U-Net网络模型(注意力改进版本)
这一段时间做项目用到了U-Net网络模型,但是原始的U-Net网络还有很大的改良空间,在卷积下采样的过程中加入了通道注意力和空间注意力
常规的U-net模型如下图:

红色箭头为可以添加的地方:即下采样之间。

通道空间注意力是一个即插即用的注意力模块(如下图):

代码加入之后对于分割效果是有提升的:(代码如下)
CBAM代码:
class ChannelAttentionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, ratio=16):
super(ChannelAttentionModule, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.shared_MLP = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // ratio, 1, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(channel // ratio, channel, 1, bias=False)
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avgout = self.shared_MLP(self.avg_pool(x))
maxout = self.shared_MLP(self.max_pool(x))
return self.sigmoid(avgout + maxout)
class SpatialAttentionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SpatialAttentionModule, self).__init__()
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=2, out_channels=1, kernel_size=7, stride=1, padding=3)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avgout = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
maxout, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
out = torch.cat([avgout, maxout], dim=1)
out = self.sigmoid(self.conv2d(out))
return out
class CBAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel):
super(CBAM, self).__init__()
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttentionModule(channel)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttentionModule()
def forward(self, x):
out = self.channel_attention(x) * x
out = self.spatial_attention(out) * out
return out
网络模型结合之后代码
class conv_block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,ch_in,ch_out):
super(conv_block,self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(ch_out, ch_out, kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x
class up_conv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,ch_in,ch_out):
super(up_conv,self).__init__()
self.up = nn.Sequential(
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(ch_in,ch_out,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.up(x)
return x
class U_Net_v1(nn.Module): #添加了空间注意力和通道注意力
def __init__(self,img_ch=3,output_ch=2):
super(U_Net_v1,self).__init__()
self.Maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2)
self.Conv1 = conv_block(ch_in=img_ch,ch_out=64) #64
self.Conv2 = conv_block(ch_in=64,ch_out=128) #64 128
self.Conv3 = conv_block(ch_in=128,ch_out=256) #128 256
self.Conv4 = conv_block(ch_in=256,ch_out=512) #256 512
self.Conv5 = conv_block(ch_in=512,ch_out=1024) #512 1024
self.cbam1 = CBAM(channel=64)
self.cbam2 = CBAM(channel=128)
self.cbam3 = CBAM(channel=256)
self.cbam4 = CBAM(channel=512)
self.Up5 = up_conv(ch_in=1024,ch_out=512) #1024 512
self.Up_conv5 = conv_block(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
self.Up4 = up_conv(ch_in=512,ch_out=256) #512 256
self.Up_conv4 = conv_block(ch_in=512, ch_out=256)
self.Up3 = up_conv(ch_in=256,ch_out=128) #256 128
self.Up_conv3 = conv_block(ch_in=256, ch_out=128)
self.Up2 = up_conv(ch_in=128,ch_out=64) #128 64
self.Up_conv2 = conv_block(ch_in=128, ch_out=64)
self.Conv_1x1 = nn.Conv2d(64,output_ch,kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) #64
def forward(self,x):
# encoding path
x1 = self.Conv1(x)
x1 = self.cbam1(x1) + x1
x2 = self.Maxpool(x1)
x2 = self.Conv2(x2)
x2 = self.cbam2(x2) + x2
x3 = self.Maxpool(x2)
x3 = self.Conv3(x3)
x3 = self.cbam3(x3) + x3
x4 = self.Maxpool(x3)
x4 = self.Conv4(x4)
x4 = self.cbam4(x4) + x4
x5 = self.Maxpool(x4)
x5 = self.Conv5(x5)
# decoding + concat path
d5 = self.Up5(x5)
d5 = torch.cat((x4,d5),dim=1)
d5 = self.Up_conv5(d5)
d4 = self.Up4(d5)
d4 = torch.cat((x3,d4),dim=1)
d4 = self.Up_conv4(d4)
d3 = self.Up3(d4)
d3 = torch.cat((x2,d3),dim=1)
d3 = self.Up_conv3(d3)
d2 = self.Up2(d3)
d2 = torch.cat((x1,d2),dim=1)
d2 = self.Up_conv2(d2)
d1 = self.Conv_1x1(d2)
return d1
YOLOv8最新改进系列:YOLOv8融合BiFPN网络,亲测显著涨点!
BiFPN网络
BiFPN 的主要思想:高效双向跨尺度连接和加权特征融合。
多尺度特征表示是目标检测的重点方向之一,作者认为其主要困难是如何有效地表示和处理多尺度特征。
早期的检测器通常直接根据从骨干网络中提取的金字塔特征层次结构进行预测 。
特征金字塔网络 (FPN)提出了一种自上而下的途径来组合多尺度特征。
基于FPN,PANet 在 FPN 之上添加了一个额外的自下而上的路径聚合网络;
NAS‑FPN [8]利用神经架构搜索来自动设计特征网络拓扑。虽然实现了更好的性能,但 NAS‑FPN 在搜索过程中需要数千 GPU 小时,并且生成的特征网络是不规则的,因此难以解释。
BiFPN:引入可学习的权重来学习不同输入特征的重要性,同时重复应用自上而下和自下而上的多尺度特征融合.
下图表示各类网络模型的结构:

