1 简介
Grey wolf optimization (GWO) algorithm is a new emerging algorithm that is based on the social hierarchy of grey wolves as well as their hunting and cooperation strategies. Introduced in 2014, this algorithm has been used by a large number of researchers and designers, such that the number of citations to the original paper exceeded many other algorithms. In a recent study by Niu et al., one of the main drawbacks of this algorithm for optimizing real﹚orld problems was introduced. In summary, they showed that GWO's performance degrades as the optimal solution of the problem diverges from 0. In this paper, by introducing a straightforward modification to the original GWO algorithm, that is, neglecting its social hierarchy, the authors were able to largely eliminate this defect and open a new perspective for future use of this algorithm. The efficiency of the proposed method was validated by applying it to benchmark and real﹚orld engineering problems.
2 部分代码
clcclearglobal NFENFE=0;nPop=30; % Number of search agents (Population Number)MaxIt=1000; % Maximum number of iterationsnVar=30; % Number of Optimization VariablesnFun=1; % Function No, select any integer number from 1 to 14CostFunction=@(x,nFun) Cost(x,nFun); % Cost Function%% Problem DefinitionVarMin=-100; % Decision Variables Lower Boundif nFun==7VarMin=-600; % Decision Variables Lower Boundendif nFun==8VarMin=-32; % Decision Variables Lower Boundendif nFun==9VarMin=-5; % Decision Variables Lower Boundendif nFun==10VarMin=-5; % Decision Variables Lower Boundendif nFun==11VarMin=-0.5; % Decision Variables Lower Boundendif nFun==12VarMin=-pi; % Decision Variables Lower Boundendif nFun==14VarMin=-100; % Decision Variables Lower BoundendVarMax= -VarMin; % Decision Variables Upper Boundif nFun==13VarMin=-3; % Decision Variables Lower BoundVarMax= 1; % Decision Variables Upper Boundend%% Grey Wold Optimizer (GWO)% Initialize Alpha, Beta, and DeltaAlpha_pos=zeros(1,nVar);Alpha_score=inf;Beta_pos=zeros(1,nVar);Beta_score=inf;Delta_pos=zeros(1,nVar);Delta_score=inf;%Initialize the positions of search agentsPositions=rand(nPop,nVar).*(VarMax-VarMin)+VarMin;BestCosts=zeros(1,MaxIt);fitness=nan(1,nPop);iter=0; % Loop counter%% Main loopwhile iter<MaxItfor i=1:nPop% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search spaceFlag4ub=Positions(i,:)>VarMax;Flag4lb=Positions(i,:)<VarMin;Positions(i,:)=(Positions(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+VarMax.*Flag4ub+VarMin.*Flag4lb;% Calculate objective function for each search agentfitness(i)= CostFunction(Positions(i,:), nFun);% Update Alpha, Beta, and Deltaif fitness(i)<Alpha_scoreAlpha_score=fitness(i); % Update AlphaAlpha_pos=Positions(i,:);endif fitness(i)>Alpha_score && fitness(i)<Beta_scoreBeta_score=fitness(i); % Update BetaBeta_pos=Positions(i,:);endif fitness(i)>Alpha_score && fitness(i)>Beta_score && fitness(i)<Delta_scoreDelta_score=fitness(i); % Update DeltaDelta_pos=Positions(i,:);endenda=2-(iter*((2)/MaxIt)); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0% Update the Position of all search agentsfor i=1:nPopfor j=1:nVarr1=rand;r2=rand;A1=2*a*r1-a;C1=2*r2;D_alpha=abs(C1*Alpha_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));X1=Alpha_pos(j)-A1*D_alpha;r1=rand;r2=rand;A2=2*a*r1-a;C2=2*r2;D_beta=abs(C2*Beta_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));X2=Beta_pos(j)-A2*D_beta;r1=rand;r2=rand;A3=2*a*r1-a;C3=2*r2;D_delta=abs(C3*Delta_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));X3=Delta_pos(j)-A3*D_delta;Positions(i,j)=(X1+X2+X3)/3;endenditer=iter+1;BestCosts(iter)=Alpha_score;fprintf('Iter= %g, NFE= %g, Best Cost = %g\n',iter,NFE,Alpha_score);end
3 仿真结果
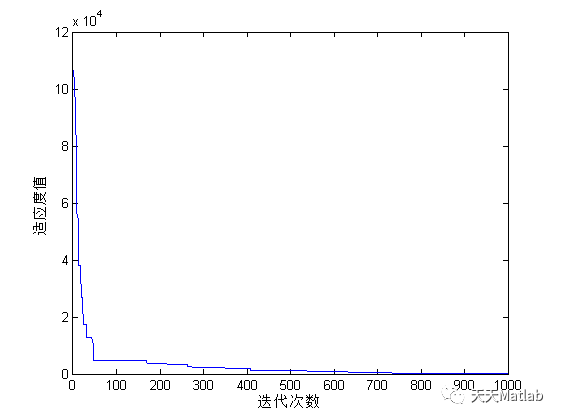
4 参考文献
[1] Akbari E , Rahimnejad A , Gadsden S A . A greedy non﹉ierarchical grey wolf optimizer for real﹚orld optimization[J]. Electronics Letters, 2021(1).
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。





 该文介绍了灰狼优化算法(GWO)的一种新改进,该算法通过忽略社会等级来解决实际问题时性能下降的问题。作者通过修改原始GWO算法,成功地提高了算法的效率,并应用于基准和实际工程问题中验证了其效果。
该文介绍了灰狼优化算法(GWO)的一种新改进,该算法通过忽略社会等级来解决实际问题时性能下降的问题。作者通过修改原始GWO算法,成功地提高了算法的效率,并应用于基准和实际工程问题中验证了其效果。

















 314
314

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










