You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
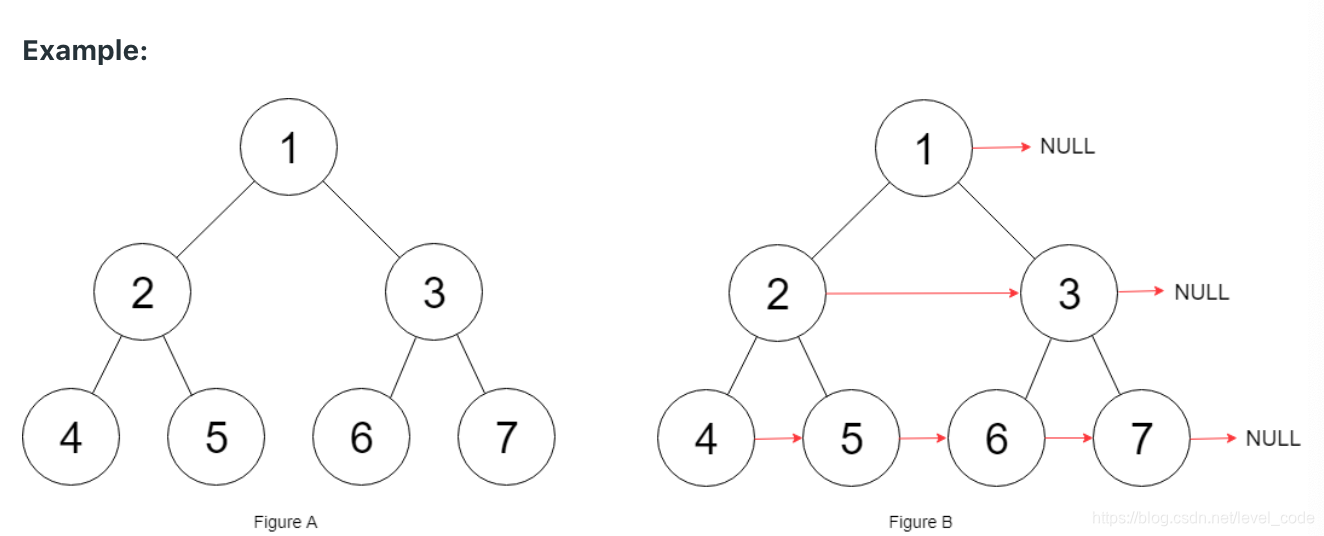
给一棵二叉树,让把每层的左边节点的next指针指向右边节点
思路
(1) BFS
每层节点直到最后一个都是next指向下一节点,每层的最后一个节点next指向null
//1ms
//BFS..
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
List<Node> current = new ArrayList<>();
List<Node> next = new ArrayList<>();
current.add(root);
root.next = null;
while (!current.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < current.size() - 1; i++) {
Node node = current.get(i);
node.next = current.get(i + 1);
if (node.left != null) {
next.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
next.add(node.right);
}
}
Node last = current.get(current.size() - 1);
last.next = null;
if (last.left != null) {
next.add(last.left);
}
if (last.right != null) {
next.add(last.right);
}
current.clear();
List<Node> tmp = current;
current = next;
next = tmp;
}
return root;
}
(2) 递归
//0ms
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
root.next = null;
helper(root.left, root.right);
return root;
}
public void helper(Node root1, Node root2) {
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {
return;
}
root1.next = root2;
helper(root1.left, root1.right);
helper(root1.right, root2.left);
helper(root2.left, root2.right);
}





 本文介绍了一种在完美二叉树中连接节点next指针的方法,通过BFS和递归两种方式实现,确保每层节点间的正确链接。
本文介绍了一种在完美二叉树中连接节点next指针的方法,通过BFS和递归两种方式实现,确保每层节点间的正确链接。

















 279
279

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