( a ) FPN 引入自上而下的路径来融合从 3 级到 7 级(P3 ‑ P7)的多尺度特征;
( b ) PANet 在 FPN 之上添加了一个额外的自下而上的路径;
( c ) NAS‑FPN 使用神经架构搜索找到不规则的特征网络拓扑,然后重复应用相同的块;
( d ) BiFPN 双向跨尺度连接和加权特征融合,具有更好的准确性和效率权衡。
简单了解过后,我们开始改进!
提示:以下是本篇文章改进内容,下面案例可供参考
一、替换yaml文件
改进后的文件如下:
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat_BiFPN, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat_BiFPN, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat_BiFPN, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
二、新建模块代码
在nn文件夹中新建bifpn.py文件
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Concat_BiFPN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dimension=1):
super(Concat_BiFPN, self).__init__()
self.d = dimension
self.w = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(3, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=True)
self.epsilon = 0.0001
def forward(self, x):
w = self.w
weight = w / (torch.sum(w, dim=0) + self.epsilon) # 将权重进行归一化
# Fast normalized fusion
x = [weight[0] * x[0], weight[1] * x[1]]
return torch.cat(x, self.d)
三、替换tasks.py文件
在nn文件夹中找到tasks.py文件,进行内容上的替换即可
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
import contextlib
from copy import deepcopy
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from ultralytics.nn.modules import (AIFI, C1, C2, C3, C3TR, SPP, SPPF, Bottleneck, BottleneckCSP, C2f, C3Ghost, C3x,
Classify, Concat, Conv, Conv2, ConvTranspose, Detect, DWConv, DWConvTranspose2d,
Focus, GhostBottleneck, GhostConv, HGBlock, HGStem, Pose, RepC3, RepConv,
RTDETRDecoder, Segment)
from ultralytics.utils import DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, DEFAULT_CFG_KEYS, LOGGER, colorstr, emojis, yaml_load
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_requirements, check_suffix, check_yaml
from ultralytics.utils.loss import v8ClassificationLoss, v8DetectionLoss, v8PoseLoss, v8SegmentationLoss
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import feature_visualization
from ultralytics.utils.torch_utils import (fuse_conv_and_bn, fuse_deconv_and_bn, initialize_weights, intersect_dicts,
make_divisible, model_info, scale_img, time_sync)
from ultralytics.nn.qlhnet import ShuffleNetV2, Conv_maxpool
from ultralytics.nn.se import SEAttention
from ultralytics.nn.bifpn import Concat_BiFPN
try:
import thop
except ImportError:
thop = None
class BaseModel(nn.Module):
"""
The BaseModel class serves as a base class for all the models in the Ultralytics YOLO family.
"""
def forward(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Forward pass of the model on a single scale.
Wrapper for `_forward_once` method.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor | dict): The input image tensor or a dict including image tensor and gt labels.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The output of the network.
"""
if isinstance(x, dict): # for cases of training and validating while training.
return self.loss(x, *args, **kwargs)
return self.predict(x, *args, **kwargs)
def predict(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False, augment=False):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
augment (bool): Augment image during prediction, defaults to False.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
if augment:
return self._predict_augment(x)
return self._predict_once(x, profile, visualize)
def _predict_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
y, dt = [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
return x
def _predict_augment(self, x):
"""Perform augmentations on input image x and return augmented inference."""
LOGGER.warning(f'WARNING ⚠️ {self.__class__.__name__} does not support augmented inference yet. '
f'Reverting to single-scale inference instead.')
return self._predict_once(x)
def _profile_one_layer(self, m, x, dt):
"""
Profile the computation time and FLOPs of a single layer of the model on a given input.
Appends the results to the provided list.
Args:
m (nn.Module): The layer to be profiled.
x (torch.Tensor): The input data to the layer.
dt (list): A list to store the computation time of the layer.
Returns:
None
"""
c = m == self.model[-1] and isinstance(x, list) # is final layer list, copy input as inplace fix
flops = thop.profile(m, inputs=[x.copy() if c else x], verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0 # FLOPs
t = time_sync()
for _ in range(10):
m(x.copy() if c else x)
dt.append((time_sync() - t) * 100)
if m == self.model[0]:
LOGGER.info(f"{'time (ms)':>10s} {'GFLOPs':>10s} {'params':>10s} module")
LOGGER.info(f'{dt[-1]:10.2f} {flops:10.2f} {m.np:10.0f} {m.type}')
if c:
LOGGER.info(f"{sum(dt):10.2f} {'-':>10s} {'-':>10s} Total")
def fuse(self, verbose=True):
"""
Fuse the `Conv2d()` and `BatchNorm2d()` layers of the model into a single layer, in order to improve the
computation efficiency.
Returns:
(nn.Module): The fused model is returned.
"""
if not self.is_fused():
for m in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(m, (Conv, Conv2, DWConv)) and hasattr(m, 'bn'):
if isinstance(m, Conv2):
m.fuse_convs()
m.conv = fuse_conv_and_bn(m.conv, m.bn) # update conv
delattr(m, 'bn') # remove batchnorm
m.forward = m.forward_fuse # update forward
if isinstance(m, ConvTranspose) and hasattr(m, 'bn'):
m.conv_transpose = fuse_deconv_and_bn(m.conv_transpose, m.bn)
delattr(m, 'bn') # remove batchnorm
m.forward = m.forward_fuse # update forward
if isinstance(m, RepConv):
m.fuse_convs()
m.forward = m.forward_fuse # update forward
self.info(verbose=verbose)
return self
def is_fused(self, thresh=10):
"""
Check if the model has less than a certain threshold of BatchNorm layers.
Args:
thresh (int, optional): The threshold number of BatchNorm layers. Default is 10.
Returns:
(bool): True if the number of BatchNorm layers in the model is less than the threshold, False otherwise.
"""
bn = tuple(v for k, v in nn.__dict__.items() if 'Norm' in k) # normalization layers, i.e. BatchNorm2d()
return sum(isinstance(v, bn) for v in self.modules()) < thresh # True if < 'thresh' BatchNorm layers in model
def info(self, detailed=False, verbose=True, imgsz=640):
"""
Prints model information
Args:
detailed (bool): if True, prints out detailed information about the model. Defaults to False
verbose (bool): if True, prints out the model information. Defaults to False
imgsz (int): the size of the image that the model will be trained on. Defaults to 640
"""
return model_info(self, detailed=detailed, verbose=verbose, imgsz=imgsz)
def _apply(self, fn):
"""
Applies a function to all the tensors in the model that are not parameters or registered buffers.
Args:
fn (function): the function to apply to the model
Returns:
A model that is a Detect() object.
"""
self = super()._apply(fn)
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, (Detect, Segment)):
m.stride = fn(m.stride)
m.anchors = fn(m.anchors)
m.strides = fn(m.strides)
return self
def load(self, weights, verbose=True):
"""
Load the weights into the model.
Args:
weights (dict | torch.nn.Module): The pre-trained weights to be loaded.
verbose (bool, optional): Whether to log the transfer progress. Defaults to True.
"""
model = weights['model'] if isinstance(weights, dict) else weights # torchvision models are not dicts
csd = model.float().state_dict() # checkpoint state_dict as FP32
csd = intersect_dicts(csd, self.state_dict()) # intersect
self.load_state_dict(csd, strict=False) # load
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f'Transferred {len(csd)}/{len(self.model.state_dict())} items from pretrained weights')
def loss(self, batch, preds=None):
"""
Compute loss
Args:
batch (dict): Batch to compute loss on
preds (torch.Tensor | List[torch.Tensor]): Predictions.
"""
if not hasattr(self, 'criterion'):
self.criterion = self.init_criterion()
preds = self.forward(batch['img']) if preds is None else preds
return self.criterion(preds, batch)
def init_criterion(self):
raise NotImplementedError('compute_loss() needs to be implemented by task heads')
class DetectionModel(BaseModel):
"""YOLOv8 detection model."""
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov8n.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, verbose=True): # model, input channels, number of classes
super().__init__()
self.yaml = cfg if isinstance(cfg, dict) else yaml_model_load(cfg) # cfg dict
# Define model
ch = self.yaml['ch'] = self.yaml.get('ch', ch) # input channels
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']:
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml nc={self.yaml['nc']} with nc={nc}")
self.yaml['nc'] = nc # override YAML value
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=ch, verbose=verbose) # model, savelist
self.names = {i: f'{i}' for i in range(self.yaml['nc'])} # default names dict
self.inplace = self.yaml.get('inplace', True)
# Build strides
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, (Detect, Segment, Pose)):
s = 256 # 2x min stride
m.inplace = self.inplace
forward = lambda x: self.forward(x)[0] if isinstance(m, (Segment, Pose)) else self.forward(x)
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
self.stride = m.stride
m.bias_init() # only run once
else:
self.stride = torch.Tensor([32]) # default stride for i.e. RTDETR
# Init weights, biases
initialize_weights(self)
if verbose:
self.info()
LOGGER.info('')
def _predict_augment(self, x):
"""Perform augmentations on input image x and return augmented inference and train outputs."""
img_size = x.shape[-2:] # height, width
s = [1, 0.83, 0.67] # scales
f = [None, 3, None] # flips (2-ud, 3-lr)
y = [] # outputs
for si, fi in zip(s, f):
xi = scale_img(x.flip(fi) if fi else x, si, gs=int(self.stride.max()))
