1.简介
本实验任务:编写前面学过的两个路径规划算法。
首先用C++编写Breadth-first搜索算法。该算法分为不同的编码测验,最终生成机器人从起点移动到目标的最短路径。
然后,将继续进行必要的更改,以编写A*算法。在对BFS和A*算法进行编码之后,将可视化地比较生成的扩展列表。仔细检查后,判断哪种算法更有效。
在本实验的后面部分,将把A*算法应用到现实世界的问题中。实际问题只是使用占用网格映射算法生成的地图。
实验:路径规划
实验的详细步骤列表如下:

2.建模问题
本实验的目的是利用不同的路径规划算法,为机器人在5x6地图中从起始位置移动到目标位置找到最短路径。机器人只能向四个方向移动:上、左、下、右。我们将首先使用C++中的类来建模这个问题,然后用BFS和A*算法来解决它。
Given
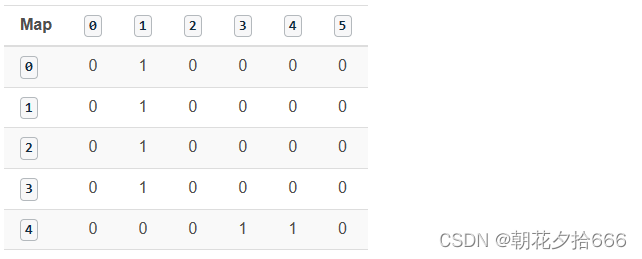
Grid(5x6):
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 0
其中1代表障碍,0代表自由空间。
机器人起始位置:0,0
机器人目标位置:4,5
移动方向:上(-1,0)-左(0,-1)-下(1,0)-右(0,1)
移动方向矢量是四个不同2D矢量的集合,每个矢量都允许在地图中的网格单元之间移动。
移动箭头:上(^)-左(<)-下(v) -右(>)
移动箭头向量存储机器人的动作,这个向量将在本实验室稍后使用,以可视化机器人在最短路径上的每个网格单元的方向。
移动成本:1
移动成本值表示从一个单元格移动到另一个单元格的成本。在这里,对于所有可能的移动,代价都是相等的。
测试
在这个测试中,为了建模问题,有三个主要任务要完成:
注意
在整个实验过程中,将使用C++中的1D和2D向量。vector允许使用预先构建的函数轻松地管理和操作数据。例如:pop_back函数可用于删除vector中的最后一个元素。
关于向量,可参阅以下两个资源:
- 2D Vectors: 学习如何在C++中定义和使用2D向量。
- Documentation: 学习向量迭代器和修饰器(modifiers)。
参考代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
/* TODO: Define a Map class
Inside the map class, define the mapWidth, mapHeight and grid as a 2D vector
*/
class Map {
public:
const static int mapWidth = 6;
const static int mapHeight = 5;
vector<vector<int> > grid = {
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 }
};
};
/* TODO: Define a Planner class
Inside the Planner class, define the start, goal, cost, movements, and movements_arrows
Note: The goal should be defined it terms of the mapWidth and mapHeight
*/
class Planner : Map {
public:
int start[2] = { 0, 0 };
int goal[2] = { mapHeight - 1, mapWidth - 1 };
int cost = 1;
string movements_arrows[4] = { "^", "<", "v", ">" };
vector<vector<int> > movements{
{ -1, 0 },
{ 0, -1 },
{ 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1 }
};
};
/* TODO: Define a print2DVector function which will print 2D vectors of any data type
Example
Input:
vector<vector<int> > a{
{ 1, 0 },{ 0, 1 }};
print2DVector(a);
vector<vector<string> > b{
{ "a", "b" },{ "c", "d" }};
print2DVector(b);
Output:
1 0
0 1
a b
c d
Hint: You need to use templates
*/
template <typename T>
void print2DVector(T Vec)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Vec.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < Vec[0].size(); ++j) {
cout << Vec[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
/*############ Don't modify the main function############*/
int main()
{
// Instantiate map and planner objects
Map map;
Planner planner;
// Print classes variables
cout << "Map:" << endl;
print2DVector(map.grid);
cout << "Start: " << planner.start[0] << " , " << planner.start[1] << endl;
cout << "Goal: " << planner.goal[0] << " , " << planner.goal[1] << endl;
cout << "Cost: " << planner.cost << endl;
cout << "Robot Movements: " << planner.movements_arrows[0] << " , " << planner.movements_arrows[1] << " , " << planner.movements_arrows[2] << " , " << planner.movements_arrows[3] << endl;
cout << "Delta:" << endl;
print2DVector(planner.movements);
return 0;
}
3.BFS:扩展列表
现在使用C++中的Map和Planner类对问题进行建模,接下来将从BFS算法的第一部分开始。在这个测试中,编写搜索函数,以最低的代价扩展单元格,直到达到目标。
为此,需要用三元组值[g, x, y]表示每个单元格,其中g表示向该单元格扩展的总代价,x是行值,y是列值。
一旦扩展到达目标,打印目标的最终三重值。
在编写搜索函数时,记住以下事项
- 当扩展到一个新的单元格时,检查是否达到了目标;一旦到达,打印它的三重值。
- 主动检查是否遇到了障碍。如果遇到了障碍,停止扩展并打印一条消息,表明未能达到目标。
- 展开g值最低的单元格,并将展开存储在一个开放向量中。如果两个单元格的g值相等,则可以选择其中一个单元格进一步展开。
提示
下面是如何使用BFS算法扩展单元,直到达到目标:
Expansion #: 0
Open List: [0 0 0 ]
Cell Picked: [0 0 0]
Expansion #: 1
Open List: [1 1 0 ]
Cell Picked: [1 1 0]
Expansion #: 2
Open List: [2 2 0 ]
Cell Picked: [2 2 0]
Expansion #: 3
Open List: [3 3 0 ]
Cell Picked: [3 3 0]
Expansion #: 4
Open List: [4 4 0 ]
Cell Picked: [4 4 0]
Expansion #: 5
Open List: [5 4 1 ]
