吴恩达《深度学习》L1W2作业2
知识点:用神经网络思想实现逻辑回归

1 安装包
略
2 问题概述
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
问题说明:你将获得一个包含以下内容的数据集(“data.h5”):
标记为cat(y = 1)或非cat(y = 0)的m_train训练图像集
标记为cat或non-cat的m_test测试图像集
图像维度为(num_px,num_px,3),其中3表示3个通道(RGB)。 因此,每个图像都是正方形(高度= num_px)和(宽度= num_px)。
你将构建一个简单的图像识别算法,该算法可以将图片正确分类为猫和非猫。
让我们熟悉一下数据集吧, 首先通过运行以下代码来加载数据。
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File(r'D:\编程\深度学习\train_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File(r'D:\编程\深度学习\test_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes = load_dataset()
我们在图像数据集(训练和测试)的末尾添加了"_orig",以便对其进行预处理。 预处理后,我们将得到train_set_x和test_set_x(标签train_set_y和test_set_y不需要任何预处理)。
train_set_x_orig和test_set_x_orig的每一行都是代表图像的数组。 你可以通过运行以下代码来可视化示例。 还可以随意更改index值并重新运行以查看其他图像。
index = 5
plt.imshow(train_set_x_orig[index])
print ("y = " + str(train_set_y_orig[:, index]) + ", it's a '" + classes[np.squeeze(train_set_y_orig[:, index])].decode("utf-8") + "' picture.")
练习: 查找以下各项的值:
m_train(训练集示例数量)
m_test(测试集示例数量)
num_px(=训练图像的高度=训练图像的宽度)
请记住,“ train_set_x_orig”是一个维度为(m_train,num_px,num_px,3)的numpy数组。 例如,你可以通过编写“ train_set_x_orig.shape [0]”来访问“ m_train”。
m_train = train_set_x_orig.shape[0]
m_test = test_set_x_orig.shape[0]
num_px = train_set_x_orig.shape[1]
print ("Number of training examples: m_train = " + str(m_train))
print ("Number of testing examples: m_test = " + str(m_test))
print ("Height/Width of each image: num_px = " + str(num_px))
print ("Each image is of size: (" + str(num_px) + ", " + str(num_px) + ", 3)")
print ("train_set_x shape: " + str(train_set_x_orig.shape))
print ("train_set_y shape: " + str(train_set_y_orig.shape))
print ("test_set_x shape: " + str(test_set_x_orig.shape))
print ("test_set_y shape: " + str(test_set_y_orig.shape))

练习: 重塑训练和测试数据集,以便将大小(num_px,num_px,3)的图像展平为单个形状的向量(num_px * num_px * 3, 1)。
train_set_x_flatten = train_set_x_orig.reshape(train_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
test_set_x_flatten = test_set_x_orig.reshape(test_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
print ("train_set_x_flatten shape: " + str(train_set_x_flatten.shape))
print ("train_set_y shape: " + str(train_set_y_orig.shape))
print ("test_set_x_flatten shape: " + str(test_set_x_flatten.shape))
print ("test_set_y shape: " + str(test_set_y_orig.shape))
print ("sanity check after reshaping: " + str(train_set_x_flatten[0:5,0]))

为了表示彩色图像,必须为每个像素指定红、绿、蓝色通道(RGB),因此像素值实际上是一个从0到255的三个数字的向量。
机器学习中一个常见的预处理步骤是对数据集进行居中和标准化,这意味着你要从每个示例中减去整个numpy数组的均值,然后除以整个numpy数组的标准差。但是图片数据集则更为简单方便,并且只要将数据集的每一行除以255(像素通道的最大值),效果也差不多。
在训练模型期间,你将要乘以权重并向一些初始输入添加偏差以观察神经元的激活。然后,使用反向梯度传播以训练模型。但是,让特征具有相似的范围以至渐变不会爆炸是非常重要的。具体内容我们将在后面的教程中详细学习!
train_set_x = train_set_x_flatten / 255
test_set_x = test_set_x_flatten / 255
train_set_y = train_set_y_orig
test_set_y = test_set_y_orig
你需要记住的内容:
预处理数据集的常见步骤是:
- 找出数据的尺寸和维度(m_train,m_test,num_px等)
- 重塑数据集,以使每个示例都是大小为(num_px \ num_px \ 3,1)的向量
- “标准化”数据
3 学习算法的一般架构
现在是时候设计一种简单的算法来区分猫图像和非猫图像了。
你将使用神经网络思维方式建立Logistic回归。 下图说明了为什么“逻辑回归实际上是一个非常简单的神经网络!”