yi = super().predict(xi)[0] # forward
yi = self._descale_pred(yi, fi, si, img_size)
y.append(yi)
y = self._clip_augmented(y) # clip augmented tails
return torch.cat(y, -1), None # augmented inference, train
@staticmethod
def _descale_pred(p, flips, scale, img_size, dim=1):
"""De-scale predictions following augmented inference (inverse operation)."""
p[:, :4] /= scale # de-scale
x, y, wh, cls = p.split((1, 1, 2, p.shape[dim] - 4), dim)
if flips == 2:
y = img_size[0] - y # de-flip ud
elif flips == 3:
x = img_size[1] - x # de-flip lr
return torch.cat((x, y, wh, cls), dim)
def _clip_augmented(self, y):
"""Clip YOLOv5 augmented inference tails."""
nl = self.model[-1].nl # number of detection layers (P3-P5)
g = sum(4 ** x for x in range(nl)) # grid points
e = 1 # exclude layer count
i = (y[0].shape[-1] // g) * sum(4 ** x for x in range(e)) # indices
y[0] = y[0][..., :-i] # large
i = (y[-1].shape[-1] // g) * sum(4 ** (nl - 1 - x) for x in range(e)) # indices
y[-1] = y[-1][..., i:] # small
return y
def init_criterion(self):
return v8DetectionLoss(self)
class SegmentationModel(DetectionModel):
"""YOLOv8 segmentation model."""
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov8n-seg.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, verbose=True):
"""Initialize YOLOv8 segmentation model with given config and parameters."""
super().__init__(cfg=cfg, ch=ch, nc=nc, verbose=verbose)
def init_criterion(self):
return v8SegmentationLoss(self)
class PoseModel(DetectionModel):
"""YOLOv8 pose model."""
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov8n-pose.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, data_kpt_shape=(None, None), verbose=True):
"""Initialize YOLOv8 Pose model."""
if not isinstance(cfg, dict):
cfg = yaml_model_load(cfg) # load model YAML
if any(data_kpt_shape) and list(data_kpt_shape) != list(cfg['kpt_shape']):
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml kpt_shape={cfg['kpt_shape']} with kpt_shape={data_kpt_shape}")
cfg['kpt_shape'] = data_kpt_shape
super().__init__(cfg=cfg, ch=ch, nc=nc, verbose=verbose)
def init_criterion(self):
return v8PoseLoss(self)
class ClassificationModel(BaseModel):
"""YOLOv8 classification model."""
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov8n-cls.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, verbose=True):
"""Init ClassificationModel with YAML, channels, number of classes, verbose flag."""
super().__init__()
self._from_yaml(cfg, ch, nc, verbose)
def _from_yaml(self, cfg, ch, nc, verbose):
"""Set YOLOv8 model configurations and define the model architecture."""
self.yaml = cfg if isinstance(cfg, dict) else yaml_model_load(cfg) # cfg dict
# Define model
ch = self.yaml['ch'] = self.yaml.get('ch', ch) # input channels
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']:
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml nc={self.yaml['nc']} with nc={nc}")
self.yaml['nc'] = nc # override YAML value
elif not nc and not self.yaml.get('nc', None):
raise ValueError('nc not specified. Must specify nc in model.yaml or function arguments.')
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=ch, verbose=verbose) # model, savelist
self.stride = torch.Tensor([1]) # no stride constraints
self.names = {i: f'{i}' for i in range(self.yaml['nc'])} # default names dict
self.info()
@staticmethod
def reshape_outputs(model, nc):
"""Update a TorchVision classification model to class count 'n' if required."""
name, m = list((model.model if hasattr(model, 'model') else model).named_children())[-1] # last module
if isinstance(m, Classify): # YOLO Classify() head
if m.linear.out_features != nc:
m.linear = nn.Linear(m.linear.in_features, nc)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): # ResNet, EfficientNet
if m.out_features != nc:
setattr(model, name, nn.Linear(m.in_features, nc))
elif isinstance(m, nn.Sequential):
types = [type(x) for x in m]
if nn.Linear in types:
i = types.index(nn.Linear) # nn.Linear index
if m[i].out_features != nc:
m[i] = nn.Linear(m[i].in_features, nc)
elif nn.Conv2d in types:
i = types.index(nn.Conv2d) # nn.Conv2d index
if m[i].out_channels != nc:
m[i] = nn.Conv2d(m[i].in_channels, nc, m[i].kernel_size, m[i].stride, bias=m[i].bias is not None)
def init_criterion(self):
"""Compute the classification loss between predictions and true labels."""
return v8ClassificationLoss()
class RTDETRDetectionModel(DetectionModel):
def __init__(self, cfg='rtdetr-l.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, verbose=True):
super().__init__(cfg=cfg, ch=ch, nc=nc, verbose=verbose)
def init_criterion(self):
"""Compute the classification loss between predictions and true labels."""
from ultralytics.models.utils.loss import RTDETRDetectionLoss
return RTDETRDetectionLoss(nc=self.nc, use_vfl=True)
def loss(self, batch, preds=None):
if not hasattr(self, 'criterion'):
self.criterion = self.init_criterion()
img = batch['img']
# NOTE: preprocess gt_bbox and gt_labels to list.
bs = len(img)
batch_idx = batch['batch_idx']
gt_groups = [(batch_idx == i).sum().item() for i in range(bs)]
targets = {
'cls': batch['cls'].to(img.device, dtype=torch.long).view(-1),
'bboxes': batch['bboxes'].to(device=img.device),
'batch_idx': batch_idx.to(img.device, dtype=torch.long).view(-1),
'gt_groups': gt_groups}
preds = self.predict(img, batch=targets) if preds is None else preds
dec_bboxes, dec_scores, enc_bboxes, enc_scores, dn_meta = preds if self.training else preds[1]
if dn_meta is None:
dn_bboxes, dn_scores = None, None
else:
dn_bboxes, dec_bboxes = torch.split(dec_bboxes, dn_meta['dn_num_split'], dim=2)
dn_scores, dec_scores = torch.split(dec_scores, dn_meta['dn_num_split'], dim=2)
dec_bboxes = torch.cat([enc_bboxes.unsqueeze(0), dec_bboxes]) # (7, bs, 300, 4)
dec_scores = torch.cat([enc_scores.unsqueeze(0), dec_scores])
loss = self.criterion((dec_bboxes, dec_scores),
targets,
dn_bboxes=dn_bboxes,
dn_scores=dn_scores,
dn_meta=dn_meta)
# NOTE: There are like 12 losses in RTDETR, backward with all losses but only show the main three losses.
return sum(loss.values()), torch.as_tensor([loss[k].detach() for k in ['loss_giou', 'loss_class', 'loss_bbox']],
device=img.device)
def predict(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False, batch=None, augment=False):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False
batch (dict): A dict including gt boxes and labels from dataloader.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
y, dt = [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model[:-1]: # except the head part
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
head = self.model[-1]
x = head([y[j] for j in head.f], batch) # head inference
return x
class Ensemble(nn.ModuleList):
"""Ensemble of models."""
def __init__(self):
"""Initialize an ensemble of models."""
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x, augment=False, profile=False, visualize=False):
"""Function generates the YOLOv5 network's final layer."""
y = [module(x, augment, profile, visualize)[0] for module in self]
# y = torch.stack(y).max(0)[0] # max ensemble
# y = torch.stack(y).mean(0) # mean ensemble
y = torch.cat(y, 2) # nms ensemble, y shape(B, HW, C)
return y, None # inference, train output
# Functions ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@contextlib.contextmanager
def temporary_modules(modules=None):
"""
Context manager for temporarily adding or modifying modules in Python's module cache (`sys.modules`).
This function can be used to change the module paths during runtime. It's useful when refactoring code,
where you've moved a module from one location to another, but you still want to support the old import
paths for backwards compatibility.
Args:
modules (dict, optional): A dictionary mapping old module paths to new module paths.
Example:
```python
with temporary_modules({'old.module.path': 'new.module.path'}):
import old.module.path # this will now import new.module.path
```
Note:
The changes are only in effect inside the context manager and are undone once the context manager exits.
Be aware that directly manipulating `sys.modules` can lead to unpredictable results, especially in larger
applications or libraries. Use this function with caution.
"""
if not modules:
modules = {}
import importlib
import sys
try:
# Set modules in sys.modules under their old name
for old, new in modules.items():
sys.modules[old] = importlib.import_module(new)
yield
finally:
# Remove the temporary module paths
for old in modules:
if old in sys.modules:
del sys.modules[old]
def torch_safe_load(weight):
"""
This function attempts to load a PyTorch model with the torch.load() function. If a ModuleNotFoundError is raised,
it catches the error, logs a warning message, and attempts to install the missing module via the
check_requirements() function. After installation, the function again attempts to load the model using torch.load().
Args:
weight (str): The file path of the PyTorch model.
Returns:
(dict): The loaded PyTorch model.
"""
from ultralytics.utils.downloads import attempt_download_asset
check_suffix(file=weight, suffix='.pt')
file = attempt_download_asset(weight) # search online if missing locally
try:
with temporary_modules({
'ultralytics.yolo.utils': 'ultralytics.utils',
'ultralytics.yolo.v8': 'ultralytics.models.yolo',
'ultralytics.yolo.data': 'ultralytics.data'}): # for legacy 8.0 Classify and Pose models
return torch.load(file, map_location='cpu'), file # load
except ModuleNotFoundError as e: # e.name is missing module name
if e.name == 'models':
raise TypeError(
emojis(f'ERROR ❌️ {weight} appears to be an Ultralytics YOLOv5 model originally trained '