Cell Picked: [5 4 1]
Expansion #: 6
Open List: [6 4 2 ]
Cell Picked: [6 4 2]
Expansion #: 7
Open List: [7 3 2 ]
Cell Picked: [7 3 2]
Expansion #: 8
Open List: [8 3 3 ], [8 2 2 ]
Cell Picked: [8 2 2]
Expansion #: 9
Open List: [9 2 3 ], [9 1 2 ], [8 3 3 ]
Cell Picked: [8 3 3]
Expansion #: 10
Open List: [9 3 4 ], [9 2 3 ], [9 1 2 ]
Cell Picked: [9 1 2]
Expansion #: 11
Open List: [10 1 3 ], [10 0 2 ], [9 3 4 ], [9 2 3 ]
Cell Picked: [9 2 3]
Expansion #: 12
Open List: [10 2 4 ], [10 1 3 ], [10 0 2 ], [9 3 4 ]
Cell Picked: [9 3 4]
Expansion #: 13
Open List: [10 3 5 ], [10 2 4 ], [10 1 3 ], [10 0 2 ]
Cell Picked: [10 0 2]
Expansion #: 14
Open List: [11 0 3 ], [10 3 5 ], [10 2 4 ], [10 1 3 ]
Cell Picked: [10 1 3]
Expansion #: 15
Open List: [11 1 4 ], [11 0 3 ], [10 3 5 ], [10 2 4 ]
Cell Picked: [10 2 4]
Expansion #: 16
Open List: [11 2 5 ], [11 1 4 ], [11 0 3 ], [10 3 5 ]
Cell Picked: [10 3 5]
Expansion #: 17
Open List: [11 4 5 ], [11 2 5 ], [11 1 4 ], [11 0 3 ]
Cell Picked: [11 0 3]
Expansion #: 18
Open List: [12 0 4 ], [11 4 5 ], [11 2 5 ], [11 1 4 ]
Cell Picked: [11 1 4]
Expansion #: 19
Open List: [12 1 5 ], [12 0 4 ], [11 4 5 ], [11 2 5 ]
Cell Picked: [11 2 5]
Expansion #: 20
Open List: [12 1 5 ], [12 0 4 ], [11 4 5 ]
Cell Picked: [11 4 5]
参考代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// Map class
class Map {
public:
const static int mapWidth = 6;
const static int mapHeight = 5;
vector<vector<int> > grid = {
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 }
};
};
// Planner class
class Planner : Map {
public:
int start[2] = { 0, 0 };
int goal[2] = { mapHeight - 1, mapWidth - 1 };
int cost = 1;
string movements_arrows[4] = { "^", "<", "v", ">" };
vector<vector<int> > movements{
{ -1, 0 },
{ 0, -1 },
{ 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1 }
};
};
// Template function to print 2D vectors of any type
template <typename T>
void print2DVector(T Vec)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Vec.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < Vec[0].size(); ++j) {
cout << Vec[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
/*#### TODO: Code the search function which will generate the expansion list ####*/
// You are only required to print the final triplet values
void search(Map map, Planner planner)
{
// Create a closed 2 array filled with 0s and first element 1
vector<vector<int> > closed(map.mapHeight, vector<int>(map.mapWidth));
closed[planner.start[0]][planner.start[1]] = 1;
// Defined the triplet values
int x = planner.start[0];
int y = planner.start[1];
int g = 0;
// Store the expansions
vector<vector<int> > open;
open.push_back({ g, x, y });
// Flags
bool found = false;
bool resign = false;
int x2;
int y2;
// While I am still searching for the goal and the problem is solvable
while (!found && !resign) {
// Resign if no values in the open list and you can't expand anymore
if (open.size() == 0) {
resign = true;
cout << "Failed to reach a goal" << endl;
}
// Keep expanding
else {
// Remove triplets from the open list
sort(open.begin(), open.end());
reverse(open.begin(), open.end());
vector<int> next;
// Stored the poped value into next
next = open.back();
open.pop_back();
x = next[1];
y = next[2];
g = next[0];
// Ch




 本文介绍了使用C++实现BFS和A*算法来解决路径规划问题的过程。首先,通过建模地图和规划者类,使用BFS找到最短路径,并可视化扩展列表。接着,扩展功能以生成和打印展开的2D向量及机器人的动作策略。然后,实现了A*算法,通过曼哈顿距离启发式函数找到更优路径。最后,讨论了如何将A*应用于真实世界地图,并进行路径可视化。
本文介绍了使用C++实现BFS和A*算法来解决路径规划问题的过程。首先,通过建模地图和规划者类,使用BFS找到最短路径,并可视化扩展列表。接着,扩展功能以生成和打印展开的2D向量及机器人的动作策略。然后,实现了A*算法,通过曼哈顿距离启发式函数找到更优路径。最后,讨论了如何将A*应用于真实世界地图,并进行路径可视化。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








