本文详细介绍AI智能体(Agentic AI)的系统架构与核心设计模式,包括单智能体与多智能体系统,以及反思、工具使用、ReAct、规划和多智能体协作五大模式。通过LangChain、LlamaIndex和AutoGen等主流框架的应用案例,展示了如何构建自主AI系统,并探讨了多智能体系统中的并行、顺序、循环等细分模式,为开发者提供从理论到实践的完整指导。
AI 智能体系统架构与设计模式
作者: [Anil Jain | AI / ML 架构师 | 数据架构师]
原文发布日期: 2025年4月9日
原文:https://medium.com/@anil.jain.baba/agentic-ai-architectures-and-design-patterns-288ac589179a
1. AI 智能体 (Agentic AI) 简介
AI 智能体 (Agentic AI) 指的是那些能够自主行动、在很少需要人类协助的情况下做出决策和执行任务的 AI 系统。你可以把它想象成一个智能助理,能独立完成规划旅行、预订航班,并根据实时信息调整计划。截至2025年4月,这种技术在客户服务(如聊天机器人处理问询)和供应链管理(如优化物流)等领域正变得越来越普遍。
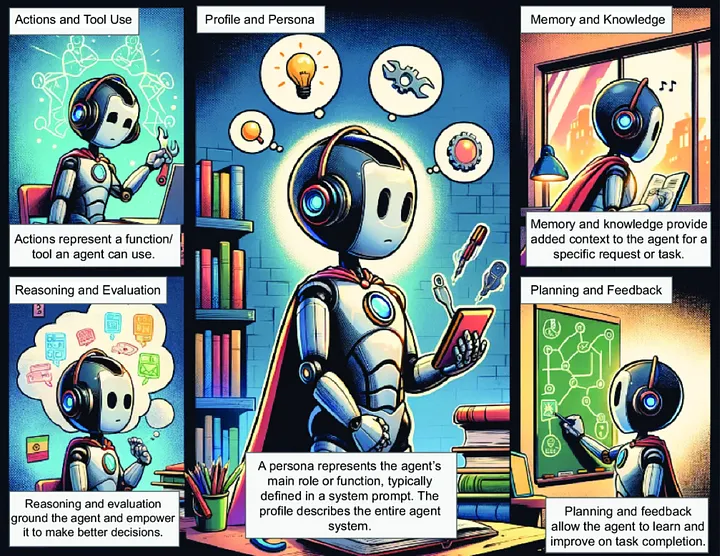
1.1 核心要点
- AI 智能体涉及自主决策的 AI 系统,只需极少的人工干预,正在改变客户服务和供应链管理等行业。
- LangChain、LlamaIndex 和 AutoGen 等框架似乎是构建这些系统的关键工具,它们支持单智能体和多智能体设置。
- 有证据表明,AI 智能体能够提高生产力,但也存在挑战,如多智能体系统中的协调问题和潜在的偏见,这些问题仍在讨论中。
- 一个值得注意的细节是,它集成了实时数据处理能力,从而增强了在金融交易等动态环境中的决策能力。
- 研究表明,AI 智能体的设计模式有助于构建用于复杂任务的自主 AI 系统,其中五个关键模式是:反思(Reflection)、工具使用(Tool Use)、ReAct、规划(Planning)和多智能体协作(Multi-Agent Collaboration)。
- LangChain 和 AutoGen 等框架很可能支持这些模式:LangChain 适用于反思、工具使用和 ReAct;AutoGen 则适用于规划和多智能体协作。
- 证据倾向于表明这些模式能提升 AI 性能,但多智能体系统中的协调等挑战仍在讨论中。
- 一个令人意外的细节是,ReAct 模式通过生成类似人类解决任务的轨迹,增强了系统的可解释性,从而提高了人们对 AI 系统的信任。
1.2 工具与框架
为了构建这些系统,开发者通常使用以下框架:
- LangChain: 非常适合创建能够使用网络搜索等工具的聊天机器人。
- LlamaIndex: 帮助将 AI 与公司内部数据连接,以做出更智能的决策。
