(1)模型,视图,代理,索引,选择模型,等,涉及的内容真多。完成了所谓的 MVC 架构。本节对于二维表模型,不再详细的举例。因为由易到难,最详细的举例,在于字符串列表模型 QStringListModel ,见第130 篇
在列表模型,对于其抽象基类 QAbstractItemModel 的扩展最少。学习列表模型的时候,对于大量的成员函数的举例,也顺带熟悉了其基类中的内容。故在这里就不详细举例了。
(2) 接着学习下本二维表类的唯一的一个信号函数 :

++测试一下 :
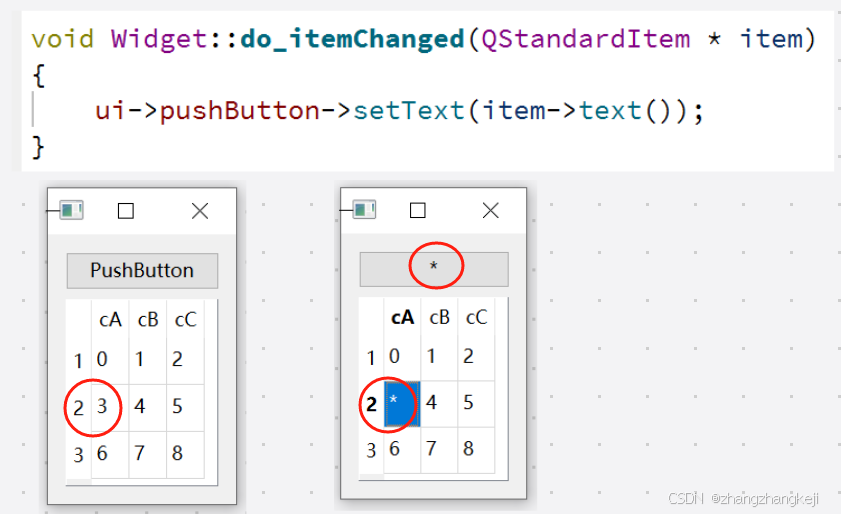
(3)接着学习一些本表格模型独有的,抽象基类模型里没有的成员函数。那些容易理解的成员函数,也不再测试了 :
(4)关于行列表头 :
++ 给出对应的源码 :
(5)接着是操作管理中元素的成员函数 :

++ 测试一下 :
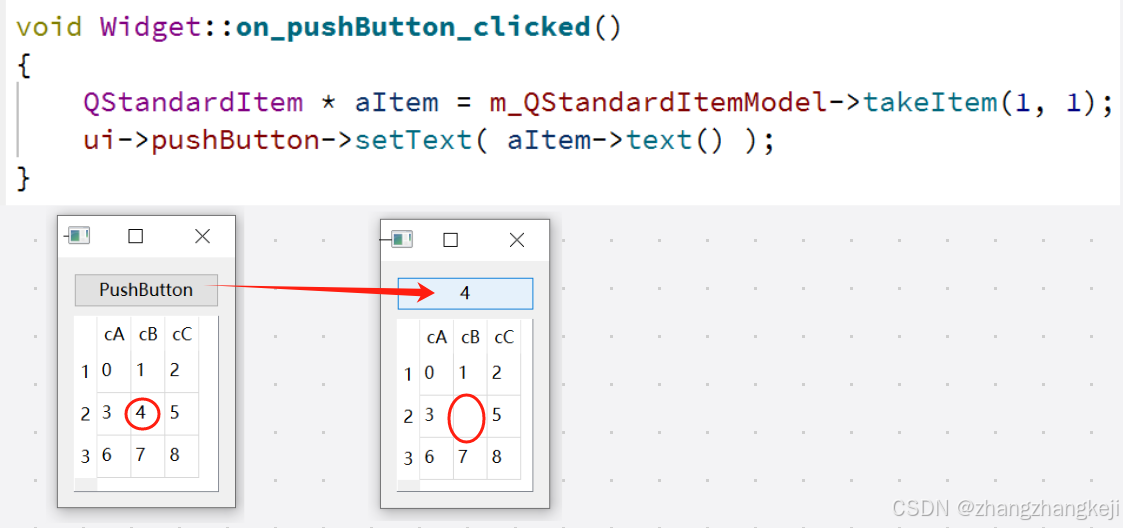
(6)条目指针与索引之间的互相转换 :
(7)关于行列操作的 :
++ 对比完基类中的同名同功能的成员函数,给出本类中的成员函数的定义 :

++ 关于列的操作 :

(8) 给出本类的源代码,定义于 qstandarditemmodel . h 头文件 :
class QStandardItemModelPrivate;
/*
The QStandardItemModel class provides a generic model for storing custom data.
