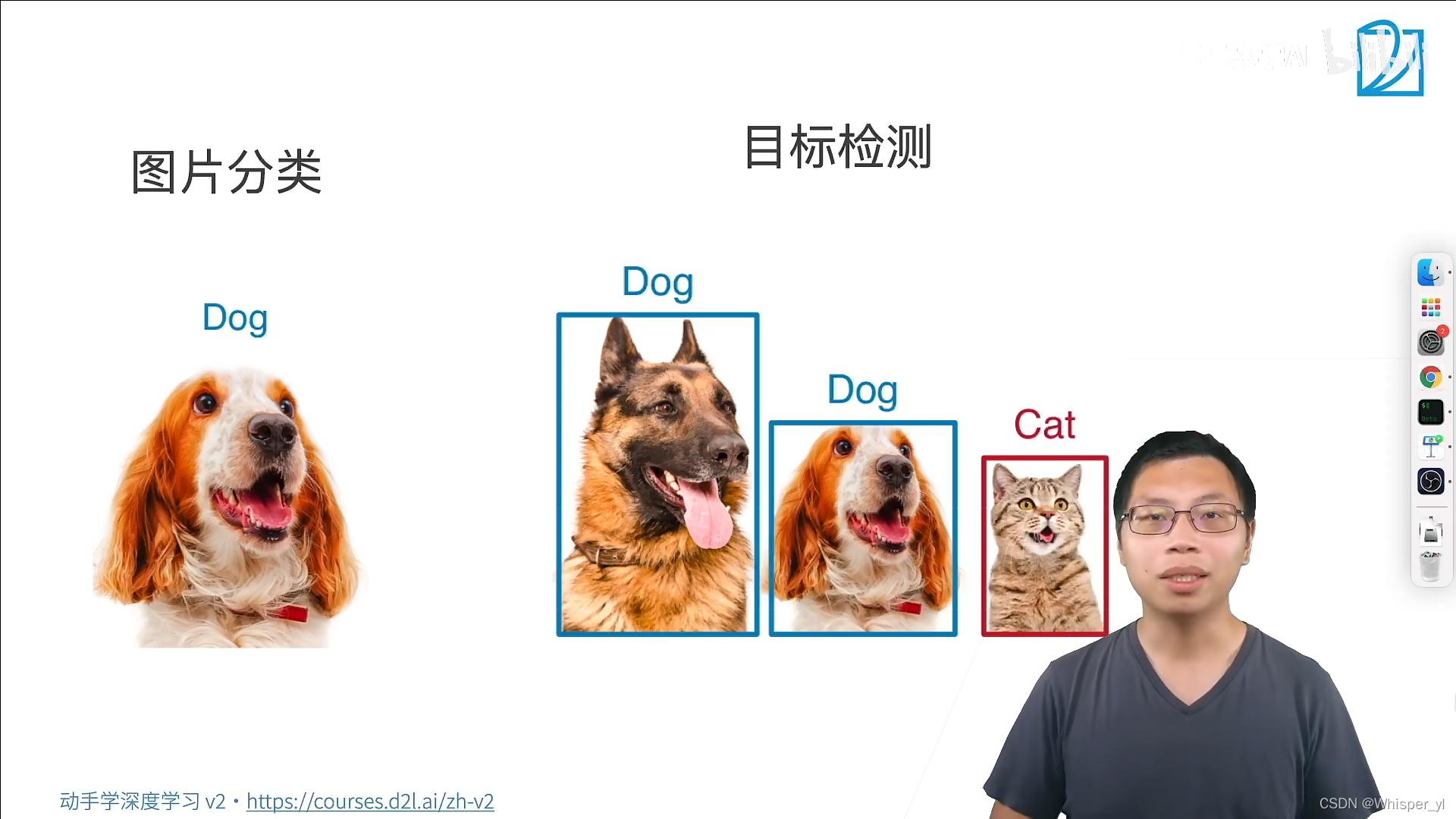
任务:识别我们所有感兴趣的物体,同时将每个物体的位置找出来


import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
d2l.set_figsize()
img = d2l.plt.imread('./img/catdog.jpg')
d2l.plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
# 定义在这两种表示之间进行转换的函数
def box_corner_to_center(boxes):
"""从(左上,右下)转换到(中间,宽度,高度)"""
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3]
cx = (x1 + x2) / 2
cy = (y1 + y2) / 2
w = x2 - x1
h = y2 - y1
boxes = torch.stack((cx, cy, w, h), axis=-1)
return boxes
def box_center_to_corner(boxes):
"""从(中间,宽度,高度)转换到(左上,右下)"""
cx, cy, w, h = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3]
x1 = cx - 0.5 * w
y1 = cy - 0.5 * h
x2 = cx + 0.5 * w
y2 = cy + 0.5 * h
boxes = torch.stack((x1, y1, x2, y2), axis=-1)
return boxes
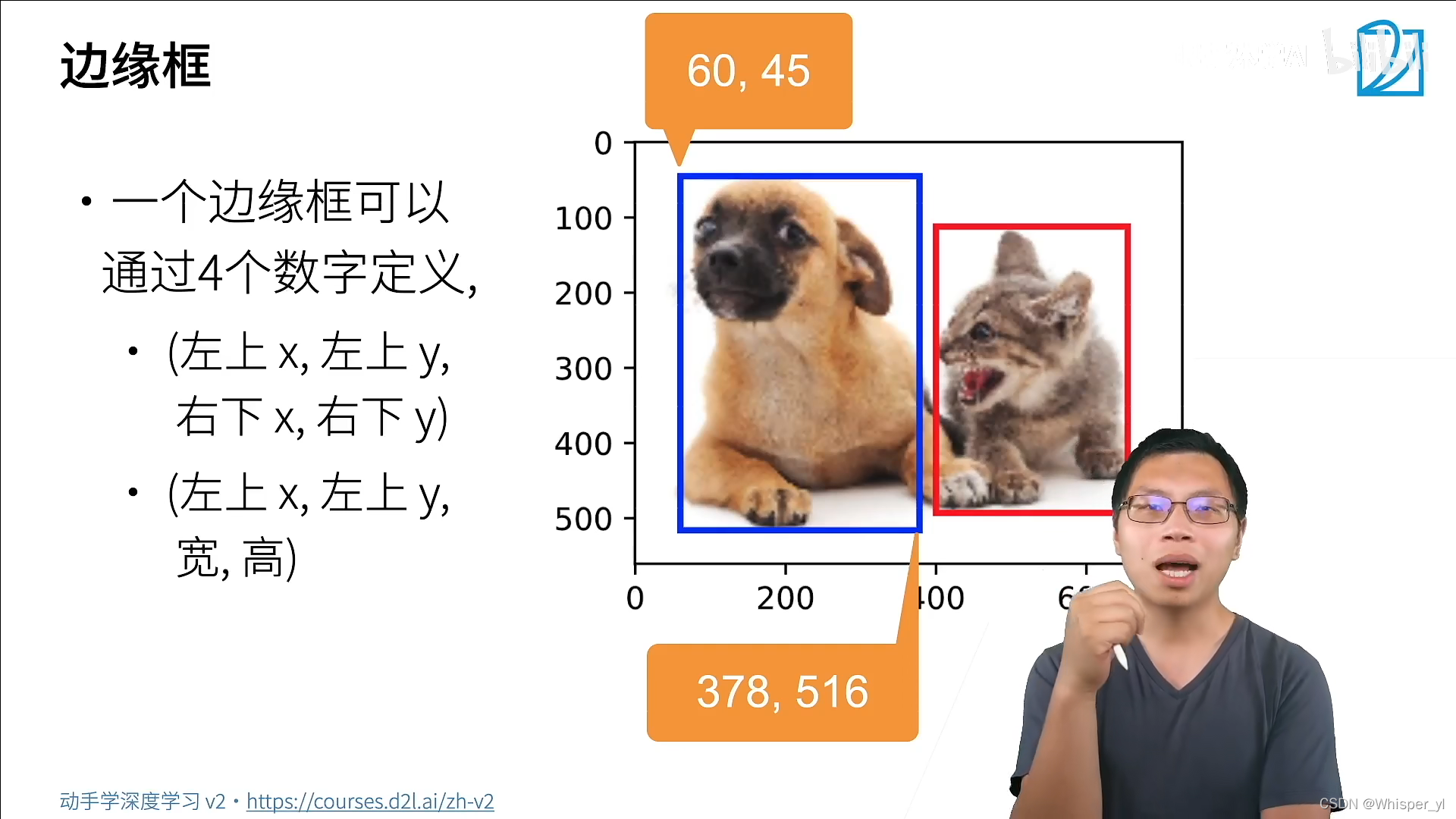
dog_bbox, cat_bbox = [60.0, 45.0, 378.0, 516.0], [400.0, 112.0, 655.0, 493.0]
boxes = torch.tensor((dog_bbox, cat_bbox))
print(box_center_to_corner(box_corner_to_center(boxes)) == boxes)
# 将边界框在图中画出
def bbox_to_rect(bbox, color):
