本周大部分时间在赶小论文的实验,终于是赶在ddl之前三小时提交了论文,希望能有机会被审稿人看中,看不中拿回来改一改再中也行。不过虽然没有做其他事情,但是研究了一下排队论,不知不觉就写了6千多字,在这里不方便发出来。本篇文章只能水一下了,下次一定好好做实验写好并发出来。还有要反思一下,本周设置的读书任务没完成,看游戏去了,不过MSI今晚就结束了,希望来一句:“恭喜RNG”!
那就写一下本周完成的英文版的DFS算法小析。
Depth first search traversal process:
Depth First Search for a graph is similar to ordering a tree traversal.
Its main idea: if the initial state is that none of the vertices in the graph have been visited, then start from someone vertex v, visit this vertex first, and then start from all of its unvisited adjacent points successively, until all the vertices in the graph that have a path to v have been visited. If there are other vertices that have not been accessed at this time, choose another vertex that has not been accessed as the starting point, and repeat the above process until all vertices in the graph have been accessed.
Obviously, depth-first search is a recursive process
The characteristic of depth-first traversal is to select a starting point and then traverse. If you can go forward, just go forward. If you can't go forward, you can go back one step and then go forward, or you can go back one more step and then continue to go forward. Repeat until all vertices connected to the selected point have been traversed. The complexity of DFS is O(V+E).
Example:
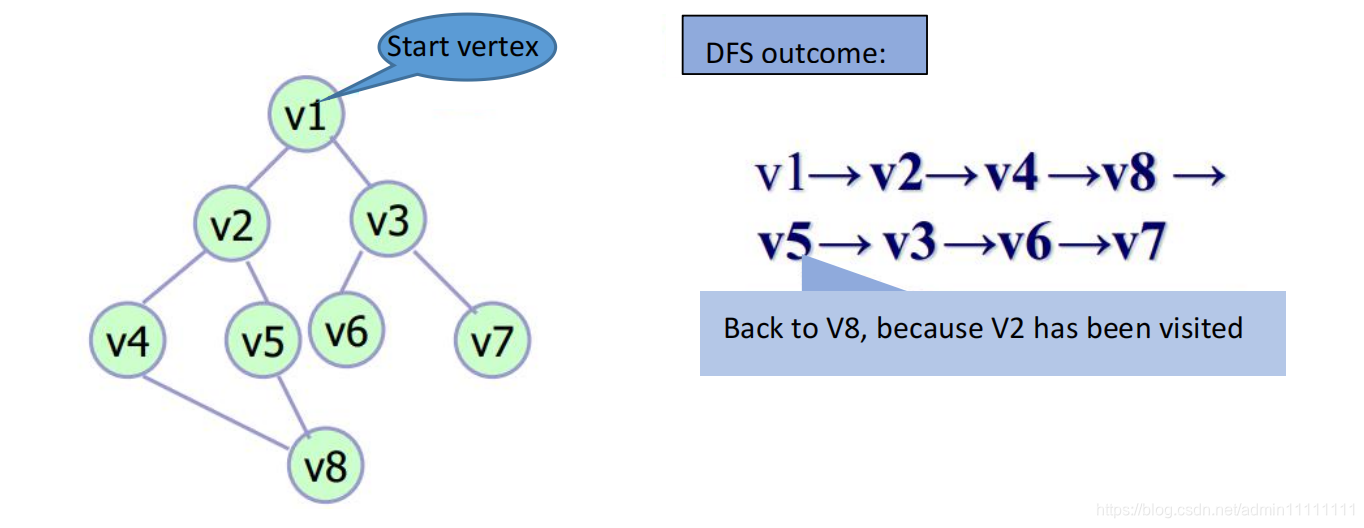
For example, as the picture depicts:
We start from vertex v1, and the next vertex is v2, keep going forward then we will go through v4 and arrived at v8, but v8 also has a path to v5, so keep visiting v5.
At this moment, although v5 connects to v2, it can not visit v5 again.
So let‘s go back to v8, there is also no path to connect other vertexes that have not visited. Then go back to v4, for the same reasons, we must go back to v1 and then can find v3 is a new vertex that does not visit.
So at v1, then go forward to visit v3 and keep to go forward to v6, then we stuck again, so we keep to go back to v3, finally, we arrive at the last vertex v7 and visit it.
Therefore, the DFS output is: v1 -> v2 -> v4 -> v8 -> v5 -> v3 -> v6 -> v7.
Source code:
In this part, I will use two methods—the Adjacency matrix and the Adjacency list—to implement the DFS.
//Adjacency matrix
void DFS( Mgraph g,int v,int visited[])
{
/* Adjacency matrix storage, starting from vertex V, carries out depth-first search on graph G*/
int j;
printf("%d ",g.vexs[v]);
visited[v]=1; /* mark that v has been visited */
for(j=0;j<g.vexnum;j++);
{
if( g.arcs[v][j]==1&&visited[j]==0) /* vertex j is the adjacency of vertex v and has not been visited */
DFS(g,j,visited); /* DFS is called recursively from j */
}/*end for*/
}/*end DFS*/
void DFSTraverse(Mgraph g)
{
/*Adjacency matrix depth-first search*/
int v;
int visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
for(v=0;v<g.vexnum;v++)
visited[v]=0; /* Initializes the visited array */
for(v=0;v<g.vexnum;v++)
if(visited[v]==0)
DFS(g,v,visited);
/* start from vertex v which does not be visited, DFS search*/
}
//Adjacency list
void DFS(ALGraph g,int v,int visited[])
{
/*Adjacency list storage, starting from vertex V, carries out a depth-first search on graph G*/
ArcNode *p;
int w;
printf("%d ",g.adjlist[v].data);
visited[v]=1; /*mark that v has been visited*/
p=g.adjlist[v].firstarc; /* p points to the vertex v single link list's head pointer */
while(p)
{
w=p->adjvex; /* vertex w is the adjacency of vertex v */
if(visited[w]==0) /* If vertex w is not visited*/
DFS(g,w,visited); /* DFS is called recursively from w */
p=p->nextarc; /* Find the next adjacency of vertex v*/
}/*end while*/
}/*end DFS*/
void DFSTraverse(ALGraph g)
{
/*Adjacency list depth-first search*/
int v;
int visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
for(v=0;v<g.vexnum;v++)
visited[v]=0; /* Initializes the visited array */
for(v=0;v<g.vexnum;v++)
if(visited[v]==0)
DFS(g,v,visited);
/*start from vertex v which does not be visited, DFS search*/
}
完整源码,不知道是忘了保存还是哪去了,没找到。就先看这个吧。





 本文详细介绍了深度优先搜索(DFS)算法在图遍历中的过程,通过邻接矩阵和邻接表两种方式实现,并提供了一段英文版的DFS代码示例。作者分享了自己在赶论文过程中对排队论的研究,以及对本周未完成读书任务的反思,同时表达了对RNG在MSI比赛中的期待。
本文详细介绍了深度优先搜索(DFS)算法在图遍历中的过程,通过邻接矩阵和邻接表两种方式实现,并提供了一段英文版的DFS代码示例。作者分享了自己在赶论文过程中对排队论的研究,以及对本周未完成读书任务的反思,同时表达了对RNG在MSI比赛中的期待。
















 4152
4152