Detailed Description :
QStandardltemModel 可以用作标准 Qt数据类型的存储库。
它是模型/视图类之,并且是Qt的模型/视图框架的一部分。
QStandardItemModel can be used as a repository存储库 for standard Qt data types.
It is one of the Model/View Classes and is part of Qt's model/view framework.
QStandardltemModel提供了一种基于项目的经典方法来处理模型。
QStandardltemModel中的项目由 QStandardltem 提供。
QStandardItemModel provides a classic item-based approach to working with the model.
The items in a QStandardItemModel are provided by QStandardItem.
QStandardltemModel实现了 QAbstractltemModel接口,
这意味着该模型可用于在支持该接口的任何视图(例如 QListView、QTableView和 QTreeView,
以及您自己的自定义视图)中提供数据。
为了提高性能和灵活性,您可能希望将QAbstractltemModel子类化,以便为不同类型的数据存储库提供支持。
例如,QFileSystemModel提供底层文件系统的型接口。
QStandardItemModel implements the QAbstractItemModel interface,
which means that the model can be used to provide data in any view
that supports that interface (such as QListView, QTableView and QTreeView,
and your own custom views).
For performance and flexibility灵活性,
you may want to subclass QAbstractItemModel to provide support for different
kinds of data repositories.
For example, the QFileSystemModel provides a model interface to the underlying file system.
当你需要一个列表或树时,你通常会创建一个空的QStandardltemModel,
并使用appendRow()将项目添加到模型中,并使用item ()访问一个项目。
如果您的模型表示一个表,则通常会将表的维度传递给0StandardltemMode构造函数,
并使用setltem()将项目定位到表中。
您还可以使用setRowCount(和setcolumnCount 来更改模型的维度。
要插入项目,请使用insertRow()或insertcolumn(),要删除项目,请使用removeRow()或removecolumn().
When you want a list or tree,
you typically create an empty QStandardItemModel and
use appendRow() to add items to the model, and item() to access an item.
If your model represents a table, you typically pass the dimensions of the table to the
QStandardItemModel constructor and use setItem() to position items into the table.
You can also use setRowCount() and setColumnCount() to alter the dimensions of the model.
To insert items, use insertRow() or insertColumn(),
and to remove items, use removeRow() or removeColumn().
尔可以使用setHorizontalHeaderLabels()和setVerticalHeaderLabels()设置模型的横列标题文本。
You can set the header labels of your model with setHorizontalHeaderLabels()
and setVerticalHeaderLabels().
你可以使用findltems()在模型中搜索项目,并通过调用sort()对模型进行排序。
You can search for items in the model with findItems(),
and sort the model by calling sort().
调用clear()方法从模型中移除所有项目。
Call clear() to remove all items from the model.
