OpenCV Native 开发环境搭建步骤请参考:
OpenCV Native开发环境搭建_tugouxp的专栏-优快云博客
YOLOV3网络吃图格式为416*416 NCWH 三通道的RGB格式图,下面的程序可以将一张JPEG图像转换为对应的格式,基于OPENCV
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
Mat img = imread("output_416x416.jpg");
if(img.empty())
{
cout <<"please confirm the name of pic is right!" <<endl;
return -1;
}
Mat imgs0, imgs1, imgs2;
Mat imgv0, imgv1, imgv2;
Mat result0, result1, result2;
Mat imgs[3];
split(img, imgs);
imgs0 = imgs[0];
imgs1 = imgs[1];
imgs2 = imgs[2];
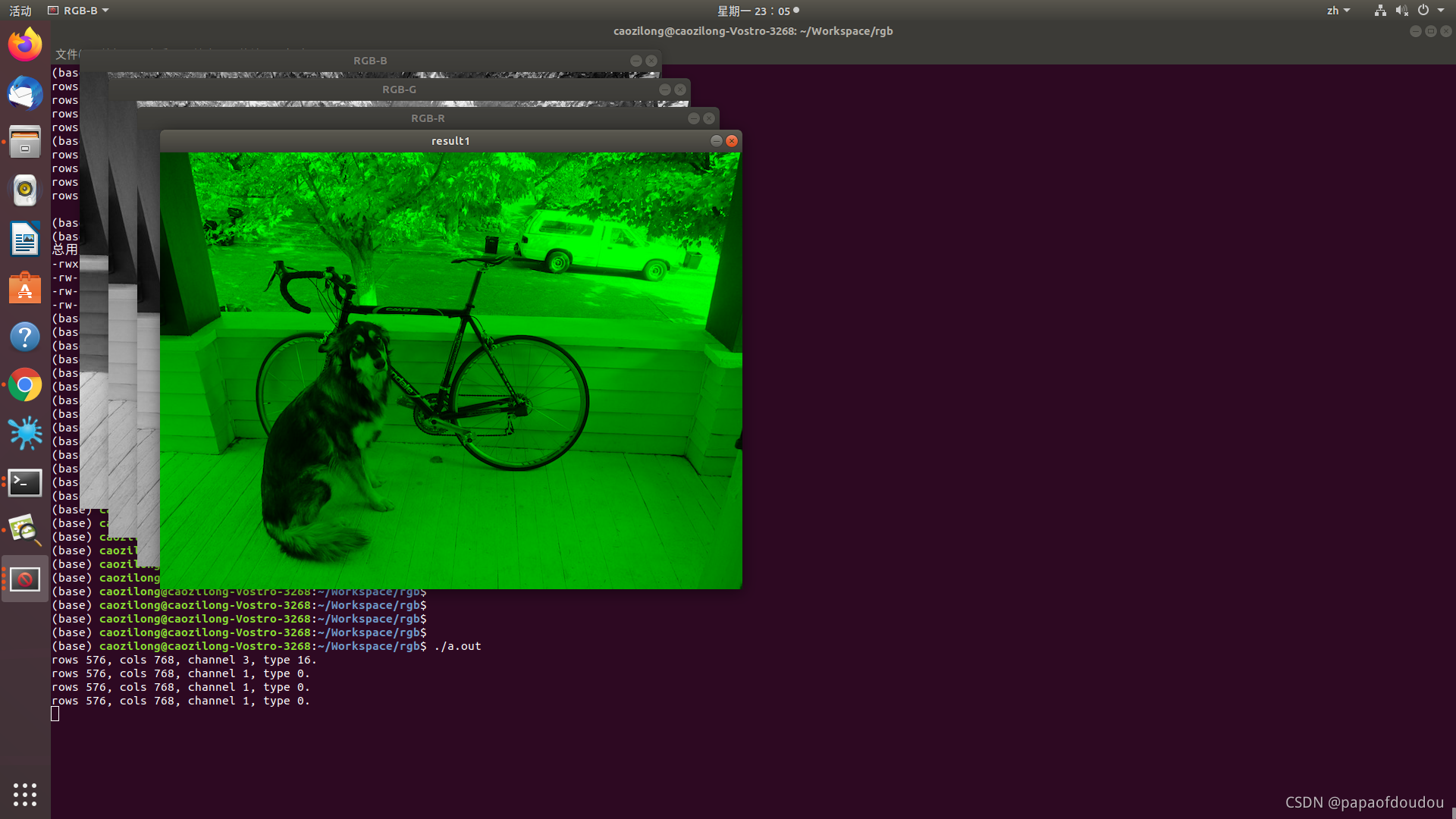
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", img.rows, img.cols, img.channels(), img.type());
imshow("RGB-B", imgs0);
imshow("RGB-G", imgs1);
imshow("RGB-R", imgs2);
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", imgs0.rows, imgs0.cols, imgs0.channels(), imgs0.type());
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", imgs1.rows, imgs1.cols, imgs1.channels(), imgs1.type());
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", imgs2.rows, imgs2.cols, imgs2.channels(), imgs2.type());
Mat zero = cv::Mat::zeros(img.rows, img.cols, CV_8UC1);
imgs[0] = zero;
imgs[2] = zero;
merge(imgs, 3, result1);
imshow("result1", result1);
FILE *file = fopen("network_input.bin", "wb+");
if(file == NULL)
{
cout << "fatal error,create file failure" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it0 = imgs0.begin<uchar>();
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it0_end = imgs0.end<uchar>();
for (int i = 0; it0 != it0_end; it0 ++, i ++)
{
unsigned char data = *it0;
int count = fwrite(&data, 1, 1, file);
if(count != 1)
{
cout << "write binary failure." << endl;
}
}
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it1 = imgs1.begin<uchar>();
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it1_end = imgs1.end<uchar>();