- AutoGen: 允许多个 AI 智能体协同工作,就像一个团队解决复杂问题。
1.3 单智能体 vs. 多智能体系统
- 单智能体系统 (Single Agent): 一个 AI 完成所有工作,比如回答问题的聊天机器人。它更简单,但可能难以处理复杂任务。
- 多智能体系统 (Multi-Agent): 多个 AI 协同工作,就像一个团队,其中一个处理物流,另一个处理客户服务。它更强大,但协调起来更困难。
1.4 多智能体系统中的设计模式
多智能体部署包含以下几种模式:
- Parallel(并行模式):智能体同时处理不同任务模块,例如同时处理文本和图像数据。
- Sequential(顺序模式):智能体按顺序执行任务,例如先清理数据、再分析数据。
- Loop(循环模式):某个智能体重复执行一项任务,直到目标达成,例如不断优化某个解决方案。
- Router(路由模式):由一个智能体将任务分配给其他智能体,例如分配客户咨询需求。
- Aggregator(聚合模式):收集并整合多个智能体的结果,例如合并多个来源的搜索结果。
- Network(网络模式):智能体以网络形式连接,共享信息。
- Hierarchical(层级模式):智能体分为不同层级,类似 “高管给经理下达目标” 的结构。
这些模式为智能体的协同提供了结构化方案,文中还包含使用 AutoGen 等工具实现这些模式的案例。
2. 智能体人工智能系统的详细分析 / 描述
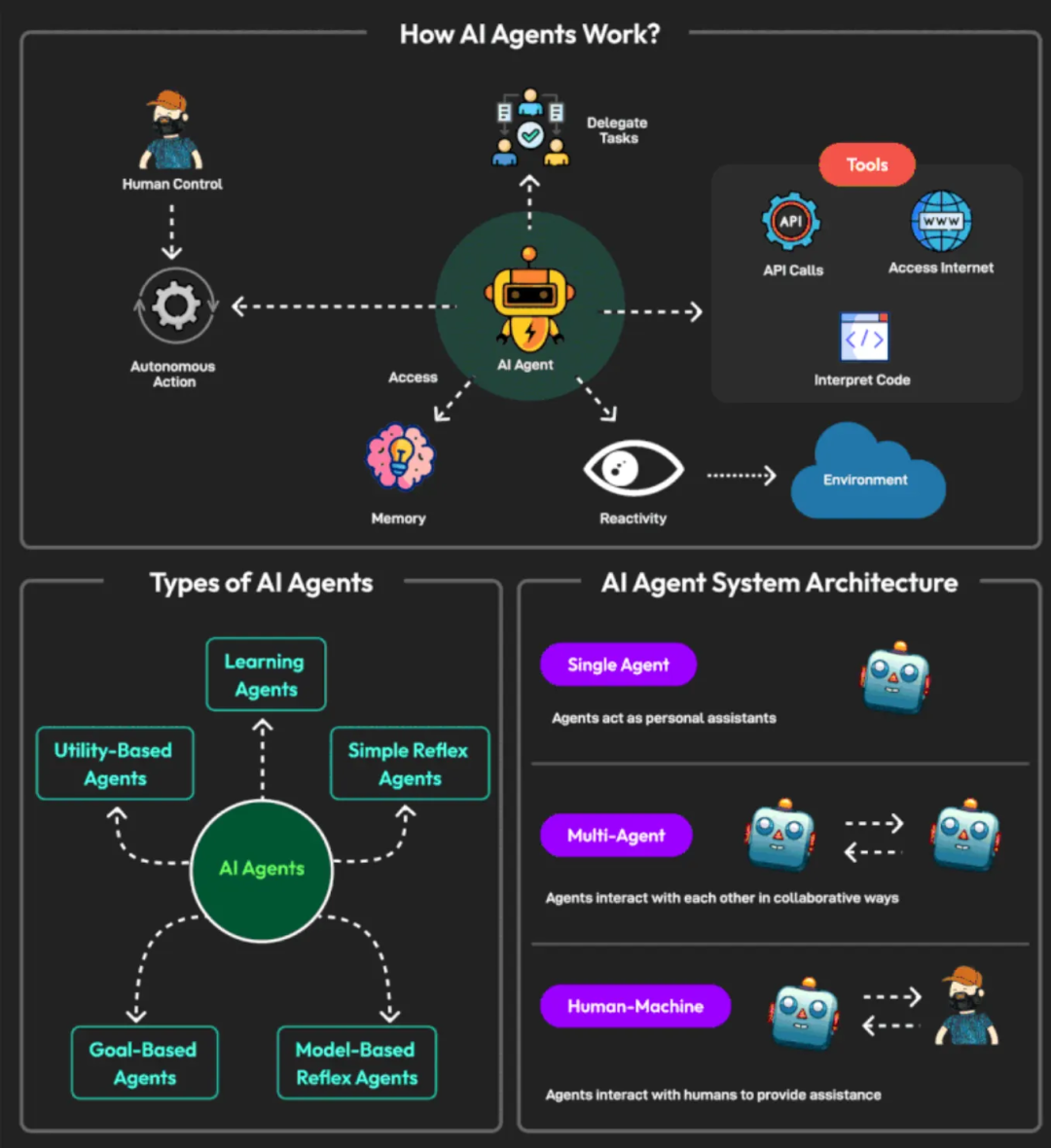
本节全面探讨了智能体人工智能,涵盖了查询中要求的所有方面,包括基础知识、组件、单智能体与多智能体架构以及设计模式。该分析基于最新研究和实际应用,反映了截至 2025 年 4 月 8 日该领域的状况。
2.1 智能体架构基础
最新研究将智能体人工智能定义为具有自主行动能力的人工智能系统,能实时适应以解决多步骤问题,且只需极少的人类监督。例如,《智能体人工智能架构:深入探讨》(Agentic AI Architecture: A Deep Dive[1])强调了它在改变人机协作方面的潜力,如人工智能驱动的旅行规划器和供应链优化器。这些系统的架构是分层的,通常包括用于数据收集的输入层、用于任务管理的智能体编排层,以及用于规划、执行和自我改进的专用智能体,正如《智能体人工智能架构:下一代人工智能解决方案的蓝图》中所指出的。
关键框架包括:
- LangChain[2]: 于2022年10月推出,它促进了大型语言模型(LLM)与工具的集成,支持聊天机器人和文档分析等应用。据维基百科[3]介绍,它以其模块化的工作流和提示管理而闻名,已有超过100万开发者使用。
- LlamaIndex[4]: 一个用于在企业数据之上构建 LLM 驱动智能体的开源框架。它支持超过160种数据格式,并因其强大的 RAG(检索增强生成)能力而备受赞誉。根据其 GitHub 仓库[5],它拥有超过300个集成包,在数据集成方面具有极高的灵活性。