使用 QStandardltemModel创建表格的一个示例用法:
An example usage of QStandardItemModel to create a table:
QStandardItemModel model(4, 4);
for (int row = 0; row < model.rowCount(); ++row) {
for (int column = 0; column < model.columnCount(); ++column) {
QStandardItem * item = new QStandardItem(
QString("row %0, column %1").arg(row).arg(column));
model.setItem(row, column, item);
}
}
使用QstandardltemModel创建树形结构的一个示例用法
An example usage of QStandardItemModel to create a tree: 树形结构
QStandardItemModel model;
QStandardItem * parentItem = model.invisibleRootItem();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
QStandardItem * item = new QStandardItem(QString("item %0").arg(i));
parentItem->appendRow(item);
parentItem = item;
}
在将模型设置到视图后,你通常希望对用户操作做出反应,例如点击一个项目。
由于QAbstractltemView提供了基于QModelIndex的信号和函数,
你需要一种方法来获取与给定QModelIndex对应的QStandardltem,反之亦然。
itemFromIndex()和indexFromItem() 提供这种映射。
itemFromlndex ()、的典型用法包括在视图中获取当前索引处的项,
以及根据由`QAbstractltemView信号(如`QAbstractltemView::clicked()`)携带的索引来获取对应的项。
首先,将视图的信号连接到你类中的一个插槽:
After setting the model on a view, you typically want to react to user actions,
such as an item being clicked.
Since a QAbstractItemView provides QModelIndex-based signals and functions,
you need a way to obtain the QStandardItem that corresponds to a given QModelIndex,
and vice versa.
itemFromIndex() and indexFromItem() provide this mapping.
Typical usage of itemFromIndex() includes obtaining the item at the current index in a view,
and obtaining the item that corresponds to an index carried by a QAbstractItemView signal,
such as QAbstractItemView::clicked().
First you connect the view's signal to a slot in your class:
QTreeView * treeView = new QTreeView(this);
treeView->setModel(myStandardItemModel);
connect(treeView, & QTreeView::clicked, this, & MyWidget::clicked);
当你收到信号时,你可以在给定的模型索引上调用 itemFromIndex()来获取项目的指针:
When you receive the signal,
you call itemFromIndex() on the given model index to get a pointer to the item:
void MyWidget::clicked(const QModelIndex & index)
{
QStandardItem * item = myStandardItemModel->itemFromIndex(index);
// Do stuff with the item ...
}
相反,当您想要调用一个接受索引作为参数的模型/视图函数时,必须获取该对象的QModellndex。
您可以通过使用模型的indexFromltem ()函数来获取索引,或者,
等效地,通过调用QStandardltem:index()来实现。
Conversely, you must obtain the QModelIndex of an item when you want to invoke a
model/view function that takes an index as argument.
You can obtain the index either by using the model's indexFromItem() function, or,
equivalently, by calling QStandardItem::index():
treeView->scrollTo(item->index());
当然,您不需要使用基于项目的方法;
相反,在使用模型时,您可以完全依赖QAbstractltemModel接口,或者根据需要使用两者的组合。
You are, of course, not required to use the item-based approach;
you could instead rely entirely on the QAbstractItemModel interface
when working with the model, or use a combination of the two as appropriate.
*/
class Q_GUI_EXPORT QStandardItemModel : public QAbstractItemModel
{
Q_OBJECT
//Note: This property supports QProperty bindings.
//This property holds the item role that is used to query the
// model's data when sorting items
//The default value is Qt::DisplayRole.
//本属性指明按列排序时候,又是按列里面的哪个角色的值排序。
Q_PROPERTY(int sortRole READ sortRole WRITE setSortRole BINDABLE bindableSortRole)
private:
friend class QStandardItemPrivate;
friend class QStandardItem;
Q_DISABLE_COPY(QStandardItemModel)
Q_DECLARE_PRIVATE(QStandardItemModel)
Q_PRIVATE_SLOT(d_func(), void _q_emitItemChanged(const QModelIndex & topLeft,
const QModelIndex & bottomRight))
protected:
QStandardItemModel(QStandardItemModelPrivate & dd, QObject * parent = nullptr);
Q_SIGNALS:
//This signal is emitted whenever the data of item has changed.