# 将边界框(左上x,左上y,右下x,右下y)格式转换成matplotlib格式:
# ((左上x,左上y),宽,高)
return d2l.plt.Rectangle(
xy=(bbox[0], bbox[1]), width=bbox[2] - bbox[0], height=bbox[3] - bbox[1],
fill=False, edgecolor=color, linewidth=2)
fig = d2l.plt.imshow(img)
fig.axes.add_patch(bbox_to_rect(dog_bbox, 'blue'))
fig.axes.add_patch(bbox_to_rect(cat_bbox, 'red'))
plt.show()import os
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torchvision
from d2l import torch as d2l
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 下载数据集
d2l.DATA_HUB['banana-detection'] = (
d2l.DATA_URL + 'banana-detection.zip',
'5de26c8fce5ccdea9f91267273464dc968d20d72')
# 读取香蕉检测数据集
def read_data_bananas(is_train=True):
"""读取香蕉检测数据集中的图像和标签"""
data_dir = d2l.download_extract('banana-detection')
csv_fname = os.path.join(data_dir, 'bananas_train' if is_train
else 'bananas_val', 'label.csv')
csv_data = pd.read_csv(csv_fname)
csv_data = csv_data.set_index('img_name')
images, targets = [], []
for img_name, target in csv_data.iterrows():
# read_image把图片读到内存里面
images.append(torchvision.io.read_image(
