一、
本文引用博主的方法进行了二次封装,使模型加载和预测进行分开,更方便后续工程的调用。https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zhenzhidemaoyi/article/details/135168405?ops_request_misc=&request_id=&biz_id=102&utm_term=yolov8-seg%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8onnxruntime%E6%8E%A8%E7%90%86&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~sobaiduweb~default-1-135168405.142^v102^pc_search_result_base1&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
二、环境配置
opencv使用的是4.5.2版本,解压到固定文件夹后,加入环境变量
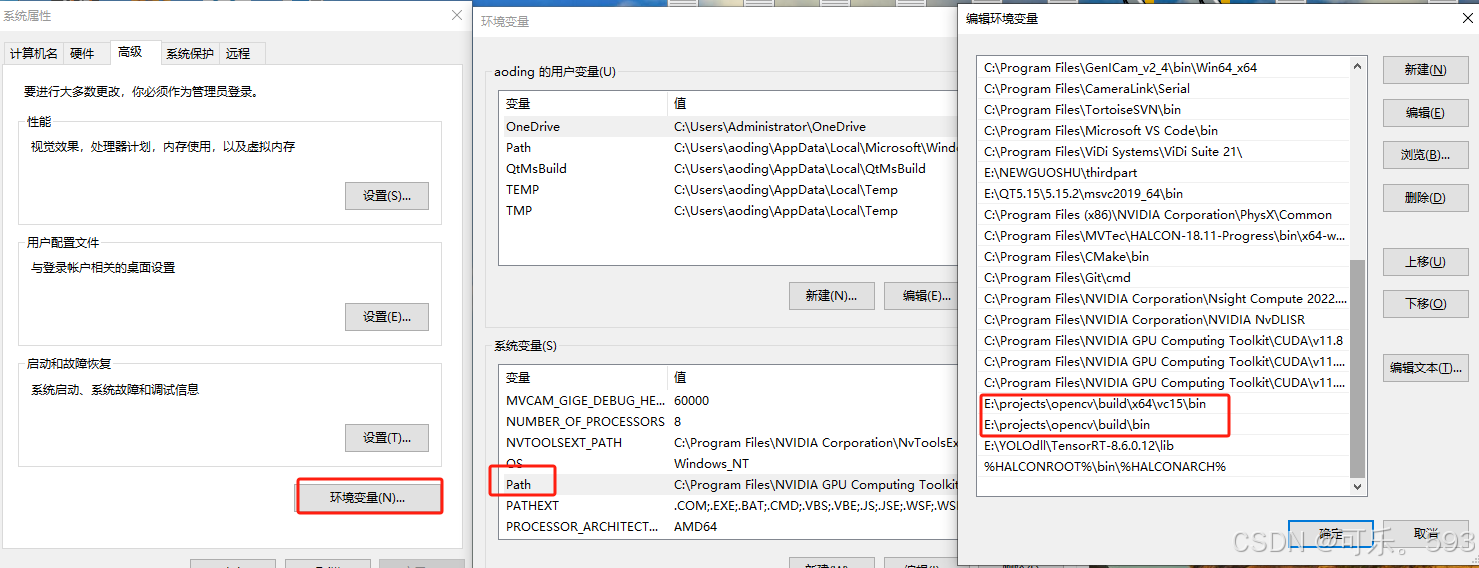
onnxruntime-gpu使用的是 1.15.1,(如果使用GPU加速的话建议下载onnxruntime-gpu版本,个人建议直接下载GPU版本的(如果想使用GPU加速的话一定要控制cuda和cudnn的版本具体可可以借鉴说明),因为GPU版本也兼容CPU运行,而基础版本只可以使用CPU不可以使用GPU)需要的去网址上下载固定版本即可(onnxruntime版本一定大于等于你转换成onnx模型的版本,否则会出现识别不出模型,而报错)
onnxruntime版本安装可以借鉴
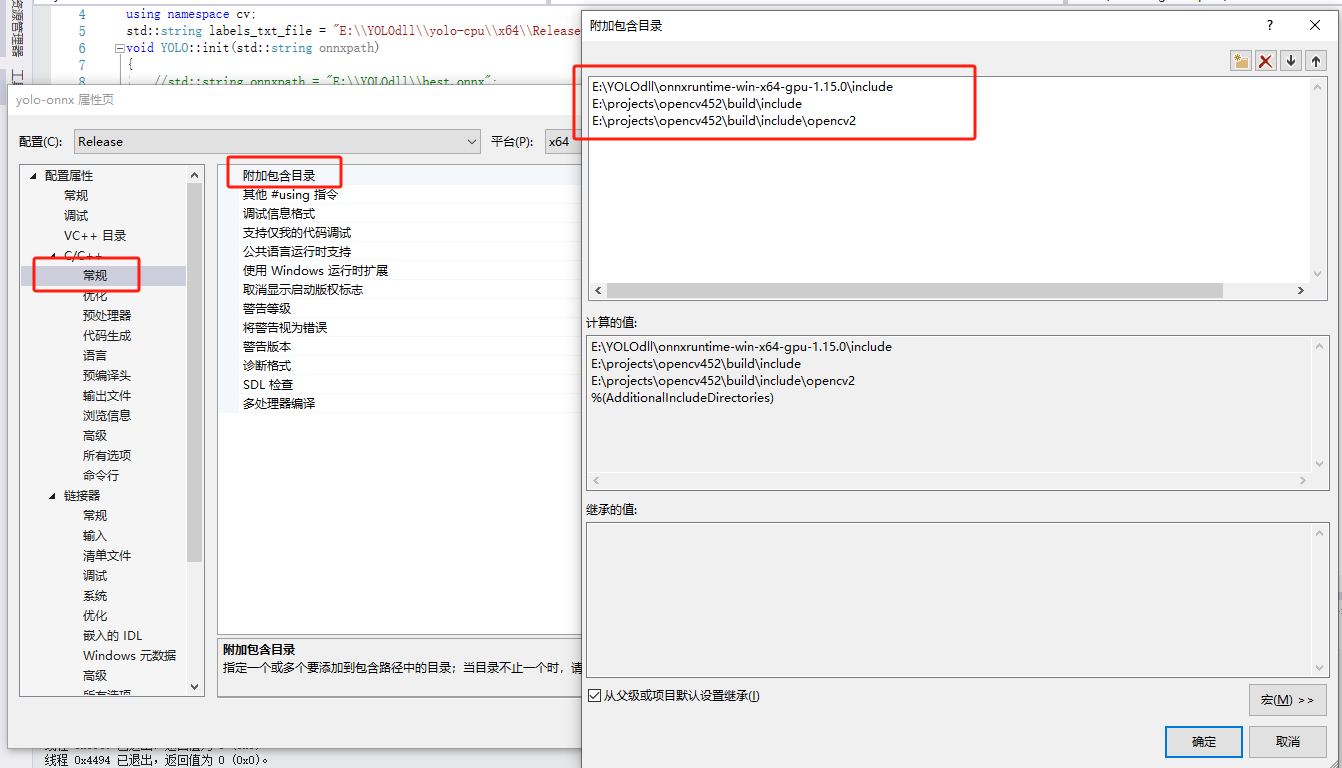
E:\projects\opencv\build\include
E:\projects\opencv\build\include\opencv2
E:\YOLOdll\onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu-1.15.0\include
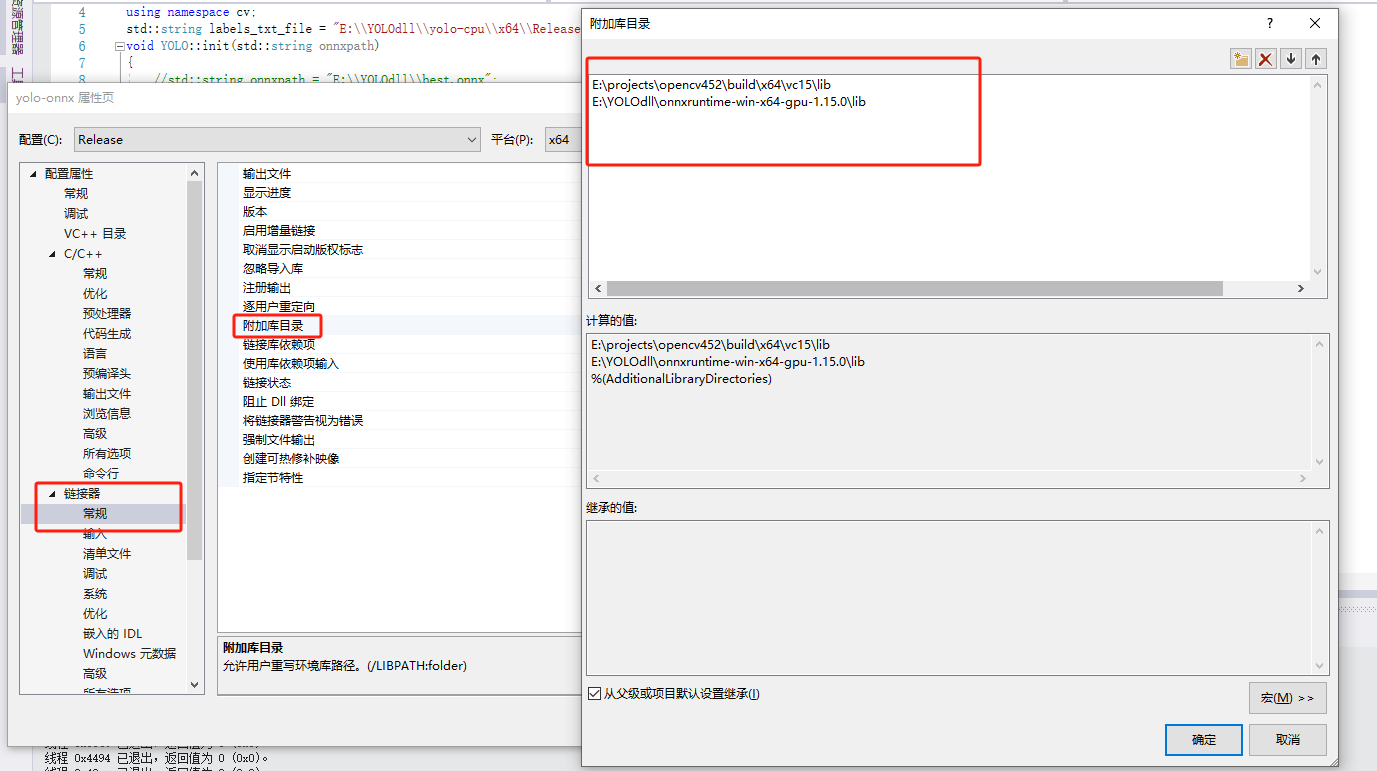
E:\projects\opencv\build\x64\vc15\lib
E:\YOLOdll\onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu-1.15.0\lib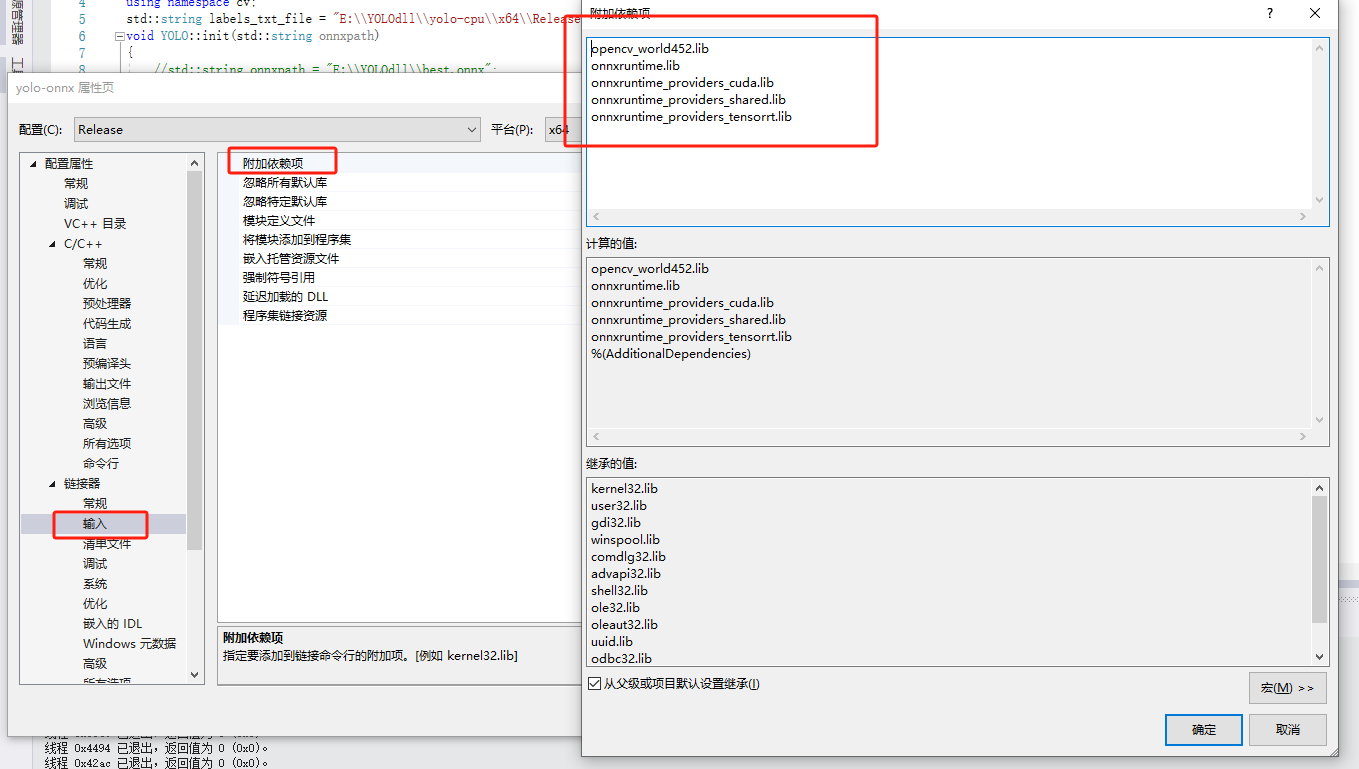
opencv_world452.lib
onnxruntime.lib
onnxruntime_providers_cuda.lib
onnxruntime_providers_shared.lib
onnxruntime_providers_tensorrt.lib全部代码如下:
三、
yolo.h
#pragma once
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "utils.h"
#include <string>
#include <onnxruntime_cxx_api.h>
#include <onnxruntime_c_api.h>
#include "cpu_provider_factory.h"
class YOLO
{
public:
void init(std::string engine_path);
void detect_img(cv::Mat& frame, cv::Mat& mask);
private:
int input_h = 0;//模型的输入维度
int input_w = 0;
Ort::Env env; // 环境对象作为成员变量
Ort::SessionOptions session_options;
Ort::Session session_{ nullptr }; // 会话对象作为成员变量(初始化为空)
std::vector<std::string> input_node_names;
std::vector<std::string> output_node_names;