void itemChanged(QStandardItem * item);
public:
explicit QStandardItemModel(QObject * parent = nullptr); //默认构造函数
QStandardItemModel(int rows, int columns, QObject * parent = nullptr); //有参构造函数
~QStandardItemModel(); //析构函数
// Q_PROPERTY(int sortRole
// READ sortRole
// WRITE setSortRole
// BINDABLE bindableSortRole)
int sortRole() const;
void setSortRole(int role);
QBindable<int> bindableSortRole();
QHash<int, QByteArray> roleNames() const override;
void setItemRoleNames(const QHash<int,QByteArray> & roleNames);
//**************以下的实现虚函数,不再注释了,因为可以参阅其模型基类的实现注释。****************
QModelIndex index(int row, int column,
const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) const override;
QModelIndex parent(const QModelIndex & child) const override;
bool hasChildren(const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) const override;
void sort(int column, Qt::SortOrder order = Qt::AscendingOrder) override;
int rowCount(const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) const override;
int columnCount(const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) const override;
QVariant data(const QModelIndex & index,
int role = Qt::DisplayRole) const override;
void multiData(const QModelIndex & index,
QModelRoleDataSpan roleDataSpan) const override;
bool setData(const QModelIndex & index, const QVariant & value,
int role = Qt::EditRole) override;
bool clearItemData(const QModelIndex & index) override;
QMap<int, QVariant> itemData(const QModelIndex & index) const override;
bool setItemData(const QModelIndex & index,
const QMap<int, QVariant> & roles) override;
QVariant headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation,
int role = Qt::DisplayRole) const override;
bool setHeaderData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation,
const QVariant & value,
int role = Qt::EditRole) override;
QStringList mimeTypes() const override;
QMimeData * mimeData (const QModelIndexList & indexes) const override;
bool dropMimeData (const QMimeData * data, Qt::DropAction action,
int row, int column, const QModelIndex & parent) override;