for (int i = 0; it1 != it1_end; it1 ++, i ++)
{
unsigned char data = *it1;
int count = fwrite(&data, 1, 1, file);
if(count != 1)
{
cout << "write binary failure." << endl;
}
}
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it2 = imgs2.begin<uchar>();
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it2_end = imgs2.end<uchar>();
for (int i = 0; it2 != it2_end; it2 ++, i ++)
{
unsigned char data = *it2;
int count = fwrite(&data, 1, 1, file);
if(count != 1)
{
cout << "write binary failure." << endl;
}
}
fsync(fileno(file));
fflush(file);
fclose(file);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
加上scale操作
scale 为416*416大小
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static void print_type(void)
{
printf("CV_8UC1=%d.\n", CV_8UC1);
printf("CV_8UC2=%d.\n", CV_8UC2);
printf("CV_8UC3=%d.\n", CV_8UC3);
printf("CV_8UC4=%d.\n", CV_8UC4);
printf("CV_8SC1=%d.\n", CV_8SC1);
printf("CV_8SC2=%d.\n", CV_8SC2);
printf("CV_8SC3=%d.\n", CV_8SC3);
printf("CV_8SC4=%d.\n", CV_8SC4);
printf("CV_16UC1=%d.\n", CV_16UC1);
printf("CV_16UC2=%d.\n", CV_16UC2);
printf("CV_16UC3=%d.\n", CV_16UC3);
printf("CV_16UC4=%d.\n", CV_16UC4);
printf("CV_16SC1=%d.\n", CV_16SC1);
printf("CV_16SC2=%d.\n", CV_16SC2);
printf("CV_16SC3=%d.\n", CV_16SC3);
printf("CV_16SC4=%d.\n", CV_16SC4);
printf("CV_32SC1=%d.\n", CV_32SC1);
printf("CV_32SC2=%d.\n", CV_32SC2);
printf("CV_32SC3=%d.\n", CV_32SC3);
printf("CV_32SC4=%d.\n", CV_32SC4);
printf("CV_32FC1=%d.\n", CV_32FC1);
printf("CV_32FC2=%d.\n", CV_32FC2);
printf("CV_32FC3=%d.\n", CV_32FC3);
printf("CV_32FC4=%d.\n", CV_32FC4);
printf("CV_64FC1=%d.\n", CV_64FC1);
printf("CV_64FC2=%d.\n", CV_64FC2);
printf("CV_64FC3=%d.\n", CV_64FC3);
printf("CV_64FC4=%d.\n", CV_64FC4);
return;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
