第一部分 大模型的调用
构建良好的大型语言模型应用程序的挑战在于如何有效地构造发送给模型的提示,并处理模型的预测以返回准确的输出
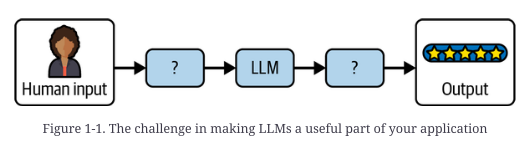
# 简单调用模型
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
# temperature
# 较低的值产生更可预测的输出(例如,0.1),而较高的值产生更有创造性或意想不到的结果(例如0.9)。
deepseek = OllamaLLM(
model="deepseek-r1:32b",
temperature=0
)
response = deepseek.invoke("The sky is")
print(response)
角色和消息
大模型调用过程中的三种角色
系统角色: 用于模型应该用来回答用户问题的说明
用户角色:用于用户的查询和用户产生的任何其他内容
助理角色:用于模型生成的内容
# HumanMessage:从人的角度发送的消息,具有用户角色
# SystemMessage:设置AI应该遵循的指令的消息,带有系统角色
# AIMessage:从人工智能的角度发出的信息,人类正在与助手角色互动
# ChatMessage:允许任意设置角色的消息
# 使用人类消息
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
model = OllamaLLM(
model="deepseek-r1:32b"
)
prompt = [HumanMessage("What is the capital of France?")]
response = model.invoke(prompt)
print(response)
# 使用人类消息和系统消息
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
model = OllamaLLM(
model="deepseek-r1:32b"
)
system_msg = SystemMessage(
"You are a helpful assistant that responds to questions with three exclamation marks."
)
human_msg = HumanMessage("What is the capital of France?")
response = model.invoke([system_msg, human_msg])
print(response)
实现模板的可复用性
# 使用{ }对内容进行占位 然后传入提示词
# 如果提示词中本身就有{ 要转义成{{
# 将提示词传入模板
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate
model = OllamaLLM(
model="deepseek-r1:32b"
)
# 定义模板 使用了系统消息和人类消息 同时可以动态传入内容
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
'Answer the question based on the context below. If the question cannot be answered using the information provided, answer with "I don\'t know".',
),
("human", "Context: {context}"),
("human", "Question: {question}"),
]
)
# 向提示词中动态写入内容
prompt = template.invoke(
{
"context": "The most recent advancements in NLP are being driven by Large Language Models (LLMs). These models outperform their smaller counterparts and have become invaluable for developers who are creating applications with NLP capabilities. Developers can tap into these models through Hugging Face's `transformers` library, or by utilizing OpenAI and Cohere's offerings through the `openai` and `cohere` libraries, respectively.",
"question": "Which model providers offer LLMs?",
}
)
# 利用动态提示词调用模型
print(model.invoke(prompt))
格式化输出
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from pydantic import BaseModel
# 先定义一个模式 生成类似JSON键值对的格式
class AnswerWithJustification(BaseModel):
answer: str
justification: str
llm = ChatOllama(model="deepseek-r1:32b",temperature=0)
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(AnswerWithJustification)
response = structured_llm.invoke(
"一斤铁和一斤棉花哪个重")
print(response)
# answer="一样重,因为它们都是以'斤'为单位测量的重量。" justification="在中国传统计量单位中,'斤'是重量单位,1斤等于500克。
# 因此,无论是铁还是棉花,只要重量都是1斤,它们的实际重量就是相同的。虽然铁和棉花在体积上差异很大,但题目问的是重量,所以答案是一样重。"
# 运行输出解释器
# 输出解析器可用于在提示符中注入一些额外的指令,这些指令将帮助指导大型语言模型以它知道如何解析的格式输出文本。
# 结构化表示大模型的输出
from langchain_core.output_parsers import CommaSeparatedListOutputParser
parser = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
response = parser.invoke("apple, banana, cherry")
print(response)
# ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
不同的输出方法
# 多种不同输入方法的调用
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM, ChatOllama
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain_core.output_parsers import CommaSeparatedListOutputParser
model = ChatOllama(
model="deepseek-r1:32b",
)
# 一次只输入一部分问题
completion = model.invoke("Hi there!")
# Hi!
# 一次输入一批次问题
completions = model.batch(["Hi there!", "Bye!"])
# print(completions)
# ['Hi!', 'See you!']
# 使用流式输出
for token in model.stream("Bye!"):
print(token)
# Good
# bye
# !
# Invoke()接受单个输入并返回单个输出。
# Batch()接受一个输出列表并返回一个输出列表。
# Stream()接受单个输入,并在输出部分可用时返回一个迭代器。
工作流构建方式
# 使用命令式构建
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM, ChatOllama
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain_core.output_parsers import CommaSeparatedListOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import chain
model = ChatOllama(
model="deepseek-r1:32b",
)
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "You are a helpful assistant."),
("human", "{question}"),
]
)
# 命令式构建
@chain
def chatbot(values):
prompt = template.invoke(values)
return model.invoke(prompt)
response = chatbot.invoke({"question": "Which model providers offer LLMs?"})
print(response.content)
# 命令式构建 但是支持流式调用
# 链的功能是输出模型返回值中的每一个token
@chain
def chatbot(values):
prompt = template.invoke(values)
for token in model.stream(prompt):
yield token
for part in chatbot.stream({"question": "Which model providers offer LLMs?"}):
print(part)
# 命令式构建 但是实现了异步执行
@chain
async def chatbot(values):
prompt = await template.ainvoke(values)
return await model.ainvoke(prompt)
async def main():
return await chatbot.ainvoke({"question": "Which model providers offer LLMs?"})
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
print(asyncio.run(main()))
# 声明式构建 就是使用了LCEL构架了一个链
chatbot = template | model
# 声明式构建普通调用
response = chatbot.invoke({"question": "Which model providers offer LLMs?"})
print(response.content)
# 声明式构建流式调用
for part in chatbot.stream({"question": "Which model providers offer LLMs?"}):
print(part)





















 634
634

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