bool insertRows(int row, int count,
const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) override;
bool removeRows(int row, int count,
const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) override;
bool insertColumns( int column, int count,
const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) override;
bool removeColumns( int column, int count,
const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex()) override;
Qt::ItemFlags flags(const QModelIndex & index) const override;
Qt::DropActions supportedDropActions() const override;
/*
enum Qt::DropAction { //本枚举类用于描述模型视图里的拖动操作的语义:复制、剪切或超链接。
CopyAction = 0x 1, //Copy the data to the target.
MoveAction = 0x 2, //Move the data from the source to the target.
LinkAction = 0x 4, //Create a link from the source to the target.
ActionMask = 0x ff,
TargetMoveAction = 0x8002, //在 Windows上,当 D&D数据的所有权应被目标应用程序接管时,
//即源应用程序不应删除这些数据时,会使用此值。
//在X11上,此值用于执行移动操作。Mac上不使用TargetMoveAction。
IgnoreAction = 0x 0 //Ignore the action (do nothing with the data).
};
Q_DECLARE_FLAGS(DropActions, DropAction)
Q_DECLARE_OPERATORS_FOR_FLAGS(DropActions)
*/
//***********************继承自父类的虚函数,到此结束。******************************
using QObject::parent;
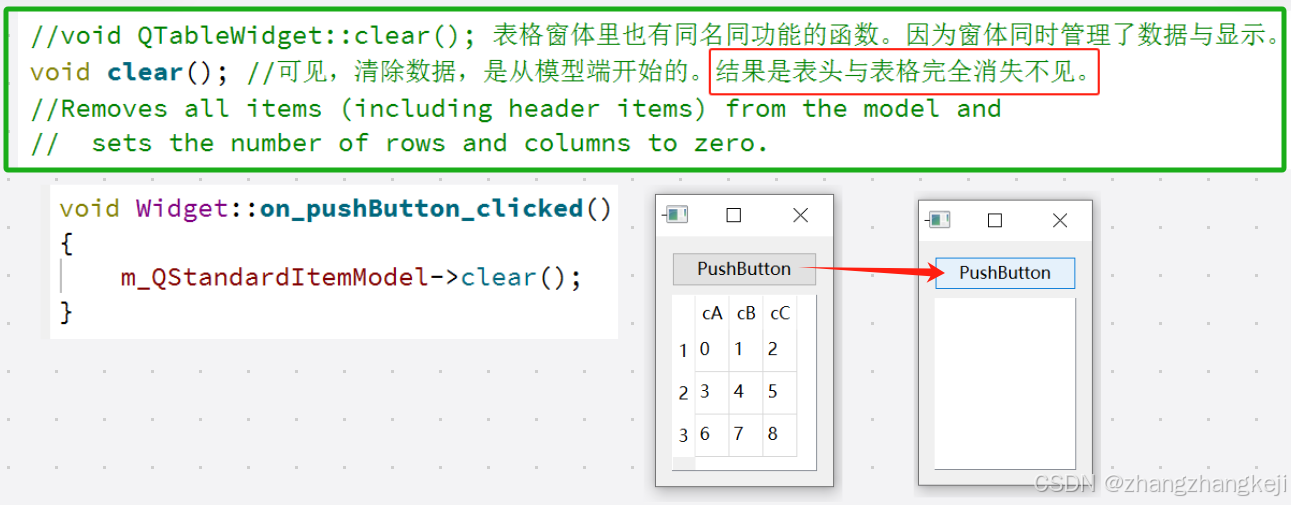
//void QTableWidget::clear(); 表格窗体里也有同名同功能的函数。因为窗体同时管理了数据与显示。
void clear(); //可见,清除数据,是从模型端开始的。结果是表头与表格完全消失不见。
//Removes all items (including header items) from the model and
// sets the number of rows and columns to zero.
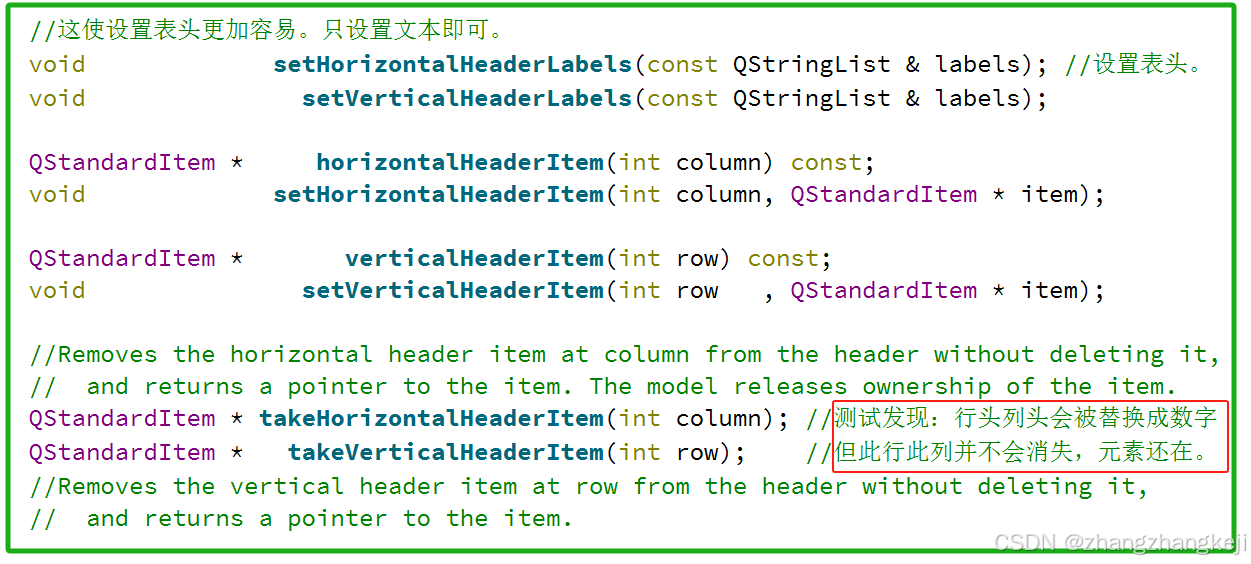
//这使设置表头更加容易。只设置文本即可。
void setHorizontalHeaderLabels(const QStringList & labels); //设置表头。
void setVerticalHeaderLabels(const QStringList & labels);
QStandardItem * horizontalHeaderItem(int column) const;
void setHorizontalHeaderItem(int column, QStandardItem * item);
QStandardItem * verticalHeaderItem(int row) const;
void setVerticalHeaderItem(int row , QStandardItem * item);
//Removes the horizontal header item at column from the header without deleting it,
// and returns a pointer to the item. The model releases ownership of the item.
