6.3 IPIPE: Xenomai/Linux双核交替调度数据结构
6.3.1 Xenomai/Linux进程/线程描述符的定义与异同
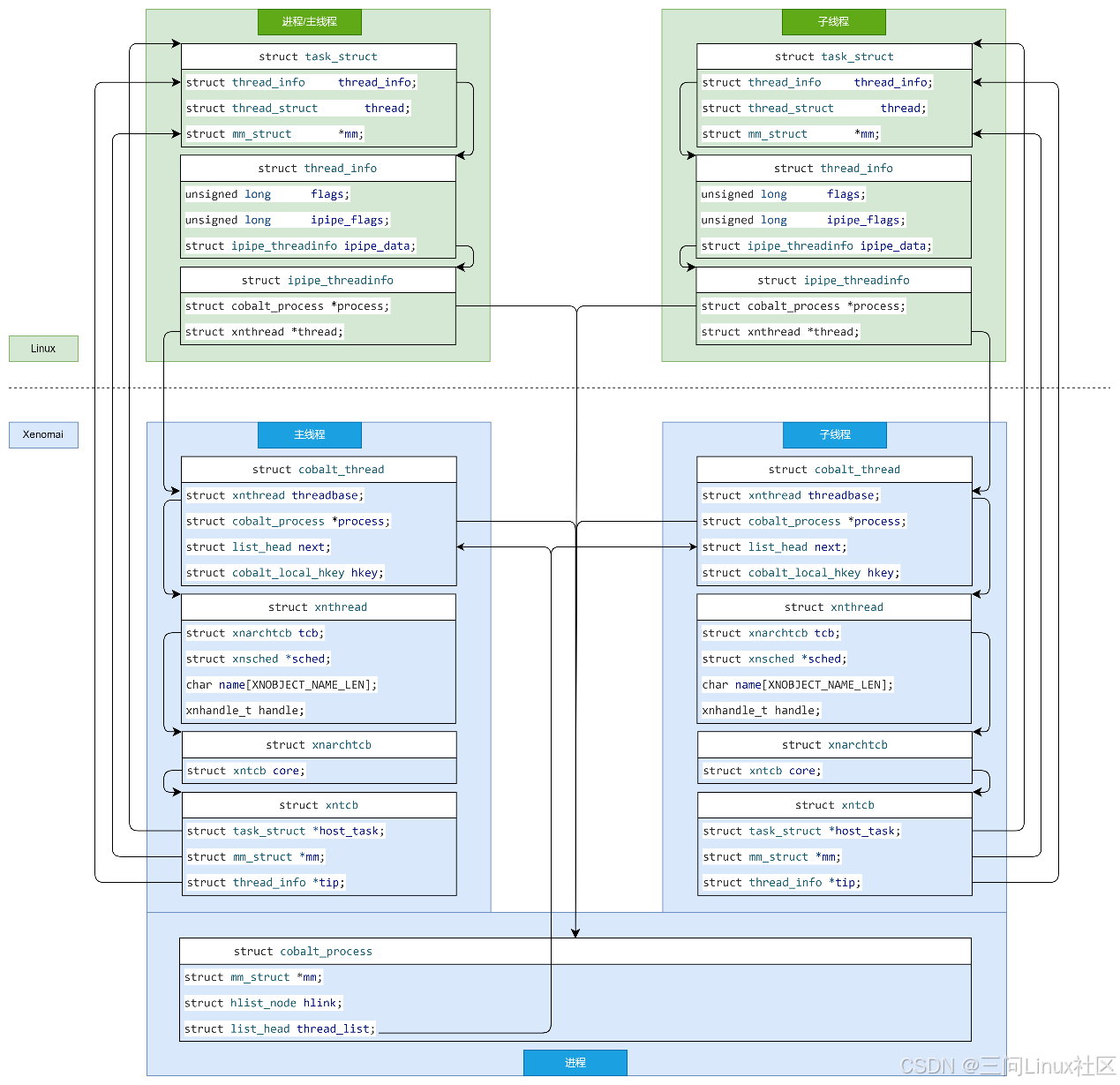
在Linux中,结构体struct task_struct是进程描述符。Linux没有为线程定义单独的线程描述符,而是复用结构体struct task_struct。struct task_struct是Linux的调度实体。
如果一个进程只有自身一个线程,那么只需要一个结构体struct task_struct即可。
如果一个进程除了自身主线程之外,还新建了一个子线程,那么需要为子线程申请一个新的结构体struct task_struct。此时,进程包含了两个线程:主线程和子线程,且两个线程是共享虚拟地址空间struct mm_struct的。
struct task_struct 中包含了struct thread_info结构体(CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK=y,否则struct thread_info在内核栈的栈底)。struct thread_info 包含了低级别的任务数据,这些数据是汇编代码(entry.S)需要立即访问的。当从用户空间切换到内核空间时(如执行系统调用或发生中断),内核需要快速获取当前线程的一些基本信息来正确地保存现场(即当前执行环境的状态)并进行上下文切换。因此,这些信息必须存储在一个可以被迅速定位和访问的位置。
IPIPE在struct thread_info中新增了struct ipipe_threadinfo ipipe_data,用于连接Xenomai/Linux双内核之间的调度实体。
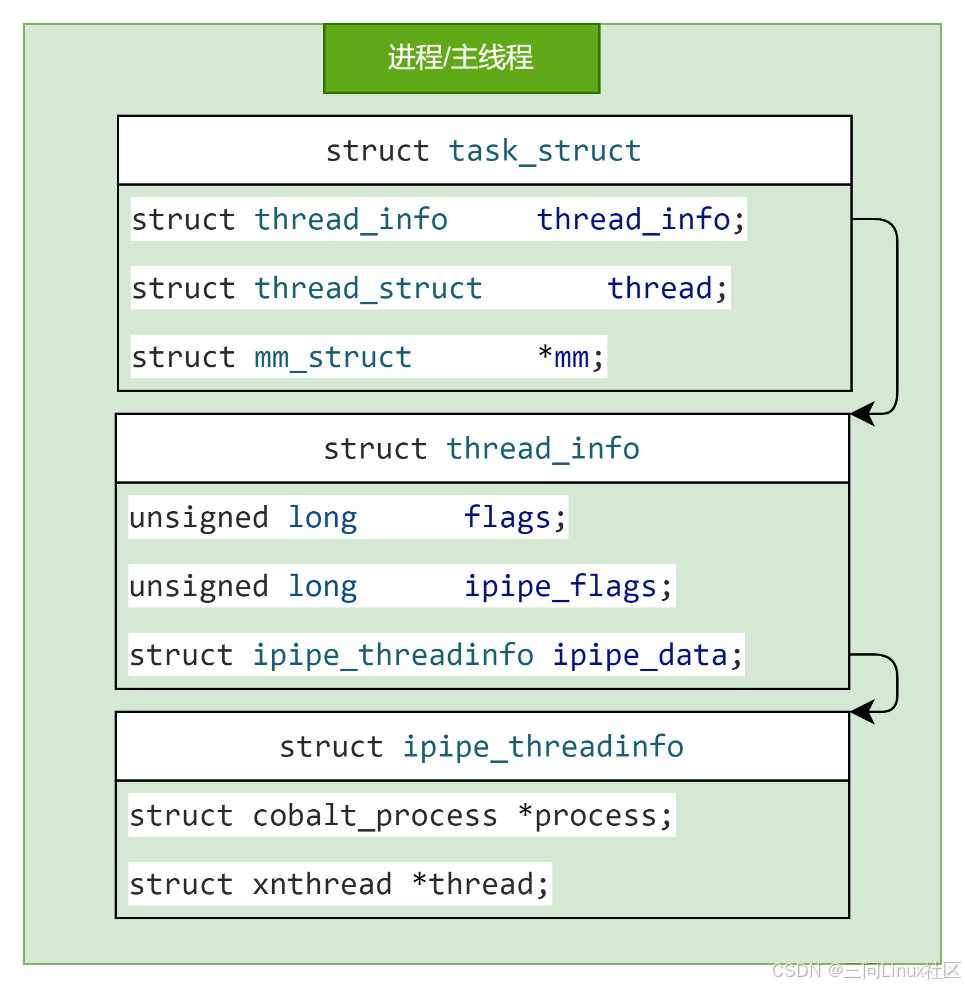
在结构体struct ipipe_threadinfo引入了两个重要的概念:
(1)Xenomai进程结构体struct cobalt_process
(2)Xenomai线程结构体struct xnthread
顾名思义,Xenomai为进程和线程分别定义了一个结构体,与Linux完全不同。
