REINFORCE
REINFORCE算法使用蒙特卡罗方法计算策略梯度,智能体根据当前策略与环境交互,生成一条状态-动作-奖励序列(轨迹)。对每条轨迹进行回报计算,通常采用折扣累计奖励(也就是下图中的r)的形式。REINFORCE的缺点就是方差大,按照论文ReMax: A Simple, Effective, and Efficient Reinforcement Learning Method for Aligning Large Language Models里的说法就是In theory, this variance can be attributed
to two main sources: the external randomness inherent in
MDP’s transitions and the internal randomness from the
policy decisions of the language model (i.e., token generation).

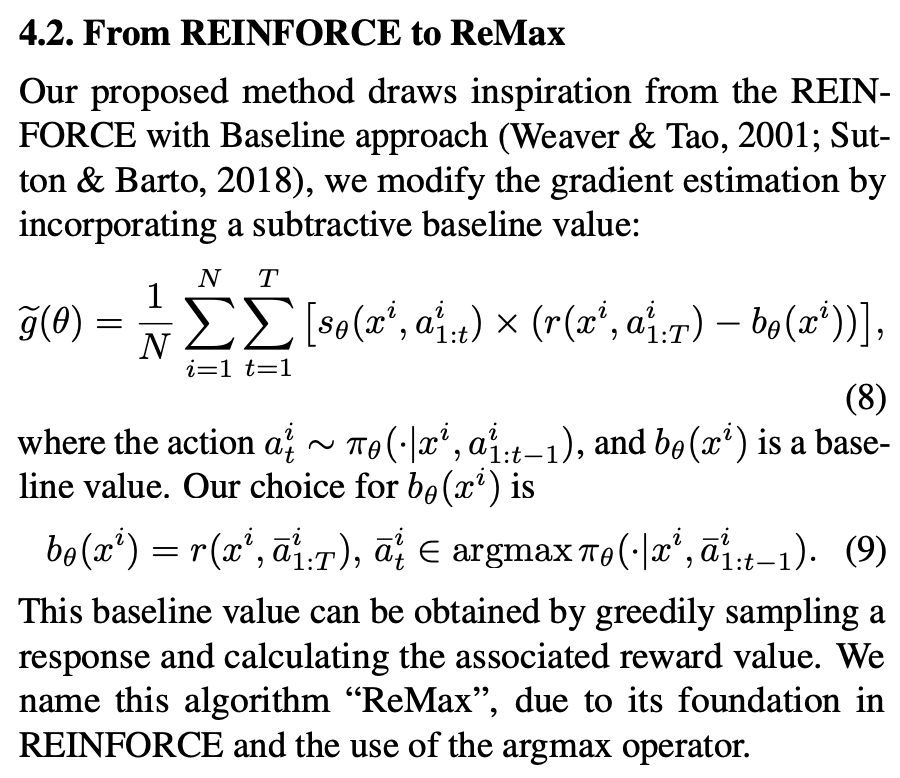
ReMax(REINFORCE+argmax)
来自ReMax: A Simple, Effective, and Efficient Reinforcement Learning Method for Aligning Large Language Models。在REINFORCE基础上加个baseline,放弃critic函数,This baseline value can be obtained by greedily sampling a
response and calculating the associated reward value
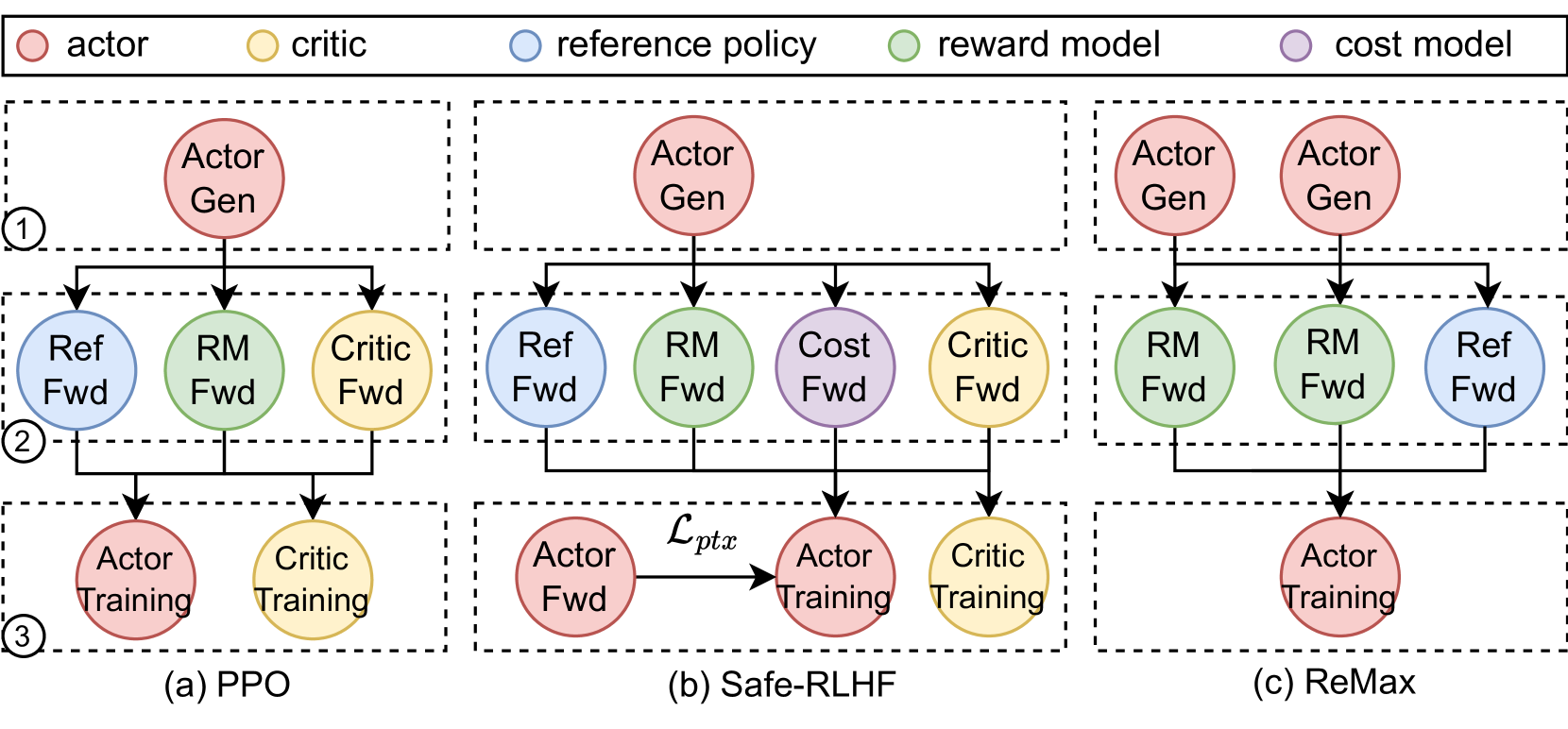
在VeRL论文(HybridFlow: A Flexible and Efficient RLHF Framework)中,ReMax被描述成了一个需要Actor Gen两次的数据流,因为baseline确实多采样了一次,而且这个baseline是通过greedy采样得到的!
来看一下VeRL中Remax advantage的实现:
@register_adv_est(AdvantageEstimator.REMAX) # or simply: @register_adv_est("remax")
def compute_remax_outcome_advantage(
token_level_rewards: torch.Tensor,
reward_baselines: torch.Tensor,
response_mask: torch.Tensor,
config: Optional[AlgoConfig] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""
Compute advantage for ReMax, operating only on Outcome reward
This implementation is based on the paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.10505
(with only one scalar reward for each response).
Args:
token_level_rewards: `(torch.Tensor)`