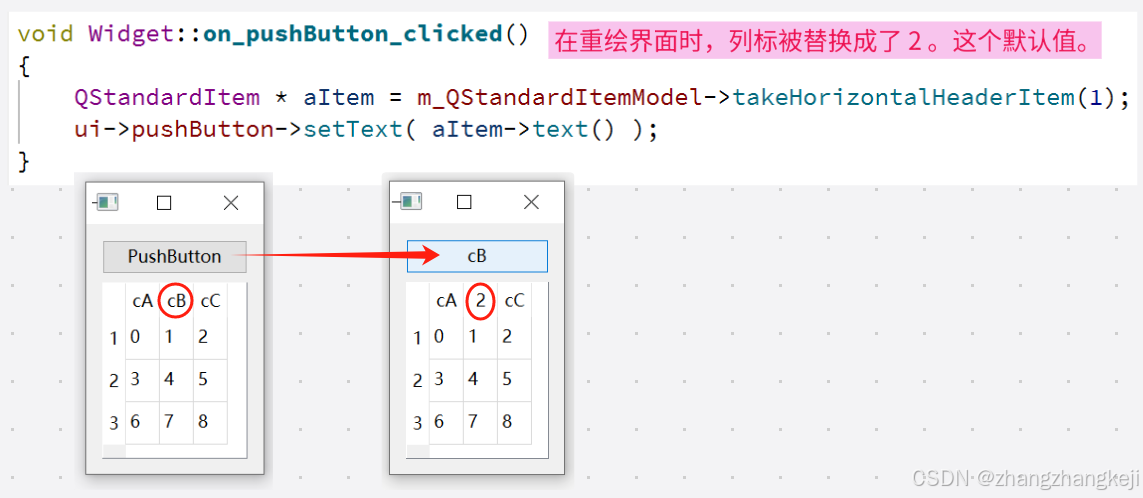
QStandardItem * takeHorizontalHeaderItem(int column); //测试发现:行头列头会被替换成数字
QStandardItem * takeVerticalHeaderItem(int row); //但此行此列并不会消失,元素还在。
//Removes the vertical header item at row from the header without deleting it,
// and returns a pointer to the item.
//不可见的根项通过 QStandardltem API提供对模型顶级项的访问,
//从而可以编写可以以统一方式处理顶级项及其子项的函数;例如,涉及树模型的递归函数。
//Note: Calling index() on the QStandardItem object retrieved from
// this function is not valid.
QStandardItem * invisibleRootItem() const; //返回模型的隐形根项。应该只对树形结构有用。
QStandardItem * item(int row, int column = 0) const;
void setItem(int row, int column, QStandardItem * item);
inline void setItem(int row, QStandardItem * item)
{ setItem(row, 0, item); }
//Returns a list of items that match the given text,
// using the given flags, in the given column.
//返回列 column里具有文本 text,按 flags匹配方式得到的条目列表。
QList<QStandardItem *> findItems(const QString & text,
Qt::MatchFlags flags = Qt::MatchExactly,
int column = 0) const;
//Removes the item at (row, column) without deleting it.