os.path.join(data_dir, 'bananas_train' if is_train else
'bananas_val', 'images', f'{img_name}')))
# 这里的target包含(类别,左上角x,左上角y,右下角x,右下角y),
# 其中所有图像都具有相同的香蕉类(索引为0)
targets.append(list(target))
return images, torch.tensor(targets).unsqueeze(1) / 256
# 创建一个自定义Dataset实例
class BananasDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
"""一个用于加载香蕉检测数据集的自定义数据集"""
# __init__把所有的数据读进来
def __init__(self, is_train):
self.features, self.labels = read_data_bananas(is_train)
print('read ' + str(len(self




 这篇博客介绍了目标检测中的关键概念,包括边界框、锚框及其转换。首先,展示了如何在图像中定位物体的边界框,并通过函数实现不同表示之间的转换。接着,详细阐述了锚框的概念,它是算法预测真实边界框的基础。博客还提供了自定义数据集的读取和处理方法,以及如何在图像上绘制锚框。最后,通过代码演示了锚框生成、分配、标注和预测的过程,包括IoU计算、非极大值抑制等步骤,展示了目标检测算法的工作原理。
这篇博客介绍了目标检测中的关键概念,包括边界框、锚框及其转换。首先,展示了如何在图像中定位物体的边界框,并通过函数实现不同表示之间的转换。接着,详细阐述了锚框的概念,它是算法预测真实边界框的基础。博客还提供了自定义数据集的读取和处理方法,以及如何在图像上绘制锚框。最后,通过代码演示了锚框生成、分配、标注和预测的过程,包括IoU计算、非极大值抑制等步骤,展示了目标检测算法的工作原理。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 3061
3061

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