};yolo.cpp
#include"yolo.h"
#include<vector>
using namespace cv;
std::string labels_txt_file = "E:\\YOLOdll\\yolo-cpu\\x64\\Release\\classes.txt";
void YOLO::init(std::string onnxpath)
{
//std::string onnxpath = "E:\\YOLOdll\\best.onnx";
std::wstring modelPath = std::wstring(onnxpath.begin(), onnxpath.end());
std::cout << "Attempting to load model from: " << onnxpath << std::endl;
env = Ort::Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_ERROR, "yolov8seg-onnx");
session_options.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(ORT_ENABLE_BASIC);//启动图形优化 加快运算速度
bool isCuda = true;
std::vector<std::string> available_providers = Ort::GetAvailableProviders();
std::cout << "Available providers: ";
for (const auto& provider : available_providers) {
std::cout << provider << "\n";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
auto cuda_available = std::find(available_providers.begin(), available_providers.end(), "CUDAExecutionProvider");
if (isCuda && (cuda_available == available_providers.end()))
{
std::cout << "Your ORT build without GPU. Change to CPU." << std::endl;
std::cout << "************* Infer model on CPU! *************" << std::endl;
}
else if (isCuda && (cuda_available != available_providers.end()))
{
std::cout << "************* Infer model on GPU! *************" << std::endl;
//#if ORT_API_VERSION < ORT_OLD_VISON
OrtCUDAProviderOptions cudaOption;
cudaOption.device_id = 0;
session_options.AppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(cudaOption);//第一种使用GPU的方法
//#else
// OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(session_options, 0);
//#endif
}
else
{
std::cout << "************* Infer model on CPU! *************" << std::endl;
OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider_CPU(session_options, 0);//CPU版本
}
session_ = Ort::Session(env, modelPath.c_str(), session_options);