//The model releases ownership of the item. 该元素会消失,显示空白项。
QStandardItem * takeItem(int row, int column = 0);
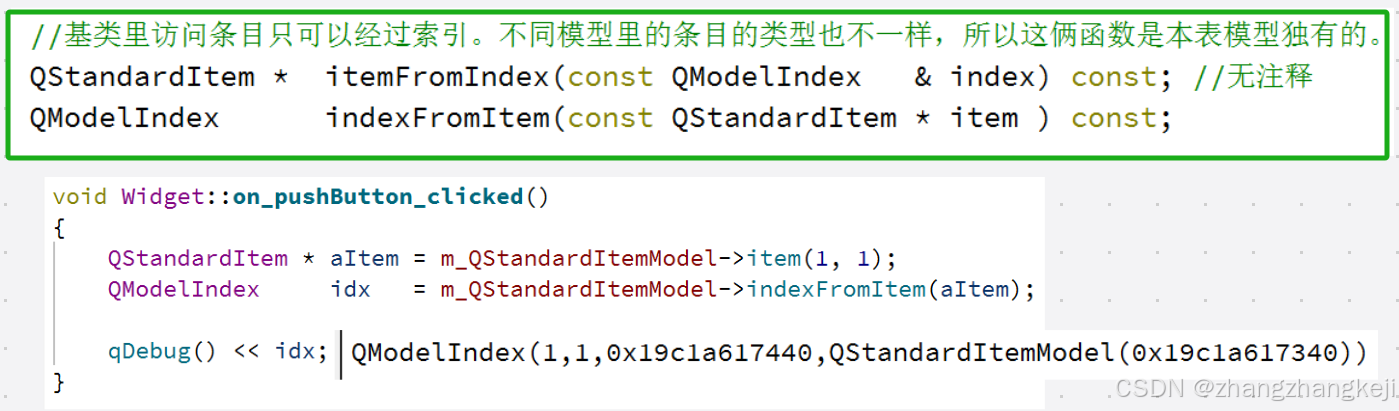
//基类里访问条目只可以经过索引。不同模型里的条目的类型也不一样,所以这俩函数是本表模型独有的。
QStandardItem * itemFromIndex(const QModelIndex & index) const; //无注释
QModelIndex indexFromItem(const QStandardItem * item ) const;
const QStandardItem * itemPrototype() const; //无注释
void setItemPrototype(const QStandardItem * item);
/*
class QAbstractItemModel {
virtual
bool insertRows(int row, int count, const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex());
inline
bool insertRow (int row, const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex());
virtual
bool moveRows (const QModelIndex & sourceParent, int sourceRow , int count,
const QModelIndex & destinationParent, int destinationChild);
bool moveRow (const QModelIndex & sourceParent, int sourceRow,
const QModelIndex & destinationParent, int destinationChild);
virtual
bool removeRows(int row, int count, const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex());
inline
bool removeRow (int row, const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex());
};
*/
void setRowCount(int rows );
void setColumnCount(int columns);
void insertRow(int row, const QList<QStandardItem *> & items); //插入一整行
inline //这些重载函数,覆盖了基类中的定义,不需要父类,而且可以插入时携带数据。
void insertRow(int row, QStandardItem * item)
{ insertRow(row, QList<QStandardItem*>() << item); }
inline
bool insertRow(int row, const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex())
{ return QAbstractItemModel::insertRow(row, parent); }
void appendRow(const QList<QStandardItem *> & items);
inline
void appendRow( QStandardItem * item )
{ appendRow(QList<QStandardItem *>() << item); }
QList<QStandardItem *> takeRow(int row);
//删除指定的行而不删除该行中的项,并返回一个指向被删除项的指针列表。
//模型将放弃对这些项的拥有权。对于行中尚未设置的项,列表中的相应指针将为空指针(nullptr)。
void insertColumn(int column, const QList<QStandardItem *> & );
inline //当 parent为空,则是插入顶层列。
bool insertColumn(int column, const QModelIndex & parent = QModelIndex());
{ return QAbstractItemModel::insertColumn(column, parent); }
void appendColumn(const QList<QStandardItem *> & items); //追加列。
QList<QStandardItem *> takeColumn(int column); //删除整列,这些操作都是在模型上。
}; //完结 class QStandardItemModel : public QAbstractItemModel
(9)
谢谢






















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










