零、 概览
本章内容主要是关于实现训练Transformer LM的相关组件。
一、 Cross-entropy loss
语言模型(Language Model, LM)的定义是一个条件概率分布,更具体而言是给定前m个token,给出第m+1一个token的概率分布
p
θ
(
x
m
+
1
∣
x
1
:
m
)
p_{\theta}(x_{m+1}|x_{1:m})
pθ(xm+1∣x1:m)
给定一个数据集D,数据集中每一个entry是seq_len的文本,定义标准的交叉熵损失函数为负的对数似然函数(取负是因为基本上使用的都是梯度下降算法,我们希望概率更大,那么负概率就应该更小):
l
(
θ
;
D
)
=
1
∣
D
∣
m
∑
x
∈
D
∑
i
=
1
m
−
l
o
g
p
θ
(
x
i
+
1
∣
x
1
:
i
)
l(\theta;D)=\frac{1}{|D|m} \sum_{x \in D}\sum_{i=1}^{m} -logp_{\theta}(x_{i+1}|x_{1:i})
l(θ;D)=∣D∣m1x∈D∑i=1∑m−logpθ(xi+1∣x1:i)
transformer计算每个位置i的logits为
o
i
o_i
oi
对于
p
θ
(
x
i
+
1
∣
x
1
:
i
)
p_{\theta}(x_{i+1}|x_{1:i})
pθ(xi+1∣x1:i)的计算如下:
p
θ
(
x
i
+
1
∣
x
1
:
i
)
=
s
o
f
t
m
a
x
(
o
i
)
[
x
i
+
1
]
=
e
x
p
(
o
i
[
x
i
+
1
]
)
∑
a
=
1
v
o
c
a
b
_
s
i
z
e
e
x
p
(
o
i
[
a
]
)
p_{\theta}(x_{i+1}|x_{1:i})=softmax(o_i)[x_{i+1}]=\frac{exp(o_i[x_{i+1}])}{\sum_{a=1}^{vocab\_size}exp(o_i[a])}
pθ(xi+1∣x1:i)=softmax(oi)[xi+1]=∑a=1vocab_sizeexp(oi[a])exp(oi[xi+1])
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch import Tensor
from einops import einsum, rearrange
from jaxtyping import Float, Int
def cross_entropy(o_i: Float[Tensor, "... vocab_size"], x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
## 和softmax一样为了数值稳定
assert o_i.dim() in (2, 3), "dim error"
if o_i.dim() == 3:
o_i = rearrange(o_i, 'B S V -> (B S) V')
x = rearrange(x, 'B S -> (B S)')
B, V = o_i.shape
o_max = torch.max(o_i, dim=-1, keepdim=True).values
shift_o = o_i - o_max
exp_o = torch.exp(shift_o)
target_logit = shift_o[torch.arange(B), x]
sum_logit = torch.sum(exp_o, dim=-1)
# 这里有一些数学运算上面的技巧
loss = torch.log(sum_logit) - target_logit
return loss.mean()
adapters代码
def run_cross_entropy(
inputs: Float[Tensor, " batch_size vocab_size"], targets: Int[Tensor, " batch_size"]
) -> Float[Tensor, ""]:
"""Given a tensor of inputs and targets, compute the average cross-entropy
loss across examples.
Args:
inputs (Float[Tensor, "batch_size vocab_size"]): inputs[i][j] is the
unnormalized logit of jth class for the ith example.
targets (Int[Tensor, "batch_size"]): Tensor of shape (batch_size,) with the index of the correct class.
Each value must be between 0 and `num_classes - 1`.
Returns:
Float[Tensor, ""]: The average cross-entropy loss across examples.