print_type();
Mat img = imread("dog.jpg");
if(img.empty())
{
cout <<"please confirm the name of pic is right!" <<endl;
return -1;
}
Size dsize = Size(416, 416);
Mat img2 = Mat(dsize, CV_8UC3);
resize(img, img2, dsize);
imwrite("./scale.jpg",img2);
printf("%s line %d, img2.type = %d, %d, %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, img2.type(), CV_8UC1, CV_8UC3);
//printf("%s line %d, img.type = %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, img.type());
Mat imgs0, imgs1, imgs2;
Mat result0, result1, result2;
Mat imgs[3];
split(img2, imgs);
imgs0 = imgs[0];
imgs1 = imgs[1];
imgs2 = imgs[2];
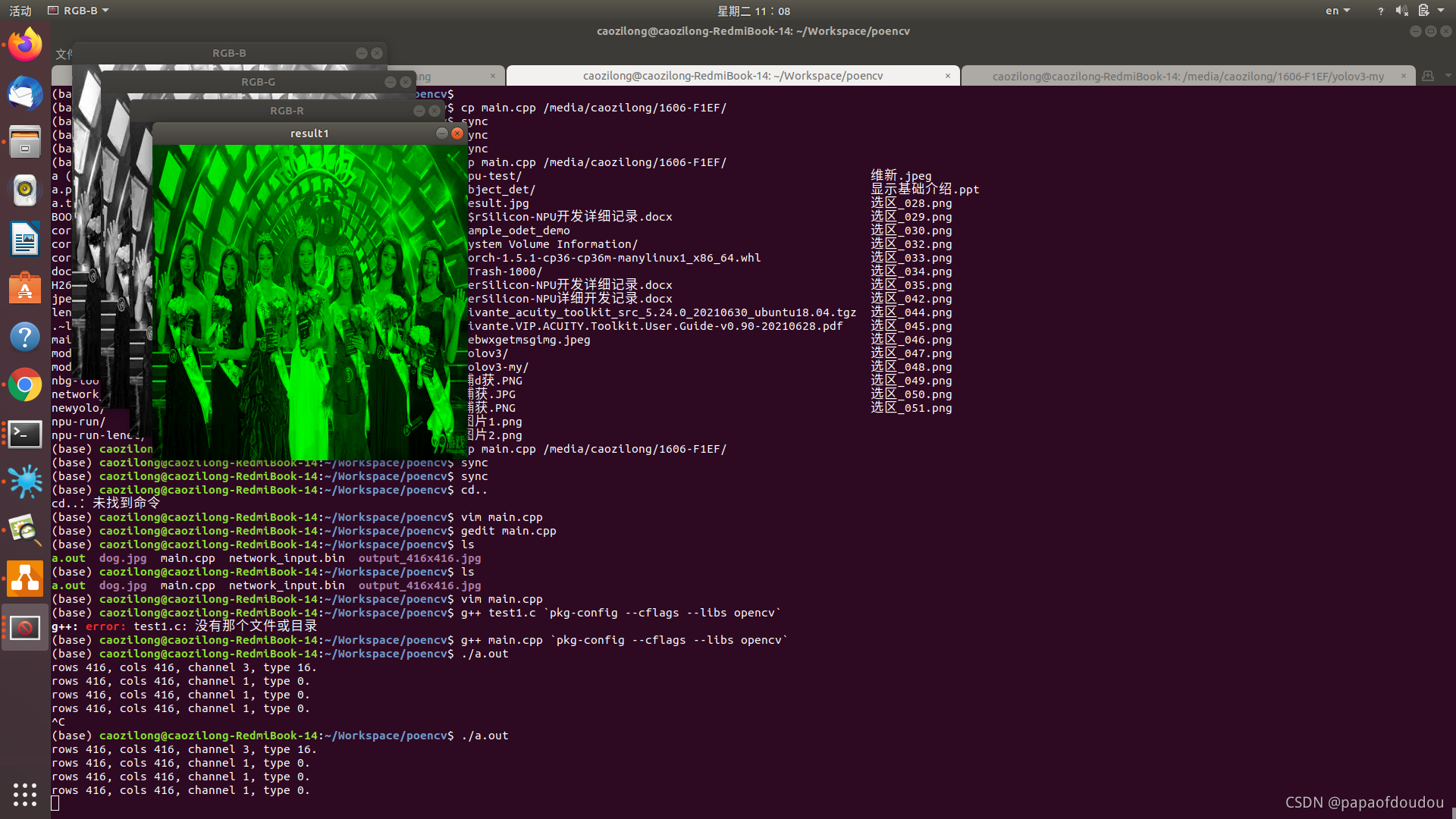
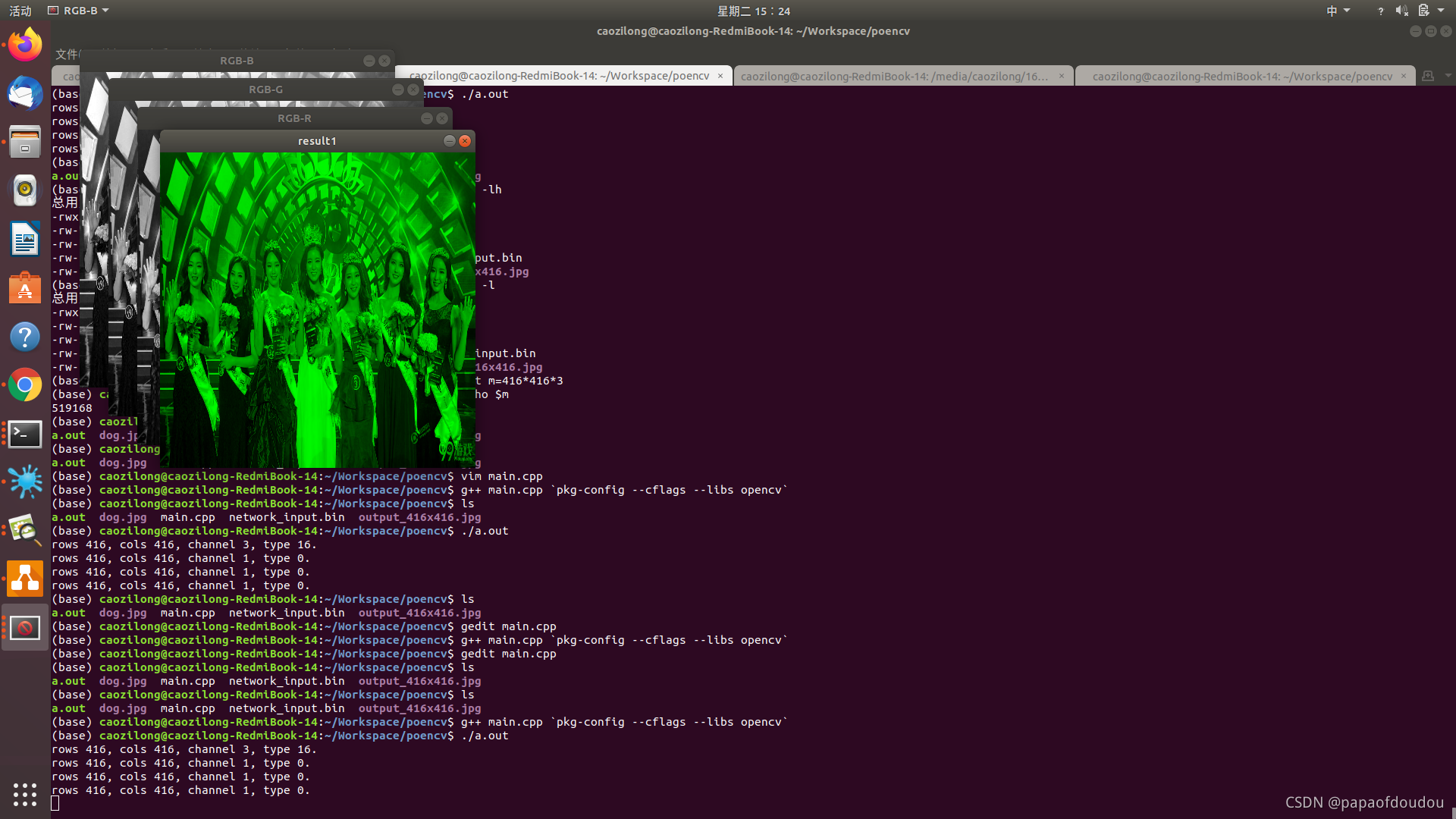
imshow("RGB-B", imgs0);
imshow("RGB-G", imgs1);
imshow("RGB-R", imgs2);
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", img2.rows, img2.cols, img2.channels(), img2.type());
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", imgs0.rows, imgs0.cols, imgs0.channels(), imgs0.type());
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", imgs1.rows, imgs1.cols, imgs1.channels(), imgs1.type());
printf("rows %d, cols %d, channel %d, type %d.\n", imgs2.rows, imgs2.cols, imgs2.channels(), imgs2.type());
Mat zero = cv::Mat::zeros(img2.rows, img2.cols, CV_8UC1);
imgs[0] = zero;
imgs[2] = zero;
merge(imgs, 3, result1);
imshow("result1", result1);
FILE *file = fopen("network_input.bin", "wb+");
if(file == NULL)
{
cout << "fatal error,create file failure" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it0 = imgs0.begin<uchar>();
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it0_end = imgs0.end<uchar>();
for (int i = 0; it0 != it0_end; it0 ++, i ++)
{
unsigned char data = *it0;
int count = fwrite(&data, 1, 1, file);
if(count != 1)
{
cout << "write binary failure." << endl;
