import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from scipy import integrate
# 设置字体
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['DejaVu Sans']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 定义不同的δ函数近似方法
def gaussian_approx(x, sigma):
"""高斯函数近似"""
return np.exp(-x**2/(2*sigma**2)) / (sigma * np.sqrt(2*np.pi))
def rect_approx(x, epsilon):
"""矩形函数近似"""
return np.where(np.abs(x) <= epsilon, 1/(2*epsilon), 0)
def lorentz_approx(x, gamma):
"""洛伦兹函数近似"""
return gamma / (np.pi * (x**2 + gamma**2))
def sinc_approx(x, a):
"""sinc函数近似"""
return np.sinc(x * a) * a / np.pi
def triangle_approx(x, epsilon):
"""三角波函数近似"""
return np.where(np.abs(x) <= epsilon, (epsilon - np.abs(x))/epsilon**2, 0)
# 创建坐标轴
x = np.linspace(-2, 2, 1000)
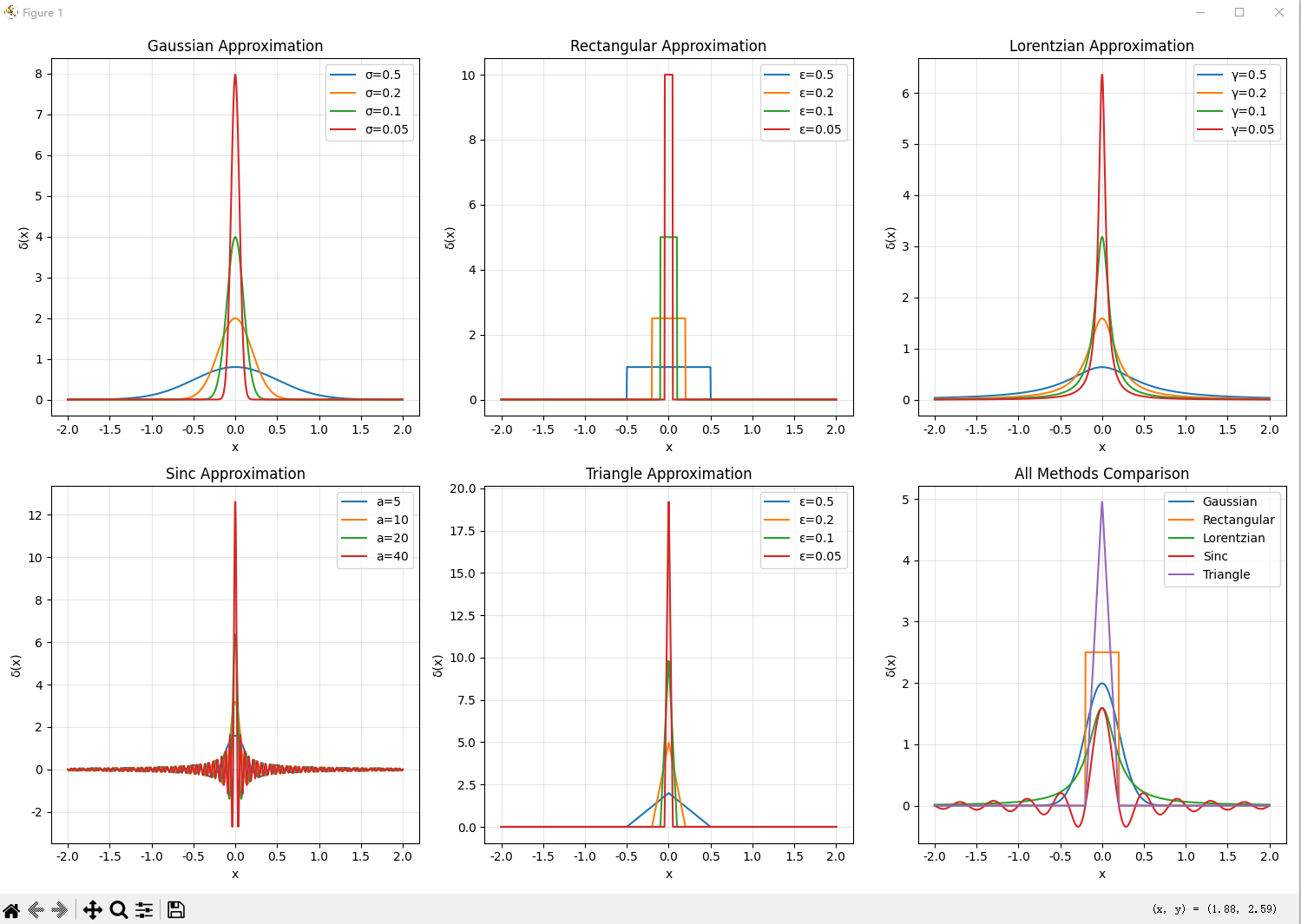
# 1. 展示不同函数的δ函数近似
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
# 高斯函数近似
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
for sigma in [0.5, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05]:
plt.plot(x, gaussian_approx(x, sigma), label=f'σ={sigma}')
plt.title('Gaussian Approximation')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('δ(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 矩形函数近似
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
for epsilon in [0.5, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05]:
plt.plot(x, rect_approx(x, epsilon), label=f'ε={epsilon}')
plt.title('Rectangular Approximation')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('δ(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 洛伦兹函数近似
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
for gamma in [0.5, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05]:
plt.plot(x, lorentz_approx(x, gamma), label=f'γ={gamma}')
plt.title('Lorentzian Approximation')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('δ(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# sinc函数近似
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
for a in [5, 10, 20, 40]:
plt.plot(x, sinc_approx(x, a), label=f'a={a}')
plt.title('Sinc Approximation')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('δ(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 三角波函数近似
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
for epsilon in [0.5, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05]:
plt.plot(x, triangle_approx(x, epsilon), label=f'ε={epsilon}')
plt.title('Triangle Approximation')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('δ(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 所有方法比较(使用相似参数)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
param = 0.2
plt.plot(x, gaussian_approx(x, param), label='Gaussian')
plt.plot(x, rect_approx(x, param), label='Rectangular')
plt.plot(x, lorentz_approx(x, param), label='Lorentzian')
plt.plot(x, sinc_approx(x, 1/param), label='Sinc')
plt.plot(x, triangle_approx(x, param), label='Triangle')
plt.title('All Methods Comparison')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('δ(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
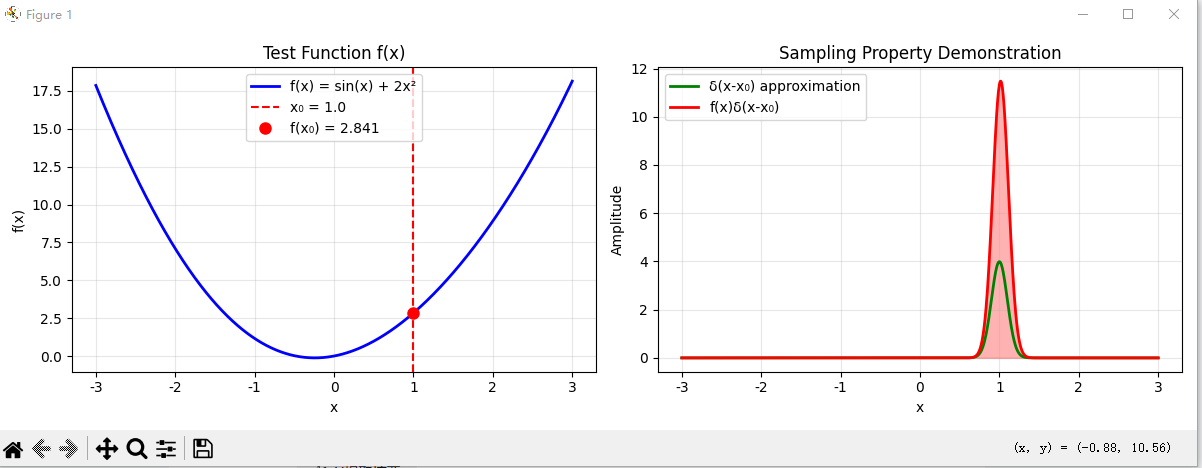
# 2. 验证筛选性质 (Sampling Property)
print("验证筛选性质: ∫f(x)δ(x-x₀)dx = f(x₀)")
def test_sampling_property():
"""测试筛选性质"""
# 测试函数
def f(x):
return np.sin(x) + 2*x**2
x0 = 1.0 # 采样点
x_range = np.linspace(-3, 3, 1000)
dx = x_range[1] - x_range[0]
# 使用高斯近似
sigma = 0.1
delta_approx = gaussian_approx(x_range - x0, sigma)
