刚接触AimRT的小伙伴可能会疑惑,这个Channel和RPC(后面讲的)到底是什么呢?
但是当我们接触了之后,就会发现,其本质类似ROS的Topic通信!(其本质基于发布订阅模型)
接下来这里我们回顾一下ROS的Topic;
一、ROS中的Topic通信

话题通信是一种以发布订阅的方式实现不同节点之间数据传输的通信模型。数据发布对象称为发布方,数据订阅对象称之为订阅方,发布方和订阅方通过话题相关联,发布方将消息发布在话题上,订阅方则从该话题订阅消息,消息的流向是单向的。
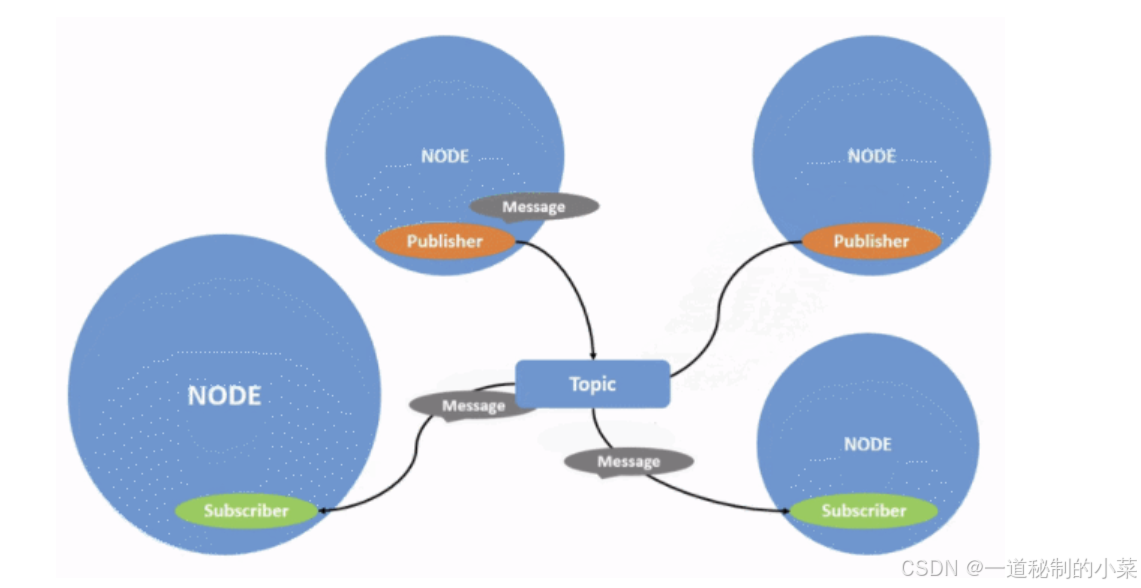
话题通信的发布方与订阅方是一种多对多的关系,也即,同一话题下可以存在多个发布方,也可以存在多个订阅方,这意味着数据会出现交叉传输的情况,当然如果没有订阅方,数据传输也会出现丢失的情况。
ROS中的话题通信用的地方非常多,对一些传统的传感器,例如雷达、相机、GPS等信息的采集,在ROS中通常可以通过节点发布采集到的数据;
二、Channel通信
目前AimRT也开发了一套基于发布-订阅的消息传递机制,其功能和ROS中的Topic等价,有关具体的AimRT的channel大家可以参考下面的链接:
AimRT 中的基本概念 — AimRT v0.10.0 documentation
在 AimRT 中,Channel 由接口层和后端两部分组成,两者相互解耦。