- AutoGen[6]: 由微软开发,专注于多智能体工作流。它提供分层设计,包括用于消息传递的核心 API 和用于快速原型设计的 AgentChat API。它以处理复杂对话的能力而著称,例如用于解决任务的群聊,详见其示例[7]。
这些框架通过为感知、决策和行动提供抽象,并结合向量存储(如 Pinecone、Chroma)和 LLM(如 OpenAI、LLaMA)等工具,使开发者能够构建 AI 智能体系统。
2.2 AI 智能体的组成部分
AI 智能体由几个关键部分组成,每个部分对实现自主性都至关重要:
2.2.1 感知 (Perception)
涉及通过自然语言处理或数据摄取来感知环境。例如,LlamaIndex 使用数据加载器从 API、PDF 和 SQL 数据库中摄取数据。参考 LlamaIndex 文档[8]。
LangChain 示例代码:
from langchain.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun
search = DuckDuckGoSearchRun()
result = search.run("What is the weather like today?")
LlamaIndex 示例代码:
from llama_index import SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader('data').load_data()
2.2.2 决策 (Decision-Making)
使用 LLM 作为推理引擎来规划行动。如 LangChain 文档[9] 所示,其智能体根据工具描述来决定使用哪个工具。而 AutoGen 的智能体则通过对话进行推理,详见。
2.2.3 行动 (Action)
执行决策,例如调用 API 或生成代码。LangChain 中的工具包括用于网页搜索的 serpapi,而 AutoGen 支持在 Docker 容器中执行代码,如 AutoGen 文档[10] 所述。
示例代码:
from langchain.tools import AIPluginTool
email_tool = AIPluginTool.from_plugin_url("[invalid url, do not cite]")
tools = [email_tool]
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent="zero-shot-react-description", verbose=True)
agent.run("Send an email to john@example.com with the subject 'Hello' and body 'How are you?'")