f'with https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.\nThis model is NOT forwards compatible with '
f'YOLOv8 at https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics.'
f"\nRecommend fixes are to train a new model using the latest 'ultralytics' package or to "
f"run a command with an official YOLOv8 model, i.e. 'yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt'")) from e
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ {weight} appears to require '{e.name}', which is not in ultralytics requirements."
f"\nAutoInstall will run now for '{e.name}' but this feature will be removed in the future."
f"\nRecommend fixes are to train a new model using the latest 'ultralytics' package or to "
f"run a command with an official YOLOv8 model, i.e. 'yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt'")
check_requirements(e.name) # install missing module
return torch.load(file, map_location='cpu'), file # load
def attempt_load_weights(weights, device=None, inplace=True, fuse=False):
"""Loads an ensemble of models weights=[a,b,c] or a single model weights=[a] or weights=a."""
ensemble = Ensemble()
for w in weights if isinstance(weights, list) else [weights]:
ckpt, w = torch_safe_load(w) # load ckpt
args = {**DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, **ckpt['train_args']} if 'train_args' in ckpt else None # combined args
model = (ckpt.get('ema') or ckpt['model']).to(device).float() # FP32 model
# Model compatibility updates
model.args = args # attach args to model
model.pt_path = w # attach *.pt file path to model
model.task = guess_model_task(model)
if not hasattr(model, 'stride'):
model.stride = torch.tensor([32.])
# Append
ensemble.append(model.fuse().eval() if fuse and hasattr(model, 'fuse') else model.eval()) # model in eval mode
# Module updates
for m in ensemble.modules():
t = type(m)
if t in (nn.Hardswish, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6, nn.SiLU, Detect, Segment):
m.inplace = inplace
elif t is nn.Upsample and not hasattr(m, 'recompute_scale_factor'):
m.recompute_scale_factor = None # torch 1.11.0 compatibility
# Return model
if len(ensemble) == 1:
return ensemble[-1]
# Return ensemble
LOGGER.info(f'Ensemble created with {weights}\n')
for k in 'names', 'nc', 'yaml':
setattr(ensemble, k, getattr(ensemble[0], k))
ensemble.stride = ensemble[torch.argmax(torch.tensor([m.stride.max() for m in ensemble])).int()].stride
assert all(ensemble[0].nc == m.nc for m in ensemble), f'Models differ in class counts {[m.nc for m in ensemble]}'
return ensemble
def attempt_load_one_weight(weight, device=None, inplace=True, fuse=False):
"""Loads a single model weights."""
ckpt, weight = torch_safe_load(weight) # load ckpt
args = {**DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, **(ckpt.get('train_args', {}))} # combine model and default args, preferring model args
model = (ckpt.get('ema') or ckpt['model']).to(device).float() # FP32 model
# Model compatibility updates
model.args = {k: v for k, v in args.items() if k in DEFAULT_CFG_KEYS} # attach args to model
model.pt_path = weight # attach *.pt file path to model
model.task = guess_model_task(model)
if not hasattr(model, 'stride'):
model.stride = torch.tensor([32.])
model = model.fuse().eval() if fuse and hasattr(model, 'fuse') else model.eval() # model in eval mode
# Module updates
for m in model.modules():
t = type(m)
if t in (nn.Hardswish, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6, nn.SiLU, Detect, Segment):
m.inplace = inplace
elif t is nn.Upsample and not hasattr(m, 'recompute_scale_factor'):
m.recompute_scale_factor = None # torch 1.11.0 compatibility
# Return model and ckpt
return model, ckpt
def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
"""Parse a YOLO model.yaml dictionary into a PyTorch model."""
import ast
# Args
max_channels = float('inf')
nc, act, scales = (d.get(x) for x in ('nc', 'activation', 'scales'))
depth, width, kpt_shape = (d.get(x, 1.0) for x in ('depth_multiple', 'width_multiple', 'kpt_shape'))
if scales:
scale = d.get('scale')
if not scale:
scale = tuple(scales.keys())[0]
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ no model scale passed. Assuming scale='{scale}'.")
depth, width, max_channels = scales[scale]
if act:
Conv.default_act = eval(act) # redefine default activation, i.e. Conv.default_act = nn.SiLU()
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f"{colorstr('activation:')} {act}") # print
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f"\n{'':>3}{'from':>20}{'n':>3}{'params':>10} {'module':<45}{'arguments':<30}")
ch = [ch]
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
m = getattr(torch.nn, m[3:]) if 'nn.' in m else globals()[m] # get module
for j, a in enumerate(args):
if isinstance(a, str):
with contextlib.suppress(ValueError):
args[j] = locals()[a] if a in locals() else ast.literal_eval(a)
n = n_ = max(round(n * depth), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
if m in (Classify, Conv, ConvTranspose, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, Focus,
BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, nn.ConvTranspose2d, DWConvTranspose2d, C3x, RepC3,SEAttention):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc: # if c2 not equal to number of classes (i.e. for Classify() output)
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in (BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, C3x, RepC3):
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is AIFI:
args = [ch[f], *args]
elif m in (HGStem, HGBlock):
c1, cm, c2 = ch[f], args[0], args[1]
args = [c1, cm, c2, *args[2:]]
if m is HGBlock:
args.insert(4, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m in [ShuffleNetV2, Conv_maxpool]:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc: # if c2 not equal to number of classes (i.e. for Classify() output)
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * width, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)
elif m is Concat_BiFPN:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)
elif m in (Detect, Segment, Pose, RTDETRDecoder):
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if m is Segment:
args[2] = make_divisible(min(args[2], max_channels) * width, 8)
else:
c2 = ch[f]
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
ch.append(c2)
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)
def yaml_model_load(path):
"""Load a YOLOv8 model from a YAML file."""
import re
path = Path(path)
if path.stem in (f'yolov{d}{x}6' for x in 'nsmlx' for d in (5, 8)):
new_stem = re.sub(r'(\d+)([nslmx])6(.+)?$', r'\1\2-p6\3', path.stem)
LOGGER.warning(f'WARNING ⚠️ Ultralytics YOLO P6 models now use -p6 suffix. Renaming {path.stem} to {new_stem}.')
path = path.with_name(new_stem + path.suffix)
unified_path = re.sub(r'(\d+)([nslmx])(.+)?$', r'\1\3', str(path)) # i.e. yolov8x.yaml -> yolov8.yaml
yaml_file = check_yaml(unified_path, hard=False) or check_yaml(path)
d = yaml_load(yaml_file) # model dict
d['scale'] = guess_model_scale(path)
d['yaml_file'] = str(path)
return d
def guess_model_scale(model_path):
"""
Takes a path to a YOLO model's YAML file as input and extracts the size character of the model's scale.
The function uses regular expression matching to find the pattern of the model scale in the YAML file name,
which is denoted by n, s, m, l, or x. The function returns the size character of the model scale as a string.
Args:
model_path (str | Path): The path to the YOLO model's YAML file.
Returns:
(str): The size character of the model's scale, which can be n, s, m, l, or x.
"""
with contextlib.suppress(AttributeError):
import re
return re.search(r'yolov\d+([nslmx])', Path(model_path).stem).group(1) # n, s, m, l, or x
return ''
def guess_model_task(model):
"""
Guess the task of a PyTorch model from its architecture or configuration.
Args:
model (nn.Module | dict): PyTorch model or model configuration in YAML format.
Returns:
(str): Task of the model ('detect', 'segment', 'classify', 'pose').
Raises:
SyntaxError: If the task of the model could not be determined.
"""
def cfg2task(cfg):
"""Guess from YAML dictionary."""
m = cfg['head'][-1][-2].lower() # output module name
if m in ('classify', 'classifier', 'cls', 'fc'):
return 'classify'
if m == 'detect':
return 'detect'
if m == 'segment':
return 'segment'
if m == 'pose':
return 'pose'
# Guess from model cfg
if isinstance(model, dict):
with contextlib.suppress(Exception):
return cfg2task(model)
# Guess from PyTorch model
if isinstance(model, nn.Module): # PyTorch model
for x in 'model.args', 'model.model.args', 'model.model.model.args':
with contextlib.suppress(Exception):
return eval(x)['task']
for x in 'model.yaml', 'model.model.yaml', 'model.model.model.yaml':
with contextlib.suppress(Exception):
return cfg2task(eval(x))
for m in model.modules():
if isinstance(m, Detect):
return 'detect'
elif isinstance(m, Segment):
return 'segment'
elif isinstance(m, Classify):
return 'classify'
elif isinstance(m, Pose):
return 'pose'
# Guess from model filename
if isinstance(model, (str, Path)):
model = Path(model)
if '-seg' in model.stem or 'segment' in model.parts:
return 'segment'
elif '-cls' in model.stem or 'classify' in model.parts:
return 'classify'
elif '-pose' in model.stem or 'pose' in model.parts:
return 'pose'
elif 'detect' in model.parts:
return 'detect'
# Unable to determine task from model
LOGGER.warning("WARNING ⚠️ Unable to automatically guess model task, assuming 'task=detect'. "
"Explicitly define task for your model, i.e. 'task=detect', 'segment', 'classify', or 'pose'.")
return 'detect' # assume detect
改进yolov8|Neck改进:GSConv+Slim-Neck,精度参数量双改进