# 计算积分
integral = np.sum(f(x_range) * delta_approx) * dx
exact_value = f(x0)
print(f"数值积分结果: {integral:.6f}")
print(f"精确值 f({x0}): {exact_value:.6f}")
print(f"相对误差: {abs(integral - exact_value)/abs(exact_value)*100:.4f}%")
# 绘图展示
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(x_range, f(x_range), 'b-', label='f(x) = sin(x) + 2x²', linewidth=2)
plt.axvline(x=x0, color='r', linestyle='--', label=f'x₀ = {x0}')
plt.plot(x0, exact_value, 'ro', markersize=8, label=f'f(x₀) = {exact_value:.3f}')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('f(x)')
plt.title('Test Function f(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(x_range, delta_approx, 'g-', label='δ(x-x₀) approximation', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x_range, f(x_range) * delta_approx, 'r-', label='f(x)δ(x-x₀)', linewidth=2)
plt.fill_between(x_range, f(x_range) * delta_approx, alpha=0.3, color='red')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.title('Sampling Property Demonstration')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return integral, exact_value
test_sampling_property()
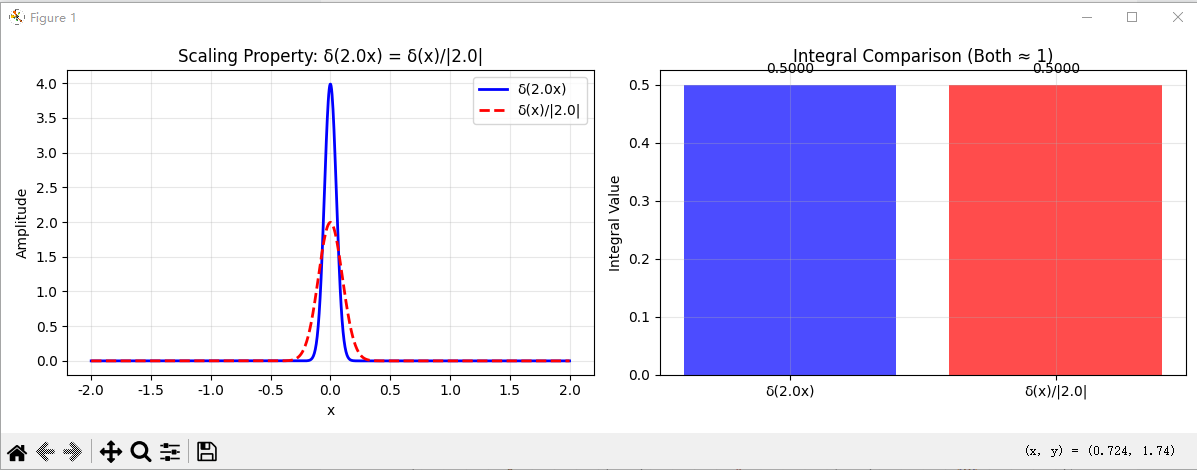
# 3. 验证缩放性质 (Scaling Property)
def test_scaling_property():
"""测试缩放性质: δ(ax) = δ(x)/|a|"""
x = np.linspace(-2, 2, 1000)
a = 2.0 # 缩放因子
sigma = 0.1
# δ(ax)
delta_ax = gaussian_approx(a * x, sigma)
# δ(x)/|a|
delta_scaled = gaussian_approx(x, sigma) / abs(a)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(x, delta_ax, 'b-', label=f'δ({a}x)', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x, delta_scaled, 'r--', label=f'δ(x)/|{a}|', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.title(f'Scaling Property: δ({a}x) = δ(x)/|{a}|')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 验证积分相等