如果一个Xenomai进程只有自身一个线程,那么只需要一个进程结构体struct cobalt_process和一个线程结构体struct xnthread。
如果一个进程除了自身主线程之外,还新建了一个子线程,那么需要为子线程申请一个新的线程结构体struct xnthread。此时,进程包含了两个线程:主线程和子线程,且两个线程共用一个进程结构体struct cobalt_process。线程结构体struct xnthread是调度实体。
结构体struct ipipe_threadinfo中的struct cobalt_process *process指针和struct xnthread *thread指针,一定会指向Xenomai中真正的结构体。
反之,Xenomai也需要反向找到Linux中的结构体struct task_struct。
这些数据结构之间是怎么发生联系的?下一章节继续!
6.3.2 Xenomai/Linux进程/主线程描述符之间的关联
本文分析进程/主线程创建的过程及相互的关联。
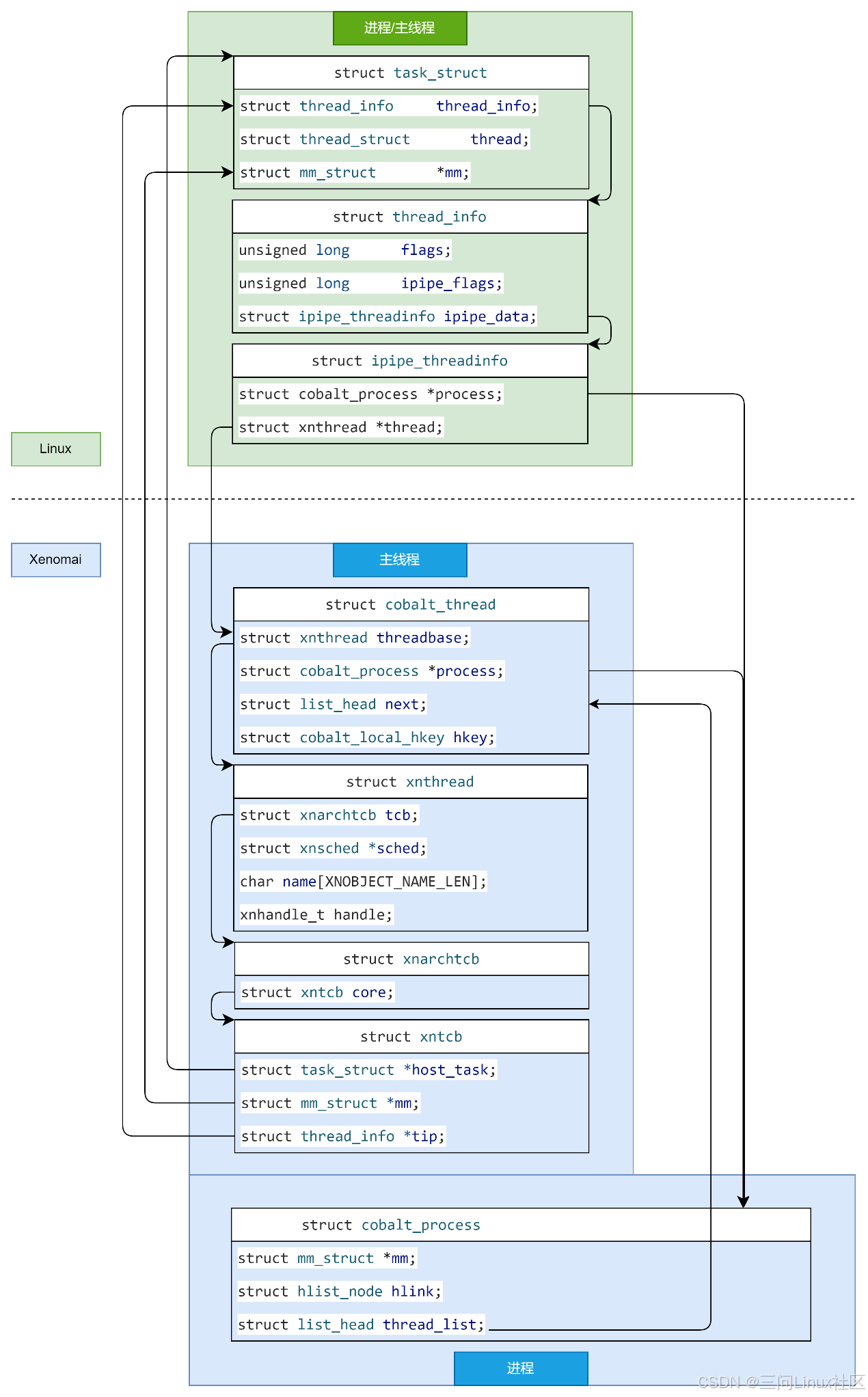
1. Linux进程描述符struct task_struct的创建
参考《6.1.4 Xenomai3: hello world如何变成Xenomai实时进程》的分析,在Linux Shell下启动应用程序,会经历如下标准流程:
(1)Fork 函数:Shell 使用 fork() 函数,调用sys_fork系统调用来创建一个新的子线程并分配struct task_struct。此时,子进程是父进程(通常是 Shell)的一个副本,包括内存空间、文件描述符等。注意,此时struct task_struct仅仅是Shell的子线程。
(2)Exec 系列函数:在子线程中,Shell 调用 execve() 或其他 exec 系列函数之一来加载并执行指定的 ELF 文件。这一步会替换当前进程的用户空间镜像为新程序的镜像。此时,子线程将拥有自己的虚拟地址空间,可用称为一个独立的进程,它的父进程为Shell。
至此,Linux进程描述符struct task_stuct已经创建完毕。
2. Xenomai进程描述符struct cobalt_process的创建