class GSConv(nn.Module):
# GSConv https://github.com/AlanLi1997/slim-neck-by-gsconv
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, g=1, act=True):
super().__init__()
c_ = c2 // 2
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k, s, None, g, 1, act)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c_, 5, 1, None, c_, 1 , act)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv1(x)
x2 = torch.cat((x1, self.cv2(x1)), 1)
# shuffle
# y = x2.reshape(x2.shape[0], 2, x2.shape[1] // 2, x2.shape[2], x2.shape[3])
# y = y.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4)
# return y.reshape(y.shape[0], -1, y.shape[3], y.shape[4])
b, n, h, w = x2.data.size()
b_n = b * n // 2
y = x2.reshape(b_n, 2, h * w)
y = y.permute(1, 0, 2)
y = y.reshape(2, -1, n // 2, h, w)
return torch.cat((y[0], y[1]), 1)
class GSConvns(GSConv):
# GSConv with a normative-shuffle https://github.com/AlanLi1997/slim-neck-by-gsconv
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, g=1, act=True):
super().__init__(c1, c2, k=1, s=1, g=1, act=True)
c_ = c2 // 2
self.shuf = nn.Conv2d(c_ * 2, c2, 1, 1, 0, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv1(x)
x2 = torch.cat((x1, self.cv2(x1)), 1)
# normative-shuffle, TRT supported
return nn.ReLU(self.shuf(x2))
class GSBottleneck(nn.Module):
# GS Bottleneck https://github.com/AlanLi1997/slim-neck-by-gsconv
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=3, s=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2*e)
# for lighting
self.conv_lighting = nn.Sequential(
GSConv(c1, c_, 1, 1),
GSConv(c_, c2, 3, 1, act=False))
self.shortcut = Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1, act=False)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv_lighting(x) + self.shortcut(x)
class DWConv(Conv):
# Depth-wise convolution class
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__(c1, c2, k, s, g=math.gcd(c1, c2), act=act)
class VoVGSCSP(nn.Module):
# VoVGSCSP module with GSBottleneck
def __init__(self, cx, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
# self.gc1 = GSConv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
# self.gc2 = GSConv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
# self.gsb = GSBottleneck(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.gsb = nn.Sequential(*(GSBottleneck(c_, c_, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
self.res = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1, act=False)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) #
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.gsb(self.cv1(x))
y = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv3(torch.cat((y, x1), dim=1))
class VoVGSCSPC(VoVGSCSP):
# cheap VoVGSCSP module with GSBottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2)
c_ = int(c2 * 0.5) # hidden channels
self.gsb = GSBottleneckC(c_, c_, 1, 1)