"""
return cross_entropy(inputs, targets)
测试脚本
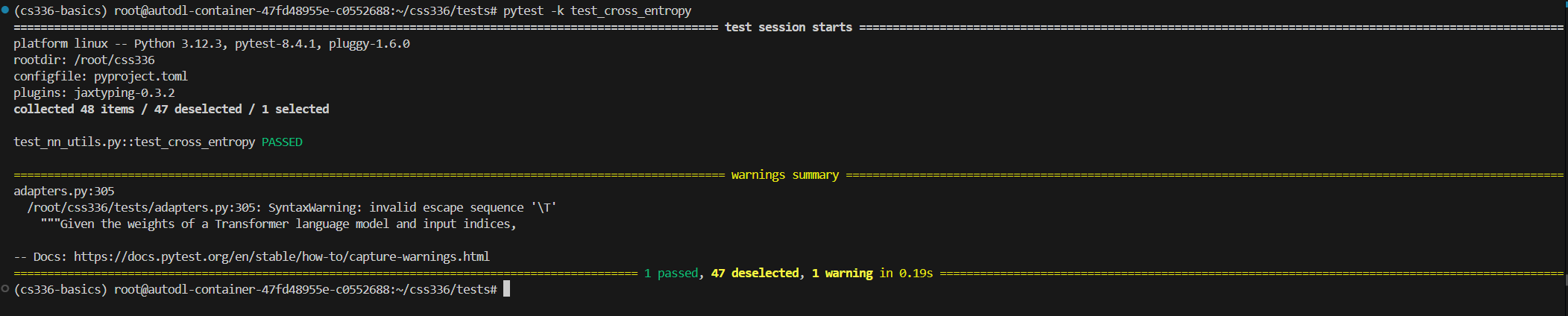
pytest -k test_cross_entropy
二、 The SGD Optimizer
具体梯度下降算法原理看这篇博客SGD 原理
from collections.abc import Callable, Iterable
from typing import Optional
import torch
import math
class SGD(torch.optim.Optimizer):
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3):
if lr < 0:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid learning rate: {lr}")
defaults = {"lr": lr}
super().__init__(params, defaults)
def step(self, closure: Optional[Callable] = None):
loss = None if closure is None else closure
for group in self.param_groups:
lr = group["lr"]
for p in group["params"]:
if p.grad is None:
continue
state = self.state[p]
t = state.get("t", 0)
grad = p.grad.data
p.data -= lr / math.sqrt(t + 1) * grad
state['t'] = t + 1
return loss
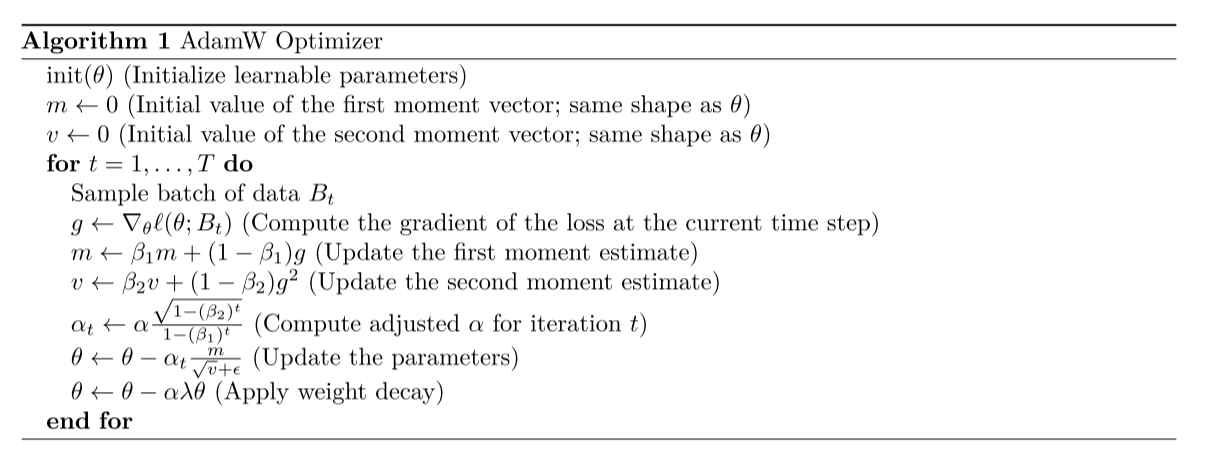
三、 AdamW
具体有关AdamW的原理可以看这篇博客AdamW原理
需要注意一点在优化器中进行参数的更新尽量原地操作。
| 方式 | 显存 | 速度 | 是否更新状态 |
|---|---|---|---|
| m.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1) # | ✅ 低(原地) | ✅ 快 | ✅ 是 |
| m = beta1 * m + (1 - beta1) * g | ❌ 高(新张量) | ❌ 慢 | ❌ 否(状态未变) |
class AdamW(torch.optim.Optimizer):
def __init__(self, params, lr: float =1e-3, betas: tuple[float, float] = (0.9, 0.999), eps: float=1e-8, weight_decay: float = 0.1):
if lr < 0:
raise ValueError(f"Invaild learning rate {lr}")
defaults = {
"lr": lr,
"betas": betas,
"eps": eps,
"weight_decay": weight_decay
}
super().__init__(params, defaults)
def step(self, closure: Optional[Callable] = None):
loss = None if closure is None else closure()
for group in self.param_groups:
for w in group['params']:
if w.grad is None:
continue
lr = group['lr']
beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
eps = group['eps']
weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
state = self.state[w]
grad = w.grad.data
t = state.get('t', 0)
if len(state) == 0:
state['t'] = 0
state['m'] = torch.zeros_like(w.data)
state['v'] = torch.zeros_like(w.data)
state['t'] += 1
t = state['t']
m, v = state['m'], state['v']
m.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1) #v = beta1 * m + (1 - beta1)
v.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - beta2) #v = beta2 * m + (1 - beta2) * grad ** 2
bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** t
bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** t
alpha = lr * math.sqrt(bias_correction2) / bias_correction1
w.data.addcdiv_(m, v.sqrt() + eps, value=-alpha)
if weight_decay != 0:
w.data.add_(w.data, alpha=-lr * weight_decay)
return loss
adapters
from optimizer import *
def get_adamw_cls() -> Any:
"""
Returns a torch.optim.Optimizer that implements AdamW.