__libc_start_main 是 glibc 内部函数,负责进一步初始化运行时环境,包括调用__libc_csu_init初始化全局构造函数和静态构造函数,即执行所有带有__attribute__((constructor))属性的函数以及C++中的静态对象构造函数。
Xenomai3 利用GCC的 __attribute__((constructor)) 特性来定义了3种优先级的构造函数。凡是有这3个宏作为前缀的函数,总是会在__libc_csu_init中被执行。

在__setup_ctor中,关注struct setup_descriptor cobalt_interface,它的init函数是cobalt_init。
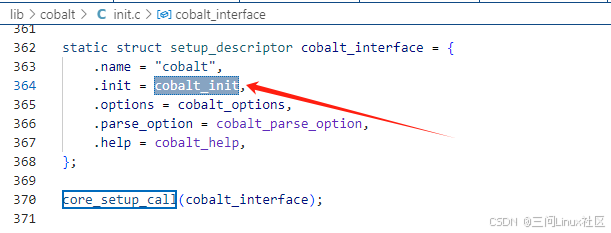
cobalt_init会调用sc_coablt_bind系统调用创建struct cobalt_process。
cobalt_init
->cobalt_init_1()
->cobalt_init_2()
->low_init() // 调用sc_coablt_bind系统调用创建cobalt_process
陷入内核,执行系统调用sc_coablt_bind,调用堆栈如下。
static COBALT_SYSCALL(bind, lostage,
(struct cobalt_bindreq __user *u_breq)) //系统调用
->cobalt_bind_core
->bind_personality(&cobalt_personality)
->personality->ops.attach_process
->cobalt_process_attach // 申请struct cobalt_process结构体
->cobalt_set_process(process); //->struct ipipe_threadinfo ipipe_data.process指向新申请的struct cobalt_process结构体
(1)cobalt_process_attach
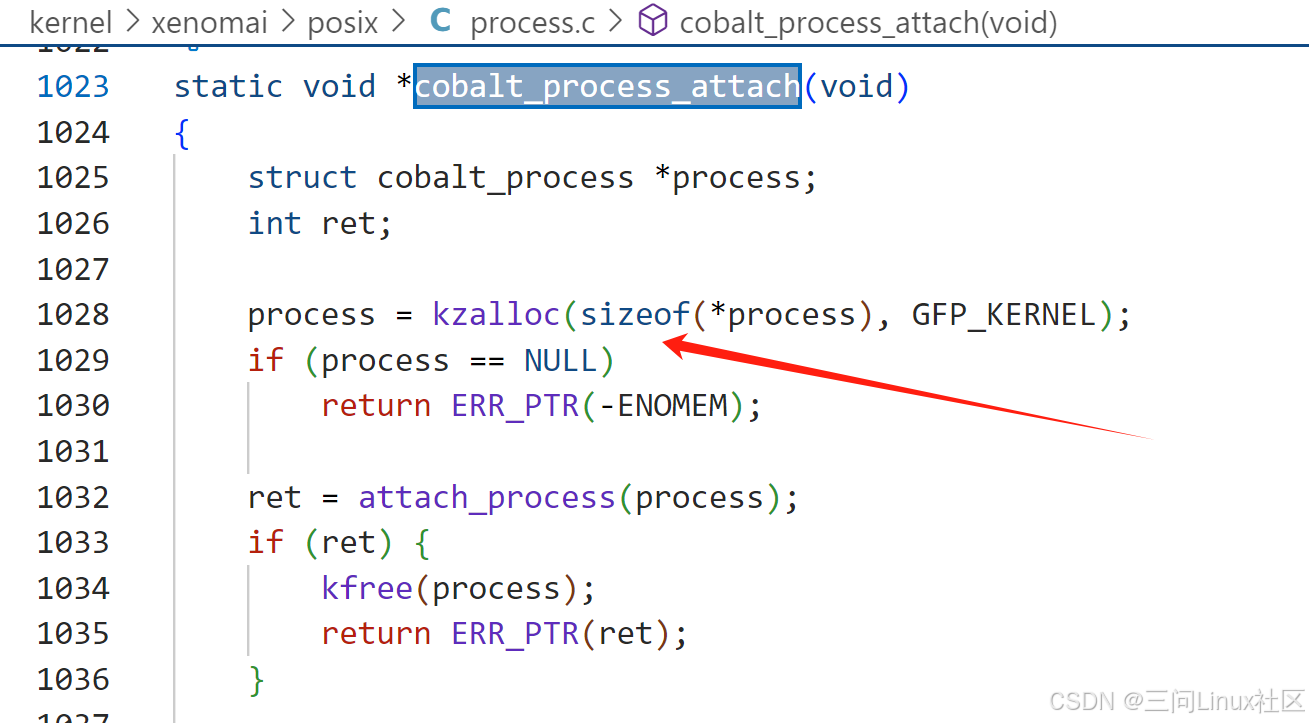
第1028行,申请struct cobalt_process结构体。