std::wcout << L"Model loaded successfully." << std::endl;
// get input and output info
int input_nodes_num = session_.GetInputCount();
int output_nodes_num = session_.GetOutputCount();
//std::vector<std::string> input_node_names;
//std::vector<std::string> output_node_names;
Ort::AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;
// query input data format
for (int i = 0; i < input_nodes_num; i++) {
auto input_name = session_.GetInputNameAllocated(i, allocator);
input_node_names.push_back(input_name.get());
auto inputShapeInfo = session_.GetInputTypeInfo(i).GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo().GetShape();
int ch = inputShapeInfo[1];
input_h = inputShapeInfo[2];
input_w = inputShapeInfo[3];
std::cout << "input format: " << "channls" << ch << "x:" << input_h << "y:" << input_w << std::endl;
}
// query output data format, 25200x85
//int num = 116;
//int nc = 8400;
for (int i = 0; i < output_nodes_num; i++) {
auto output_name = session_.GetOutputNameAllocated(i, allocator);
output_node_names.push_back(output_name.get());
auto outShapeInfo = session_.GetOutputTypeInfo(i).GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo().GetShape();
//std::cout << "output format: " << (CLASSES + 4 + _segChannels) << "x" << Num_box << std::endl;
}
}
float sigmoid_function(float a)
{
float b = 1. / (1. + exp(-a));
return b;
}
std::vector<std::string> readClassNames()
{
std::vector<std::string> classNames;
std::ifstream fp(labels_txt_file);
if (!fp.is_open())
{
printf("could not open file...\n");
exit(-1);
}
std::string name;
while (!fp.eof())
{
std::getline(fp, name);
if (name.length())
classNames.push_back(name);
}
fp.close();
return classNames;
}
void YOLO::detect_img(cv::Mat& frame, cv::Mat& mask) {
if (frame.empty()) {
return;
}
cv::RNG rng; //生成随机数
float x_factor = 0.0;
float y_factor = 0.0;