2.2.4 记忆 (Memory)
对于维持上下文至关重要。LangChain 提供 ConversationBufferMemory,而 LlamaIndex 使用向量存储实现长期记忆,详见。
LangChain 示例代码:
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory()
2.2.5 通信 (Communication)
涉及与其他智能体或人类的互动。AutoGen 的群聊功能促进了这一点,而 LangChain 支持智能体之间的工具调用,详见LangChain 文档[11]。
AutoGen 示例代码:
import autogen
groupchat = autogen.GroupChat(agents=[user_proxy, assistant], messages=[], max_round=5)
3 单智能体 vs. 多智能体架构
- 单智能体架构: 涉及一个智能体独立执行任务,适用于客户支持聊天机器人等较简单的任务。LangChain 主要为此设计,例如天气查询智能体。其优点是简单且开销较低,但对于复杂任务能力有限。
- 多智能体架构: 涉及多个智能体协作,非常适合复杂的工作流。AutoGen 在这方面表现出色,例如用于数据可视化的群聊。其优点是多样性和鲁棒性,但挑战在于协调的复杂性,正如 DeepLearning.AI 的文章[12]所指出的。LlamaIndex 也通过其
llama-agents框架支持多智能体系统。
4 AI 智能体系统的核心设计模式
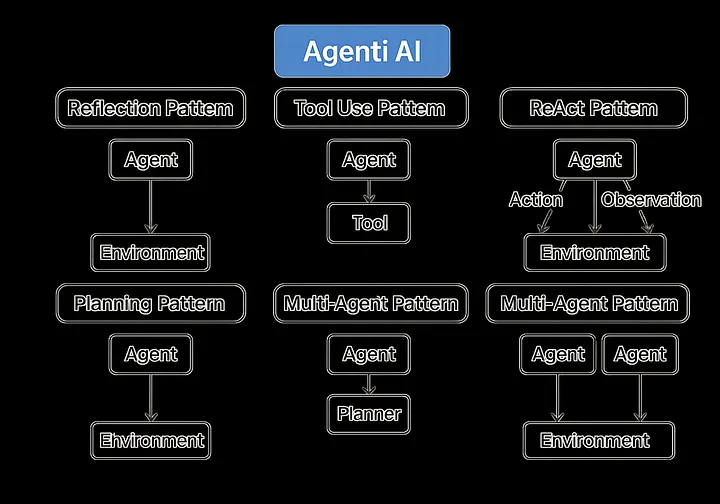
本节探讨五个关键的设计模式:反思(Reflection)、工具使用(Tool Use)、ReAct、规划(Planning)和多智能体协作(Multi-Agent Collaboration)。对于每一种模式,我们将解释它是什么、为什么重要,并展示如何使用 LangChain 和 AutoGen 等工具,并附上示例代码。
4.1 反思模式 (Reflection Pattern)
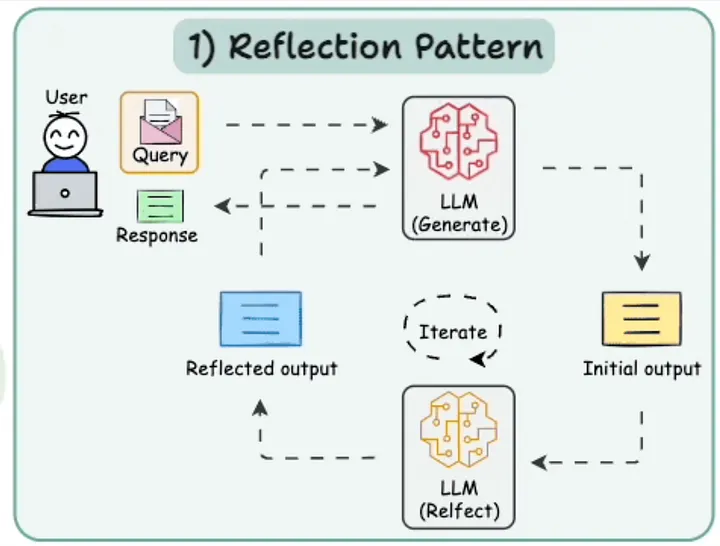
它是什么: 反思模式让 AI 能够审视自己的工作,发现错误并进行改进。就像 AI 在提交论文前检查其中的错误一样。
为何重要: 这有助于 AI 随着时间的推移不断进步,减少在编写代码或创建内容等任务中的错误,这对可靠性至关重要。
工具与框架: LangChain,特别是其 LangGraph 组件,非常适合此模式。LangGraph 允许 AI 循环审视和优化其工作。
示例代码:
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# Set up generator to write an essay
generator_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are an essay assistant tasked with writing excellent 5-paragraph essays."),
("human", "{input}"),
])
generator = generator_prompt | ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo") | AIMessage.log()
# Set up reflector to grade and give feedback
reflect_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are an essay grader tasked with grading essays and providing feedback."),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
("human", "Grade the following essay and provide feedback: {input}"),
])
reflector = reflect_prompt | ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo") | AIMessage.log()
# Combine them in a cycle, stopping after 3 iterations
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableBranch
defshould_reflect(input):
return len(input["history"]) < 3
graph = RunnableBranch(
(should_reflect, generator | reflector),
RunnablePassthrough(),
)
# Run it for an essay on AI ethics
input_text = "Write a 5-paragraph essay on 'The Importance of AI Ethics'."