}
}
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it1 = imgs1.begin<uchar>();
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it1_end = imgs1.end<uchar>();
for (int i = 0; it1 != it1_end; it1 ++, i ++)
{
unsigned char data = *it1;
int count = fwrite(&data, 1, 1, file);
if(count != 1)
{
cout << "write binary failure." << endl;
}
}
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it2 = imgs2.begin<uchar>();
cv::MatIterator_<uchar> it2_end = imgs2.end<uchar>();
for (int i = 0; it2 != it2_end; it2 ++, i ++)
{
unsigned char data = *it2;
int count = fwrite(&data, 1, 1, file);
if(count != 1)
{
cout << "write binary failure." << endl;
}
}
fsync(fileno(file));
fflush(file);
fclose(file);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
scale.jpg文件是缩放后的图像,network_input.bin即是符合VIP YOLOV3网络的 RGB NCHW格式的数据输出,可以直接喂给网络进行推理。
纯C版的矩阵转置:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define DBG(fmt, ...) do { printf("%s line %d, "fmt"\n", __func__, __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__); } while (0)
static void dump_memory(uint8_t *buf, int32_t len)
{
int i;
printf("\n\rdump file memory:");
for (i = 0; i < len; i ++)
{
if ((i % 16) == 0)
{
printf("\n\r%p: ", buf + i);
}
printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n\r");
return;
}
static double uint8_to_fp32(uint8_t val, int32_t zeropoint, double scale)
{
double result = 0.0f;
result = (val - (uint8_t)zeropoint) * scale;
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *file;
double scale;
int zeropoint;
DBG("in");
file = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
if(file == NULL)
{
DBG("fatal error, open file %s failure, please check the file status.", argv[1]);
exit(-1);
}
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);
int filelen = ftell(file);