std::vector<std::string> labels = readClassNames();
// 图象预处理 - 格式化操作
int64 start = cv::getTickCount();
int w = frame.cols;
int h = frame.rows;
int _max = std::max(h, w);
cv::Mat image = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(_max, _max), CV_8UC3);
cv::Rect roi(0, 0, w, h);
frame.copyTo(image(roi));
//x_factor = image.cols / static_cast<float>(640);
//y_factor = image.rows / static_cast<float>(640);
x_factor = image.cols / static_cast<float>(input_w);
y_factor = image.rows / static_cast<float>(input_h);
cv::Mat blob = cv::dnn::blobFromImage(image, 1.0 / 255.0, cv::Size(input_w, input_h), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
size_t tpixels = input_h * input_w * 3;
std::array<int64_t, 4> input_shape_info{ 1, 3, input_h, input_w };
// set input data and inference
auto allocator_info = Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU);
Ort::Value input_tensor_ = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(allocator_info, blob.ptr<float>(), tpixels, input_shape_info.data(), input_shape_info.size());
const std::array<const char*, 1> inputNames = { input_node_names[0].c_str() };
const std::array<const char*, 2> outNames = { output_node_names[0].c_str(), output_node_names[1].c_str() };
std::vector<Ort::Value> ort_outputs;
try {
ort_outputs = session_.Run(Ort::RunOptions{ nullptr }, inputNames.data(), &input_tensor_, 1, outNames.data(), outNames.size());
}
catch (std::exception e) {
std::cout << e.what() << std::endl;
}
// 116x8400, 1x32x160x160
const float* pdata = ort_outputs[0].GetTensorMutableData<float>();
const float* mdata = ort_outputs[1].GetTensorMutableData<float>();
auto data_detect_shape = ort_outputs[0].GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo().GetShape();
auto data_proto_shape = ort_outputs[1].GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo().GetShape();