from .conv import (....,VoVGSCSP, VoVGSCSPC, GSConv)
![]()
from ultralytics.nn.modules import (....VoVGSCSP, VoVGSCSPC, GSConv)
![]()
if m in (..., VoVGSCSP, VoVGSCSPC,GSConv,SwinTransformer):
![]()
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, VoVGSCSP, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, VoVGSCSP, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, GSConv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, VoVGSCSP, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, GSConv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, VoVGSCSP, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
YOLOv5改进 | 注意力篇 | 一文带你改进GAM、CBAM、CA、ECA等通道注意力机制和多头注意力机制




import torch
import torch.nn as nn
'''
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.05561
'''
class GAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, rate=4):
super().__init__()
out_channels = in_channels
in_channels = int(in_channels)
out_channels = int(out_channels)
inchannel_rate = int(in_channels/rate)
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(in_channels, inchannel_rate)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(inchannel_rate, in_channels)
self.conv1=nn.Conv2d(in_channels, inchannel_rate,kernel_size=7,padding=3,padding_mode='replicate')
self.conv2=nn.Conv2d(inchannel_rate, out_channels,kernel_size=7,padding=3,padding_mode='replicate')
self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inchannel_rate)
self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self,x):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
# B,C,H,W ==> B,H*W,C
x_permute = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(b, -1, c)
# B,H*W,C ==> B,H,W,C
x_att_permute = self.linear2(self.relu(self.linear1(x_permute))).view(b, h, w, c)
# B,H,W,C ==> B,C,H,W
x_channel_att = x_att_permute.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
x = x * x_channel_att
x_spatial_att = self.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
x_spatial_att = self.sigmoid(self.norm2(self.conv2(x_spatial_att)))
out = x * x_spatial_att
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = torch.rand(1,64,32,48)
b, c, h, w = img.shape
net = GAM(in_channels=c, out_channels=c)
output = net(img)
print(output.shape)