"""
return AdamW
测试
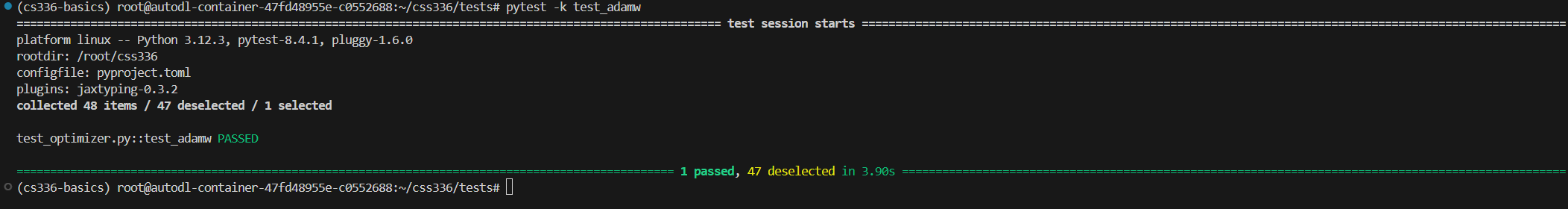
pytest -k test_adamw
四、 Learning rate scheduling
这里要求实现的是llama的余弦退火学习率调度器
余弦退火分为三个阶段
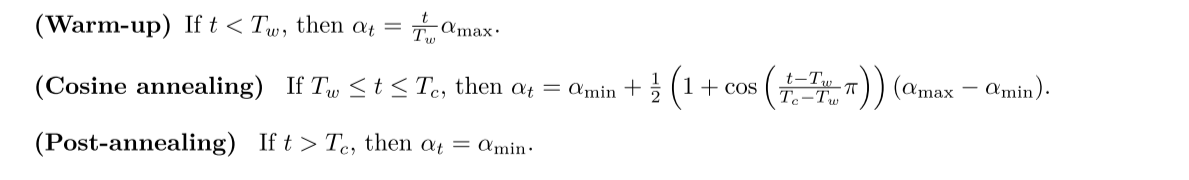
def lr_cosine_schedule(t, alpha_max, alpha_min, T_w, T_c) -> float:
alpha = 0
if t < T_w:
alpha = t * alpha_max / T_w
elif t >= T_w and t <= T_c:
alpha = alpha_min + 0.5 * (1 + math.cos((t - T_w) * math.pi / (T_c - T_w))) * (alpha_max - alpha_min)
else:
alpha = alpha_min
return alpha
adapters
def run_get_lr_cosine_schedule(
it: int,
max_learning_rate: float,
min_learning_rate: float,
warmup_iters: int,
cosine_cycle_iters: int,
):
"""
Given the parameters of a cosine learning rate decay schedule (with linear
warmup) and an iteration number, return the learning rate at the given
iteration under the specified schedule.
Args:
it (int): Iteration number to get learning rate for.
max_learning_rate (float): alpha_max, the maximum learning rate for
cosine learning rate schedule (with warmup).
min_learning_rate (float): alpha_min, the minimum / final learning rate for
the cosine learning rate schedule (with warmup).
warmup_iters (int): T_w, the number of iterations to linearly warm-up
the learning rate.
cosine_cycle_iters (int): T_c, the number of cosine annealing iterations.
Returns:
Learning rate at the given iteration under the specified schedule.