result = graph.invoke({"input": input_text, "history": []})
print(result)
这段代码展示了 AI 撰写一篇文章,然后检查并改进它,最多重复三次,每一轮都让文章质量变得更好。
4.2 工具使用模式 (Tool Use Pattern)
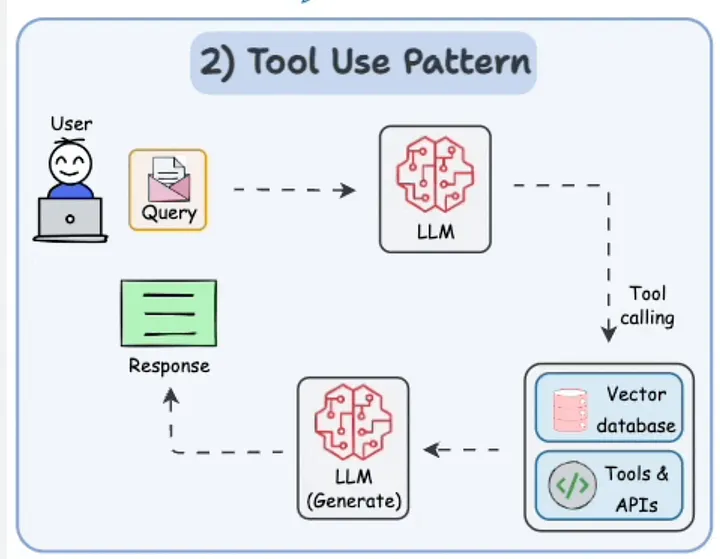
它是什么: 工具使用模式允许 AI 使用外部工具,如网络搜索或 API,来获取信息或执行其自身无法完成的任务。
为何重要: 这使得 AI 更加多才多艺,能够处理现实世界的任务,如在线查找事实或进行数学计算,而这些是仅凭其记忆无法完成的。
工具与框架: LangChain 在这方面非常出色,提供了像 DuckDuckGoSearchRun 这样的网页搜索工具,可以轻松扩展 AI 的能力。
示例代码:
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, load_tools
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
# Set up the AI model
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
# Load tools for web search and math
tools = load_tools(["serpapi", "llm-math"], llm=llm)
# Create an agent that uses these tools
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent="zero-shot-react-description", verbose=True)
# Ask a complex question
result = agent.run("Who is Olivia Wilde's boyfriend? What is his current age raised to the 0.23 power?")
print(result)
在这里,AI 搜索网页以找到 Olivia Wilde 的男友,并使用数学工具计算他年龄的0.23次方,展示了工具如何扩展其能力。
4.3 ReAct 模式 (Reason and Act)
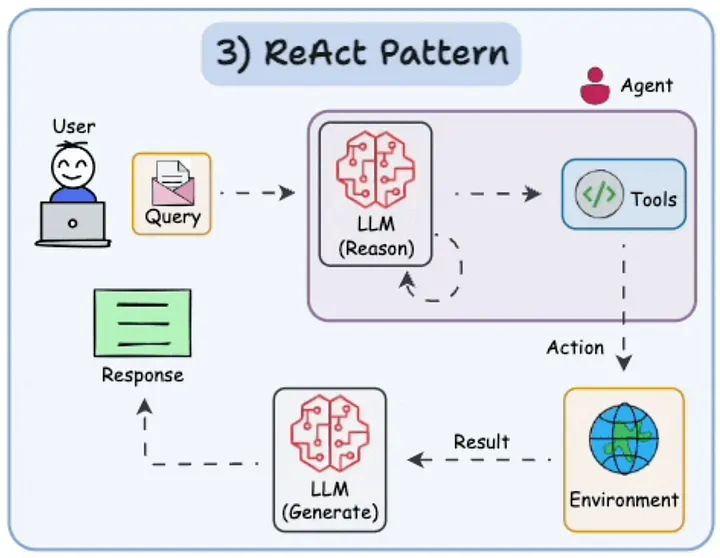
它是什么: ReAct 模式,即“推理与行动”(Reason and Act),意味着 AI 会一步步地思考问题,然后根据思考结果采取行动,比如使用工具。这就像是同时进行规划和执行。
为何重要: 这有助于 AI 通过结合思考和行动来解决棘手的问题,使其更具动态性,能够处理需要两者结合的任务,例如回答多部分问题。
工具与框架: LangChain 通过其 “zero-shot-react-description” 智能体支持此模式,该智能体在一个循环中进行推理和使用工具,非常适合 ReAct。
示例代码:
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, load_tools
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
# Set up the AI model
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
# Load tools for web search and math
tools = load_tools(["serpapi", "llm-math"], llm=llm)
# Create a ReAct agent
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent="zero-shot-react-description", verbose=True)
# Ask a question needing both reasoning and action
result = agent.run("What is the current population of France? How does it compare to Germany?")