dx = x[1] - x[0]
integral_ax = np.sum(delta_ax) * dx
integral_scaled = np.sum(delta_scaled) * dx
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
methods = [f'δ({a}x)', f'δ(x)/|{a}|']
integrals = [integral_ax, integral_scaled]
plt.bar(methods, integrals, color=['blue', 'red'], alpha=0.7)
plt.ylabel('Integral Value')
plt.title('Integral Comparison (Both ≈ 1)')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
for i, v in enumerate(integrals):
plt.text(i, v + 0.02, f'{v:.4f}', ha='center')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print(f"缩放性质验证:")
print(f"∫δ({a}x)dx = {integral_ax:.6f}")
print(f"∫[δ(x)/|{a}|]dx = {integral_scaled:.6f}")
test_scaling_property()
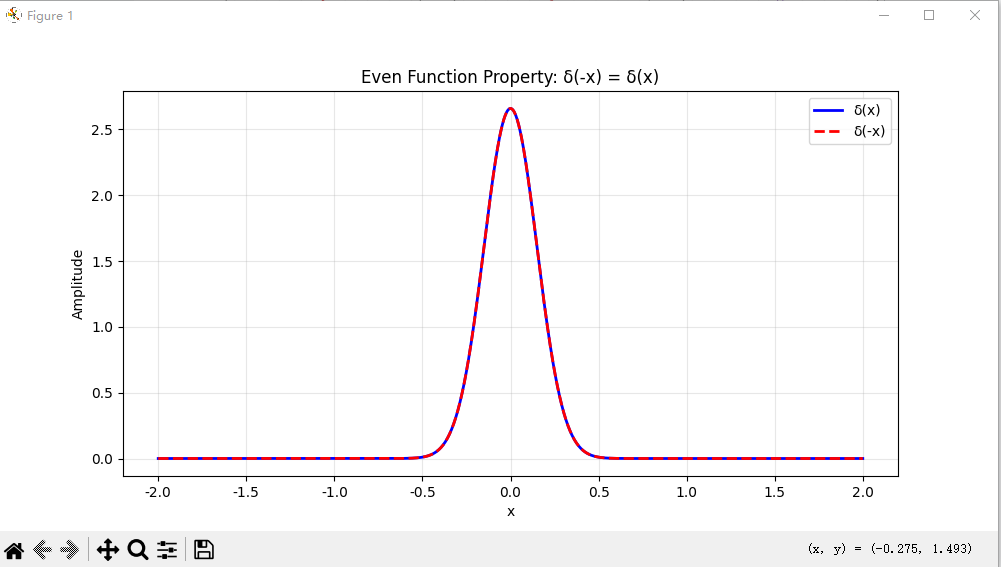
# 4. 验证偶函数性质 (Even Function Property)
def test_even_property():
"""测试偶函数性质: δ(-x) = δ(x)"""
x = np.linspace(-2, 2, 1000)
sigma = 0.15
delta_x = gaussian_approx(x, sigma)
delta_minus_x = gaussian_approx(-x, sigma)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.plot(x, delta_x, 'b-', label='δ(x)', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x, delta_minus_x, 'r--', label='δ(-x)', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.title('Even Function Property: δ(-x) = δ(x)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 计算最大差异
max_diff = np.max(np.abs(delta_x - delta_minus_x))
print(f"偶函数性质验证:")
print(f"δ(x) 和 δ(-x) 的最大差异: {max_diff:.6e} (应该接近0)")
plt.show()
test_even_property()
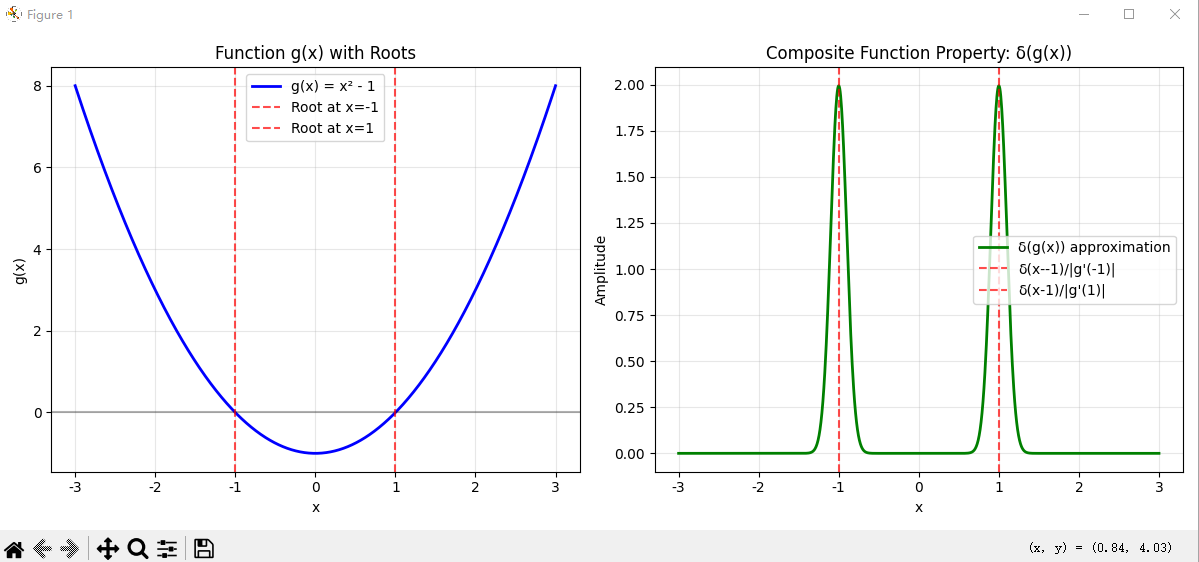
# 5. 验证复合函数性质
def test_composite_property():
"""测试复合函数性质: δ(g(x))"""
x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 1000)
# 定义 g(x) = x² - 1,根在 x = ±1
def g(x):
return x**2 - 1