std::cout << "output 0 format: " << data_detect_shape[1] << "x" << data_detect_shape[2] << std::endl;
std::cout << "output 1 format: " << "_segChannels:" << data_proto_shape[1] << "_segWidth:" << data_proto_shape[2] << "_segHeigh:" << data_proto_shape[3] << std::endl;
// 后处理, 1x116x8400, 84 - box, 80- min/max, 32 feature
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
std::vector<int> classIds;
std::vector<float> confidences;
std::vector<cv::Mat> masks;
cv::Mat dout(int(data_detect_shape[1]), int(data_detect_shape[2]), CV_32F, (float*)pdata);
cv::Mat det_output = dout.t(); // 116x8400 => 8400x116
cv::Mat mask1(int(data_proto_shape[1]), int(data_proto_shape[2])*int(data_proto_shape[3]), CV_32F, (float*)mdata);
float sx = float(data_proto_shape[2]) / float(input_w);
float sy = float(data_proto_shape[3]) / float(input_h);
for (int i = 0; i < det_output.rows; i++) {
cv::Mat classes_scores = det_output.row(i).colRange(4, int(data_detect_shape[1]) - int(data_proto_shape[1]));
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double score;
minMaxLoc(classes_scores, 0, &score, 0, &classIdPoint);
if (score > 0.25)
{
cv::Mat mask2 = det_output.row(i).colRange(int(data_detect_shape[1]) - int(data_proto_shape[1]), int(data_detect_shape[1]));
float cx = det_output.at<float>(i, 0);
float cy = det_output.at<float>(i, 1);
float ow = det_output.at<float>(i, 2);
float oh = det_output.at<float>(i, 3);
int x = static_cast<int>((cx - 0.5 * ow) * x_factor);
int y = static_cast<int>((cy - 0.5 * oh) * y_factor);
int width = static_cast<int>(ow * x_factor);
int height = static_cast<int>(oh * y_factor);
cv::Rect box;
box.x = x;
box.y = y;
box.width = width;
box.height = height;
boxes.push_back(box);
classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x);
confidences.push_back(score);
masks.push_back(mask2);
}
}
std::vector<int> indexes;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45, indexes);