print(result)
AI 推理出需要做什么(查找人口并进行比较),然后使用网络搜索获取数字,并通过推理完成比较,展示了 ReAct 模式的实际应用。
4.4 规划模式 (Planning Pattern)
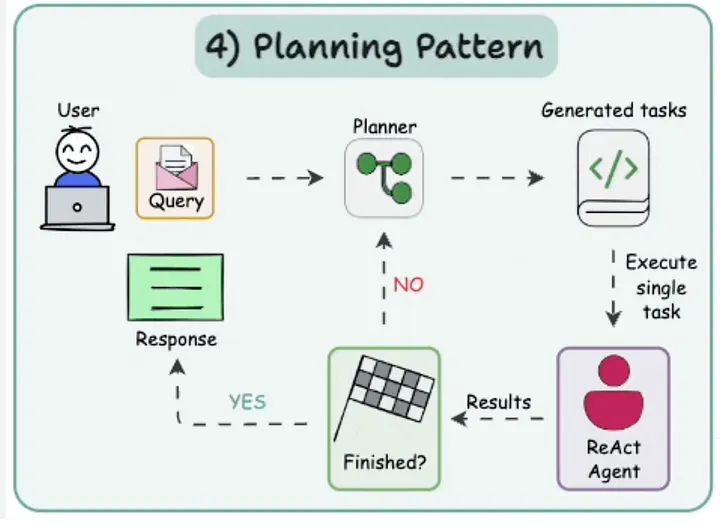
它是什么: 规划模式意味着 AI 将大任务分解为更小的步骤,并制定一个计划来处理它们,就像在开始项目前先列出大纲一样。
为何重要: 这对于复杂任务至关重要,确保 AI 将工作组织成可管理的部分,使其在处理长期目标(如规划旅行或诊断病人)时更有效率。
工具与框架: AutoGen 非常适合此模式,其多智能体系统功能允许一个规划者智能体协调子任务,例如在医疗诊断中。
示例代码:
import autogen
# Define agents for each part of the task
symptom_agent = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Symptom_Agent", ...)
history_agent = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="History_Agent", ...)
analysis_agent = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Analysis_Agent", ...)
recommendation_agent = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Recommendation_Agent", ...)
# Define planner to coordinate
planner = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Planner", ...)
# Set up user proxy to start the chat
user_proxy = autogen.UserProxyAgent(name="User_Proxy", ...)
# Create a group chat with all agents
groupchat = autogen.GroupChat(agents=[user_proxy, planner, symptom_agent, history_agent, analysis_agent, recommendation_agent], ...)
# Run the chat, starting with a diagnosis task
manager = autogen.GroupChatManager(groupchat, llm_config=...)
user_proxy.initiate_chat(manager, message="Diagnose a patient with symptoms X, Y, Z")
在这里,规划者智能体勾勒出收集症状和分析数据等步骤,每个智能体处理其各自的部分,展示了规划如何组织复杂任务。
4.5 多智能体协作模式 (Multi-Agent Collaboration Pattern)
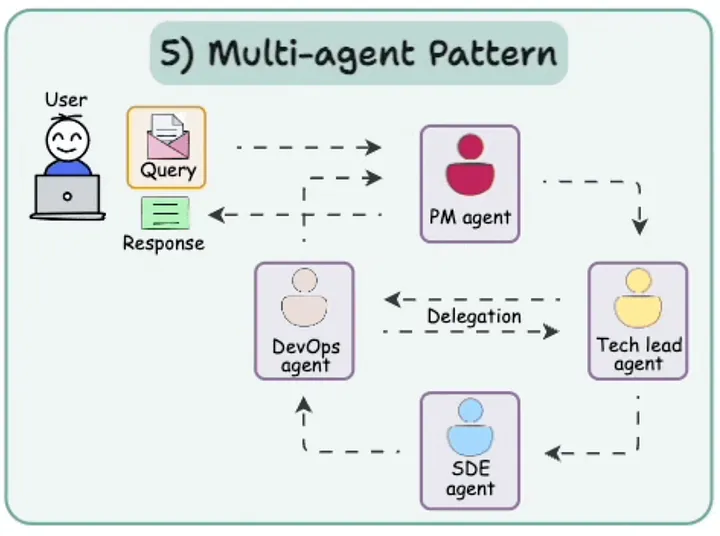
它是什么: 多智能体协作模式意味着多个 AI 智能体协同工作,每个智能体都有特定的角色,就像一个团队,其中一个负责规划,一个负责编码,另一个负责检查工作。
为何重要: 这对于大型项目非常有用,允许智能体专门化并进行协作,使系统在处理软件开发或客户支持等任务时更加强大。
工具与框架: AutoGen 专为此设计,其群聊功能允许智能体进行沟通和委派任务,非常适合团队式工作流。
示例代码:
import autogen
# Define agents with different roles
planner = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Planner", ...)
coder = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Coder", ...)
critic = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Critic", ...)