第1032行,调用attach_process把cobalt_process加入process_hash哈希链表。
(2)cobalt_set_process
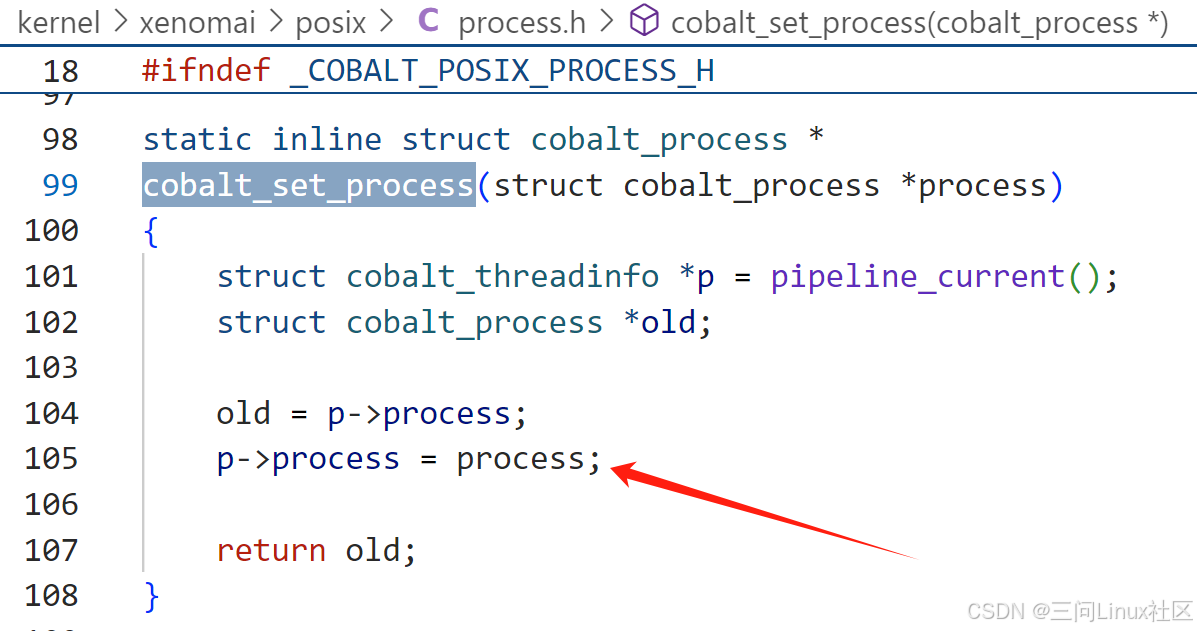
最终在cobalt_set_process中,struct ipipe_threadinfo ipipe_data.process指向新申请的struct cobalt_process结构体。
至此,Linux进程描述符struct task_struct通过struct ipipe_threadinfo中的process指针,指向了Xenomai进程描述符struct cobalt_process结构体。
3. Xenomai主线程描述符struct cobalt_thread的创建
回到上文提到的cobalt_init,它不仅会调用sc_coablt_bind系统调用创建cobalt_process,而且会继续创建Xenomai主线程描述符struct cobalt_thread。
cobalt_init
->cobalt_init_1()
->cobalt_init_2()
->low_init() // 调用sc_coablt_bind系统调用创建cobalt_process
-> __RT(pthread_setschedparam(ptid, policy, &parm))
->pthread_setschedparam_ex // 调用系统调用sc_cobalt_thread_setschedparam_ex创建struct cobalt_thread。
pthread_setschedparam_ex调用系统调用sc_cobalt_thread_setschedparam_ex创建struct cobalt_thread。
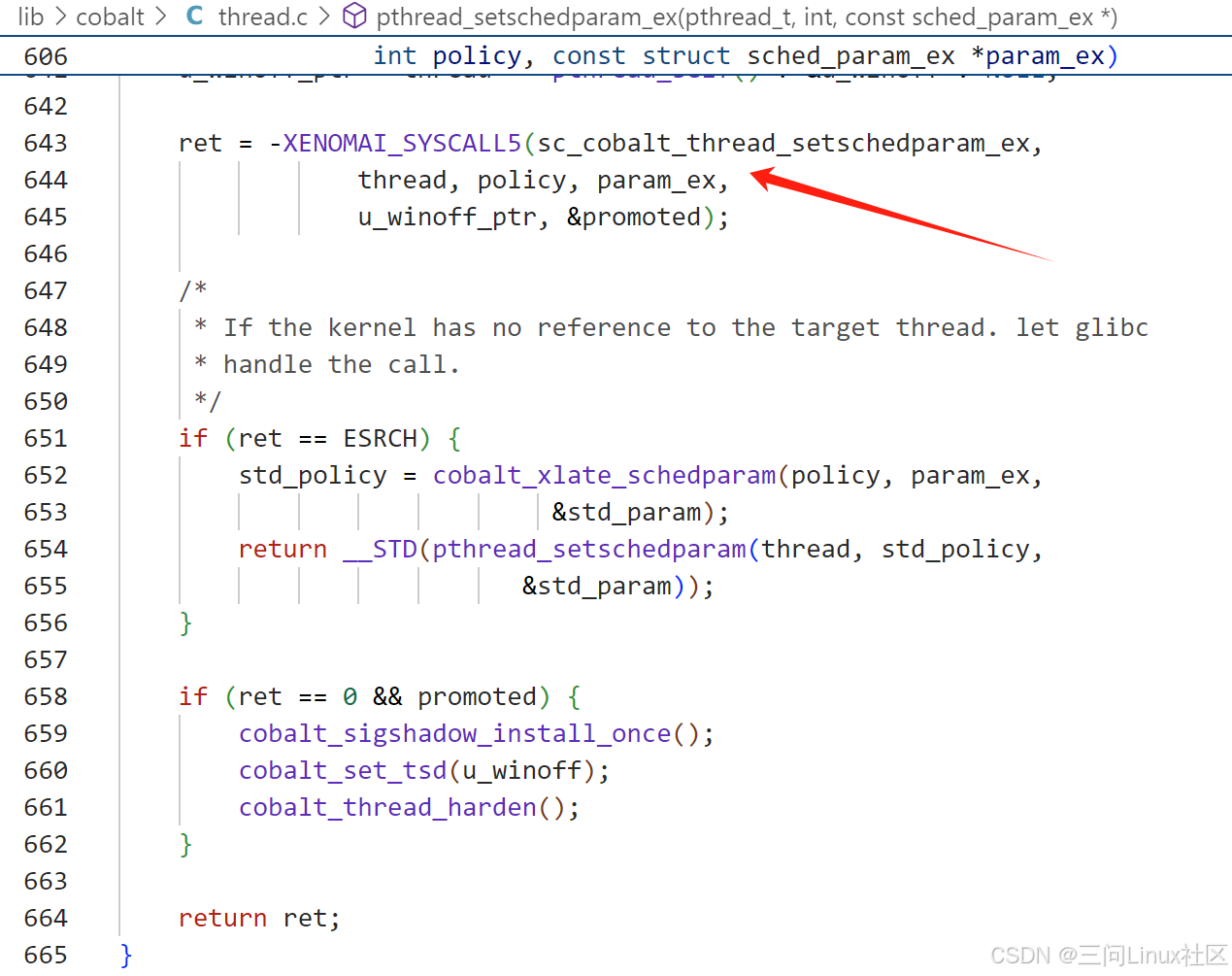
系统调用sc_cobalt_thread_setschedparam_ex在Xenomai内核中的实现如下。
COBALT_SYSCALL(thread_setschedparam_ex, conforming,
(unsigned long pth,
int policy,