接口层:我认为这里大家可以类比网络的应用层和网络层等,这里的接口层主要是进行:用户书写代码,确定Channel的名字,确定发布者和接收者的Protocol;
后端:这里是实际上Channel的传输,在我们写的程序当中,我们可以通过配置文件设置后端使用得到协议;AimRT 官方提供了一些 Channel 后端,例如 mqtt、ros2 等,使用者也可以自行开发新的 Channel 后端。
protocol
Protocol表示的是两个module之间通信的接口层的协议,目前支持以下两种:
- Protobuf
- ROS2 msg/srv
除此之外,AimRT 的 Channel 通讯方式(后端)支持底层多种协议实现(http、mqtt、tcp、ROS2等),因此在 Channel 通讯时, AimRT 可以无缝兼容 ROS2;
接下来我们分别以基于Protobuf和基于ROS2 msg/srv两种消息接口的形式进行发布者和订阅者的相关操作;
三、基于Protobuf消息的发布者与订阅者
编写.proto文件
关于Protobuf的相关基本语法,大家可以参考我之前发的博客;
Protubuf入门 --- 01基本语法与编译使用-优快云博客
下面给出一个简单的示例消息:
syntax = "proto3";
package aimrt.protocols.example;
message ExampleEventMsg {
string msg = 1;
int32 num = 2;
}然后我们可以将其编译为对应的.cc文件和.h文件:
protoc --cpp_out=. event.proto此时会生成对应的event.pb.h头文件;
接下来我们编写发布者module模块代码;
.proto文件的编译(话题通信的框架下)
对于正常情况下.proto文件的编译,大家可以参考我的之前写的博客;
这里AimRT对于protobuf的编译提供了下面的编译指令,即我们可以在CMakeLists.txt进行相关文件的配置:
add_protobuf_gencode_target_for_proto_path:为某个路径下的.proto文件生成 C++ 代码,参数如下:
-
TARGET_NAME:生成的 CMake Target 名称;
-
PROTO_PATH:协议存放目录;
-
GENCODE_PATH:生成的桩代码存放路径;
-
DEP_PROTO_TARGETS:依赖的 Proto CMake Target;
-
OPTIONS:传递给 protoc 的其他参数;
例如下面的例子:
add_protobuf_gencode_target_for_proto_path(
TARGET_NAME example_pb_gencode
PROTO_PATH ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}
GENCODE_PATH ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR})然后当我们调用这个编译的.proto生成的.h的文件的时候,此时还需要在CMakeLists.txt里面添加以下指令:
target_link_libraries(my_lib PUBLIC example_pb_gencode)此时即可正常使用!
publisher_module.h
#pragma once
#include <atomic>
#include <future>
#include "aimrt_module_cpp_interface/module_base.h"
namespace aimrt::examples::cpp::pb_chn::normal_publisher_module {
class NormalPublisherModule : public aimrt::ModuleBase {
public:
NormalPublisherModule() = default;
~NormalPublisherModule() override = default;
ModuleInfo Info() const override {
return ModuleInfo{.name = "NormalPublisherModule"};
}
bool Initialize(aimrt::CoreRef core) override;
bool Start() override;
void Shutdown() override;
private:
auto GetLogger() { return core_.GetLogger(); }
void MainLoop();
private:
aimrt::CoreRef core_;
aimrt::executor::ExecutorRef executor_;
std::atomic_bool run_flag_ = false;
std::promise<void> stop_sig_;
std::string topic_name_ = "test_topic";
double channel_frq_ = 0.5;
aimrt::channel::PublisherRef publisher_;
};
}接下来我们依次对上面的代码模块进行分析:
- 主要的模块(初始化、开始和结束)与我们之前进行的模块一样;
- 除此之外,还有一个executor,这里是用于发送者将任务投递到执行器,然后执行器可以发送对应的任务;
- run_flag:用来标识模块是否在运行;
- stop_sig_n:当发送任务循环结束时,此时会给发送对应的信号给关闭模块,shutdown收到后此时就对模块进行关闭;
- 除此之外,这里还定义了话题名、发布者和发布的频率;
publisher_module.cc
#include "normal_publisher_module/normal_publisher_module.h"
#include "aimrt_module_protobuf_interface/channel/protobuf_channel.h"
#include "aimrt_module_protobuf_interface/util/protobuf_tools.h"
#include "yaml-cpp/yaml.h"
#include "event.pb.h"
namespace aimrt::examples::cpp::pb_chn::normal_publisher_module {
bool NormalPublisherModule::Initialize(aimrt::CoreRef core) {
core_ = core;
try {
// Read cfg
auto file_path = core_.GetConfigurator().GetConfigFilePath();
if (!file_path.empty()) {
YAML::Node cfg_node = YAML::LoadFile(std::string(file_path));
topic_name_ = cfg_node["topic_name"].as<std::string>();
channel_frq_ = cfg_node["channel_frq"].as<double>();
}
// Get executor handle
executor_ = core_.GetExecutorManager().GetExecutor("work_thread_pool");
AIMRT_CHECK_ERROR_THROW(executor_ && executor_.SupportTimerSchedule(),
"Get executor 'work_thread_pool' failed.");
// Register publish type
publisher_ = core_.GetChannelHandle().GetPublisher(topic_name_);
AIMRT_CHECK_ERROR_THROW(publisher_, "Get publisher for topic '{}' failed.", topic_name_);
bool ret = aimrt::channel::RegisterPublishType<aimrt::protocols::example::ExampleEventMsg>(publisher_);
AIMRT_CHECK_ERROR_THROW(ret, "Register publish type failed.");
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
AIMRT_ERROR("Init failed, {}", e.what());
return false;
}
AIMRT_INFO("Init succeeded.");
return true;
}
bool NormalPublisherModule::Start() {
try {
run_flag_ = true;
executor_.Execute(std::bind(&NormalPublisherModule::MainLoop, this));
} catch (const std::excepti




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