# Set up user proxy to interact
user_proxy = autogen.UserProxyAgent(name="User_Proxy", ...)
# Create a group chat for collaboration
groupchat = autogen.GroupChat(agents=[user_proxy, planner, coder, critic], ...)
# Run the chat, asking for a coding task
manager = autogen.GroupChatManager(groupchat, llm_config=...)
user_proxy.initiate_chat(manager, message="Write a function to calculate Fibonacci sequence")
5. 多智能体系统的细分设计模式
多智能体系统还有更细分的模式:
5.1 并行多智能体 (Parallel Multi Agents)
多个智能体同时处理子任务。例如:使用文本和图像智能体处理文档。在 AutoGen 中,可以使用群聊实现并行执行。
assistant1 = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Assistant1", ...)
assistant2 = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Assistant2", ...)
groupchat = autogen.GroupChat(agents=[user_proxy, assistant1, assistant2], ...)
5.2 顺序智能体 (Sequential Agents)
智能体按顺序执行任务。例如:数据管道(清洗 → 分析)。在 LangChain 中,可以使用链(Chains)实现顺序执行。
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm) | Tool("tool_name") | LLMChain(llm=llm)
5.3 循环智能体 (Loop Agents)
智能体重复执行任务,直到满足某个条件。例如:迭代优化解决方案。在 AutoGen 中通过自定义逻辑实现。
whilenot condition_met:
response = assistant.generate()
5.4 路由智能体 (Router Agent)
一个智能体将任务分发给专门的智能体。例如:客户支持路由。在 AutoGen 中,可以使用一个路由智能体。
router = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Router", ...)
worker1 = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Worker1", ...)
5.5 聚合智能体 (Aggregator Agent)
收集并合并来自多个智能体的结果。例如:合并搜索结果。在 AutoGen 中通过自定义聚合器实现。
aggregator = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Aggregator", ...)
5.6 网络智能体 (Network Agent)
智能体在网络拓扑中连接以进行通信。例如:传感器网络。在 LangChain 或 AutoGen 中进行自定义设置。
agent1.add_tool(agent2.tool)
agent2.add_tool(agent3.tool)
5.7 层级智能体 (Hierarchical Agents)
智能体按层级组织,上级控制下级。例如:公司结构。在 AutoGen 中,使用层级智能体设置。
executive = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Executive", ...)
manager = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Manager", ...)
worker = autogen.AssistantAgent(name="Worker", ...)
6. 结论
AI 智能体正在改变 AI 开发的格局,LangChain、LlamaIndex 和 AutoGen 等框架为构建自主系统提供了强大的工具。单智能体和多智能体架构的选择取决于任务的复杂性,而设计模式为多智能体交互提供了结构化的解决方案。截至2025年4月8日,该领域仍在不断发展,正在进行的研究致力于解决偏见和对齐等挑战,预示着将对各行业产生重大影响。
参考文献
- Agentic AI Architecture: A Deep Dive[13]
- What is Agentic AI? Definition, Examples and Trends in 2025[14]
- What Is Agentic Architecture? | IBM[15]
- Agentic AI Architecture: The Blueprint for Next-Gen AI Solutions[16]
- Agentic AI design: An architectural case study | CIO[17]
- An AI Agent Architecture & Framework Is Emerging | by Cobus Greyling | Medium[18]
- What Is Agentic AI? | NVIDIA Blog[19]
- A Guide to Agentic AI Architecture | by DataStax | Building Real-World, Real-Time AI | Medium[20]
- Agentic AI Frameworks, Tools and Use Cases[21]
- Designing Agentic AI Systems, Part 1: Agent Architectures - Vectorize[22]
- GitHub - langchain-ai/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications[23]
- LangChain[24]
- Introduction | 🦜️🔗 LangChain[25]
- LangChain - Wikipedia[26]
- What Is LangChain and How to Use It: A Guide | Definition from TechTarget[27]