# 使用性质: δ(g(x)) = Σ δ(x-xᵢ)/|g'(xᵢ)|
roots = [-1, 1] # g(x) = 0 的根
derivatives = [abs(2*root) for root in roots] # |g'(xᵢ)|
sigma = 0.1
delta_composite = np.zeros_like(x)
for root, deriv in zip(roots, derivatives):
delta_composite += gaussian_approx(x - root, sigma) / deriv
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(x, g(x), 'b-', label='g(x) = x² - 1', linewidth=2)
plt.axhline(y=0, color='k', linestyle='-', alpha=0.3)
for root in roots:
plt.axvline(x=root, color='r', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7, label=f'Root at x={root}')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('g(x)')
plt.title('Function g(x) with Roots')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(x, delta_composite, 'g-', label='δ(g(x)) approximation', linewidth=2)
for root, deriv in zip(roots, derivatives):
plt.axvline(x=root, color='r', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7,
label=f'δ(x-{root})/|g\'({root})|')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.title('Composite Function Property: δ(g(x))')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
test_composite_property()
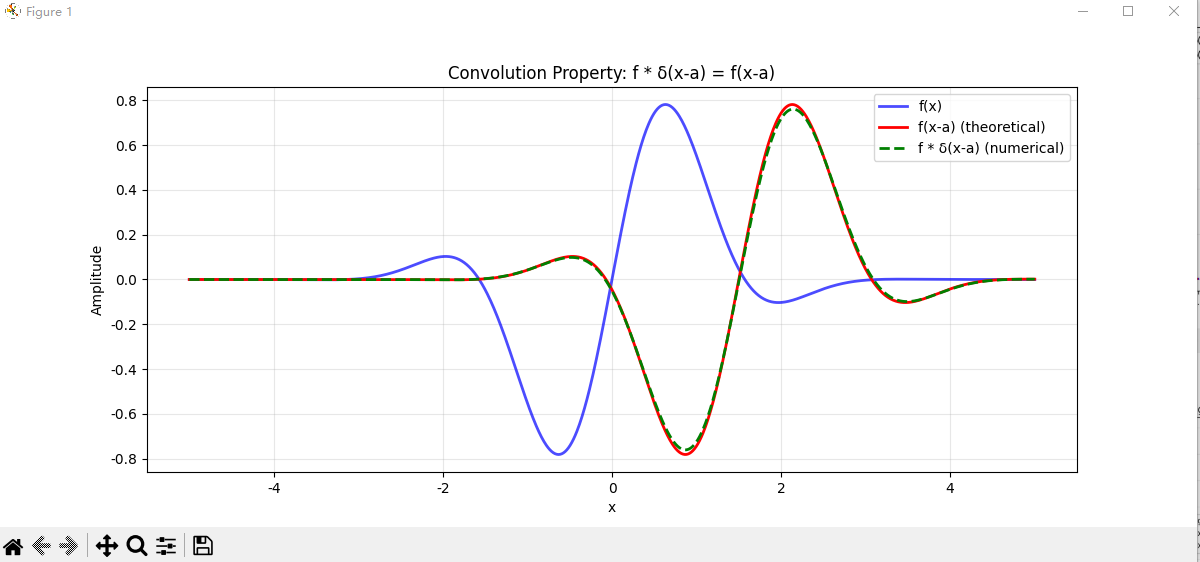
# 6. 验证卷积性质 (Convolution Property)
def test_convolution_property():
"""测试卷积性质: f * δ(x-a) = f(x-a)"""
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 1000)
dx = x[1] - x[0]
# 测试函数
def f(x):
return np.exp(-x**2/2) * np.sin(2*x)
a = 1.5 # 平移量
sigma = 0.1
# δ(x-a)
delta_shifted = gaussian_approx(x - a, sigma)
# 数值卷积
convolution = np.convolve(f(x), delta_shifted, mode='same') * dx
# 理论结果: f(x-a)
theoretical = f(x - a)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.plot(x, f(x), 'b-', label='f(x)', linewidth=2, alpha=0.7)