算法的数学表达式:
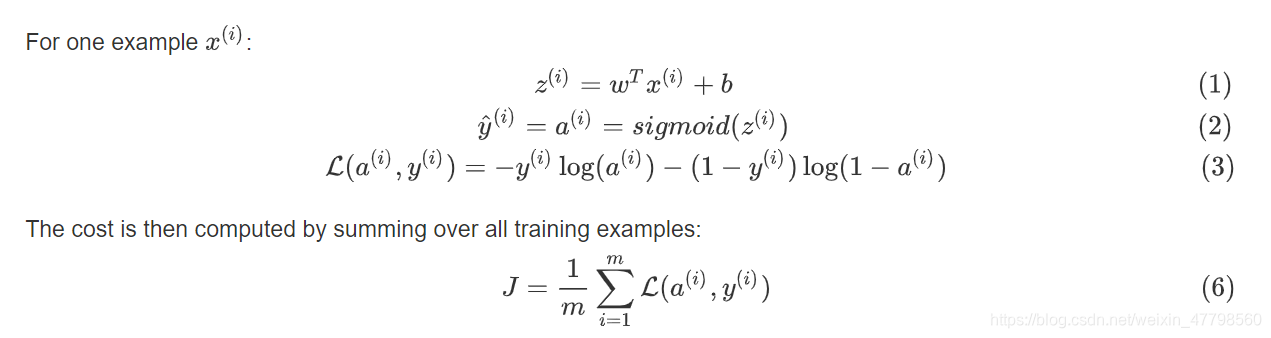
关键步骤:
在本练习中,你将执行以下步骤:
初始化模型参数
通过最小化损失来学习模型的参数
使用学习到的参数进行预测(在测试集上)
分析结果并得出结论
4 构建算法的各个部分
建立神经网络的主要步骤是:
1.定义模型结构(例如输入特征的数量)
2.初始化模型的参数
3.循环:
计算当前损失(正向传播)
计算当前梯度(向后传播)
更新参数(梯度下降)
你通常会分别构建1-3,然后将它们集成到一个称为“ model()”的函数中。
4.1 辅助函数
练习:使用“Python基础”中的代码,实现sigmoid()。 如上图所示,你需要计算
去预测。 使用np.exp()。
def sigmoid(z):
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
return s
4.2 初始化参数
练习: 在下面的单元格中实现参数初始化。 你必须将w初始化为零的向量。 如果你不知道要使用什么numpy函数,请在Numpy库的文档中查找np.zeros()。
def initializee_with_zeros(dim):
w = np.zeros((dim,1))
b = 0
return w,b
dim = 2
w, b = initialize_with_zeros(dim)
print ("w = " + str(w))
print ("b = " + str(b))
4.3 前向和后向传播
练习: 实现函数propagate()来计算损失函数及其梯度。
提示:

def propagate(w,b,x,y):
"""
Implement the cost function and its gradient for the propagation explained above
Arguments:
w -- weights, a numpy array of size (num_px * num_px * 3, 1)
b -- bias, a scalar
X -- data of size (num_px * num_px * 3, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat) of size (1, number of examples)
Return:
cost -- negative log-likelihood cost for logistic regression
dw -- gradient of the loss with respect to w, thus same shape as w
db -- gradient of the loss with respect to b, thus same shape as b
Tips:
- Write your code step by step for the propagation. np.log(), np.dot()
"""
m = x.shape[1]
a = sigmoid(w.T @ x + b)
cost = - 1 / m * np.sum(y * np.log(a) +(1-y) * np.log(1-a))
dw = 1 / m * x @ (a - y).T
db = 1 / m * np.sum(a - y)
return cost,dw,db
w, b, x, y = np.array([[1],[2]]), 2, np.array([[1,2],[3,4]]), np.array([[1,0]])
cost,dw,db = propagate(w,b,x,y)
print('cost='+str(cost))
print('dw='+str(dw))
print('db='+str(db))

优化函数

def optimize(w,b,x,y,iterations,learning_rate):
for i in range(iterations):
cost,dw,db = propagate(w,b,x,y)
w = w - learning_rate * dw
b = b - learning_rate * db
return w,b,dw,db
w,b,dw,db = optimize(w,b,x,y,100,0.02)
print(w,b,dw,db)
练习: 上一个函数将输出学习到的w和b。 我们能够使用w和b来预测数据集X的标签。实现**predict()**函数。 预测分类有两个步骤:
1.计算
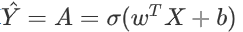
2.将a的项转换为0(如果激活<= 0.5)或1(如果激活> 0.5),并将预测结果存储在向量“ Y_prediction”中。 如果愿意,可以在for循环中使用if / else语句。
def predict(w,b,x,y):
m = x.shape[1]
y_predict = np.zeros((1,m))
w = w.reshape(x.shape[0],1)
a = sigmoid(w.T @ x + b)
for i in range(a.shape[1]):
if a[0,i] > 0.5:
y_predict[i] = 1
return y_predict
print(predict(w,b,x,y))
你需要记住以下几点:
你已经实现了以下几个函数:
初始化(w,b)
迭代优化损失以学习参数(w,b):
计算损失及其梯度
使用梯度下降更新参数
使用学到的(w,b)来预测给定示例集的标签
5 将所有功能合并到模型中
练习: 实现模型功能,使用以下符号:
Y_prediction对测试集的预测
Y_prediction_train对训练集的预测
w,损失,optimize()输出的梯度
def model(train_set_x,train_set_y,test_set_x,test_set_y):
w,b = initializee_with_zeros(train_set_x.shape[0])
cost,dw,db = propagate(w,b,train_set_x,train_set_y)
w, b, dw, db = optimize(w, b, train_set_x, train_set_y, 100, 0.02)
y_train = predict(w,b,train_set_x)
y_train_acc =np.mean(np.abs(y_train - train_set_y)) * 100
y_test = predict(w,b,test_set_x)
y_test_acc = np.mean(np.abs(y_test - test_set_y)) * 100
return y_train,y_train_acc,y_test,y_test_acc
print(model(train_set_x,train_set_y,test_set_x,test_set_y))











 本文介绍了如何使用吴恩达的深度学习课程中的知识点,通过神经网络构建逻辑回归模型来识别猫和非猫的图像。首先加载数据集,然后对数据进行预处理,包括重塑和标准化。接着,实现逻辑回归的组成部分,包括sigmoid函数、参数初始化、前向和后向传播。最后,训练模型并在测试集上进行预测,评估模型的准确率。
本文介绍了如何使用吴恩达的深度学习课程中的知识点,通过神经网络构建逻辑回归模型来识别猫和非猫的图像。首先加载数据集,然后对数据进行预处理,包括重塑和标准化。接着,实现逻辑回归的组成部分,包括sigmoid函数、参数初始化、前向和后向传播。最后,训练模型并在测试集上进行预测,评估模型的准确率。
















 1187
1187

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