const struct sched_param_ex __user *u_param,
__u32 __user *u_winoff,
int __user *u_promoted))
-> cobalt_thread_setschedparam_ex
-> thread_lookup_or_shadow
-> cobalt_thread_shadow
-> pthread_create //创建struct cobalt_thread,插入struct cobalt_process中thread_list链表!
-> cobalt_map_user //将struct cobalt_thread变成Linux struct task_struct的影子
(1)thread_lookup_or_shadow
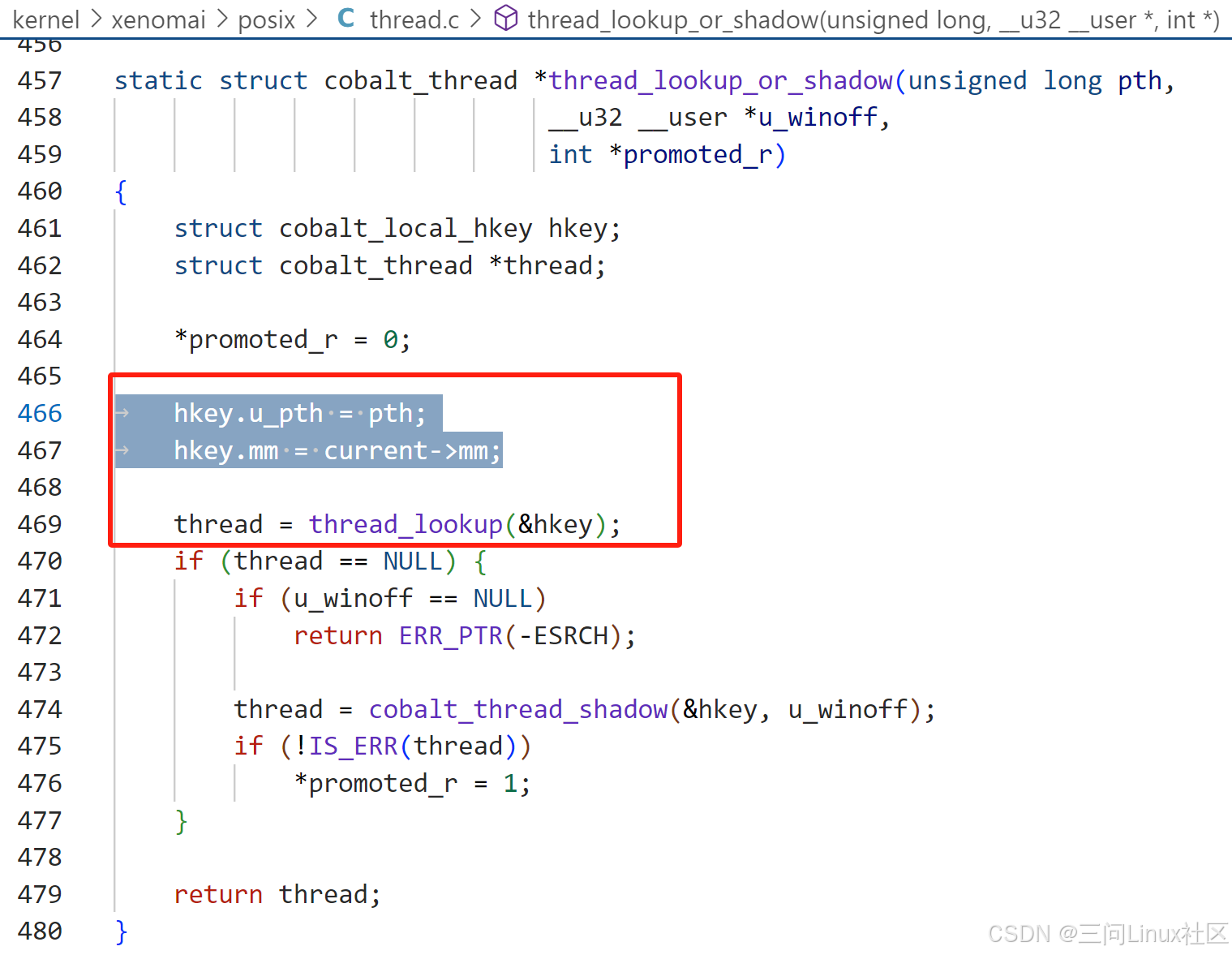
第469行,调用thread_lookup,通过hkey在哈希链表来查找是否有匹配的struct cobalt_thread。
hkey.u_pth是从用户层传下来的pthread_t thread。pthread_t thread是 用户层POSIX 线程库中的一个数据类型,用来表示线程的标识符。在用户层这个标识符可以用来在程序中唯一地标识当前线程,而IPIPE借用了这个标识符。
hkey.mm是复用Linux中struct task_struct中的struct mm_struct指针,对于一个进程来说,主线程和所有子线程是共享虚拟地址空间的,所以struct mm_struct指针是唯一的。
第474行,因为当前处于新的进程创建过程,所以肯定是无法查找出匹配的struct cobalt_thread,会走到cobalt_thread_shadow创建新的struct cobalt_thread。
(2)cobalt_thread_shadow
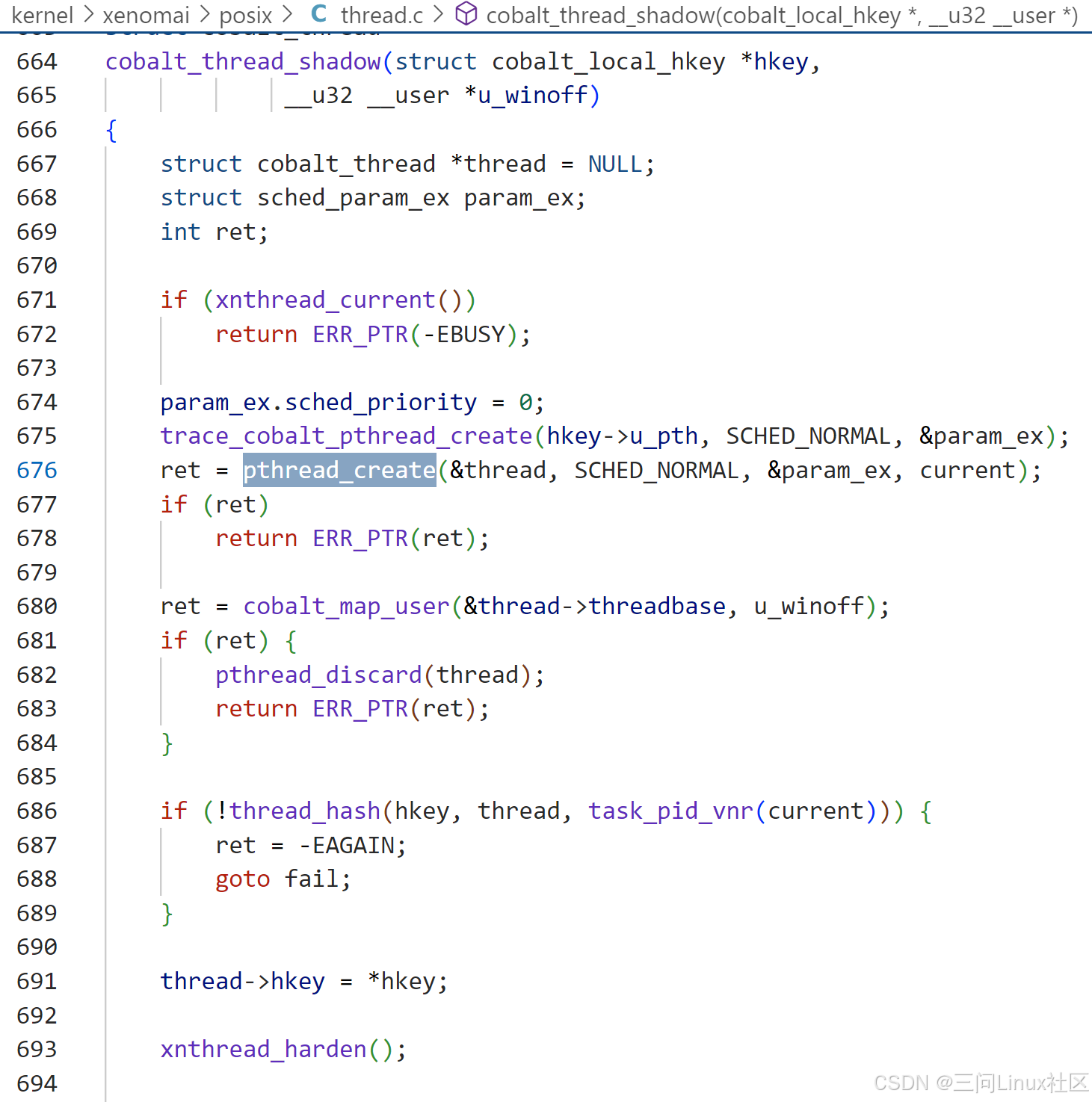
第676行,pthread_create 函数是 Cobalt 实时扩展中用于创建新线程的核心函数。它负责为新的线程结构体 (struct cobalt_thread) 分配内存,初始化线程的基本属性(如名称、标志、亲和性等)到 iattr 结构体中,调用 xnthread_init 函数初始化线程对象,插入struct cobalt_process中thread_list链表!初始化完成后,线程处于休眠状态,直到通过 xnthread_start() 显式启动。