import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
"""Channel-attention module https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/tree/v3.0.0rc1/configs/rtmdet."""
def __init__(self, channels: int) -> None:
"""Initializes the class and sets the basic configurations and instance variables required."""
super().__init__()
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Applies forward pass using activation on convolutions of the input, optionally using batch normalization."""
return x * self.act(self.fc(self.pool(x)))
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
"""Spatial-attention module."""
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
"""Initialize Spatial-attention module with kernel size argument."""
super().__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), "kernel size must be 3 or 7"
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.cv1 = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
"""Apply channel and spatial attention on input for feature recalibration."""
return x * self.act(self.cv1(torch.cat([torch.mean(x, 1, keepdim=True), torch.max(x, 1, keepdim=True)[0]], 1)))
class CBAM(nn.Module):
"""Convolutional Block Attention Module."""
def __init__(self, c1, kernel_size=7):
"""Initialize CBAM with given input channel (c1) and kernel size."""
super().__init__()
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(c1)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention(kernel_size)
def forward(self, x):
"""Applies the forward pass through C1 module."""
return self.spatial_attention(self.channel_attention(x))


![]()
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
import torch.nn.functional as F
class h_sigmoid(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_sigmoid, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return self.relu(x + 3) / 6
class h_swish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_swish, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid = h_sigmoid(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.sigmoid(x)
class CoordAtt(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, reduction=32):
super(CoordAtt, self).__init__()
oup = inp
self.pool_h = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1))
self.pool_w = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None))
mip = max(8, inp // reduction)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inp, mip, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mip)
self.act = h_swish()
self.conv_h = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_w = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
n,c,h,w = x.size()
x_h = self.pool_h(x)
x_w = self.pool_w(x).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
y = torch.cat([x_h, x_w], dim=2)
y = self.conv1(y)
y = self.bn1(y)
y = self.act(y)
x_h, x_w = torch.split(y, [h, w], dim=2)
x_w = x_w.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
a_h = self.conv_h(x_h).sigmoid()
a_w = self.conv_w(x_w).sigmoid()
out = identity * a_w * a_h
return out

![]()
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
class ECA(nn.Module):
"""Constructs a ECA module.
Args:
channel: Number of channels of the input feature map
k_size: Adaptive selection of kernel size
"""
def __init__(self, channel, k_size=3):
super(ECA, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=(k_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# feature descriptor on the global spatial information
y = self.avg_pool(x)
# Two different branches of ECA module
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2)).transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
# Multi-scale information fusion
y = self.sigmoid(y)
return x * y.expand_as(x)