"""
return lr_cosine_schedule(it, max_learning_rate, min_learning_rate, warmup_iters, cosine_cycle_iters)
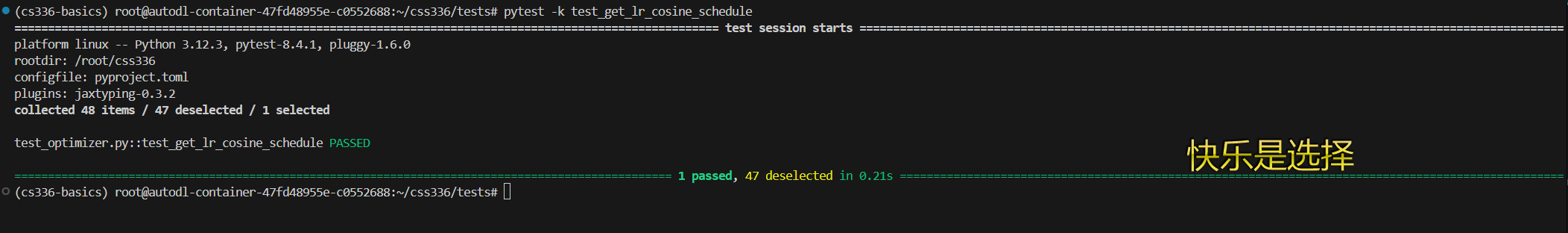
测试
pytest -k test_get_lr_cosine_schedule
五、 Gradient clipping
梯度裁剪的目的主要是防止梯度过大导致梯度爆炸以及造成训练不稳定。
需要注意的就是对梯度的操作也是需要原地操作。
这里采用的梯度裁剪方法是按全局范数裁剪(Global Norm Clipping)
设所有参数的梯度拼接成一个大向量
g
=
[
∇
θ
1
,
∇
θ
2
,
.
.
.
]
g = [ \nabla_{\theta_1}, \nabla_{\theta_2}, ... ]
g=[∇θ1,∇θ2,...],其L2范数为:
∣
∣
g
∣
∣
2
=
∑
i
(
∇
θ
i
)
2
||g||_2 = \sqrt{\sum_i(\nabla_{\theta_i})^2}
∣∣g∣∣2=i∑(∇θi)2
如果
∣
∣
g
∣
∣
2
>
m
a
x
n
o
r
m
||g||_2 > max_norm
∣∣g∣∣2>maxnorm,那么就将所有梯度缩放
g
←
g
M
a
x
n
o
r
m
∣
∣
g
∣
∣
2
+
ϵ
g \leftarrow g \frac{Max_norm}{||g||_2 + \epsilon}
g←g∣∣g∣∣2+ϵMaxnorm
def gradient_clipping(params: list[Tensor], M: float, eps: float = 1e-6) -> None:
# 原地操作不需要返回
flattened_grads = [p.grad.flatten() for p in params if p is not None and p.grad is not None]
all_grads = torch.cat(flattened_grads, dim=0)
norm = torch.norm(all_grads)
if norm >= M:
for p in params:
if p is not None and p.grad is not None:
p.grad *= M/(norm + eps)
adapter
def run_gradient_clipping(parameters: Iterable[torch.nn.Parameter], max_l2_norm: float) -> None:
"""Given a set of parameters, clip their combined gradients to have l2 norm at most max_l2_norm.
Args:
parameters (Iterable[torch.nn.Parameter]): collection of trainable parameters.
max_l2_norm (float): a positive value containing the maximum l2-norm.
The gradients of the parameters (parameter.grad) should be modified in-place.
"""
return gradient_clipping(parameters, max_l2_norm)
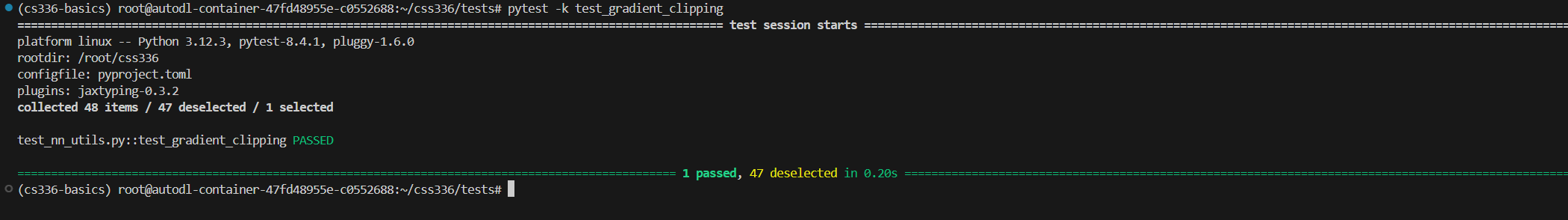
测试
pytest -k test_gradient_clipping
完整代码
完整代码在github仓库完整代码
如果对你有用可以给个star吗?
























 1158
1158

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