cv::Mat rgb_mask = cv::Mat::zeros(frame.size(), frame.type());
// 显示
for (size_t i = 0; i < indexes.size(); i++) {
int idx = indexes[i];
int cid = classIds[idx];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];
int x1 = std::max(0, box.x);
int y1 = std::max(0, box.y);
int x2 = std::max(0, box.br().x);
int y2 = std::max(0, box.br().y);
cv::Mat m2 = masks[idx];
cv::Mat m = m2 * mask1;
for (int col = 0; col < m.cols; col++) {
m.at<float>(0, col) = sigmoid_function(m.at<float>(0, col));
}
//cv::Mat m1 = m.reshape(1, 160);
cv::Mat m1 = m.reshape(1, { int(data_proto_shape[2]), int(data_proto_shape[3]) });
int mx1 = std::max(0, int((x1 * sx) / x_factor));
int mx2 = std::max(0, int((x2 * sx) / x_factor));
int my1 = std::max(0, int((y1 * sy) / y_factor));
int my2 = std::max(0, int((y2 * sy) / y_factor));
if (mx2 >= m1.cols) {
mx2 = m1.cols - 1;
}
if (my2 >= m1.rows) {
my2 = m1.rows - 1;
}
cv::Mat mask_roi = m1(cv::Range(my1, my2), cv::Range(mx1, mx2));
cv::Mat rm, det_mask;
cv::resize(mask_roi, rm, cv::Size(x2 - x1, y2 - y1));
for (int r = 0; r < rm.rows; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < rm.cols; c++) {
float pv = rm.at<float>(r, c);
if (pv > 0.5) {
rm.at<float>(r, c) = 1.0;
}
else {
rm.at<float>(r, c) = 0.0;
}
}
}
rm = rm * rng.uniform(0, 255);
rm.convertTo(det_mask, CV_8UC1);
if ((y1 + det_mask.rows) >= frame.rows) {
y2 = frame.rows - 1;
}
if ((x1 + det_mask.cols) >= frame.cols) {
x2 = frame.cols - 1;
}
// std::cout << "x1: " << x1 << " x2:" << x2 << " y1: " << y1 << " y2: " << y2 << std::endl;
//cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(frame.cols, frame.rows), CV_8UC1);
det_mask(cv::Range(0, y2 - y1), cv::Range(0, x2 - x1)).copyTo(mask(cv::Range(y1, y2), cv::Range(x1, x2)));
add(rgb_mask, cv::Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255)), rgb_mask, mask);