# YOLOv5 🚀 by Ultralytics, AGPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.25 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[
[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head: [
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[-1, 1, CBAM, []], # 24 这里默认先用的CBAM大家使用那个只需要把其他的注释掉即可
# [-1, 1, ECA, []],
# [-1, 1, CoordAtt, []],
# [-1, 1, GAM, []],
[[17, 20, 24], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
# YOLOv5 🚀 by Ultralytics, AGPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.25 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[
[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[ -1, 1, CBAM, [ ] ], # 9 这里默认先用的CBAM大家使用那个只需要把其他的注释掉即可
# [-1, 1, ECA, []],
# [-1, 1, CoordAtt, []],
# [-1, 1, GAM, []],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 10
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head: [
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 14
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 18 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 15], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 21 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 11], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 24 (P5/32-large)
[[18, 21, 24], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]![]()
YOLOv5改进 | EIoU、SIoU、WIoU、DIoU、FocusIoU等二十余种损失函数
这篇文章介绍了YOLOv5的重大改进,特别是在损失函数方面的创新。它不仅包括了多种IoU损失函数的改进和变体,如SIoU、WIoU、GIoU、DIoU、EIOU、CIoU,还融合了“Focus”思想,创造了一系列新的损失函数。这些组合形式的损失函数超过了二十余种,每种都针对特定的目标检测挑战进行优化。文章会详细探讨这些损失函数如何提高YOLOv5在各种检测任务中的性能,包括提升精度、加快收敛速度和增强模型对复杂场景的适应性。本文章主要是为了发最近新出的Inner思想改进的各种EIoU的文章服务,其中我经过实验在绝大多数下的效果都要比本文中提到的各种损失效果要好。

二、各种损失函数的基本原理
2.1 交集面积和并集面积
在理解各种损失函数之前我们需要先来理解一下交集面积和并集面积,在数学中我们都学习过集合的概念,这里的交集和并集的概念和数学集合中的含义是一样的。

2.2 IoU
论文地址:IoU Loss for 2D/3D Object Detectio
适用场景:普通的IoU并没有特定的适用场景
概念: 测量预测边界框和真实边界框之间的重叠度(最基本的边界框损失函数,后面的都是居于其进行计算)。

2.3 SIoU
论文地址:SIoU: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:适用于需要高精度边界框对齐的场景,如精细的物体检测和小目标检测。
概念: SIoU损失通过融入角度考虑和规模敏感性,引入了一种更为复杂的边界框回归方法,解决了以往损失函数的局限性,SIoU损失函数包含四个组成部分:角度损失、距离损失、形状损失和第四个未指定的组成部分。通过整合这些方面,从而实现更好的训练速度和预测准确性。

2.4 WioU
论文地址:WIoU: Bounding Box Regression Loss with Dynamic Focusing Mechanism
适用场景:适用于需要动态调整损失焦点的情况,如不均匀分布的目标或不同尺度的目标检测。
概念:引入动态聚焦机制的IoU变体,旨在改善边界框回归损失。

2.5 GIoU
论文地址:GIoU: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:适合处理有重叠和非重叠区域的复杂场景,如拥挤场景的目标检测。
概念: 在IoU的基础上考虑非重叠区域,以更全面评估边界框

2.6 DIoU
论文地址:DIoU: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:适用于需要快速收敛和精确定位的任务,特别是在边界框定位精度至关重要的场景。
概念:结合边界框中心点之间的距离和重叠区域。

2.7 EIoU
论文地址:EIoU:Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:可用于需要进一步优化边界框对齐和形状相似性的高级场景。
概念:EIoU损失函数的核心思想在于提高边界框回归的准确性和效率。它通过以下几个方面来优化目标检测:
1. 增加中心点距离损失:通过最小化预测框和真实框中心点之间的距离,提高边界框的定位准确性。
2. 考虑尺寸差异:通过惩罚宽度和高度的差异,EIoU确保预测框在形状上更接近真实框。
3. 结合最小封闭框尺寸:将损失函数与包含预测框和真实框的最小封闭框的尺寸相结合,从而使得损失更加敏感于对象的尺寸和位置。
EIoU损失函数在传统IoU基础上增加了这些考量,以期在各种尺度上都能获得更精确的目标定位,尤其是在物体大小和形状变化较大的场景中。
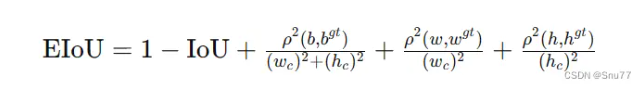
2.8 CIoU
论文地址:CIoU:Enhancing Geometric Factors in Model Learning
适用场景:适合需要综合考虑重叠区域、形状和中心点位置的场景,如复杂背景或多目标跟踪。
概念:综合考虑重叠区域、中心点距离和长宽比。

2.9 FocusLoss
论文地址:Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection
适用场景:适用于需要高精度边界框对齐的场景,如精细的物体检测和小目标检测。
Focal Loss由Kaiming He等人在论文《Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection》中提出,旨在解决在训练过程中正负样本数量极度不平衡的问题,尤其是在一些目标检测任务中,背景类别的样本可能远远多于前景类别的样本。
Focal Loss通过修改交叉熵损失,增加一个调整因子,这个因子降低了那些已经被正确分类的样本的损失值,使得模型的训练焦点更多地放在难以分类的样本上。这种方式特别有利于提升小目标或者在复杂背景中容易被忽视的目标的检测性能。简而言之,Focal Loss让模型“关注”(或“专注”)于学习那些对提高整体性能更为关键的样本。
加入sECANet通道注意力机制的mask-rcnn的优势
sECANet(Spatial-Channel-SENet)通道注意力机制是一种新型的注意力机制,结合了空间注意力和通道注意力,可以更好地捕捉物体在图像中的空间和通道信息。在Mask R-CNN中加入sECANet通道注意力机制,可以使模型更加精确地定位和分割物体,提高模型的准确率和鲁棒性。
具体来说,加入sECANet通道注意力机制的Mask R-CNN的优势有以下几点:
1.更好的特征表示:sECANet通道注意力机制可以提高特征的表达能力,使得模型可以更好地捕捉物体的空间和通道信息,从而提高特征表示的质量。
2.更精确的定位和分割:通过加入sECANet通道注意力机制,模型可以更加准确地定位和分割物体,从而提高模型的准确率和鲁棒性。
3.更高的效率:sECANet通道注意力机制可以帮助模型更快地收敛,从而提高模型的训练效率和推理速度。
综上所述,加入sECANet通道注意力机制的Mask R-CNN具有更好的特征表示、更精确的定位和分割以及更高的效率等优势。























 295
295

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