shape: (bs, response_length)
reward_baselines: `(torch.Tensor)`
shape: (bs,)
response_mask: `(torch.Tensor)`
shape: (bs, response_length)
config: (AlgoConfig) algorithm config
Returns:
advantages: `(torch.Tensor)`
shape: (bs, response_length)
Returns: `(torch.Tensor)`
shape: (bs, response_length)
"""
with torch.no_grad():
returns = (token_level_rewards * response_mask).flip(dims=[-1]).cumsum(dim=-1).flip(dims=[-1])
advantages = returns - reward_baselines.unsqueeze(-1) * response_mask
return advantages, returns
问题1: 为什么减去Baseline对于Policy-Gradient来说是无偏的?
减去基线的操作是将梯度修改为:
∇θJ(θ)=Eτ∼πθ[(R(τ)−b)∇θlogπθ(τ)] \nabla_\theta J(\theta) = \mathbb{E}_{\tau \sim \pi_\theta} \left[ \left( R(\tau) - b \right) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(\tau) \right] ∇θJ(θ)=Eτ∼πθ[(R(τ)−b)∇θlogπθ(τ)]
其中b是基线(通常为状态值函数 (V(s)(V(s)(V(s)))。关键问题在于:为何这种修改不引入偏差?
无偏性的数学本质
无偏性要求修改后的梯度期望值与原梯度一致:
Eτ∼πθ[(R(τ)−b)∇θlogπθ(τ)]=Eτ∼πθ[R(τ)∇θlogπθ(τ)] \mathbb{E}_{\tau \sim \pi_\theta} \left[ \left( R(\tau) - b \right) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(\tau) \right] = \mathbb{E}_{\tau \sim \pi_\theta} \left[ R(\tau) \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(\tau) \right] Eτ∼πθ[(R(τ)−b)∇θlogπθ(τ)]=Eτ∼πθ[R(τ)∇θlogπθ(τ)]
只需证明基线项期望为零:
Eτ∼πθ[b⋅∇θlogπθ(τ)]=0 \mathbb{E}_{\tau \sim \pi_\theta} \left[ b \cdot \nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta(\tau) \right] = 0 Eτ
 主流强化学习算法对比分析
主流强化学习算法对比分析





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 867
867

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