//cv::rectangle(frame, boxes[idx], cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
putText(frame, labels[cid].c_str(), boxes[idx].tl(), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.0, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, 8);
}
float t = (cv::getTickCount() - start) / static_cast<float>(cv::getTickFrequency());
putText(frame, cv::format("FPS: %.2f", 1.0 / t), cv::Point(20, 40), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 2.0, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8);
//cv::Mat result;
//cv::addWeighted(frame, 0.5, rgb_mask, 0.5, 0, result);
//result.copyTo(frame);
//cv::Mat ori = frame.clone();
//cv::namedWindow("ori", 0);
//cv::imshow("ori", ori);
//cv::namedWindow("seg", 0);
//cv::imshow("seg", frame);
//cv::imwrite("E:\\YOLOdll\\seg.bmp", frame);
//cv::waitKey(0);
session_options.release();
session_.release();
}
test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include"yolo.h"
#include <onnxruntime_cxx_api.h>
#include <onnxruntime_c_api.h>
int main()
{
std::string model_path = "E:\\YOLOdll\\best.onnx";
YOLO* yolo = new YOLO();
yolo->init(model_path);
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("E:\\YOLOdll\\1.bmp");
//cv::imwrite("E:\\YOLOdll\\crop_Image.bmp", crop_Image);
//创建一个与裁剪后的图像一样大小的全黑图像
//cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat(img.rows, img.cols, img.type(), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(img.cols, img.rows), CV_8UC1);
//yolo预测 将掩码绘制到mask上
yolo->detect_img(img, mask);
cv::imwrite("E:\\YOLOdll\\mask2.bmp", mask);
return 0;
}
四、一些注意事项
1、需要将onnxruntime的几个dll放到对应的exe目录下
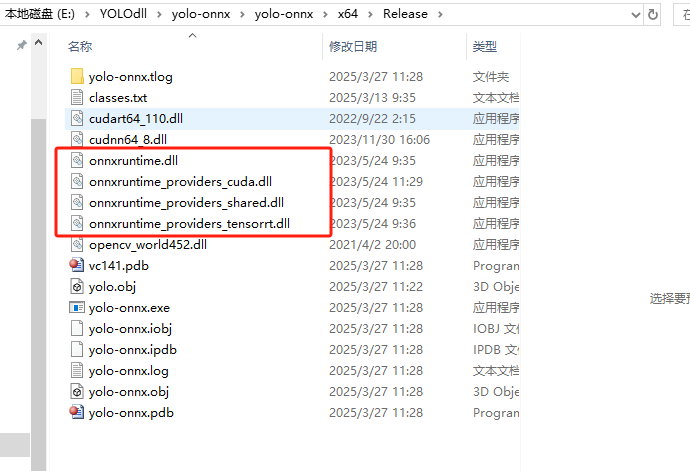
2、如果使用GPU加速的话需要将cuda、cudnn(前文已经说过加速的注意事项,可见标题二)的两个dll放到exe目录下
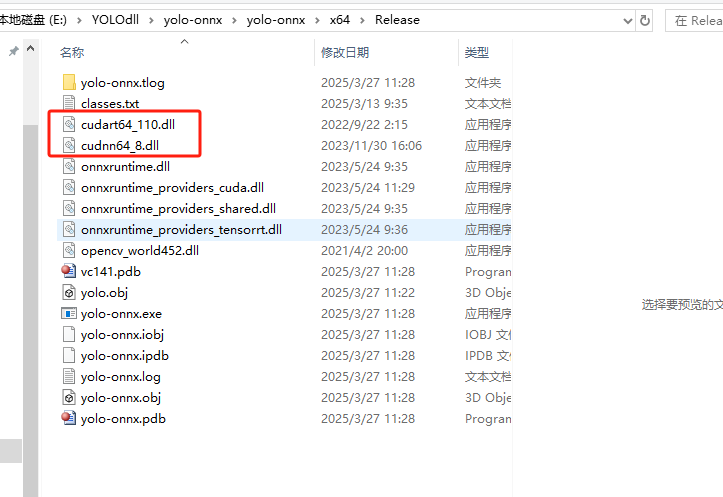
3、默认将opencv对应的dll放到exe目录下

























 1504
1504

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








