原文参考链接:[https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/icefire_tyh/article/details/52064910]
习题
3.1
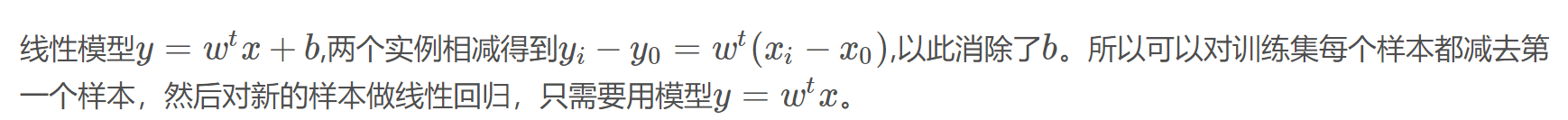
3.2
如果一个多元函数是凸的,那么它的Hessian矩阵是半正定的

3.3
#导入需要的包
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#导入数据
data = np.array([[0.697, 0.460, 1],
[0.774, 0.376, 1],
[0.634, 0.264, 1],
[0.608, 0.318, 1],
[0.556, 0.215, 1],
[0.403, 0.237, 1],
[0.481, 0.149, 1],
[0.437, 0.211, 1],
[0.666, 0.091, 0],
[0.243, 0.267, 0],
[0.245, 0.057, 0],
[0.343, 0.099, 0],
[0.639, 0.161, 0],
[0.657, 0.198, 0],
[0.360, 0.370, 0],
[0.593, 0.042, 0],
[0.719, 0.103, 0]])
定义变量
X = data[:,0:2]
y = data[:,2]
#随机划分训练集和测试集
X_train,X_test,Y_train,Y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.25,random_state=33)
#定义sigmoid
def sigmoid(z):
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
return s
def initialize_with_zeros(dim):
"""
This function creates a vector of zeros of shape (dim, 1) for w and initializes b to 0.
"""
w = np.zeros((dim, 1))
b = 0
assert (w.shape == (dim, 1))
assert (isinstance(b, float) or isinstance(b, int))
return w, b
def propagate(w, b, X, Y):
"""
Implement the cost function and its gradient for the propagation explained above
"""
m = X.shape[1]
A = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T, X) + b)
# 计算损失
cost = -np.sum(Y * np.log(A) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - A))/ m
dw = np.dot(X, (A - Y).T) / m
db = np.sum(A - Y) / m
assert (dw.shape == w.shape)
assert (db.dtype == float)
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
assert (cost.shape == ())
grads = {
"dw": dw,
"db": db}








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 5120
5120

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