- Introduction to LangChain | GeeksforGeeks[28]
- What is LangChain? - LangChain Explained - AWS[29]
- LangChain: The Trendiest Web Framework of 2023, Thanks to AI - The New Stack[30]
- LlamaIndex - Build Knowledge Assistants over your Enterprise Data[31]
- GitHub - run-llama/llama_index: LlamaIndex is the leading framework for building LLM-powered agents over your data.[32]
- Framework - LlamaIndex[33]
- LlamaIndex: A Data Framework for the Large Language Models (LLMs) based applications | DataCamp[34]
- What is LlamaIndex ? | IBM[35]
- Llama Hub[36]
- What is LlamaIndex? Exploring LLM Orchestration Frameworks | DataStax[37]
- GitHub - microsoft/autogen: A programming framework for agentic AI 🤖[38]
- AutoGen - Microsoft Research[39]
- Getting Started | AutoGen 0.2[40]
- AutoGen | AutoGen 0.2[41]
- AI Agentic Design Patterns with AutoGen - DeepLearning.AI[42]
- AutoGen: Enabling next-generation large language model applications - Microsoft Research[43]
- A Developer’s Guide to the AutoGen AI Agent Framework - The New Stack[44]
- Microsoft’s Agentic Frameworks: AutoGen and Semantic Kernel | AutoGen Blog[45]
- Agents | 🦜️🔗 LangChain[46]
- Introducing LangChain Agents: 2024 Tutorial with Example | Bright Inventions[47]
- Beginner’s Guide to Creating AI Agents With LangChain | by Vijaykumar Kartha | Medium[48]
- Build an Agent | 🦜️🔗 LangChain[49]
- Build an AI coding Agent with LangGraph by LangChain[50]
- Langflow | Low-code AI builder for agentic and RAG applications[51]
- Using LangChain Tools to Build an AI Agent | IBM[52]
- Agents - LlamaIndex[53]
- Using Agents in LlamaIndex - Hugging Face Agents Course[54]
- Building a basic agent - LlamaIndex[55]
- Beyond Static Pipelines: Enhancing AI Agents with LlamaIndex[56]
- Introducing llama-agents: A Powerful Framework for Building Production Multi-Agent AI Systems - LlamaIndex[57]
- Building AI Agents with AutoGen[58]
- Examples | AutoGen 0.2[59]
- AutoGen Tutorial : How to Build AI Agents[60]
如何系统学习掌握AI大模型?
AI大模型作为人工智能领域的重要技术突破,正成为推动各行各业创新和转型的关键力量。抓住AI大模型的风口,掌握AI大模型的知识和技能将变得越来越重要。
学习AI大模型是一个系统的过程,需要从基础开始,逐步深入到更高级的技术。
这里给大家精心整理了一份
全面的AI大模型学习资源,包括:AI大模型全套学习路线图(从入门到实战)、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习、面试题等,资料免费分享!

1. 成长路线图&学习规划
要学习一门新的技术,作为新手一定要先学习成长路线图,方向不对,努力白费。
这里,我们为新手和想要进一步提升的专业人士准备了一份详细的学习成长路线图和规划。可以说是最科学最系统的学习成长路线。

2. 大模型经典PDF书籍
书籍和学习文档资料是学习大模型过程中必不可少的,我们精选了一系列深入探讨大模型技术的书籍和学习文档,它们由领域内的顶尖专家撰写,内容全面、深入、详尽,为你学习大模型提供坚实的理论基础。(书籍含电子版PDF)

3. 大模型视频教程
对于很多自学或者没有基础的同学来说,书籍这些纯文字类的学习教材会觉得比较晦涩难以理解,因此,我们提供了丰富的大模型视频教程,以动态、形象的方式展示技术概念,帮助你更快、更轻松地掌握核心知识。

4. 大模型行业报告
行业分析主要包括对不同行业的现状、趋势、问题、机会等进行系统地调研和评估,以了解哪些行业更适合引入大模型的技术和应用,以及在哪些方面可以发挥大模型的优势。

5. 大模型项目实战
学以致用 ,当你的理论知识积累到一定程度,就需要通过项目实战,在实际操作中检验和巩固你所学到的知识,同时为你找工作和职业发展打下坚实的基础。

6. 大模型面试题
面试不仅是技术的较量,更需要充分的准备。
在你已经掌握了大模型技术之后,就需要开始准备面试,我们将提供精心整理的大模型面试题库,涵盖当前面试中可能遇到的各种技术问题,让你在面试中游刃有余。

全套的AI大模型学习资源已经整理打包,有需要的小伙伴可以
微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码,免费领取【保证100%免费】





















 739
739

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