第680行,cobalt_map_user用于将一个 Xenomai 线程映射到当前运行在用户空间的普通 Linux 任务。这个过程称为“影子线程上下文”(shadow thread context)创建,具体是调用pipeline_init_shadow_tcb完成的,例如cobalt_thread.threadbase.tcb.core中的struct task_struct *host_task指向Linux 任务task_struct结构体。在此之后,struct cobalt_thread称为struct task_struct的影子!最后,显示调用xnthread_start,启动线程。
第693行,xnthread_harden用于将当前运行的 Linux 任务迁移到 Xenomai 域。这个过程通常称为“硬化”(hardening),它使得当前任务从标准 Linux 调度器切换到 Xenomai 实时调度器,并在 head域中继续执行。
至此,Xenomai/Linux进程/主线程描述符之间的关联完全建立完毕,且struct cobalt_thread称为struct task_struct的影子。
6.3.3 Xenomai/Linux进程/多线程描述符之间的关联
本章节在《6.3.2 Xenomai/Linux进程/主线程描述符之间的关联》的基础上,增加多线程的分析。为了简化,仅分析新建一个子线程的情况。
1. Linux子线程描述符struct task_struct的创建
参考《6.2 Xenomai线程的创建流程》,helloworld.c中的pthread_create被改头换面为__wrap_pthread_create,走到pthread_create_ex()函数,最终会调用__real_pthread_create意味着直接调用pthread库中的pthread_create函数。但是线程入口函数并不是原始入口函数,而被移花接木的改为跳板入口函数cobalt_thread_trampoline!
