' display simulation info...');
% 5.1 - display info
[sim] = display_simulation_info_0201(sim);
% 5.2 - the end
disp(' voila!'); disp(' ');
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]王展,方积年.高场核磁共振波谱在多糖结构研究中的应用[J].分析化学, 2000, 28(2):240-247.DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2000.02.026.
[2]王为民,赵刚,谷长春,et al.核磁共振岩屑分析技术的实验及应用研究[J].石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(1):56-59.DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.01.014.
[3]林东海,吴钦义.强偶合AB体系NMR实验的密度算符演化描述[J].波谱学杂志(3期):279-285[2024-01-18].DOI:10.1088/0256-307X/12/7/010.




 本文详细介绍了如何利用Matlab编程语言,通过密度算符、超算符、利维尔演化和不可约张量分解等技术,对钠核磁共振系统进行模拟研究,以理解其原理和优化成像技术。文章还展示了相关代码片段和实例,适用于生物医学领域的研究和实践。
本文详细介绍了如何利用Matlab编程语言,通过密度算符、超算符、利维尔演化和不可约张量分解等技术,对钠核磁共振系统进行模拟研究,以理解其原理和优化成像技术。文章还展示了相关代码片段和实例,适用于生物医学领域的研究和实践。
















 384
384

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