DBG("file %s len %d byets.", argv[1], filelen);
unsigned char *p = malloc(filelen);
if(p == NULL)
{
DBG("malloc buffer failure for %s len %d.", argv[1], filelen);
exit(-1);
}
memset(p, 0x00, filelen);
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET);
if(fread(p, 1, filelen, file) != filelen)
{
DBG("read file failure, size wrong.");
exit(-1);
}
char outputname[255];
memset(outputname, 0x00, 255);
memcpy(outputname, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));
memcpy(outputname+strlen(argv[1]), ".rgb", 7);
DBG("output tensor name %s", outputname);
FILE *outensor = fopen(outputname, "wb+");
if(outensor == NULL)
{
DBG("fatal error, create output tensor file %s failure, please check the file status.", outputname);
exit(-1);
}
dump_memory(p, 32);
unsigned char *w = malloc(filelen);
if(w == NULL)
{
DBG("malloc buffer failure for %s len %d.", argv[1], filelen);
exit(-1);
}
memset(w, 0x00, filelen);
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i ++)
{
for(j = 0; j < 416; j ++)
{
for(k = 0; k < 416; k ++)
{
//w[i][j][k] = p[j][k][i];
//w[i*416 * 416 + j*416 + k] = p[j*416*3 + k*3 + i];
w[(2-i)*416 * 416 + j*416 + k] = p[j*416*3 + k*3 + i];
}
}
}
if(fwrite(w, 1, filelen, outensor) != filelen)
{
DBG("write file failure, size wrong.");
exit(-1);
}
fflush(outensor);
fsync(fileno(outensor));
fclose(outensor);
fclose(file);
free(p);
DBG("out");
return 0;
}参考博客
转置算子(transpose)的一种实现_papaofdoudou的博客-优快云博客_transpose算子








 该博客介绍了如何使用OpenCV将JPEG图像转换为YOLOV3网络所需的416*416 NCWH RGB格式,并提供了C++代码示例。此外,还展示了纯C版的矩阵转置实现,将数据从RGBNCHW格式转换,适用于深度学习推理。
该博客介绍了如何使用OpenCV将JPEG图像转换为YOLOV3网络所需的416*416 NCWH RGB格式,并提供了C++代码示例。此外,还展示了纯C版的矩阵转置实现,将数据从RGBNCHW格式转换,适用于深度学习推理。



















 27万+
27万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