plt.plot(x, theoretical, 'r-', label='f(x-a) (theoretical)', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x, convolution, 'g--', label='f * δ(x-a) (numerical)', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.title('Convolution Property: f * δ(x-a) = f(x-a)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 计算误差
error = np.max(np.abs(convolution - theoretical))
print(f"卷积性质验证:")
print(f"最大误差: {error:.6f}")
plt.show()
test_convolution_property()
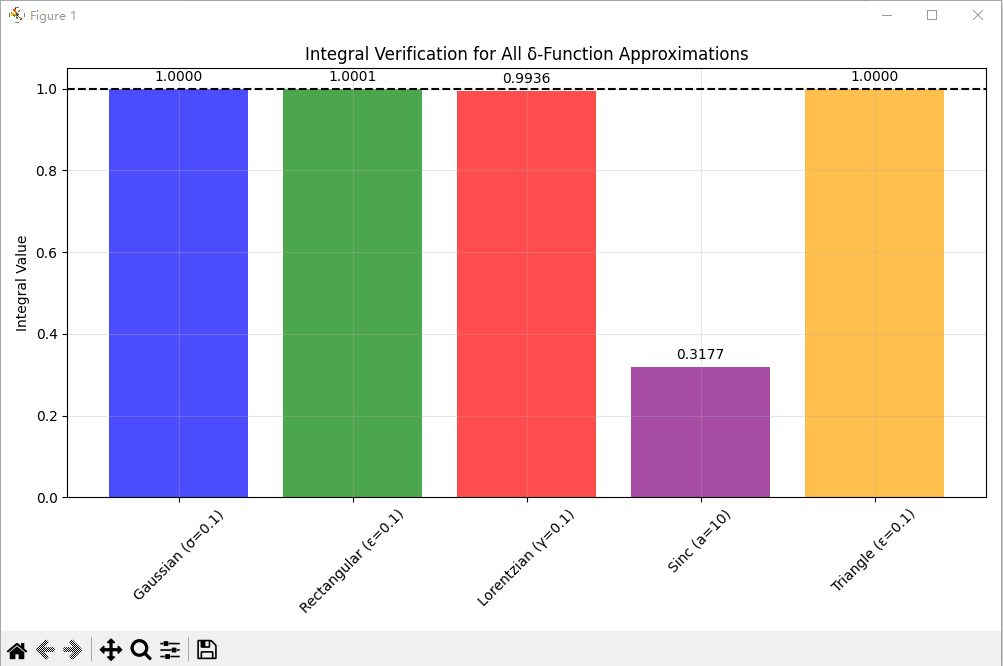
# 7. 总结:所有近似的积分验证
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("所有δ函数近似的积分验证 (应该都接近1)")
print("="*50)
x_test = np.linspace(-10, 10, 10000)
dx_test = x_test[1] - x_test[0]
methods = {
'Gaussian (σ=0.1)': gaussian_approx(x_test, 0.1),
'Rectangular (ε=0.1)': rect_approx(x_test, 0.1),
'Lorentzian (γ=0.1)': lorentz_approx(x_test, 0.1),
'Sinc (a=10)': sinc_approx(x_test, 10),
'Triangle (ε=0.1)': triangle_approx(x_test, 0.1)
}
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
integrals = []
names = []
for name, approx in methods.items():
integral = np.sum(approx) * dx_test
integrals.append(integral)
names.append(name)
print(f"{name:20s}: {integral:.6f}")
plt.bar(names, integrals, color=['blue', 'green', 'red', 'purple', 'orange'], alpha=0.7)
plt.axhline(y=1, color='k', linestyle='--', label='Theoretical value: 1')
plt.ylabel('Integral Value')
plt.title('Integral Verification for All δ-Function Approximations')
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
for i, v in enumerate(integrals):
plt.text(i, v + 0.02, f'{v:.4f}', ha='center')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()































 1518
1518

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