重点是,pthread_create最终依赖 clone 系统调用来创建新线程,当 clone 系统调用被触发时,控制权从用户空间转移到内核空间。Linux内核开始处理这个系统调用请求。
Linux内核会为新线程创建一个新的 task_struct 数据结构,如图中的右上角所示。task_struct 是 Linux 内核中用于表示进程或线程的数据结构,包含状态、调度信息、资源管理等信息。
内核将新线程的 task_struct 插入到调度器的就绪队列中,以便它可以被调度运行。
2. Xenomai子线程描述符struct cobalt_thread的创建
子线程会调用入口函数cobalt_thread_trampoline,并将 iargs 作为参数传递给该函数。
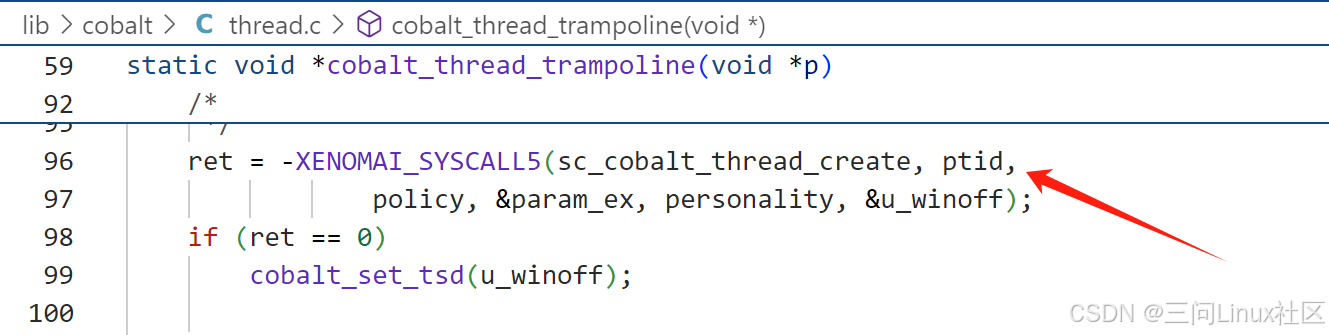
cobalt_thread_trampoline在第96行指向sc_cobalt_thread_create系统调用。
sc_cobalt_thread_create系统调用触发,陷入内核层,最终执行Xenomai系统调用函数CoBaLt_thread_create,定义如下:
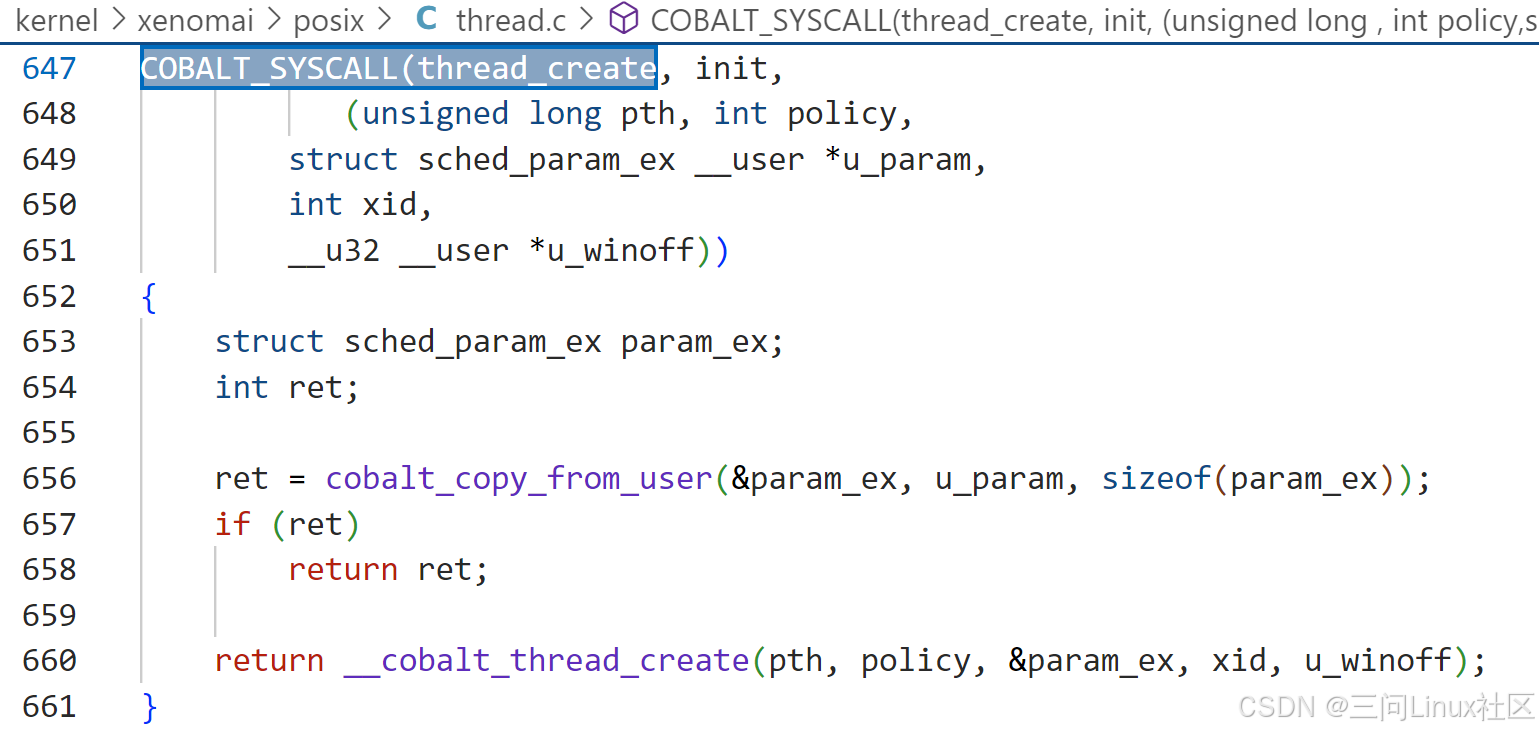
第660行,这是实际执行线程创建的内部函数__cobalt_thread_create。它负责初始化新线程的上下文、设置调度参数、分配资源等操作,并最终启动新线程。
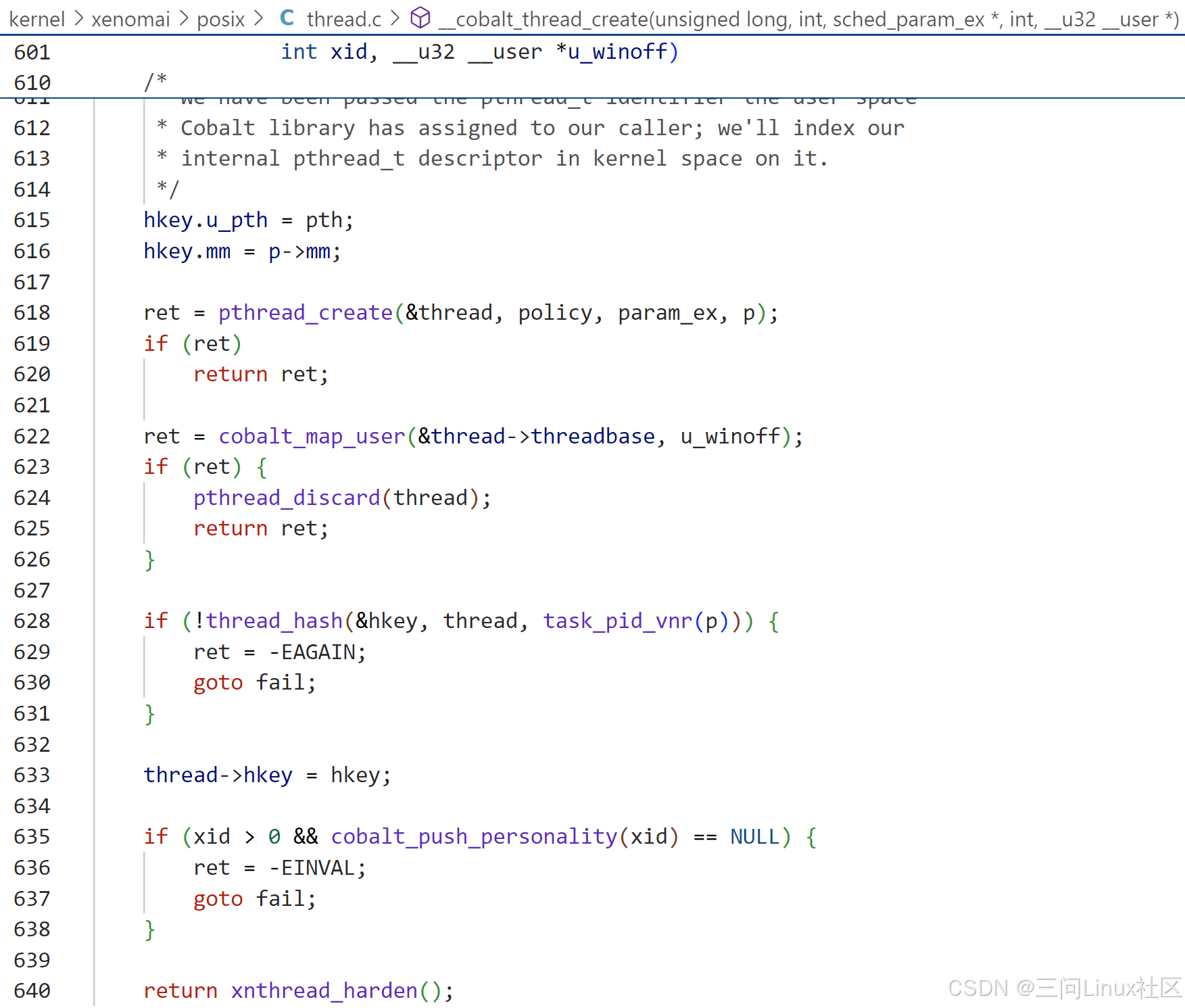
第618行,pthread_create 函数是 Cobalt 实时扩展中用于创建新线程的核心函数。它负责为新的线程结构体 (struct cobalt_thread) 分配内存,初始化线程的基本属性(如名称、标志、亲和性等)到 iattr 结构体中,调用 xnthread_init 函数初始化线程对象,插入struct cobalt_process中thread_list链表!初始化完成后,线程处于休眠状态,直到通过 xnthread_start() 显式启动。
第622行,cobalt_map_user用于将一个 Xenomai 线程映射到当前运行在用户空间的普通 Linux 任务。这个过程称为“影子线程上下文”(shadow thread context)创建,具体是调用pipeline_init_shadow_tcb完成的,例如cobalt_thread.threadbase.tcb.core中的struct task_struct *host_task指向Linux 任务task_struct结构体。最后,显示调用xnthread_start,启动线程。
第640行,xnthread_harden用于将当前运行的 Linux 任务迁移到 Xenomai 域。这个过程通常称为“硬化”(hardening),它使得当前任务从标准 Linux 调度器切换到 Xenomai 实时调度器,并在 head域中继续执行。
至此,子线程对应的Linux结构体struct task_struct和Xenomai结构体struct cobalt_thread创建完毕。
-
主线程和子线程结构体struct cobalt_thread中的struct cobalt_process指针,都指向同一个struct struct cobalt_process。
-
主线程和子线程结构体struct cobalt_thread都会加入到同一个struct struct cobalt_process中的thread_list链表!






















 979
979

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








